Opinion
Protecting Sri Lanka’s maritime rights
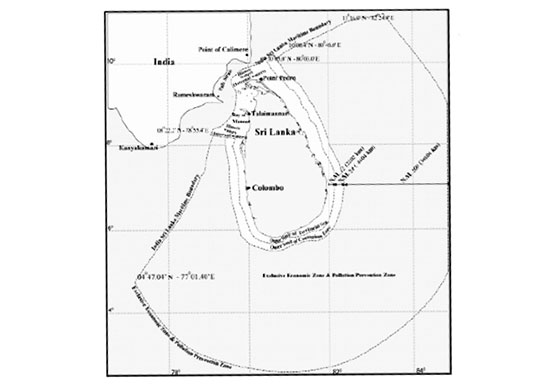
Your editorial, Poaching: Grasp the nettle (The Island of 09 June), provides a good analysis of the issue concerning the poaching of fishery resources in Sri Lanka waters, particularly in the Palk Bay and the Gulf of Mannar.
The maritime boundary between Sri Lanka and India was settled by two agreements entered into by the two countries in 1974 and 1976. Accordingly, fishing vessels and fishers of the two countries were debarred from fishing in the waters, the territorial sea and the exclusive economic zone of each other.
Subsequently, the Maritimes Zones Law, No. 22 of 1976 was enacted with provisions for the President to declare the limits of the agreed maritime boundary between the two countries, and different maritime zones of Sri Lanka, such as the historic waters, territorial sea, contiguous zone, exclusive economic zone, pollution prevention zone and the continental shelf. This law prohibits unauthorised fishing in any of the maritime zones of Sri Lanka by any foreign vessel. The President did declare the maritime zones of Sri Lanka by a proclamation published in the Gazette 248/1 of 15-01-1977. Since then unauthorized fishing by Indian vessels on the Sri Lanka side of the Palk Bay and the Gulf of Mannar became illegal.
However, part of the agreement relating to fishing has never been honoured by India, whose fishers continued to fish on the Sri Lanka side of the Palk Bay, and on the Sri Lanka side of the Gulf of Mannar, which jointly form the historic waters of Sri Lanka. According to the Presidential Proclamation, waters on the Sri Lanka side of the Palk Bay form part of the internal waters of Sri Lanka while those on the Sri Lanka side of the Gulf of Mannar form part of the territorial sea (provisions of the Law of the Sea Convention of 1982 relating to internal waters and territorial sea do not contradict such declarations provided they are made on the provisions of the customary international law). On the other hand, although prior to signing of the Maritime Boundary Agreement of 1976, Sri Lankan fishing vessels were fishing in the Wadge Bank, which fell in the EEZ of India since the Agreement came into effect, no Sri Lankan vessels has been found fishing in that area.
At present, three days a week more than 1,000 Indian trawlers fish on the Sri Lanka side of the maritime boundary in violation of the law relating to fisheries in Sri Lanka. Any Sri Lankan vessel, irrespective of the part of Sri Lanka where it is fishing, should have been registered as a fishing vessel of Sri Lanka and obtained a fishing licence. Further, no such vessel is allowed to engage in mechanised bottom trawling.
There have been many discussions between the two countries since the 1990s to stop this illegal practice by Indian trawlers. Such discussions only end up with agreed minutes, but no solution. Fisheries (Regulation of Foreign Fishing Boats) Act, No 59 of 1979 provides for a High Court Judge to impose a penalty of a fine of Rs. 1.5 million on any foreign vessels engaged in unauthorised fishing in Sri Lanka waters. However, this provision was never used against any Indian trawler caught in Sri Lanka waters with unauthorised fishing, owing to practical difficulties. Subsequently, in 2017, the Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (Amendment) Act, No. 11 was enacted to impose a two-year jail term or a fine of at least Rs. 50,000 with a view to controlling this problem. Although the Sri Lanka Navy takes into custody Indian trawlers and hands them over with fishers to Fisheries authorities, the moment they get a letter from the Indian High Commission asking for their release, all are released. In this context, sinking unusable buses in the sea in this area appears to be a practical solution to the problem. For that also India has expressed objections. Sri Lanka has sovereign rights to take any decision in regard to its internal waters, and territorial sea (subject to the right of innocent passage of any foreign vessel) and historic waters (these form part of either internal waters or the territorial sea). Therefore, it is not necessary to stop this activity, just because India is objecting.
As regards the claim by India that Sri Lankan vessels also engage in unauthorised fishing in India waters, it should be noted that they are taken into custody rarely in very small numbers; that, too, mostly in the Indian EEZ, while they are returning after fishing in the Arabian sea. Any vessel has the right to navigation in the EEZ of any country. Even when innocent Sri Lankan fishers happen to be caught by the Indian authorities, they are made to suffer in Indian jails.
A few years earlier also, you expressed concern on this issue by an editorial, Saying it with fish, when Sri Lanka released all Indian fishers who were in jail in Sri Lanka pending trials, as a gesture of thanks for India’s vote at the UN in favour of Sri Lanka. Thank you for your concerns.
A. HETTIARACHCHI
hetti-a@sltnet.lk
Opinion
We do not want to be press-ganged

Reference ,the Indian High Commissioner’s recent comments ( The Island, 9th Jan. ) on strong India-Sri Lanka relationship and the assistance granted on recovering from the financial collapse of Sri Lanka and yet again for cyclone recovery., Sri Lankans should express their thanks to India for standing up as a friendly neighbour.
On the Defence Cooperation agreement, the Indian High Commissioner’s assertion was that there was nothing beyond that which had been included in the text. But, dear High Commissioner, we Sri Lankans have burnt our fingers when we signed agreements with the European nations who invaded our country; they took our leaders around the Mulberry bush and made our nation pay a very high price by controlling our destiny for hundreds of years. When the Opposition parties in the Parliament requested the Sri Lankan government to reveal the contents of the Defence agreements signed with India as per the prevalent common practice, the government’s strange response was that India did not want them disclosed.
Even the terms of the one-sided infamous Indo-Sri Lanka agreement, signed in 1987, were disclosed to the public.
Mr. High Commissioner, we are not satisfied with your reply as we are weak, economically, and unable to clearly understand your “India’s Neighbourhood First and Mahasagar policies” . We need the details of the defence agreements signed with our government, early.
RANJITH SOYSA
Opinion
When will we learn?

At every election—general or presidential—we do not truly vote, we simply outvote. We push out the incumbent and bring in another, whether recycled from the past or presented as “fresh.” The last time, we chose a newcomer who had spent years criticising others, conveniently ignoring the centuries of damage they inflicted during successive governments. Only now do we realise that governing is far more difficult than criticising.
There is a saying: “Even with elephants, you cannot bring back the wisdom that has passed.” But are we learning? Among our legislators, there have been individuals accused of murder, fraud, and countless illegal acts. True, the courts did not punish them—but are we so blind as to remain naive in the face of such allegations? These fraudsters and criminals, and any sane citizen living in this decade, cannot deny those realities.
Meanwhile, many of our compatriots abroad, living comfortably with their families, ignore these past crimes with blind devotion and campaign for different parties. For most of us, the wish during an election is not the welfare of the country, but simply to send our personal favourite to the council. The clearest example was the election of a teledrama actress—someone who did not even understand the Constitution—over experienced and honest politicians.
It is time to stop this bogus hero worship. Vote not for personalities, but for the country. Vote for integrity, for competence, and for the future we deserve.
Deshapriya Rajapaksha
Opinion
Chlorophyll –The Life-giver is in peril
Chlorophyll is the green pigment found in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. It is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy to sustain life on Earth. As it is green it reflects Green of the sunlight spectrum and absorbs its Red and Blue ranges. The energy in these rays are used to produce carbohydrates utilising water and carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen in the process. Thus, it performs, in this reaction, three functions essential for life on earth; it produces food and oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to maintain equilibrium in our environment. It is one of the wonders of nature that are in peril today. It is essential for life on earth, at least for the present, as there are no suitable alternatives. While chlorophyll can be produced in a lab, it cannot be produced using simple, everyday chemicals in a straightforward process. The total synthesis of chlorophyll is an extremely complex multi-step organic chemistry process that requires specialized knowledge, advanced laboratory equipment, and numerous complex intermediary compounds and catalysts.
Chlorophyll probably evolved inside bacteria in water and migrated to land with plants that preceded animals who also evolved in water. Plants had to come on land first to oxygenate the atmosphere and make it possible for animals to follow. There was very little oxygen in the ocean or on the surface before chlorophyll carrying bacteria and algae started photosynthesis. Now 70% of our atmospheric oxygen is produced by sea phytoplankton and algae, hence the importance of the sea as a source of oxygen.
Chemically, chlorophyll is a porphyrin compound with a central magnesium (Mg²⁺) ion. Factors that affect its production and function are light intensity, availability of nutrients, especially nitrogen and magnesium, water supply and temperature. Availability of nutrients and temperature could be adversely affected due to sea pollution and global warming respectively.
Temperature range for optimum chlorophyll function is 25 – 35 C depending on the types of plants. Plants in temperate climates are adopted to function at lower temperatures and those in tropical regions prefer higher temperatures. Chlorophyll in most plants work most efficiently at 30 C. At lower temperatures it could slow down and become dormant. At temperatures above 40 C chlorophyll enzymes begin to denature and protein complexes can be damaged. Photosynthesis would decline sharply at these high temperatures.
Global warming therefore could affect chlorophyll function and threaten its very existence. Already there is a qualitative as well as quantitative decline of chlorophyll particularly in the sea. The last decade has been the hottest ten years and 2024 the hottest year since recording had started. The ocean absorbs 90% of the excess heat that reaches the Earth due to the greenhouse effect. Global warming has caused sea surface temperatures to rise significantly, leading to record-breaking temperatures in recent years (like 2023-2024), a faster warming rate (four times faster than 40 years ago), and more frequent, intense marine heatwaves, disrupting marine life and weather patterns. The ocean’s surface is heating up much faster, about four times quicker than in the late 1980s, with the last decade being the warmest on record. 2023 and 2024 saw unprecedented high sea surface temperatures, with some periods exceeding previous records by large margins, potentially becoming the new normal.
Half of the global sea surface has gradually changed in colour indicating chlorophyll decline (Frankie Adkins, 2024, Z Hong, 2025). Sea is blue in colour due to the absorption of Red of the sunlight spectrum by water and reflecting Blue. When the green chlorophyll of the phytoplankton is decreased the sea becomes bluer. Researchers from MIT and Georgia Tech found these color changes are global, affecting over half the ocean’s surface in the last two decades, and are consistent with climate model predictions. Sea phytoplankton and algae produce more than 70% of the atmospheric oxygen, replenishing what is consumed by animals. Danger to the life of these animals including humans due to decline of sea chlorophyll is obvious. Unless this trend is reversed there would be irreparable damage and irreversible changes in the ecosystems that involve chlorophyll function as a vital component.
The balance 30% of oxygen is supplied mainly by terrestrial plants which are lost due mainly to human action, either by felling and clearing or due to global warming. Since 2000, approximately 100 million hectares of forest area was lost globally by 2018 due to permanent deforestation. More recent estimates from the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) indicate that an estimated 420 million hectares of forest have been lost through deforestation since 1990, with a net loss of approximately 4.7 million hectares per year between 2010 and 2020 (accounting for forest gains by reforestation). From 2001 to 2024, there had been a total of 520 million hectares of tree cover loss globally. This figure includes both temporary loss (e.g., due to fires or logging where forests regrow) and permanent deforestation. Roughly 37% of tree cover loss since 2000 was likely permanent deforestation, resulting in conversion to non-forest land uses such as agriculture, mining, or urban development. Tropical forests account for the vast majority (nearly 94%) of permanent deforestation, largely driven by agricultural expansion. Limiting warming to 1.5°C significantly reduces risks, but without strong action, widespread plant loss and biodiversity decline are projected, making climate change a dominant threat to nature, notes the World Economic Forum. Tropical trees are Earth’s climate regulators—they cool the planet, store massive amounts of carbon, control rainfall, and stabilize global climate systems. Losing them would make climate change faster, hotter, and harder to reverse.
Another vital function of chlorophyll is carbon fixing. Carbon fixation by plants is crucial because it converts atmospheric carbon dioxide into organic compounds, forming the base of the food web, providing energy/building blocks for life, regulating Earth’s climate by removing greenhouse gases, and driving the global carbon cycle, making life as we know it possible. Plants use carbon fixation (photosynthesis) to create their own food (sugars), providing energy and organic matter that sustains all other life forms. By absorbing vast amounts of CO2 (a greenhouse gas) from the atmosphere, plants help control its concentration, mitigating global warming. Chlorophyll drives the Carbon Cycle, it’s the primary natural mechanism for moving inorganic carbon into the biosphere, making it available for all living organisms.
In essence, carbon fixation turns the air we breathe out (carbon dioxide) into the food we eat and the air we breathe in (oxygen), sustaining ecosystems and regulating our planet’s climate.
While land plants store much more total carbon in their biomass, marine plants (like phytoplankton) and algae fix nearly the same amount of carbon annually as all terrestrial plants combined, making the ocean a massive and highly efficient carbon sink, especially coastal ecosystems that sequester carbon far faster than forests. Coastal marine plants (mangroves, salt marshes, seagrasses) are extremely efficient carbon sequesters, absorbing carbon at rates up to 50 times faster than terrestrial forests.
If Chlorophyll decline, which is mainly due to human action driven by uncontrolled greed, is not arrested as soon as possible life on Earth would not be possible.
(Some information was obtained from Wikipedia)
by N. A. de S. Amaratunga ✍️
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoSajith: Ashoka Chakra replaces Dharmachakra in Buddhism textbook
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoDialog and UnionPay International Join Forces to Elevate Sri Lanka’s Digital Payment Landscape
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoThe Paradox of Trump Power: Contested Authoritarian at Home, Uncontested Bully Abroad
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoSubject:Whatever happened to (my) three million dollars?
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoLevel I landslide early warnings issued to the Districts of Badulla, Kandy, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya extended
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoNational Communication Programme for Child Health Promotion (SBCC) has been launched. – PM
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days ago65 withdrawn cases re-filed by Govt, PM tells Parliament
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoThe minstrel monk and Rafiki, the old mandrill in The Lion King – II











