Features
Options for Foreign Debt Management in Sri Lanka: Can we escape from IMF/ISB Debt Trap?
by Luxman Siriwardena,
Managing Director,
Veemansa Innitiative,
Think Tank and Advocacy Group
The setback due to the pandemic has aggravated some of the perennial macro-economic and sectoral problems in Sri Lanka. For example, borrowing and accumulating external debts has been a practice of successive governments since 1978, which was the year of partial liberalization of the economy. During the early periods, when Sri Lanka was considered a low-income country, we were entitled to substantial grant aid as well as concessionary finances.
This relatively low interest facilities and lenient conditionalities provided incentives for the governments to keep borrowing for many development projects, from bi-lateral and multi-lateral lending agencies, irrespective of inflated costs of many of these projects. In most of these cases, financial benefits also have spilled over to Sri Lankan politicians, bureaucrats, and technocrats. Notwithstanding such leakages, these foreign funded projects increased the availability of more sophisticated infrastructure and utilities in sectors such as, electricity, highways, drinking and irrigation water, as well as the Colombo port and airports. In addition, education, agriculture and health were the prime targets of both Sri Lankan policy makers and donors/lenders.
There was a period when Sri Lanka was termed as “a Donor Darling” (see figure).
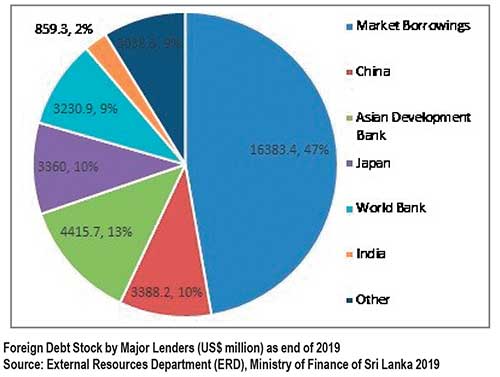
Sri Lanka became a darling of the Western donors primarily due its subservience to the West under Jayawardena-Premadasa regime). However, since we attained lower-middle income country status, concessionary funding has not been available and therefore, most borrowings have been at commercial or near commercial lending rates. In this context, the country has accumulated over US$ 34.7bn debt1 up to 2019. These borrowings have been for development projects, import of consumption items and direct budgetary support to meet current expenditure, including debt servicing. The current debt situation.
At the moment, one of the most critical challenges for the Rajapaksa administration is managing or preferably reducing Sri Lanka’s debt while meeting the current level of foreign exchange requirements and hopefully implementing necessary development projects.
While the selected development projects are generally presented to the multilateral donors; World Bank and ADB as well as bilateral lending institutions such as JICA, US-AID and similar institutions in China and European countries, seeking loan financing, the rates of lending are equal or closer to the market rates. Since 2007, borrowing through International Sovereign Bonds (ISBs), which became a common practice, has now emerged as the most serious challenge for the current government to ensure sustainability or reduction foreign debt.
The focus of this article is to discuss alternative methods of managing the debt in spite of the COVID-19 pandemic that has pushed almost the entire world (other than China) into a recession.
In this context, conventional economic policy pandits, academics and consultants recommend that the emerging economies such as Sri Lanka should seek the refuge in International Monetary Fund (IMF) Programmes. Based on the IMF guarantees the countries in foreign debt crisis will be eligible for further assistance from other multilateral and bilateral lenders, while qualifying for accessing the International Sovereign Bond Market. According to this prescription, without the support and blessing of the IMF, we have no way of securing sufficient funding for re-payment of maturing debt, balance of payment requirements or development programmes.
Since the election of the new government all our well-known economists, and many so-called experts have been promoting the above policy prescription as Sri Lanka is, according their assessment, at the verge of a default and economic collapse. Most if not, all these pandits were expecting the government will continue to proceed with the borrowing from the international markets subscribing to Samurai or Panda bonds. Surprisingly our conventional economic advisors are increasingly becoming impatient and critical of the Government for not negotiating with the IMF to enter into a programme which will be entitled and receive loan facility and more importantly in turn qualify for raising finance through ISBs. Does this process lead to a reduction of debt or payback of loans? Of course not, nor reduction of debt burden or the severity of the debt problem.
As an IMF programme is likely to impose conditionalities to meet the Fund’s debt sustainability parameters, the readers may perhaps understand that, this approach is not even to reduce the severity of the debt problem but for reducing the burden over the next few years by extending maturities probably through some form of ‘Grace Period’. The bottom line will be that Sri Lanka will continue to have challenging debt dynamics which I would like to call it as ‘IMF/ISB DEBT TRAP’ as long as we fail to achieve substantial increase of exports and FDI. In other words, we will merely be postponing and aggravating the debt problem unless we can accelerate growth by increasing production of tradable goods and services which will earn or save foreign exchange.
Cost of raising funds through International Sovereign Bonds
A sovereign bond is defined as a debt instrument issued by a national government to raise generally foreign currency requirements in case of countries such as Sri Lanka. Sovereign bonds are denominated in foreign currencies such as USD, the Euro, Japanese Yen and Chinese Yuan. The successful issue of ISBs require several steps engaging highly professional individuals and institutions including global banking giants. Under each of these steps many upfront costs are to be incurred by the government. A typical bond issue involves, fees (commissions) and other expenses. Three large components of the fees, according to a World Bank document are for the lead-managers, rating costs and legal expenses. Interestingly those transaction costs are paid at time of issuance (upfront). In spite of the competition among the banks there is little transparency specially with regard to bond issues of countries like Sri Lanka. Another major expense is often for obtaining a rating for each bond which is generally similar to the fee for the lead-managers. There are also expenses for legal counsel, marketing especially road shows, fiscal and paying agents and advisors. Cost will also depend on which markets are targeted for the road shows undertaken in major cities in developed market economies.
Throughout the Sri Lankan history of issuing ISBs people have only learned about the total value of the bond issues and subscribed but not the direct and indirect costs that have been incurred in the process, for example, officials of the Central Bank, Ministry of Finance, etc. will be travelling to several capitals in the world for negotiations, road shows and other associated events etc. incurring scarce foreign exchange of Sri Lanka. Of course it should have provided very tempting incentive for this approach
Some economists who are faithful followers of IMF policy prescriptions prefers to identify the IMF/ISB Debt Trap as the symptom not the cause of the problem. According to them the debt trap was caused by poor fiscal outcomes over many years and IMF/ISB debt was incurred to meet deficit financing.
In this article, the most pertinent and decisive issue to raise is, what should be the alternative policy recommendations of our learned economists. As we all are well aware if Sri Lanka qualifies to receive assistance from the IMF, such funding will be for as balance of payment support subject to certain conditionality which are likely to include; removal or reduction of subsidies, removal of import controls, non-strategic assets privatization, etc. and many such measures of government interventions.
Many, if not all these adjustments will be painful to the ordinary citizens and therefore, make it difficult to sell politically. If Sri Lanka for that matter, any other country in our predicament is not willing to go through an IMF austerity programme with its stringent conditionalities, what options are available for them. Let’s discuss what appears to be the economic management strategy of the current government. With the lockdown of the world economies and disruption of global value-chains, Sri Lankan government was compelled to ‘Close the Economy’ to some degree. Subsequently, the government policy makers seem to be implementing a fairly well-managed import administration scheme and associated measures to ensure enhanced foreign exchange savings. Current import management scheme has selectively targeted non-essential ‘big-ticket’ items.
In order to prevent further deterioration of the debt situation the government seems to be minimizing new borrowings for implementation of numerous development projects with commercial characteristics. Both acceding to IMF austerity programme, as well as, controls imposed by the government will have contractionary impact on the local economy. Of course, second option will reduce the confidence of capital markets, foreign equity investors and even some local enterprises. Generally, IMF programs are sold to a government in-need of balance of payment support on the basis that agreement with the Fund would pave way for the country to achieve a higher sovereign rating and confidence of the investors in ISBs.
Pertinent question here is, as learned economists, professionals and advisors, are they in a position to develop an alternative development strategy for Sri Lanka in order to overcome the current difficulties reducing the severity of the debt burden created primarily through borrowings from ISBs. It appears that the, current administration is developing a strategy that will cause less pain to the people than under an IMF program and have more positive outcomes in terms of output, employment and incomes.
Unfortunately, however, in the past, we have rarely seen Sri Lankan policy makers or even academics develop alternative concepts or strategies instead of repeating what they have learned as classical, neo-classical or Keynesian schools and reinforced by the training programs conducted by multilateral or bilateral lending agencies.
In conclusion, let me quote once again from my recently published article;
“Whatever the reasons are, instead of thinking independently on their own most of our economists parrot their mentors in the west for short-term gains like easy recognition and self-fulfillment PROMOTING THE SAME FORMULA AGRAVATING the vicious circle and perpetuating the misery of our people. Irony is that when a solution is needed the only thing some of our experts are capable of recommending is to seek refuge in borrowing from multilateral or bilateral lending agencies. Most Sri Lankans need to be reminded that, Sri Lanka has already gone under 16-IMF Programs and have reached the current predicament. This reminds us the famous saying attributed to Einstein that “insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting different outcomes’’.
Signs are that the current administration is deviating from the orthodoxy and searching for innovative and pragmatic development path.
(Article is based on a key-note address delivered by the writer at the 08th International Research Conference conducted by the department of Economics and Statistics, University of Peradeniya)
Features
Sheer rise of Realpolitik making the world see the brink
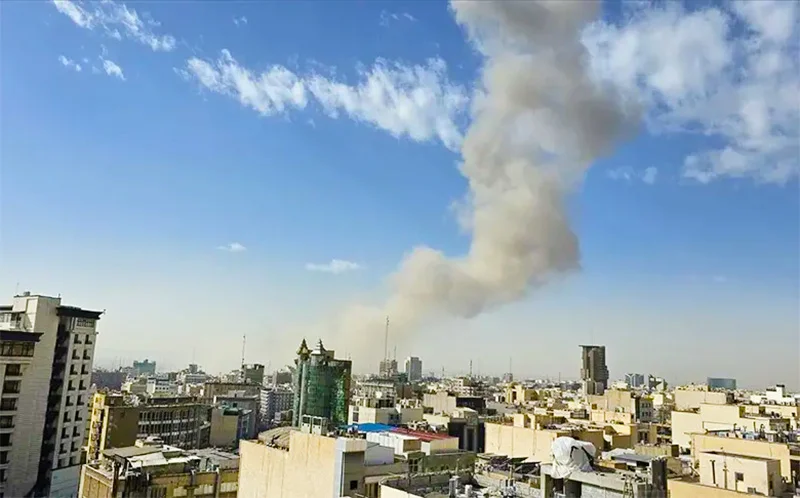

 The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
As matters stand, there seems to be no credible evidence that the Indian state was aware of the impending torpedoing of the Iranian vessel but these acerbic-tongued politicians of Sri Lanka’s South would have the local public believe that the tragedy was triggered with India’s connivance. Likewise, India is accused of ‘embroiling’ Sri Lanka in the incident on account of seemingly having prior knowledge of it and not warning Sri Lanka about the impending disaster.
It is plain that a process is once again afoot to raise anti-India hysteria in Sri Lanka. An obligation is cast on the Sri Lankan government to ensure that incendiary speculation of the above kind is defeated and India-Sri Lanka relations are prevented from being in any way harmed. Proactive measures are needed by the Sri Lankan government and well meaning quarters to ensure that public discourse in such matters have a factual and rational basis. ‘Knowledge gaps’ could prove hazardous.
Meanwhile, there could be no doubt that Sri Lanka’s sovereignty was violated by the US because the sinking of the Iranian vessel took place in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While there is no international decrying of the incident, and this is to be regretted, Sri Lanka’s helplessness and small player status would enable the US to ‘get away with it’.
Could anything be done by the international community to hold the US to account over the act of lawlessness in question? None is the answer at present. This is because in the current ‘Global Disorder’ major powers could commit the gravest international irregularities with impunity. As the threadbare cliché declares, ‘Might is Right’….. or so it seems.
Unfortunately, the UN could only merely verbally denounce any violations of International Law by the world’s foremost powers. It cannot use countervailing force against violators of the law, for example, on account of the divided nature of the UN Security Council, whose permanent members have shown incapability of seeing eye-to-eye on grave matters relating to International Law and order over the decades.
The foregoing considerations could force the conclusion on uncritical sections that Political Realism or Realpolitik has won out in the end. A basic premise of the school of thought known as Political Realism is that power or force wielded by states and international actors determine the shape, direction and substance of international relations. This school stands in marked contrast to political idealists who essentially proclaim that moral norms and values determine the nature of local and international politics.
While, British political scientist Thomas Hobbes, for instance, was a proponent of Political Realism, political idealism has its roots in the teachings of Socrates, Plato and latterly Friedrich Hegel of Germany, to name just few such notables.
On the face of it, therefore, there is no getting way from the conclusion that coercive force is the deciding factor in international politics. If this were not so, US President Donald Trump in collaboration with Israeli Rightist Premier Benjamin Natanyahu could not have wielded the ‘big stick’, so to speak, on Iran, killed its Supreme Head of State, terrorized the Iranian public and gone ‘scot-free’. That is, currently, the US’ impunity seems to be limitless.
Moreover, the evidence is that the Western bloc is reuniting in the face of Iran’s threats to stymie the flow of oil from West Asia to the rest of the world. The recent G7 summit witnessed a coming together of the foremost powers of the global North to ensure that the West does not suffer grave negative consequences from any future blocking of western oil supplies.
Meanwhile, Israel is having a ‘free run’ of the Middle East, so to speak, picking out perceived adversarial powers, such as Lebanon, and militarily neutralizing them; once again with impunity. On the other hand, Iran has been bringing under assault, with no questions asked, Gulf states that are seen as allying with the US and Israel. West Asia is facing a compounded crisis and International Law seems to be helplessly silent.
Wittingly or unwittingly, matters at the heart of International Law and peace are being obfuscated by some pro-Trump administration commentators meanwhile. For example, retired US Navy Captain Brent Sadler has cited Article 51 of the UN Charter, which provides for the right to self or collective self-defence of UN member states in the face of armed attacks, as justifying the US sinking of the Iranian vessel (See page 2 of The Island of March 10, 2026). But the Article makes it clear that such measures could be resorted to by UN members only ‘ if an armed attack occurs’ against them and under no other circumstances. But no such thing happened in the incident in question and the US acted under a sheer threat perception.
Clearly, the US has violated the Article through its action and has once again demonstrated its tendency to arbitrarily use military might. The general drift of Sadler’s thinking is that in the face of pressing national priorities, obligations of a state under International Law could be side-stepped. This is a sure recipe for international anarchy because in such a policy environment states could pursue their national interests, irrespective of their merits, disregarding in the process their obligations towards the international community.
Moreover, Article 51 repeatedly reiterates the authority of the UN Security Council and the obligation of those states that act in self-defence to report to the Council and be guided by it. Sadler, therefore, could be said to have cited the Article very selectively, whereas, right along member states’ commitments to the UNSC are stressed.
However, it is beyond doubt that international anarchy has strengthened its grip over the world. While the US set destabilizing precedents after the crumbling of the Cold War that paved the way for the current anarchic situation, Russia further aggravated these degenerative trends through its invasion of Ukraine. Stepping back from anarchy has thus emerged as the prime challenge for the world community.
Features
A Tribute to Professor H. L. Seneviratne – Part II

A Living Legend of the Peradeniya Tradition:
(First part of this article appeared yesterday)
H.L. Seneviratne’s tenure at the University of Virginia was marked not only by his ethnographic rigour but also by his profound dedication to the preservation and study of South Asian film culture. Recognising that cinema is often the most vital expression of a society’s aspirations and anxieties, he played a central role in curating what is now one of the most significant Indian film collections in the United States. His approach to curation was never merely archival; it was informed by his anthropological work, treating films as primary texts for understanding the ideological shifts within the subcontinent
The collection he helped build at the UVA Library, particularly within the Clemons Library holdings, serves as a comprehensive survey of the Indian ‘Parallel Cinema’ movement and the works of legendary auteurs. This includes the filmographies of directors such as Satyajit Ray, whose nuanced portrayals of the Indian middle class and rural poverty provided a cinematic counterpart to H.L. Seneviratne’s own academic interests in social change. By prioritising the works of figures such as Mrinal Sen and Ritwik Ghatak, H.L. Seneviratne ensured that students and scholars had access to films that wrestled with the complex legacies of colonialism, partition, and the struggle for national identity.
These films represent the ‘Parallel Cinema’ movement of West Bengal rather than the commercial Hindi industry of Mumbai. H.L. Seneviratne’s focus initially cantered on those world-renowned Bengali masters; it eventually broadened to encompass the distinct cinematic languages of the South. These films refer to the specific masterpieces from the Malayalam and Tamil regions—such as the meditative realism of Adoor Gopalakrishnan or the stylistic innovations of Mani Ratnam—which are culturally and linguistically distinct from the Bengali works. Essentially, H.L. Seneviratne is moving from the specific (Bengal) to the panoramic, ensuring that the curatorial work of H.L. Seneviratne was not just a ‘Greatest Hits of Kolkata’ but a truly national representation of Indian artistry. These films were selected for their ability to articulate internal critiques of Indian society, often focusing on issues of caste, gender, and the impact of modernisation on traditional life. Through this collection, H.L. Seneviratne positioned cinema as a tool for exposing the social dynamics that often remain hidden in traditional historical records, much like the hidden political rituals he uncovered in his early research.
Beyond the films themselves, H.L. Seneviratne integrated these visual resources into his curriculum, fostering a generation of scholars who understood the power of the image in South Asian politics. He frequently used these screenings to illustrate the conflation of past and present, showing how modern cinema often reworks ancient myths to serve contemporary political agendas. His legacy at the University of Virginia therefore encompasses both a rigorous body of writing that deconstructed the work of the kings and a vivid archive of films that continues to document the work of culture in a rapidly changing world.
In his lectures on Sri Lankan cinema, H.L. Seneviratne has frequently championed Lester James Peries as the ‘father of authentic Sinhala cinema.’ He views Peries’s 1956 film Rekava (Line of Destiny) as a watershed moment that liberated the local industry from the formulaic influence of South Indian commercial films. For H.L. Seneviratne, Peries was not just a filmmaker but an ethnographer of the screen. He often points to Peries’s ability to capture the subtle rhythms of rural life and the decline of the feudal elite, most notably in his masterpiece Gamperaliya, as a visual parallel to his own research into the transformation of traditional authority. H.L. Seneviratne argues that Peries provided a realistic way of seeing for the nation, one that eschewed nationalist caricature in favour of complex human emotion.
However, H.L. Seneviratne’s praise for Peries is often tempered by a critique of the broader visual nationalism that followed. He has expressed concern that later filmmakers sometimes misappropriated Peries’s indigenous style to promote a narrow, majoritarian view of history. In his view, while Peries opened the door to an authentic Sri Lankan identity, the state and subsequent commercial interests often used that same door to usher in a simplified, heroic past. This critique aligns with his broader academic stance against the rationalization of culture for political ends.
Constitutional Governance:
H.L. Seneviratne’s support for independent commissions is best described as a hopeful pragmatism; he views them as essential, albeit fragile, instruments for diffusing the hyper-concentration of executive power. Writing to Colombo Page and several news tabloids, H.L. Seneviratne addresses the democratic deficit by creating a structural buffer between partisan interests and public institutions, theoretically ensuring that the judiciary, police, and civil service operate on merit rather than political whim. However, he remains deeply aware that these commissions are not a panacea and are indeed inherently susceptible to the ‘politics of patronage.’
In cultures where power is traditionally exercised through personal loyalties, there is a constant risk that these bodies will be subverted through the appointment of hidden partisans or rendered toothless through administrative sabotage. Thus, while H.L. Seneviratne advocates for them as a means to transition a state from a patron-client culture to a rule-of-law framework, his anthropological lens suggests that the success of such commissions depends less on the law itself and more on the sustained pressure of civil society to keep them honest.
Whether discussing the nuances of a film’s narrative or the complexities of a constitutional clause, H.L. Seneviratne’s approach remains consistent in its focus on the spirit behind the institution. He maintains that a healthy democracy requires more than just the right laws or the right symbols; it requires a citizenry and a clergy capable of critical self-reflection. His career at the University of Virginia and his continued engagement with Sri Lankan public life stand as a testament to the idea that the intellectual’s work is never truly finished until the work of the people is fully realized.
In the context of H.L. Seneviratne’s philosophy, as discussed in his work of the kings ‘the work of the people’ is far more than a populist catchphrase; it represents the practical application of critical consciousness within a democracy. Rather than defining ‘work’ as labour or voting, H.L. Seneviratne views it as the transition of a population from passive subjects to an active, self-reflective citizenry. This means that a democracy is only truly ‘realized’ when the public possesses the intellectual autonomy to look beyond the ‘right laws’ or ‘right symbols’ and instead engage with the underlying spirit of their institutions. For H.L. Seneviratne, this work is specifically tied to the ability of the people—including influential groups like the clergy—to perform rigorous self-critique, ensuring that they are not merely following tradition or authority, but are actively sustaining the ethical health of the nation. It is a perpetual process of civic education and moral vigilance that moves a society from the ‘paper’ democracy of a constitution to a lived reality of accountability and insight.
This decline of the ‘intellectual monk’ had a catastrophic impact on the political landscape, particularly surrounding the watershed moment of 1956 and the ‘Sinhala Only’ movement. H.L. Seneviratne posits that when the Sangha exchanged their role as impartial moral advisors for that of political kingmakers, they became the primary obstacle to ethnic reconciliation. He suggests that politicians, fearing the immense grassroots influence of the monks, entered a state of monachophobia, where they felt unable to propose pluralistic or fair policies toward minority communities for fear of being branded as traitors to the faith. In H.L. Seneviratne’s framework, the monk’s transition from a social servant to a political vanguard effectively trapped the state in a cycle of majoritarian nationalism from which it has yet to escape.
H.L. Seneviratne’s work serves as a multifaceted critique of the modern Sri Lankan state and its cultural foundations. Whether he is dissecting what he sees as the betrayal of the monastic ideal or celebrating the humanistic vision of an Indian filmmaker, his goal remains the same: to champion a world where intellect and compassion are not sacrificed on the altar of political power. His legacy at the University of Virginia and his continued voice in Sri Lankan discourse remind us that the work of the intellectual is to provide a moral compass even, indeed especially, when the nation has lost its way.
(Concluded)
by Professor
M. W. Amarasiri de Silva
Features
Musical journey of Nilanka Anjalee …

 Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe is, in fact, a reputed doctor, but the plus factor is that she has an awesome singing voice, as well., which stands as a reminder that music and intellect can harmonise beautifully.
Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe is, in fact, a reputed doctor, but the plus factor is that she has an awesome singing voice, as well., which stands as a reminder that music and intellect can harmonise beautifully.
Well, our spotlight today is on ‘Nilanka – the Singer,’ and not ‘Nilanka – the Singing Doctor!’
Nilanka’s journey in music began at an early age, nurtured by an ear finely tuned to nuance and a heart that sought expression beyond words.
Under the tutelage of her singing teachers, she went on to achieve the A.T.C.L. Diploma in Piano and the L.T.C.L. Diploma in Vocals from Trinity College, London – qualifications recognised internationally for their rigor and artistry.
These achievements formally certified her as a teacher and performer in both opera singing and piano music, while her Performer’s Certificate for singing attested to her flair on stage.
Nilanka believes that music must move the listener, not merely impress them, emphasising that “technique is a language, but emotion is the message,” and that conviction shines through in her stage presence –serene yet powerful, intimate yet commanding.
Her YouTube channel, Facebook and Instagram pages, “Nilanka Anjalee,” have become a window into her evolving artistry.
Here, audiences find not only her elegant renditions of local and international pieces but also her original songs, which reveal a reflective and modern voice with a timeless sensibility.
Each performance – whether a haunting ballad or a jubilant interpretation of a traditional hymn – carries her signature blend of technical finesse and emotional depth.
Beyond the concert hall and digital stage, Nilanka’s music is driven by a deep commitment to meaning.
Her work often reflects her belief in empathy, inner balance, and the beauty of simplicity—values that give her performances their quiet strength.
She says she continues to collaborate with musicians across genres, composing and performing pieces that reflect both her classical discipline and her contemporary outlook.
Widely acclaimed for her ability to adapt to both formal and modern stages, with equal grace, and with her growing repertoire, Nilanka has become a sought-after soloist at concerts and special events,
For those who seek to experience her artistry, firsthand, Nilanka Anjalee says she can be contacted for live performances and collaborations through her official channels.
Her voice – refined, resonant, and resolutely her own – reminds us that music, at its core, is not about perfection, but truth.
Dr. Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe also indicated that her newest single, an original, titled ‘Koloba Ahasa Yata,’ with lyrics, melody and singing all done by her, is scheduled for release this month (March)
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPeradeniya Uni issues alert over leopards in its premises
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoFemale lawyer given 12 years RI for preparing forged deeds for Borella land
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoLibrary crisis hits Pera university
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days ago‘IRIS Dena was Indian Navy guest, hit without warning’, Iran warns US of bitter regret
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoSri Lanka evacuates crew of second Iranian vessel after US sunk IRIS Dena