Midweek Review
Science mega-projects: India’s moon mission

By Prof. Kirthi Tennakone
ktenna@yahoo.co.uk
Centuries ago, inquisitive people did their experimentation in backyard sheds. They communicated with their peers, contributing to knowledge. This was the beginning of science.
In 1610, Galileo made a telescope himself, looked at the moon and declared its surface was rugged and covered with craters. Thereafter, astronomers constructed larger and larger telescopes until further size increases were beyond the capability of an amateur. Astronomer William Hershel succeeded in convincing King George III of England, that very large telescopes would see more wonders of the sky. He obtained funding to install a telescope with a 40 – feet mirror, the first mega-project in science, completed 1785.
The launching of Sputnik by the Soviet Union in 1957 opened the space age, going beyond terrestrial confines to probe the universe. Landing of two men on the moon in 1969 and missions to explore the moon and planets by the United States, China, the European Union and India were costly undertakings by the respective governments.
Parallely, the quest for understanding the structure of matter, which started in kitchens and backyards by chemists and physicists, and later in the laboratories of academic institutions, also demanded exceptionally expensive experimentation. The research of Marie Curie, Ernest Rutherford and others in the early 1900s disclosed the atomic constitution of matter. Understanding the nature of the constituents of the atom required accelerators and detection systems extending over kilometers. The Large Hadron Collider of the Central European Organisation for Nuclear Research was built for 4.75 billion dollars. One of the most expensive science projects ever to be commissioned.
Space mega-projects revealed the details of lunar terrain, rivers existed on Mars billions of years ago; the composition of asteroids; the universe expands faster, and many other pieces of strange information.
Investigations of similar magnitude in terms of cost, geared to understanding the structure of matter, found that the particles of the atomic nucleus, the protons and neutrons, are made of sub-units termed quarks, and the elusive entity ‘Higgs Boson”, needed to justify the modern theory of matter, indeed exists.
Many raise the question, “Of what use are these findings to justify the expenditure? “
Man’s forward march to prosperity, to live without fear, and to address cropping problems owes much to his inquisitiveness about things not immediately relevant to his livelihood. And this effort needs to be continued for the sake of humanity’s future.
The soft landing of Chandrayan-3 at a far southern latitude of the moon is scientifically, culturally and politically significant not only to India but also to Sri Lanka, the region, and the world at large. Prime Minister Narendra Modi said India’s moon landing belongs to all humanity.
The moon’s south polar cap is a perplexingly peculiar and adventurous site. We cannot see the region, as it always points away from the earth. The sun poorly lit the south most lunar latitudes, because of the tilt of the moon’s axis of rotation. Consequently, the locations permanently shadowed by mountains and craters are the darkest and coldest spots in the solar system. For that reason, water and other volatile substances would have accumulated there, providing an opportunity for astrochemical investigations. Perhaps the signs of the origins of life outside the earth are hidden at the lunar South Pole.Chandrayaan-3 mission plans conducting experimentation to determine the chemical composition of the soil and the tenuous atmosphere immediately above the surface

One of the pictures of the moon surface sent by Pragyan rover
The southern polar region of the moon lacks sizable flat expanses free of rocks and craters. A landing spacecraft identifies obstacles and avoids those using the images of the terrain below. Because of poor illumination, soft landings near the moon’s South Pole present challenges that require more advanced technology. India’s landing of a module with a rover is an impressive first in space technology. Compared to similar moon missions, the cost of Chandraayan-3 is reported to be low and less than the production cost of a science fiction Hollywood movie, another positive for India’s space effort.
Indian space research was initiated in the early 1960s by the Gujarat-born physicist Vikram Sarabhai and the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) founded in 1969.A policy of emphasizing basic science, the dedication of scientists and engineers and sound administration enabled this achievement in a relatively short period, when Russia, Japan, Israel and the United Arab Emirates failed in their attempts. The United States and China are planning missions to the lunar South Pole.
Science mega-projects boost the morale and confidence of a nation. They encourage students to take up science and feel that they have opportunities in their homeland to prosper and shine. The faith in science created by fascinating scientific projects induces far-reaching non-material benefits for society. Pundit Jawaharlal Nehru, commenting on moon probes launched by the Soviet Union and the United States in the early days of space rocketry, said. “If a spacecraft could reach the Moon, why could not nations and societies discard old beliefs about this constellation and other planets?”
Some people prayed for the safe landing of Chandrayaan-3 at the moment it began approaching the lunar surface. Would they realise that their support for science and the dedication of scientists were true causes of landing without a crash?
Today, the political power and economic strength of a nation are determined largely by its scientific and technological capabilities. Existence few technological super giants has been the cause of many disputes, divisions and inability arrive at negotiations for the benefit of all. More and more political systems, equalising power will lead to a beneficial balancing influence. The world’s most populous nation gaining momentum competitively in advanced scientific research and technology signals promising future for all of us.
It is a pity that Sri Lanka has thus far not engaged itself in a major scientific project, competitive the with rest of the world. Saying that we didn’t have resources would not be a valid argument. All great scientific endeavours of highly original standing began in a small way. This was the situation in India. Visionaries such as physicists Homi Bhabha and Vikram Sarabhai and the mathematician cum aerodynamist Satish Dhawan who pursued advanced studies in the West before independence returned to India and started research from scratch, pointing out the necessity of engagement in fundamental studies indigenously and building institutions.
The scientific atmosphere in Sri Lanka at the time was similar. Arumugam Mailvagnam worked in Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge at the time of Ernest Rutherford, the discoverer of atomic structure. Jayarathnam Eliezer studied under Paul Murice Dirac, the foremost quantum theorist at the time. They returned to the University of Ceylon, Colombo and in the early 1950s, initiated research and did groundwork to establish an institution in Sri Lanka devoted to Physics and Mathematics as they were the catalysts that promote all areas of science and technology. Sir Nicolas Attygala, Vice-chancellor, University of Ceylon and eminent archaeologist Dr. Senarath Paranavithna, who had good rapport with the Ceylon Government at the time, supported the initiative. Institute of Fundamental Studies was established in 1981. Unfortunately, it didn’t stick to the originally intended mandate, and things far away from fundamental research in its true spirit were entertained, no significant difference compared to themes in other institutions devoted applied research. And there is no evidence of research there in key disciplines such as fundamental physics and mathematics that require more brains than costly instrumentation.
Homi Bhabha once said, “It is absolutely in the interest of India to have a vigorous school of research in fundamental physics, for such a school forms the spearhead of research not only in less advanced branches of physics but also in problems of immediate practical application in industry”
It is the above thinking that was implemented which gave India n clear reactors, biotechnological pharmaceutical, metallurgical industries etc. and enabled soft landing of a module on lunar South Pole, which no one else could achieve.
Chandrayaan-3 is a timely reminder for our policymakers to revive fundamental studies in Sri Lanka.
Midweek Review
Courtroom killings:From Attanagalle to Aluthkade
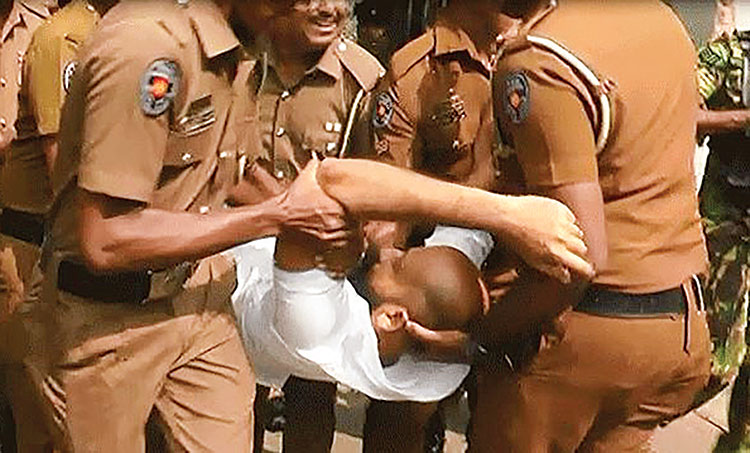

By Shamindra Ferdinando
Since the mid-1970s this country has seen so much bloodshed, beginning with the cold blooded killing of SLFP Jaffna Mayor Alfred Duraiappah on 27 July, 1975, by the LTTE, that even many of us journos, who have lived through and recorded much of that gory past, too, have literally lost the exact count from our memories, so no wonder having read last week’s midweek piece ‘A second killing in a courtroom, a question of national security and overall deterioration of law enforcement’ former Irida Divaina editor and one time colleague in our sister paper, Anura Soloman, reawakened the writer’s memory to the Wavulkelle killings. The writer inadvertently failed to at least refer to the Wavulkelle massacre that was also a grim reminder of the direct nexus between the party in power and law enforcers that had also become a cancer in this country, whether the rulers are corrupt capitalists or fake Marxists and opportunists or those somewhere in between.
We must also note that over the years our rulers also exacerbated feelings of resentment among Tamils as a result of many rotten cops, or those deemed politically undesirable, being posted to faraway places on punishment transfers. One can imagine how they would have taken out their own frustrations when discharging their duties in such places if they were so bad here, to start with. And that practice ironically continues to this day.
Sub Inspector Dhammika Amarasena, who had been interdicted over the Wavulkelle massacre, was shot dead inside the Attanagalle Magistrate court in Nov. 1991. Amarasena, who had been one of the accused in the Wavulkelle carnage where 12 persons were shot dead in late Feb. 1990, was the first suspect to die in a courtroom. Among the Wavulkelle victims had been a young woman who, according to the only survivor, was sexually abused by several male prisoners at the behest of a posse of bestial policemen before being killed.
The media reported at that time that the victims had been stripped naked and shot in single file by two gunmen. Amarasena had been among the gang of policemen responsible for the heinous crime that was carried out after the eradication of the Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna’s second armed uprising 1987-89. The victims were believed to be sympathizers of the then main Opposition Sri Lanka Freedom Party (SLFP).
Of the 13 people abducted and taken to a clearing, 12 had been shot dead and their naked and charred bodies were found by villagers. The crime would have remained a mystery if not for one of the abductees managing to flee from the clutches of those killers.
Solomon emphasized that the recent high profile courtroom killing of Sanjeewa Kumara Samararatne aka Ganemulle Sanjeewa, the fourth inside a courtroom, couldn’t be discussed without examining the killings carried out in the Attanagalle Magistrate court. Amarasena’s father-in-law, who had been seated next to the interdicted policeman, was also killed. The killer escaped.
Of the 14 suspects attached to the Weeragula and Attanagalla police taken into custody in connection with the CID investigation, the Attanagalle Magistrate discharged seven of the suspects and the remaining were charged with unlawful assembly, abduction, murder and lesser charges. The mastermind was never punished.
The Wavulkelle killings and the subsequent Attanagalla courtroom killing attracted international attention. The London headquartered Amnesty International (AI) dealt with this issue. It would be pertinent to stress that the Wavulkelle killings were carried out several months after the arrest and the execution of JVP leader Rohana Wijeweera and the elimination of its top leadership, barring Somawansa Amarasinghe, who managed to escape with clandestine Indian help.
The Nov. 1991 Attanagalle courtroom killings, during Ranasinghe Premadasa’s presidency, were followed up by the elimination of Dhamamika Amarasinghe in January 2004 during Chandrika Kumaratunga presidency, inside the Hulftsdorp court complex, and the most recent killing of Ganemulle Sanjeewa (Anura Kumara Dissanayake presidency/Aluthkade court complex).
The Attanagalle hit is widely believed to have been ordered by a businessman whose family happened to be among the victims of the Wavulkelle massacre. During the second JVP-led insurgency (1987-1990) both the government and the insurgents perpetrated heinous crimes. There cannot be any dispute that the ruling UNP exploited a murderous counter insurgency campaign to eliminate its political rivals as well. However, courtroom killings have to be thoroughly investigated and perpetrators (read masterminds) arrested and punished. The Attanagalle courtroom killings mastermind must have taken the law into his own hands as he felt the perpetrators of the Wavulkelle carnage wouldn’t be punished.
Parties in Parliament, as well as those not represented, have conveniently forgotten the murderous political culture that prevailed during that time. The Wavulkelle carnage never received the public attention it deserved. The police and successive governments never made an honest effort to investigate law enforcement officers’ alleged involvement in extrajudicial killings.
The second Aluthkade hit
Over the past three decades, the law and order situation has deteriorated to such an extent, that the corrupt elements in the police are now directly enmeshed in the underworld. Ganemulle Sanjeewa’s killing underscored the responsibility on the part of the National People’s Power (NPP) government to conduct a no holds barred investigation, particularly against the backdrop of the disclosure that the Colombo Chief Magistrate Court hadn’t directed the Prions Department to produce Ganemulle Sanjeewa in court on the morning of 19th February.
Colombo Chief Magistrate Thanuja Lakmali is on record as having questioned the senior Prisons Department officer present in court as to why Ganemulle Sanjeewa was produced in court in the absence of a specific court order in that regard.
Let me remind you what police constable Hewapathiranage Tharanga told the inquest into Ganemulle Sanjeewa killing held before Colombo Chief Magistrate Thanuja Lakmali on 24th February. PC Tharanga, of the Keselwatta police, said that the gunman, who had been dressed as a lawyer, fired several shots in rapid succession at Ganemulle Sanjeewa the moment Magistrate Thanuja Lakmali asked for an explanation from a Prisons’ Department officer. What the Colombo Chief Magistrate said was that Ganemulle Sanjeewa had been brought to Hulftsdorp from maximum security Boossa prison without a court order.
The Magistrate’s shocking declaration should be examined taking into consideration IGP Priyantha Weerasooriya revelation that he intervened to prevent Ganemulle Sanjeewa being produced in the Gampaha court the previous week following intelligence warning of a possible attempt on the underworld kingpin’s life. Therefore, the crux of the matter is who decided to produce Ganemulle Sanjeewa in court without any such order. That issue has to be addressed without further delay.
The possibility of the assassin – a legally discharged soldier who had undergone the basic commando training course – having access to those in charge of Ganemulle Sanjeewa’s security cannot be ruled out. If notorious underworld figure Kehelbaddara Padme, operating from overseas, had ordered the elimination of Ganemulle Sanjeewa to avenge the killing of his father, as alleged by some, targeting him while being escorted by a squad of elite police commandos wouldn’t have been feasible. In addition to police commandos, Ganemulle Sanjeewa ostensibly also received armed protection from the Prisons Department.
The latest underworld hit exposed glaring shortcomings in security. The police and the Bar Association of Sri Lanka (BASL) owed the public an explanation why lawyers weren’t subject to routine security checks before entering courtrooms during high profile cases.
Especially against the backdrop of IGP Weerasooriya’s disclosure that they had been aware of an attempt that was to be made on the life of Ganemulle Sanjeewa on the previous week at the Gampaha court, why were not special security arrangements made on 19 February?
Perhaps, the Justice Ministry, the police and the judiciary should reach consensus on the deployment of armed police within courts for the protection of criminals under threat. It would be pertinent to mention that police assigned to provide security to judges are authorized to carry side arms in courts.
The Aluthkade killing, coupled with the Middeniya triple murder where the one-time henchman of the Rajapaksas was killed with two of his children, and two deaths in police custody, placed the NPP government in an extremely difficult situation.
Twelve persons have so far been taken into custody in connection with the Aluthkade killing. However, the woman accomplice of the assassin, who smuggled in the weapon into the courtroom, remains at large.
The recent issuance of an order by the Matara Magistrate to arrest eight policemen, including ex-IGP Deshabandu Tennakoon, over an alleged conspiracy to commit murder with regard to an incident at W 15 hotel in Weligama on the night of 31 Dec., 2023. If it is true that further underscores the deterioration of law enforcement. The predicament of a once powerful cop on whose behalf the previous President went to the extent of clashing with even the judiciary stresses the responsibility on the part of all parties to exercise caution.
Midweek Review
Truth and Reconciliation

By Lynn Ockersz
Ill-concealed by the sands of time,
Skeletons continue to scramble out,
Telling inconvenient, face-reddening truths,
Of smoking guns never brought to justice,
Of equity undelivered or miscarried,
Pointing to the error of the land’s ways,
But also warning it to be reconciled ere long,
Lest the Isle wanders dangerously once again,
Down blood-splattered tracks of self-harm,
And drives home the brutal truth of nation-breaking.
Midweek Review
The price of losing economic sovereignty
by Shiran Illanperuma
On 17 February, President Dissanayake delivered his maiden budget speech. The second reading was passed by a majority of votes on 25 February, and a vote on the third reading will be taken up on 21 March.
Amid the day-to-day politicking surrounding budget debates, it is important to remind ourselves of the socioeconomic context in which this budget has been presented. It has now been three years since Sri Lanka experienced its worst economic crisis in the modern era. In May 2022, Sri Lanka defaulted on its external debt for the first time in history. In September 2022, the country entered into a staff-level agreement with the IMF for a 2.9 billion US dollar bailout.
The effects of the austerity measures undertaken in order to earn the IMF bailout were plain to see in 2023. According to recent research the Centre for Poverty Analysis, poverty in Sri Lanka soared from 26% in 2022 to 31% in 2023. In raw numbers, this means that about 7.1 million people fell into poverty. To put this into perspective, 7.1 million people is a population greater than the entire Western Province (which was about 6 million according to the last census in 2012).
It would be unreasonable to expect a single budget to resolve the colossal humanitarian crisis brought about by the 2022 default and ensuing IMF programme. However, what is reasonable to expect is a contextual analysis of the factors, both local and global, that brought us here, and an outline of the way forward. Unfortunately, such analysis was entirely missing from the President’s maiden budget speech. In its place was the pronouncement of some lofty, but admirable, principles.
No democracy without sovereignty
During his budget speech, President Dissanayake said, “What is needed going forward is for a greater democratisation of the economy” – a noble goal given the socialist aspirations of Sri Lanka’s republican constitution. In this same speech, Dissanayake also said that achieving economic sovereignty was necessary to implement the NPP’s agenda.
Two days later, at a post-budget forum organised by the MBA Alumni Association, University of Colombo, and Daily FT, Dissanayake conceded, “Our economy is running on conditions. There is no economic independence or sovereignty – it is under probation and being monitored.” The implication is stark: Sri Lanka has no economic sovereignty, and therefore the mandate of a democratically elected government cannot be carried out.
What is left out of this equation is that the mandate of the NPP was to fight for the very economic sovereignty needed to carry out its programme – that is, to renegotiate the unfavourable debt-restructuring deal which would see Sri Lanka carrying a public debt-to-GDP burden of up to 95% even in 2032. This mandate was reneged in November 2024 when President Dissanayake endorsed the IMF programme, arguing that, “This is not the time to discuss if the terms are good or bad.”
One does not need a political science degree to understand that there can be no democracy without sovereignty. Any pretences of democracy in conditions of non-sovereignty are a façade. Economic sovereignty is not something that will magically reappear once the current IMF programme comes to an end. Rather, active work will be required to undo the worst of the policies undertaken under the auspices of the programme.
In other words, the confrontation with capital required to restore economic sovereignty is inevitable. To pretend otherwise is either naïve or dishonest. To say now is not the time is to ignore that there will likely never be a good enough time, especially as all forecasts point to Sri Lanka enduring a heavy debt burden to private foreign creditors even after the IMF programme concludes.
Citizen’s budget or creditor’s budget?
This budget was promoted as a citizen’s budget. The implication is that it is a budget that prioritises the mass of people, workers, farmers, fishers etc. over the interests of big business both local and foreign. To that end, there are many welcome proposals, including the move to increase public investment as a share of expenditure from 13% of GDP in 2024 to 18% of GDP in 2025.
However, this pales in comparison to the mammoth 41% of expenditure taken up by interest payments. Sri Lanka had one of the highest interest burdens in the world before defaulting on its external debt in 2022. This was predominantly due to the shift in borrowing from multilateral and bilateral creditors to private creditors. According to data from the World Bank, private bondholders accounted for 36% of Sri Lanka’s outstanding debt but 70% of interest payments in 2021.
In fact, the greatest fiscal burden for the governments is not the public sector wage bill or subsidies, but interests’ payments, particularly those from foreign debt. In the past decade or so, Sri Lanka has made the reckless move of borrowing externally to finance its domestic budget deficit. This creates massive exchange rate risks in serving that debt, as Sri Lanka maintains a yawning trade deficit due to its underdeveloped industrial base.
The Central Bank Act, a key condition of the IMF programme, and one that even the US ambassador seemed keen Sri Lanka adopt, will exacerbate this trend. With the newly ‘independent’ Central Bank unable to finance the government’s budget deficit, the government must rely even more on private creditors, both local and foreign, in the event of an external shock to the economy. This loss of monetary sovereignty remains the single most damaging element of the IMF’s conditions.
Changing international order
A void in the President’s budget speech was any reference to the implications of a changing international economic order to the future trajectory of the Sri Lankan economy. With the second inauguration of President Donald Trump in the US, there is an ongoing tactical shift in the US ruling class’s approach to maintaining a preponderance of power in a world where the economic centre of gravity is shifting to Asia.
First, the suspension of foreign aid leaves several government programmes without funding. Second, the combination of diminished consumer sentiment and a rise of protectionism in the Global North leaves the future of Sri Lanka’s exports highly uncertain. Third, the Global North’s attempts to reshore and “friend-shore” industrial production, leaves prospects for productive FDI uncertain. Fourth, NATO’s tactical withdrawal from the Ukraine’s proxy war in order to consolidate a US-EU defence industrial base and contain China, poses serious security threats to Sri Lanka which is situated at the heart of the Indo-Pacific Strategy.
The key countervailing force to these trends is the new mood in the Global South, characterised by a return to ideas of as South-South cooperation. In purchasing power parity terms, BRICS members account for around 37% of world GDP, surpassing that of the G7. Sri Lanka’s position in these ongoing conversations about restructuring the international economic order remain vague and uncertain. To argue for greater engagement is not a mere moral or theoretical imperative.
Going back to the question of economic sovereignty, the fact is that Sri Lanka was never going to be able to negotiate a better deal on its own. That would require coordinated multilateral action, through the formation of something like a debtor’s club. While it is not immediately clear whether forums such as BRICS will provide a platform for this, what is undeniable is that these forums are where the important conversations are happening.
something like a debtor’s club. While it is not immediately clear whether forums such as BRICS will provide a platform for this, what is undeniable is that these forums are where the important conversations are happening.
(The writer is a researcher at Tricontinental: Institute for Social Research and a co-editor of Wenhua Zongheng: A Journal of Contemporary Chinese Thought. He is also a co-convenor of the Asia Progress Forum.)
(Asia Progress Forum is a collective of like-minded intellectuals, professionals, and activists dedicated to building dialogue that promotes Sri Lanka’s sovereignty, development, and leadership in the Global South. They can be contacted at asiaprogressforum@gmail.com).
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoSusantha Chandramali passes away at the age of 61
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoDid Rani miss manorani ?
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoElectoral reform and abolishing the executive presidency
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoLawyers’ Collective raises concerns over post-retirement appointments of judges
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoSummary Justice is Indefensible
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoErstwhile chums’ fake wrestling
-

 Editorial5 days ago
Editorial5 days agoFrom ‘chits’ to ‘lists’
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoSeagrasses: The Unsung Guardians of Our Oceans











