Opinion
Reconciliation Initiative- the bigger picture

By Dr Nirmala Chandrahasan
It has been announced that the government of Sri Lanka is on a reconciliation initiative. In pursuance thereof, President Wickremesinghe has invited all Tamil MPs for talks next week to discuss issues faced by the Tamil people and how to resolve them amicably without outside interference before the 75th Independence Day. This is Indeed a laudable project, although some sceptics have described it as being due to the result of relentless pressure from outside and future international economic assistance and support being tied to the resolution of this issue. If this is true then it is all the more important that it be approached in a way which goes to the root of the problem and brings the ethnic parties together again in friendship and harmony, which is what reconciliation means.
President Wickremesinghe has mentioned certain subjects for the discussion which include the release of prisoners presumably those held in respect of the civil war, issues pertaining to truth and reconciliation again presumably those arising from the civil war. The list also includes development plans for the North and East which includes assessment of renewable energy potential in the North, and finally development of Trincomalee for Tourism.
Although the above are all worthy objectives, it fails to deal with the subject of reconciliation per se. Reconciliation means restoring friendship and harmony between parties who have been divided, and would include settling or resolving the differences between them. To my mind the most important question to be resolved is whether this Country is to be regarded as a Sinhala Buddhist State where all the other ethnic, religious groups are treated as guests, or as a multi- ethnic- multi-religious, secular country where all citizens have equal rights.
During the previous regime of President Gotabaya Rajapaksa, it was publicly asserted to be a Sinhalese Buddhist state where other ethnic and religious entities were being allowed to live. This ideology was propounded by ethno-nationalist Sinhalese politicians, academics and media houses. The sole Sinhalese Politician of Stature who was brave enough to repudiate this claim was the late Mangala Samaraweera. He had to bear the consequences of stating that the country belonged to all the ethnicities and religious groups and was denigrated by ethno- nationalists. Even today this policy continues in the Eastern province, where under the pretext of Archaeology, and Buddhist ruins, Tamil speaking farmers of the area are being dispossessed of their lands, although historically many of these ruins are Tamil Buddhist ruins. In the Trincomalee district, administrative boundaries are being sought to be changed so as to make demographic changes to the population of the district. All these actions are analogous to those of Israeli settlements in Palestinian lands, and is only breeding bad blood between the communities, instead of reconciliation. It is also noteworthy that the Archaeological Task force for the Eastern province appointed during the previous regime does not contain a single member of either the Tamil or Muslim communities who constitute the majority in this Province. The above actions would call in question the credibility of the present reconciliation process to even the international observers, and should be discontinued.
This claim that the island belongs only to one ethnic religious group, is not entirely new, although it was given a public endorsement in the regime of President Gotabaya. From 1949 itself with the passing of the Acts disenfranchising the upcountry Tamils and the passing of the Sinhala only Act in 1956, this policy began to reveal itself. There were also pogroms against Tamil speaking people from 1956 onwards, culminating in the pogrom of 1983 which was said to be state inspired and directed. In the aftermath of the 1983 holocaust, the non-violent Satyagraha methods which had marked the earlier Tamil political resistance movement came to an end as people began to doubt its efficacy.
I might add that in my view, it was not the Sinhalese people who were responsible for this policy and the consequences thereof, but self-serving politicians and members of a political class, who found a path to power, position and wealth by espousing this ideology and deceiving their own people. It was this ideology that resulted in Sri Lanka losing so many of its professionals and talent, as sections of the population began to feel that they had no place in this Country. First the Burgher community which had made this their home since the 17th century, emigrated to Australia, subsequently many Tamil professionals who had skills that could benefit the country left for the UK, USA, Canada, Australia, and other first world countries. After the major pogrom of 1983, there was an outflow of Tamil refugees who had suffered the effects of the violence, to all parts of the world. The armed struggle also began to take shape, as the military repression caused many young people of the Tamil community to join the ranks of the militants and take up arms because they did not see themselves as equal citizens in this nation. All these factors had a bearing on the present catastrophic economic downturn which we now see. This of course is not the only reason as the incompetence and corruption of the rulers and the political class was also a major factor.
So, we can see that for true reconciliation to take place there must be a recognition that this Country is a Multi- ethnic, multi- religious country in which all citizens are equal and have an equal stake. We must welcome and be proud of our diversity as do countries like Canada and South Africa. Even in the United Kingdom our former colonial ruler, a Hindu of Indian origin is able to take his place as Prime minister. The British Conservative party has chosen to give recognition to ability and talent and not race or religion. We have to look to the day when the Sri Lankan nation will do likewise. In a country where all the citizens of diverse ethnic and religious backgrounds are accepted as equal partners, all the constituent peoples would be enthused to work together for the upliftment of ‘their’ country. The Tamil diaspora too would come forward to assist and invest in the Country. For this change of heart /mindset to take place there must be a revamp of the text books in the schools and particularly in the- Sinhalese medium. History books must show the common cultural links between the communities and not portray them in an adversarial way. The historical linkages between the South Indian kingdoms and Lanka should be brought out. The fact that South India was Buddhist too for many centuries, and the Chola Kings who ruled Lanka for almost a century were also patrons of Buddhism should be made known to the public, both Sinhalese and Tamil, as Tamils too are largely unaware of the common heritage they share.
It also behoves the Tamil community to move away from a mindset of victimisation and constant harping on the Civil war. Every war has its brutalities and crimes and these are not confined to one party alone. The Tamil community has to look to the future and while safeguarding their culture and identity they also have to break away from their insularity. Where the hand of friendship and reconciliation is genuinely extended, they should take it and go forward. We might take a lesson from the civil war in the USA, between the Northern States of the Union and the Southern states in the 1860s. Here too the Southern states, (the Confederacy) tried to secede from the Union and form their own state. The war that followed was a very brutal one. It is said that the northern Army of General Sherman followed a scorched earth policy while marching through the Southern states. But once the war was over and the North had won, the Union government followed a policy of Reconciliation. In the National War Memorial in Arlington Virginia, there is a memorial to the Confederate soldiers of the South too, thus honouring the dead on both sides. The reunited USA, a Federal state, went on to become a great power and one of the most prosperous nations in the world. In Sri Lanka too as a measure of reconciliation some memorial to those who died fighting for their cause would go a long way in assuaging the feelings of their relatives and friends, rather than the policy of destroying their cemeteries and preventing their family members from remembering them, as hitherto. The release of the prisoners who participated in the Civil war, some of them still imprisoned, while awaiting trial after so many years, is a good beginning, as too the idea of a Truth and Reconciliation commission which is being envisaged.
Next, I would also like to touch on the question of sharing of powers, as a necessary constituent of reconciliation. Since the Indo- Sri Lanka peace Accord of July 1987, there has been a process of putting in place a system of Devolution of powers. This Treaty gave recognition to the Tamil people as Historical inhabitants of the Northern and Eastern Provinces and provided for a system of devolution of powers through Provincial Councils. Under the 13th Amendment to the Constitution and the Provincial Councils Act the Provincial Councils were set up. Under the 13th Amendment, powers are given in respect of a wide spectrum of subjects, which are set out in the annexed Lists and Annexures. However, the Provincial Councils Act stultified many of these powers by giving the Governor control of Finances and the Provincial administrative services. Furthermore, the Central Authorities kept encroaching on the subjects allocated to the Provincial Councils. Hence the Provincial Councils have not been as effective as they might have been. This has given rise to the view expressed by some persons including Tamil politicians that the Provincial Council system is not workable, and should hence be done away with. To this, it must be pointed out that since independence seventy-five years ago the Tamil parties have been agitating for some measure of power sharing while seeing a federal Constitution as the ultimate goal. This agitation has been through Parliament and through peaceful ‘satyagrahas’, and through negotiations and pacts with Sinhalese majority Parties and Governments. Finally, the militants having lost faith in negotiations took up arms and a protracted civil war of almost 30 years ensued. But for all this the only political gains in the way of power sharing and devolution that the Tamils have obtained has been the Provincial Councils and that too through the good offices of the Government of India.
Hence good sense dictates that the Tamil political leaders make the best use of what they have in hand. With the ongoing reconciliation process, they could press for the necessary amendments to be made to the Provincial Councils Act, which could be done through legislation with a simple majority in Parliament, or a two third majority where some Provincial Councils do not agree to the changes. No Referendum is required Furthermore, it must be conceded that the Northern Provincial Council could have exercised greater authority and made more progress by making use of the powers to pass statutes on subjects allocated to the Councils, which I might point out the Northern Province Council as of date has been very remiss in doing. Even in the matter of spending funds allocated to it by the Centre the Council has been remiss and even returned such funds in some instances. So in my view, with greater commitment on the part of the stakeholders a more efficient administration can be ensured, once the necessary amendments are put in place.
The alternative is to return to the long-drawn-out process of endless negotiations and drafting committees. After the passing of the legislation in 1987, efforts to make improvements and changes were many, i.e. the Mangala Moonesinghe committee report in the 1990s, the Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga draft Constitution of 2000, which was incidentally the closest to a federal form of Government. Again in 2006 there was a multi -ethnic expert Committee appointed under the Mahinda Rajapaksa government which presented a report which was not implemented, next the APRC, (All Party Representative Committee) Report 2010, was shelved by the Government. With the change of Government in 2015 it was sought to revive the process and in 2016 a Constituent Assembly was formed to work on a new Constitution. Speaking on the recent reconciliation proposals Mr. Sumanthiran, MP on behalf of the TNA said that President Wickremesinghe had presented a draft of the new Constitution proposals to Parliament on 16th January 201 9 in the capacity of Prime minister, and this has to be taken forward. This is a sensible proposal as it is not worth restarting the same process again. I might mention that the Parliamentary Sub- Committee on Centre-Periphery relations, which was part of the above Constituent Assembly, made some very good proposals on the reforms to the Provincial Council system in its Report of 2019, which incorporated proposals in the 2006 Expert Committee Report and the APRC Report, and these can be drawn upon when making the amendments to the Provincial Councils Act, as proposed above.
With a view to making reconciliation a reality and restoring friendly relations and harmony between the communities, I have examined the background to, and underlying ideologies which have contributed to the estrangement between the communities. The strategies and steps to be taken in order to change perceptions and fixed prejudices and ideologies will require courage and transformational steps some outlined above. Reconciliation cannot be a one sided effort and both communities must be willing to make the effort. President Ranil Wickremesinghe is well suited to taking this process forward given his long experience of the political processes and understanding of the historical background.
Opinion
“Let My Country Awake …”

Where the mind is without fear, and the head is held high;
Where knowledge is free;
Where the world has not been broken up into fragments by narrow domestic walls;
Where words come out from the depth of truth;
Where tireless striving stretches its arms towards perfection;
Where the clear stream of reason has not lost its way into the dreary desert sand of dead habit;
Where the mind is led forward by thee into ever-widening thought and action
Into that heaven of freedom, my Father, let my country awake.
– Rabindranath Tagore, Gitanjali, 35
As Sri Lanka marks seventy-seven years of independence, this moment demands more than flags, ceremonies, or familiar slogans. It demands memory, honesty, and moral courage. Once spoken of with affection and hope as Mother Lanka, the nation today increasingly resembles a wounded child—carried again and again across fragile hanging bridges, suspended between survival and collapse. This image is not new to our cultural consciousness. Long before today’s crises, Sri Lankans encountered it through literature and radio, most memorably in Henry Jayasena’s Hunuwataye Kathawa (1967), the Sinhala radio drama adaptation of Bertolt Brecht’s The Caucasian Chalk Circle, written during World War II (WWII), broadcast by Radio Ceylon and later staged across the island. Heard in village homes and city neighborhoods, the story quietly shaped a moral imagination we now seem to have forgotten.
In Hunuwataye Kathawa, a child is placed at the center of a chalk circle, claimed by two women. One is Natella, the biological mother who abandons the child during a moment of danger and later returns—not out of love, but driven by entitlement, inheritance, and power. The other is Grusha, a poor servant who risks everything to protect the child, feeding her, carrying her across perilous terrain, and choosing care over comfort. When ordered by the judge to pull the child out of the circle, Grusha refuses. She would rather let go than injure the child. Justice, the story teaches, belongs not to those who claim ownership most loudly, but to those who practice responsibility and restraint. For generations of Sri Lankans, this lesson entered the heart not through policy or economics, but through art.
Beneath Sri Lanka’s recurring failures lies a deeper wound: collective forgetfulness. It is indeed incredible how a nation colonised by foreign powers for over four centuries, battered by people’s insurrections and national struggles ever since, divided by a 30-year-long ethnic war, shaken by a Tsunami, inflamed by Easter Bombings 2019, hit by Covid-19 shutdown, and bankrupt by economic crisis, just to mention a few before the devastating Cyclone Ditwah that rocked the entire nation not many weeks ago, could be so forgetful of its tragedies. This insight was articulated with striking clarity by Dr. Arvind Subramanian, the former Chief Economic Advisor to the Government of India, speaking at an event organised by The Examiner in Colombo on Jan 21, 2026. Subramanian observed the nation’s troubling tendency to forget its own history—its tragedies, hard-earned lessons, and warnings—and to embrace uncritically whatever is new in a pattern-line manner. This historical amnesia traps Sri Lanka in vicious cycles of debt, dependency, and unscientific thinking. When memory fails, every crisis feels unprecedented; when learning fails, every mistake is repeated.
Consequently, after seventy-eight years of independence from the last colonial rule, Sri Lanka still stands inside that chalk circle. Mother Lanka, once admired for free education, public health, and social mobility, has over the decades been reduced to a wounded child carried across unstable political, economic, and environmental bridges. Different governments, armed with different ideologies and promises, have taken turns holding her. Some carried her carefully; others dropped her midway; still others claimed her loudly while burdening her with unsustainable debt, weakened institutions, superstitious demeanors, and short-term fixes that mortgaged the future. This mother-made-child nation was perpetually oscillating between collapse and recovery. Yet instead of healing her wounds, with every passing Independence Day, we repeatedly celebrated and argued over who owned her.
This long post-independence journey reveals two recurring patterns. There have been many Natella-like approaches—entitlement without responsibility, nationalism without sacrifice, populism without prudence. These abandon the child in moments of crisis, only to return when power, contracts, or prestige are at stake. Alongside them, however, there have also been Grusha-like moments—imperfect, painful, often unpopular, yet rooted in reform, discipline, and care. These moments prioritise institutions over personalities, education over spectacle, sustainability over extraction, science over superstitions, and responsibility over applause. They are the moments that keep the child alive. The thorough cleaning that the whole nation recently experienced with Cyclone Ditwah also reminds us, among many other lessons, about the power and the need of these Grusha-like moments. It reminds us that the real celebration of freedom requires not slogans but breaking free from Natella-like approaches and, after the immersion that she just experienced, that it is only possible in and through at least three kinds of voluntary and ongoing immersions (3P Immersions)—disciplines that reshape not only policy but also personal and national character—Immersion of Poverty, Immersion of Plurality, and Immersion of Prudence.
The immersion of poverty, both spiritual and material, is deeply rooted in Buddhist teaching of tanhaā and āśā—the restless craving for more than one truly needs or can sustain. It is that which enables us to be constantly mindful of ourselves, not only who we really were, who we actually are, and what we continue to become, but also what we are really in need of. Nationally speaking, it involves acknowledging the country’s geopolitical placement, the strengths of its proud history and civilisation, and the limitations of its repeated struggles and political dismay. While material realism, when faced honestly, disciplines excess and teaches gratitude for what we already have, the immersion in poverty should remind us about how greed can lead to corruption and about the illusion that fulfillment lies in accumulation. A nation that does not discern its desires with its own resources and real capacity—human, historical, cultural, and environmental—will always mortgage its future to satisfy temporary cravings. We must ask ourselves honestly: how different are we today from the colonial era, when our decisions were shaped by external powers, if we remain bound by foreign debts, external models, and a forgetting of our own identity?
The immersion of plurality should not be understood as a slogan, but as a lived ethic. Sri Lanka’s diversity of language, religion, culture, geography, and memory is not the problem; it is the unfinished promise. Sinhala and Tamil, Muslim and Burgher, Buddhist, Hindu, Christian, and Muslim, village and city, coast and hill—all belong to the child in the chalk circle. While Natella-like politics weaponise difference and division, pulling the child apart to claim possession, Grusha-like care holds plurality together, recognising that it is the unity in diversity that sustains, protects, and frees the child, carrying it safely home. Freedom figures like Siddi Lebbe, Veera Puran Appu, Sir Ponnambalam Ramanathan, Sir Ponnambalam Arunachalam, C. W. W. Kannangara, T. B. Jayah, Anagarika Dharmapala, and D. S. Senanayake emerged from different faiths, languages, and regions, yet shared a common ethic: the country mattered more than self, party, or community. They were not perfect, but they were Grusha-like—unwilling to pull the child apart to prove ownership, willing instead to carry her patiently across danger.
Grusha-like care, therefore, holds plurality together, recognizing that no single group can carry the country alone. Rather, it is plurality which is the ground of freedom from coercion, selective justice, and hostage-taking—whether by professions, ideologies, or institutions that prioritize self-interest over the common good. It also demands freedom from resistance to positive change, especially when that resistance is motivated by private gain rather than the common welfare. A plural society asks: Does this serve the nation, or merely my group, my party, my advantage?
The immersion in prudence is perhaps the rarest and most neglected virtue. Prudence calls us to move from myth to science, from avidyā to vidyā, from superstition to evidence. Recent floods and landslides were not merely natural disasters; they were moral warnings. Thy painfully revealed what happens when desire overrides restraint, when planning ignores science, when land is abused, when short-term gain overrides long-term responsibility, and when development forgets sustainability. Freedom from disaster is inseparable from freedom from ignorance. Prudence teaches us to listen actively, speak intentionally, plan with evidence, build with environmental awareness, and govern with foresight. Prudence is not only about grand reforms; it is also very much about our everyday civic behaviour, such as how we treat Mother Earth and shared spaces.
For example, freedom from spitting on the ground, freedom from littering public places, and freedom from leaving behind what we refuse to clean or return. These are not small matters; they are indicators of whether people see the nation as a common home or as a place to be used and discarded. These are only a handful of many instances where we need to hear what JFK (John F. Kennedy) asked the Americans in 1961: “Ask not what your country can do for you – ask what you can do for your country”. The WWII-devastated Japan’s development is not built merely on technology, but on discipline, as systems like 5S cultivate order, responsibility, and respect for shared space. Clean Sri Lanka and the proposed Education Reforms 2026 can become transformative moments—but only if truth replaces pretense, cooperation replaces cynicism, and ownership replaces vengeful rhetoric. Prudence allows a nation to appreciate its ownness—its history, institutions, cultural resources, and the agendas for the common good—without rejecting learning from the world. Without prudence, novelty becomes addiction, and reform becomes fashion.
Before the history repeats itself for another 77 years, either as a series of tragedy or comedy, it is important, therefore, to recognise that freedom from debt, disaster, and dependency (national or personal) is impossible without all three types of immersions working together—poverty of desire, plurality of belonging, and prudence of action. Initiatives such as education reform and Clean Sri Lanka offer genuine opportunities, but only if we cooperate, think long-term, and resist turning reform into another slogan. This raises an uncomfortable question: Do we truly want to be free? Or are we content to remain in the same rut, so long as ignorance is preserved, education is left unreformed, and distractions are supplied by a handful of greedy politicians—their vengeful rhetoric, their allies, lopsided media, and mushrooming content creators—while the powerful continue to benefit from it all? Freedom is demanding. It asks for memory, restraint, cooperation, and courage. Dependency, by contrast, is easy.
Therefore, the question before us is not who shouts the loudest, who claims patriotism most aggressively, or who promises instant miracles. It is who remembers, who renounces, who embraces plurality, and who acts with prudence as her stewards and not owners. When are we going to immerse ourselves in these three immersions and be free? After Rabindranath Tagore’s poem, W. D. Amaradeva once sang, “Patu adahasnam paurinen lokaya kabaliwalata nobedi, jnanaya iwahal we… Ehew nidahase swarga rajyataṭ, mage dæśaya avadi karanu mena, Piyanani…“— Where knowledge keeps the world from being divided by the walls of narrow thoughts… Into that heaven of freedom, Father, let my country awake. How many poems, how many Amaradevas, how many freedom speeches, how many religious sermons, how many inundations, and how many struggles must come and go before we awaken to that truth and let Mother Lanka be out of that vicious pattern or circle of collapse and recovery—whole, healed, and free?
By Dr. Rashmi M. Fernando, S.J.
Loyola Marymount University, Los Angeles, CA, USA
Rashmi.Fernando@lmu.edu | https://orcid.org/0009-0006-3310-721X
Opinion
South Asian Regional Conference on State of Higher Education 2026 and Education Diplomacy
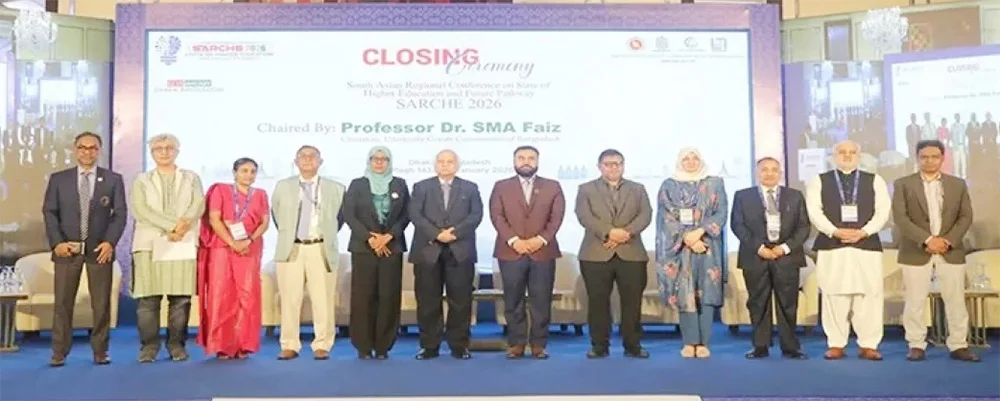

On the 15January 2026, the ‘Dhaka Declaration’ was adopted with eight strategic commitments, aimed at building a stable, inclusive, innovative and globally acceptable higher education system in the South Asian region at the third South Asian Regional Conference on State of Higher Education (SARCHE), 2026.
Advisors of the interim government, vice-chancellors of different public and private universities, scholars, researchers and diplomats were present at the third SARCHE 2026 Conference in Dhaka, emphasising the paramount importance of Education diplomacy.
The Nobel Laureate, Chief Adviser of the government, Professor Muhammad Yunus on 12th January 2026 inaugurated a three-day South Asian regional conference on higher education in Dhaka. The conference titled “South Asian Regional Conference on State of Higher Education and Future Pathway (SARCHE 2026)” organised by the Bangladesh government and World Bank funded Higher Education Acceleration and Transformation (HEAT) Project of the University Grants Commission (UGC) of Bangladesh.
Prof. Yunus’s call
Chief Adviser Professor Muhammad Yunus, has called upon the academics to align the education system with the youths’ expectations and aspirations and stressed on revival of the SAARC to enhance regional academic cooperation. “Today, I feel very excited that academics at the highest level could get together in Dhaka. It’s important that this is Dhaka. I hope you will have a chance to kind of review of the things that have happened in Dhaka in the past few months,” he said, referring to post-2024 July Uprising events in Bangladesh. Prof Yunus said review of those events will clarify what university education and education as a whole are really about, adding, this should be the core subject of discussion at the gathering.Highlighting the role of students in the 2024 uprising, he said, “Who are these young people that we are dealing with? They have their own mind. They stood up and raised their voices and brought down the ugliest fascist regime you could ever think of given their lives”.The Chief Adviser made the remarks while addressing the inaugural ceremony of the three-day “South Asian Regional Conference on State of Higher Education and Future Pathway (SARCHE 2026)” at a city hotel in Dhaka, Bangladesh. A total of 30 international representatives, including delegates from the United Kingdom, the Maldives, Malaysia, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka as well as representatives from the World Bank were represented in the event.”It would be a missed opportunity if you don’t spend some time on understanding what they did a few months back in this very city. What was their expectation? What was their aspiration? Why did they stand up in front of guns and give their lives knowingly it will happen,” the Chief Adviser said.To reflect the students’ motivation behind joining the uprising, he referred to school student Shaheed Shahriar Khan Anas’s letter, which he wrote to his mother before embracing the martyrdom, stating that it was his duty to take to the street with his friends, who were subjected to state-sponsored crackdown.Noting that the event was not a sudden outburst, Prof Yunus said it happened in Sri Lanka and in Nepal too, but it happened in a bigger way in Dhaka.
WB thanked for organisng event
He thanked the World Bank for organizing the conference, saying, “This was our responsibility to organize, but we failed. The World Bank has to step into make it happen”.Organizing such gatherings was part of the responsibility under the South Asian Association for Region-al Cooperation (SAARC), the Chief Adviser said, adding, but the SAARC as a word has been forgotten and “that’s a shame on us”. “This was supposed to be the idea of SAARC that we get together and make exchanges and learn from each other,” he said, noting his efforts since he has taken the responsibility as the Chief Adviser to revive the SAARC. “I am repeatedly reminding that we must get back to SAARC. That’s where our family belongs to. And I will not give up repeating that appeal to the governments of the region,” Prof Yunus said,Speaking about the forthcoming national elections and the referendum on February 12, he said the uprising tore everything apart and that the young people created their own July Charter to undo what the country was stuck with.
Referendum on Constitution
Chief Adviser said there would be a referendum to decide what the future constitution of Bangladesh should be, because they believed the root of the problems lay in the constitution. He said those issues were not taught in classrooms and questioned where universities stood in this reality. Noting that the young people have now formed their own political party, Prof Yunus said, “I’m sure some of them will get elected. “He called on educators to reflect on what education and university education should be in this very different world, warning that old ways of doing things are self-destructing and that change must happen quickly, just as the youth acted quickly during the July and August uprising.”So this is one issue, I hope this will be taken up seriously in this gathering where we are, what is being missed, how we can run and be in the front, rather than falling behind,” the Chief Adviser said.
He then said that the education system was not appropriate because it is job-oriented, adding, the system is designed around the idea that students must become suitable for jobs, and “If he or she fails to take a job, we think failure on the part of that student, not us”.Prof Yunus questioned whether the purpose of education is to prepare people for the job market. Human beings are not born as slaves and that each human being is a free person, he said, adding, jobs come from the tradition of slavery, where people work under orders for pay, which he equated with slavery.Stating that the young people who marched on the state refused to be slaves, he said, “So, what kind of education that you will be giving? This is a question I raise with you. You may dismiss it. You may pause for a while. But this is my point. Should we continue this education to create slaves? Turning creative beings into slaves, that’s a criminal job”. Prof Yunus said he translated creativity into entrepreneurship and argued that education should teach young people to be entrepreneurs rather than job seekers. He said young people should be told they are job creators and agents of change, driven by imagination, adding that imagination is the essence of human beings, and that people are born with enormous imagi-native power, which drove the youth to give their lives for the vision of a new Bangladesh.
Besides, representatives of UGCs and higher education commissions from SAARC member countries, vice-chancellors of universities from different countries, academicians and researchers took part in the conference.
Aim of the conference
According to the UGC, Bangladesh the conference has been organised aimed at elevating higher education in Bangladesh to a new height and further strengthen the UGC network among SAARC countries.
A total of eight sessions were held over the three-day conference. Emphasizing on “The Current State of Higher Education in South Asia: Governance, Quality and Inclusion” and “Research, Innovation, Sustainability and Social Engagement, Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration, Digital Transformation and Smart Learning Ecosystems”, “Increasing Employment for Graduates and Industry–Academia collaboration”, “Future Pathways of Higher Education: Cooperation, Solidarity and Networking, “Stakeholder Dialogue on Higher Education Transformation: Voices of Civil Society”, and “Dialogue with Vice-Chancellors: the Context of the HEAT Project, gender issues in higher education will be held while the conference l ended following the adoption of the “Dhaka Higher Education Declaration”.
UGC, Bangladesh warns against fake foreign university branches in Bangladesh. Reports in various media outlets have highlighted several foreign universities, institutes are running unauthorized branch campuses, tutorial centers, and study centers across the country. The University Grants Commission (UGC) has cautioned students and parents against enrolling in three unauthorized foreign universities reportedly operating branch campuses in Bangladesh. According to the commission, American World University, USA; Trinity University, USA; and the Spiritual Institute of New York (State University) have no government or UGC approval to conduct academic activities in the country.
On the other hand, higher education has considered as a strategic necessity for the Maldives and called for enhanced regional cooperation, industry – academia collaboration, and impact – oriented research to support inclusive growth and resilience across the region.
While Pakistan has reached its greater heights in implementation of their AI policy, World bank is acting as a strong partner in developing these endeavors of regional partners.
Lessons to be learnt
We as a country has spent huge amount of expenditure in higher education, grants and research endeavors where majority of them have took place in western academic scenario. Our attitude as Sri Lankans do not wish to learn from regional partners and we highly embrace western based cultures and their development, while regional partners have emerged beyond Sri Lanka. Very few academia is passionately engaged in development initiatives while majority have violated bonds and residing in overseas lavishly having used government expenditure which should have spent on the public wellbeing of this Country. I wonder how many governments should take control of this paradise isle to understand this reality, still we are grappling with 17 universities under the Universities act with very few international student recruitments. The case of other State Universities cannot cater the increasing local demand as they need to keep their standards. In such a scenario admission of international students and their increasing demands are questionable? Our immigration do not facilitate as a separate compartment to facilitate international student recruitment like in Malaysia.
The government enacted the Private University Act in Bangladesh in 1992 and replaced in 2010. These laws were enacted to enable private universities to supplement the governments efforts in meeting the growing demand for higher education. Under the Act, private individuals, groups and philanthropic organizations are permitted to establish and operate self -financed, degree-awarding universities by fulfilling prescribed conditions. Due to rapid increase, the 2010 Act introduced Stricker provisions focused on quality assurance, accountability and good governance. It mandates statutory bodies such as Board of trustees, Syndicate and Academic Council and clearly defines their roles and responsibilities. The Vice chancellor serves as the chief executive and academic officer of the university and is the ex-officio member the Board of Trustees. The honorable president of Bangladesh act as the chancellor of all private universities and appoint key officials upon recommendations of the Board of trustees. The Act also mandates establishment of an accreditations council to ensure quality assurance UGC supervises and monitors private universities on behalf of the Ministry of Education, approves academic programs, curricula, prescribe minimum faculty qualifications and requires transparency through annual audited financial reporting.
However, many decades have gone and the Transnational education specifically in higher education in Sri Lanka is a struggle of Authority and Power. Many of the view that the Ministry of Higher Education does not cater the entire gamut of private Higher Education Institutes operating in Sri Lanka and do not address public issues. While UGC alone handles many of the public issues even in the transnational education with no authority in non-state sector. Hence, proper enactments under one umbrella need to be empowered for the sake of public. Sri Lankan practice is the Committees appointed to address public issues does not have genuine interest or knowledge to serve this sector rather depend on benefits derived.
Therefore, SARCHE 2026 has opened eyes of Sri Lanka on how the private sector should have healthy competition with public sector, while contributing massively to strengthen the economy.
Transnational Education in Sri Lanka
According to British Council reports on transnational Education,20224 and the SAARC regional Coordinator for the British Council was of the view that Sri Lanaka does not maintain a official repository for transnational education. The Company registrar or the Board of investment do not have a official repository which serves only for higher education purpose. There is no regulatory authority to address the agency problem engaged in transnational education where finally many have reported as unethical business practices.
While India, Pakistan, Maldives and Bangladesh massively invest on Transnational education to strengthen their economies we still do not have a national plan to address this with a regulatory mechanism with proper licensing, listing for Agents to operate in Sri Lanka in order to mitigate Education fraud.
Conclusion
There was a time when students who could not secure admissions to public universities turned to private universities as a last option. That really has changed significantly. Today, many students who qualify for public universities still choose private universities because they do not get admission to their preferred subjects. The primary reason is the freedom to study the subject of their choice. However, in Sri Lanka very few private entities provides a truly a university experience. While regional partners have improved beyond 100 in establishing private universities, still private public partnership in those countries are very best examples for Sri Lanka. According to the UGC,2023 Annual report there were 341,000 students enrolled across 110 private universities in Bangladesh, now has increased to 170 according to SARCHE,2026.
Pakistan maintains best examples of Artificial Intelligence models with World Bank Funding to their University System. University Business linkages in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh provide strong examples in Transfer of Technology. While Maldives will cater for the next round of SAARC conference on the state of higher education. They invite Sri Lanka along with regional partners for preparation of qualification framework with mutual recognition of qualifications with credit transfer facility. The “Dhaka declaration of Higher Education “was adopted at the SARCHE 2026, It intend to cooperate with regional partners in many aspects in Higher Education. With these concluding remarks it is high time to consider different aspects of higher education in the proposed reforms.
By Dr. Janadari Wijesinghe
Opinion
English as used in scientific report writing
The scientific community in the English-speaking world publishes its research findings using technical and scientific English (naturally!). It has its own particular vocabulary. Many words are exclusive for a particular technology as they are specialised technical terms. Also, the inclusion in research papers of mathematical and statistical terms and calculations is important where they support the overall findings.
There is a whole array of specialist publications, journals, papers and letters serving the scientific community world-wide. These publications are by subscription only but can easily be found in university libraries upon request.
Academics quote the number of their research papers published with pride. They are the status symbols of personal achievement par excellence! And most importantly, these are used to help justify the continuation of funding for the upcoming academic year.
Such writings are carefully crafted works of precision and clarity. Not a word is out of place. All words used are nuanced to fit exactly the meaning of what the authors of the paper wish to convey. No word is superfluous (= extra, not needed); all is well manicured to convey the message accurately to a knowledgeable, receptive reader. As a result, people from all around the world are using the Internet to access these research findings thus establishing the English language as a major form of information dissemination.
Reporting is best when it is measurable and can be quantified. Figures mean a lot in the scientific world. Sizes, quantities, ranges of acceptance, figures of probability, etc., all are used to lend authority to the research findings.
Before a paper can be accepted for publication it must be submitted to a panel for peer review. This is where several experts in the subject or speciality form a panel to assess the work and approve or reject it. Careers depend on well-presented reports.
Preparation Before Starting Research
There is a standard procedure for a researcher to follow before any practical work is done. It is necessary to evaluate the current status of work in this subject. This requires reading all the relevant, available literature, books, papers, etc., on this subject. This is done for the student to get ‘up to speed’ and in tune with the preceding research work in this field. During this process new avenues for research and investigation may open up for investigation.
Much research is done incorporating the ‘design of experiments’ statistical approach. Research these days rely heavily on statistics to prove an argument and the researcher has to be familiar and conversant with these statistical techniques of inquiry and evaluation to add weight to his or her findings.
We are all much richer due to the investigations done in the English-speaking world by the investigative scientific community using English as a tool of communication. In scientific research, the best progress in innovation, it seems, is when students can all collaborate. Then the best ideas develop and come out.
Sri Lankans should not exclude themselves from this process of knowledge creation and dissemination. Sri Lanka needs to enter this scientific world and issue its own publications in good English. Sri Lanka needs experts who have mastered this form of scientific communication and who can participate in the progress of science!
The most wonderful opportunities open up from time to time for graduates of the STEM subjects (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) mainly in companies using modern technology. The reputation of Sri Lanka depends on having a horse in this race – quite apart from the need to provide suitable careers for its own population. People have ambitions and need to be able rise up intellectually and get ahead. Therefore, students in the STEM subjects need to be able to read, analyse and compare several different research papers, i.e., students need to have critical thinking skills – in English. Often, these skills have to be communicated. Students need to be able to write to this high standard of English.
Students need to be able to put their thoughts on paper in a logical, meaningful way, their thoughts backed up by facts and figures according to the principles of the academic, research world. But natural speakers of English have difficulties in mastering this type of English and doing analyses and critical thinking – therefore, it must be multiple times more difficult for Sri Lankans to master this specialised form if English. Therefore, special attention needs to be paid to overcoming this disadvantage.
In addition, the researcher needs to have knowledge of the “design of experiments,” and be familiar with everyday statistics, e.g., the bell curve, ranges of probability, etc.
How can this high-quality English (and basic stats) possibly be taught in Sri Lanka when most campuses focus on the simple passing of grammar exams?
Sri Lanka needs teachers with knowledge of this advanced, specialist form of English supported with statistical “design of experiments” knowledge. Secondly, this knowledge has to be organised and systematized and imparted over a sufficient time period to students with ability and maturity. Over to you NIE, Maharagama!
by Priyantha Hettige
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoSri Lanka, the Stars,and statesmen
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoClimate risks, poverty, and recovery financing in focus at CEPA policy panel
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHayleys Mobility ushering in a new era of premium sustainable mobility
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoSLIM-Kantar People’s Awards 2026 to recognise Sri Lanka’s most trusted brands and personalities
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoAdvice Lab unveils new 13,000+ sqft office, marking major expansion in financial services BPO to Australia
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoArpico NextGen Mattress gains recognition for innovation
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoAltair issues over 100+ title deeds post ownership change
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoSri Lanka opens first country pavilion at London exhibition













