Business
Reform or perish, it’s not too late
Sri Lankan economy in historic crisis
By K.D.D.B Vimanga and Naqiya Shiraz
The Sri Lankan economy faces a historical crisis. The root causes are the twin deficits. First, the persistent fiscal deficit – the gap between government expenditure and income. Second, the external current account deficit – the gap between total exports and imports. The problems have been festering for too long. Without urgent reforms, the crisis could easily morph into a full-blown debt crisis.
Sovereign debt workouts are extremely painful for citizens. A mangled debt restructuring can perpetuate the sense of crisis for years or even decades. A return to normal economic activity may be delayed, credit market access frozen, trade finance unavailable.
 With the global pandemic, these are unusual and difficult times. The next five years are going to be crucial for the country. The problems can no longer be avoided and should be faced squarely. The journey ahead is going to be painful but the longer these are delayed the worse the problem becomes and the magnitude of the damage compounds.
With the global pandemic, these are unusual and difficult times. The next five years are going to be crucial for the country. The problems can no longer be avoided and should be faced squarely. The journey ahead is going to be painful but the longer these are delayed the worse the problem becomes and the magnitude of the damage compounds.
State of the Economy
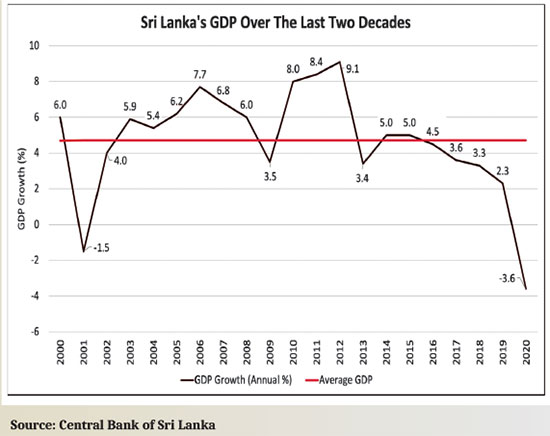
The new government inherited a fragile economy, battered by the Easter attacks of 2019, the constitutional crisis of October 2018 and the worst drought in 40 years in 2017. With the pandemic in 2020 Sri Lanka’s economy shrank by 3.6% with all sectors of the economy contracting.
Yet, the pandemic is not the sole cause – it only accelerated the decline of Sri Lanka’s economy that was weak to begin with. The country has long been plagued by structural weaknesses, with growth rates in the last few years even below the average growth rate during the war. Mismanaged government expenditure coupled with a long term decline in revenue have characterised Sri Lanka’s fiscal policy. As of 2020 total tax as a percentage of GDP fell to just 8%, while recurrent expenditure increased.
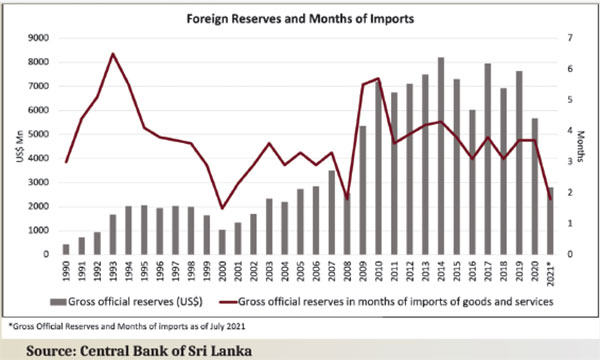
Borrowing to finance the persistent budget deficits is proving to be unsustainable. Total government debt rose to 101% of GDP in 2020 and has grown since. Sovereign downgrades have shut the country from international debt markets. The foreign reserves declined from US$ 7.6 bn in 2019 to US$ 5.7bn at the end of 2020 and to US$ 2.8 bn by July 2021. This level of reserves is equivalent to less than two months of imports. With future debt obligations also in need of financing, the situation is dire.
The import restrictions placed to combat this foreign exchange crisis have failed to achieve their purpose and are doing more harm than good. imports rose 30% in the first half of 2021 compared to 2020 despite stringent restrictions.
The problem lies not in the trade policy but in loose fiscal and monetary policy that has increased demand pressures within the economy, drawing in imports and leading to the balance of payments crisis and consequently the depreciation of the currency.
Measures by the Central Bank to address this by exchange rate controls and moral suasion have caused a shortage of foreign currency leading to a logjam in imports.
Fundamental and long-running macroeconomic problems were intensified by the pandemic.Import restrictions, price and exchange controls do not address the real causes.
Treating symptoms instead of the underlying causes is a recipe for disaster.
The continuation of such policies will lead to the deterioration of the economy, elevate scarcities, disadvantage the poor who are more vulnerable and in the long run lead to even higher prices and lower output due to lack of investment.
Sri Lanka’s GDP growth over the last decade has been alternating between short periods of high growth and prolonged periods of low growth. This is a result of the state-led, inward looking policies of the last decade.
A comprehensive reform agenda must be built around five fundamental pillars:
i) fiscal consolidation – The need to manage government spending within available resources and to reduce debt are paramount. Revenue mobilization must improve but the control of expenditure cannot be ignored. Budgetary institutions must be strengthened and there must be reviews not only of the scale of spending but also the scope of Government.
ii) Much of government expenditure is rigid – the bulk comprises salaries, pensions and interest so reducing these is a long term process. Reforming State Enterprises, especially in the energy sector and Sri Lankan Airlines is less difficult and could yield substantial savings. Continued operation of inefficient and loss-making SOE’s is untenable under such tight fiscal conditions. Financing SOE’s from state bank borrowings and transfers from government reduces the funds available for vital and underfunded sectors such as healthcare and education. Excessive SOE debt also weakens the financial sector and increases the contingent liabilities of the state. Therefore SOE reforms commencing with improving governance, transparency, establishing cost reflective pricing and privatisation are necessary. This can take a significant weight off the public finances and by fostering competition contribute to improvements in overall economic productivity.

iii) Tighten monetary policy and maintain exchange rate flexibility. Immediate structural reforms include, Inflation targeting, ensuring the independence of the central bank by way of legislation and enabling the functioning of a flexible exchange rate regime. Further significant attention has to be placed on the financial sector stability with a cohesive financial sector consolidation plan, with special emphasis on restructuring of SOE debt.
iv) Supporting trade and investment. Sri Lanka cannot achieve economic growth without international trade which means linking to global production sharing networks. Special focus has to be given to reducing Sri Lanka’s high rates of protection which creates a domestic market bias in the economy along with measures to improve trade facilitation and attract new export oriented FDI.
Attempts to build local champions supported by high levels of protection have
(a) diverted resources away from competitive businesses,
(b) created a hostile environment for foreign investment,
(c) been detrimental to consumer welfare,
(d) dragged down growth
v) Structural reforms to increase productivity and attract FDI – Productivity levels in Sri Lanka have not matched pace with the rest of the growing economies. The reforms mentioned above are extensively discussed in Advocata’s latest publication “Framework for Economic Recovery”.
Sri Lanka stumbled into the coronavirus crisis in bad shape,with weak finances; high debt and widening fiscal deficits. It no longer has the luxury to delay painful reforms. Failure to do so will not only jeopardize the economy; it could even spawn social and humanitarian crises.
Naqiya Shiraz is the Research Analyst at the Advocata Institute and can be contacted at naqiya@advocata.org.K.D.D.B. Vimanga is a Policy Analyst at the Advocata Institute. He can be contacted at kdvimanga@advocata.org.
Business
Pathfinder Foundation lays out a practical vision for Sri Lanka’s economic future

Two groundbreaking reports launched by the Pathfinder Foundation in collaboration with the Australian Trade and Investment Commission have laid out a practical vision for Sri Lanka’s economic future, pinpointing the mineral and clean energy sectors as twin engines for sustainable growth and investment.
The reports, unveiled on December 17 in Colombo, present actionable roadmaps for project developers and technology providers, positioning Sri Lanka as an emerging frontier in the global clean energy and critical minerals supply chain.
Key content from the minerals report:
Sri Lanka’s largely underutilised mineral sector holds significant potential, with resources increasingly vital to global industries. The country boasts high-purity graphite, rare earth elements (REEs), mineral sands, and phosphate – all critical for electric vehicles, renewable energy technologies, and high-tech manufacturing.
While current mineral exports are around USD 389 million, the International Trade Centre estimates a potential of USD 778 million, with primary data suggesting the true figure could reach USD 2 billion. To capture this value, the report stresses moving beyond exporting raw materials to domestic refining and beneficiation.
A key strategic recommendation is deeper regional collaboration, particularly under the South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA). It highlights an opportunity for Sri Lanka to partner with India’s booming automotive and clean energy sectors, where demand for REEs and permanent magnets is soaring. This could involve upstream Indian investment in Sri Lankan REE resources or exports of rare earth oxides for India’s EV, wind, and electronics industries.
Key content from Clean Energy report:
Parallel to its mineral potential, Sri Lanka is pursuing an ambitious transition to clean energy, targeting carbon neutrality by 2050. The country’s renewable energy sector offers a diverse range of investment and trade opportunities for international stakeholders, spanning large-scale utility projects, distributed generation, and service-based collaborations.
Specific opportunities include utility-scale solar and wind projects, offshore wind resource mapping, and rooftop solar in urban corridors. There is also growing momentum for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) to stabilise the grid, green hydrogen pilot plants, and the development of net-zero industrial parks powered entirely by renewables.
The reports highlight a powerful synergy: Sri Lanka’s minerals are essential for the very clean technologies it seeks to deploy. For instance, its phosphate can be used in lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, while its high-purity quartz is vital for solar-grade silicon.
Australia is identified as a key partner in both sectors. Australian Mining Equipment, Technology, and Services (METS) firms can provide cutting-edge, sustainable mining technology, while Australian expertise in smart grids, BESS, and green hydrogen aligns with Sri Lanka’s long-term energy strategy.
While outlining vast potential, the reports also acknowledge challenges, including regulatory complexities, infrastructure gaps, and the need for enhanced skills development. Proposed solutions include modernising approval processes, developing a national critical minerals strategy, and fostering public-private partnerships.
The consensus from keynote speakers at the event – including Pathfinder Foundation Chairman Bernard Goonetilleke, Australian High Commissioner Matthew Duckworth, and senior representatives from academia, government, and Austrade – was clear. Their collective insight underscored the reports’ central thesis: Sri Lanka is presented with a unique, synergistic opportunity. By strategically developing its mineral wealth and accelerating its clean energy transition in tandem, the nation can attract significant foreign investment, create high-value jobs, and secure a competitive position in the Indo-Pacific’s sustainable economic future.
By Sanath Nanayakkare ✍️
Business
ComBank and Prime Lands join forces to offer full financing on homes

The Commercial Bank of Ceylon has signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Prime Lands and Prime Land Residencies to provide up to 100% financing for customers purchasing condominium units or gated houses developed by the Prime Group, demonstrating the Bank’s unwavering commitment to empowering more Sri Lankans to achieve their dream of home ownership.
The agreement enables prospective homeowners to seamlessly access Commercial Bank’s home loan facilities with tripartite agreements involving the developer, the buyer and the Bank. As the market leader in home loans, Commercial Bank brings unmatched expertise and flexibility to borrowers seeking to invest in properties developed by one of Sri Lanka’s most trusted names in real estate.
Commenting on the partnership, S. Ganeshan, Deputy General Manager – Personal Banking at Commercial Bank said: “This agreement with Prime Lands and Prime Land Residencies creates an excellent opportunity for us to expand our housing loan portfolio while enabling more Sri Lankans to realise one of their life goals. Commercial Bank’s strong home loan offering, combined with Prime Group’s reputation as a leading developer, ensures customers benefit from both financial strength and quality of construction.”
The Prime Group, which positions itself as the leader of real estate artistry in Sri Lanka, comprises subsidiaries associated with lands, houses, finance and condominiums. With over 30 years of trust and excellence and a base of more than 300,000 customers, the Group says it is driven by its evergreen vision: ‘Committed to Creating a Better Place on Earth,’ which continues to inspire its passion to deliver homes that bring customers’ dreams to life.
Business
Mahogany Masterpieces celebrates grain’s beauty

Mahogany Masterpieces, a Sri Lankan luxury furniture brand, has launched the “An Ode to Grain” collection. This showcase honors mahogany’s natural beauty and the brand’s craftsmanship. The philosophy is to let the wood’s grain guide the design, creating timeless pieces that respect the material. The collection includes new architectural elements like architraves, paneling, and corbels, designed to bring lasting warmth and character to interiors.
Visitors can view the full collection at the Mahogany Masterpieces Showroom and Design Studio which is located at No. 87, Dr. Lester James Peiris Mawatha (Dickman’s Road), Colombo – 05. www.mahoganymasterpieces.com
-

 Midweek Review5 days ago
Midweek Review5 days agoHow massive Akuregoda defence complex was built with proceeds from sale of Galle Face land to Shangri-La
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoPope fires broadside: ‘The Holy See won’t be a silent bystander to the grave disparities, injustices, and fundamental human rights violations’
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoPakistan hands over 200 tonnes of humanitarian aid to Lanka
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoBurnt elephant dies after delayed rescue; activists demand arrests
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoUnlocking Sri Lanka’s hidden wealth: A $2 billion mineral opportunity awaits
-

 Editorial5 days ago
Editorial5 days agoColombo Port facing strategic neglect
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoArmy engineers set up new Nayaru emergency bridge
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoSri Lanka, Romania discuss illegal recruitment, etc.













