Features
My clash with Philip Gunawardene in the parliament restaurant

(Excerpted from Falling Leaves, an anthology of memoirs
by LC Aulpragasam)
A Personal Note
In early 1958, I was appointed Deputy Commissioner of the Agrarian Services Department, in charge of implementing the Paddy Lands Act of 1958, under the general direction of the Commissioner. As an officer of the CCS I already had some training and experience in law and administration as well as experience in wet and dry zone agriculture and irrigation.
In setting out to draft the Administrative Regulations under the Act, I came across a number of structural, legal and operational considerations, which probably had not been foreseen by its authors – probably because this was the first time it was being looked at by an administrator with field experience.
The deeper I delved, the more the legal challenges that I foresaw, and the greater the problems from an implementation point of view. First from the conceptual side, the concept and design of the Act did not fit, for example, the agrarian conditions in the Batticaloa district, which raised some problems of implementation. Secondly, because of the Act’s highly contentious nature, its legal provisions were likely to be challenged and its implementation obstructed.
This made it necessary to examine its provisions from an adversarial point of view – which revealed many legal and administrative vulnerabilities. Thirdly, there were new problems of implementation. For example, new records of land ownership, tenancy, etc. would have to be created from scratch (since no such records ever existed) before implementation could even begin. In comparison, the land records in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh had been built up over a period of 200-300 years by the British colonial power. How could such records be created within the six months before the Act would become operational in six districts of the country? And so on.
The Commissioner of Agrarian Services happened to be abroad for three weeks. Thus, not only was I the Acting Head of a Class I, Grade 1 Department at the age of 28 years, but I also needed policy-level help, because this was hitherto uncharted territory in the country. So I asked for an appointment with the Minister of Agriculture, Mr. Phillip Gunawardene, the author of the Act.
I had never met or seen him before. The Minister was charming, affable and even fatherly, over a cup of tea and cakes in Parliament. Getting down to business, I brought to his notice the number of legal difficulties and some of the administrative problems that needed his guidance. I was so intent on my presentation that I failed to notice that he had tossed his spectacles on the table, which was a sign (I was told later) that he was losing his patience – and his temper. I was only halfway through my list when he suddenly banged his fist on the table with a loud noise, stopping me abruptly. “Young man” he exclaimed: “Have you come across these difficulties in the field – or are they in your head?”
When I pointed feebly to my head, “Go and work”, he thundered! “And when you come across these problems, then you come to me!” In complete disarray, I scooped up my files and scooted from Parliament, leaving a trail of paper in my wake! This was the first and last time that I saw Mr. Phillip Gunawardene. He was isolated and pushed out of the Cabinet, to be succeeded as Minister of Agriculture by Mr. C.P. de Silva.
Although upset by my encounter with Mr. Phillip Gunawardene, I came later to recognize that I had been looking at it only from my own administrative and legal point of view, not appreciating his political difficulties in going back to Parliament for amendments, before implementation had even begun! Although I never met Mr. Gunawardene thereafter, he must have appreciated my work: for he later paid me a handsome compliment in Parliament, as recorded in the Hansard. However, within one year of implementation, the Act proved to be unimplementable: for I had proved to be correct on all the legal and administrative points I had brought up with him.
The above resulted in two difficulties that I had to face. Within one year, every one of the legal and administrative problems that I had raised with the Minister (Mr. Philip Gunawardene) had actually come to pass. But secondly, when I needed ministerial help, there was a new Minister, Mr. C.P de Silva, who was actually opposed to the Act and who decided to let it stew in its own legal difficulties, so as to discredit it countrywide. In fact, I had to battle with the new Minister as late as 1960 to get the same loopholes plugged that I had pointed out to the former Minister in 1958.
Innovations of the Cultivation Committees
Starting from the premise that the state machinery, especially at lower levels, was subject to the semi-feudal influence of the landlords, the Paddy Lands Act created a new Department of Agrarian Services at the national level, devoted to its implementation. Moreover, in order to bypass the lower level of administration at field level (which was thought to be under landlord influence), it created Cultivation Committees with assured majorities for the actual cultivators.
This attempt to bias the administration in favour of the weaker sections of the agrarian society represented a change from the view prevailing from colonial times, namely, that the administration would be neutral in its dealings with all sections of the public. It is relevant to note here that most of the agrarian reform programs in Latin America starting from the same premise, opted for separate, dedicated agencies for the implementation of their land reforms. The experiences of Japan, South Korea and Taiwan were quite different because their land reforms were carried out under martial law, or with active military backing; hence they did not need separate, devoted ministries/agencies.
The Act was also innovatory in that it represented the first time in any country in South and Southeast Asia that legal powers in the implementation of tenurial reforms and the management of irrigation and cultivation at field levels were given to an elected body. The idea that an elected body of semi-educated farmers could take over functions from the government bureaucracy was clearly revolutionary at that time. For example, since the rent payable on a particular field was fixed as one-fourth share of the harvest, how could a distant court know how much the gross harvest of a particular field was?
The Act recognized that such factual questions at field level could only be answered at field level. The failure to recognize this and to provide for beneficiary participation in implementing such reforms has been one of the greatest weaknesses of similar programs in other countries of the region at that time.
The first role of the Cultivation Committees was to help in the implementation of the tenancy provisions of the Act (Sections 8-19). The Committees were also authorized to act as intermediaries between landlord and tenant in the collection of rents, etc., thus reducing the personal hold of landlords over their tenants. The Cultivation Committees were thus expected to play an important socio-psychological role in bolstering the confidence of the tenant-cultivators to actively claim their rights under the law.
Secondly, the Cultivation Committees were given important development functions, with powers for the advancement of paddy cultivation in their areas. They were given access to technical advice in the form of Agricultural Extension Officers and Village Cultivation Officers, who were made ex-officio members of the Committees; but with a right only to speak but not to vote at their meetings. It was hoped that with such technical advice emanating from within, and adopted by the Committees, would enable both paddy production and water-management to be greatly improved by the farmers, acting on their own volition.
A third major innovatory function of the Cultivation Committees was in respect of (irrigation) water management, with the Committees taking over the functions of the Irrigation Headmen (Vel Vidanes) at field level. These functions, among others, included enforcement of rules relating to cultivation dates, clearing of channels, fencing, etc, as well as improving water management.
This was in a context where bureaucratic and technical means of water management at field level had already failed. The Paddy Lands Act of 1958 thus predated international recognition of the need for farmer participation in water-management by at least 20 years! This was in the law: in practice, however, the Cultivation Committees under the Act of 1958 never made any progress in this field because they were legally invalidated soon after their formation.
A fourth innovation was in the field of agricultural extension. It was evident then, and more evident now, that agricultural extension systems based on the western models of one extension worker dealing face-to-face with each individual farmer were completely unrealistic in most developing countries with a multitude of small farmers. For example, in Nepal, an extension agent would have to walk one whole day to even reach 20 farmers in remote villages! No developing country in the world could afford such a system in the context of multiple small farmers, which would require a quadrupling or more of extension workers.
Ironically, this has been the recommendation of FAO and the World Bank for decades since the Paddy Lands Act of 1958! It is therefore obvious that a two-stage system or a group system of extension had to be devised, either with the extension agent working through farmer leaders, or through a system of group-extension, as envisaged by the Paddy Lands Act. Thus, the Act’s introduction of such a group extension system with farmer education and participation in the planning and implementation of such self-decided programs of agricultural development was at least 40 years ahead of its time.
Lastly, the tenurial provisions of the Paddy Lands Act needed to be supported by a broader package of institutional support for smallholder agriculture, in order for the Act itself to be effective. Such a package was provided by the establishment of the multipurpose cooperatives, agricultural credit for smallholders, a fertilizer subsidy, a guaranteed price for paddy and a pilot crop insurance scheme. It is important to recognize that the green revolution could not have taken off in Sri Lanka if the institutional support structure for small-scale paddy farming had not been laid in the late 1950s, along with the Paddy Lands Act.
While the Act provided for an active role by farmers’ organizations (the Cultivation Committees), it is clear that the latter were not neutral farmer organizations. It was known, for example, that the village cooperatives in most countries of South Asia were under the control of the big landlords. The Paddy Lands Act, therefore, went to great lengths to neutralize the overweening power of the landlords by weighting these Committees heavily in favour of the actual cultivators.
The landlords, however, retaliated by getting the Cultivation Committees declared legally invalid. This had the effect of cutting off the implementation structure at the knees, with no feet on the ground, making field level implementation impossible. Thus one of the main laudatory features of the Act, namely, its provision for beneficiary participation, proved also to be its Achilles heel, leading ultimately to its collapse. Although such local farmers’ associations weighted in favour of the actual tillers succeeded in Japan, Taiwan and South Korea, they were supported by martial law or military force.
In contrast, our Cultivation Committees were subject to a judicial system under the rule of law in a democracy. In fact, it even allowed a President of a Village Tribunal to famously declare from the bench: “Pillippua Parippua-ge kumburu panatha apita epa” (We do not want lousy Phillip’s Paddy Lands Act!)
The Department of Agrarian Services organized rounds of field-level meetings, trying to encourage the Cultivation Committees to hold fast, promising that legal amendments would soon be forthcoming to remedy their legal incapacity. But in fact, these amendments came too late. They were passed only after the landlords had already evicted their tenants, and only after the Cultivation Committees had been seen to have failed in their cultivation and irrigation duties, thus losing the confidence of the farmers themselves.
It is also necessary to consider the socio-political climate in the villages at that time. There was euphoria among the tenant-cultivators and agricultural workers when the Act was passed. This was heightened by their participation in the election of the Cultivation Committees. This enthusiasm was reflected in other aspects of cultivation too. Fertilizer consumption doubled in the first year of the formation of the Cultivation Committees, but collapsed in the year following their legal invalidation.
This collapse caused great demoralization among the cultivators, since they had gained great psychological support from the Committees in standing up for their rights. With their collapse, many tenants surrendered their rights, accepting their plight as “hidden tenants” with no rights under the law. There was chaos in the paddy fields too, since there was no agency left to ensure that the fields were fenced, or the irrigation water issued.
Hence, by the time the Cultivation Committees were re-legalized by the Paddy Lands (Amendment) Acts of 1961 and 1964, the latter served only to close the stable door after the horse had bolted. The Committees never regained the vigour and vibrancy that accompanied the first flush of their formation under the Act of 1958.
Unfortunately, the subsequent amendments to the Act (i.e. the amendments of 1961, 1964, 1972 and 1979) increased the heavy hand of the bureaucracy within the Cultivation Committees and Agricultural Productivity Committees that took their place. As in other cases, such bureaucratization has been accompanied by politicization of the institutions and processes dealing with paddy cultivation, making a mockery of the elected and participatory nature of the Cultivation Committees under the Paddy Lands Act of 1958.
Features
India shaping-up as model ‘Swing State’

 The world of democracy is bound to be cheering India on as it conducts its 77th Republic Day celebrations. The main reasons ought to be plain to see; in the global South it remains one of the most vibrant of democracies while in South Asia it is easily the most successful of democracies.
The world of democracy is bound to be cheering India on as it conducts its 77th Republic Day celebrations. The main reasons ought to be plain to see; in the global South it remains one of the most vibrant of democracies while in South Asia it is easily the most successful of democracies.
Besides, this columnist would go so far as to describe India as a principal ‘Swing State.’ To clarify the latter concept in its essentials, it could be stated that the typical ‘Swing State’ wields considerable influence and power regionally and globally. Besides they are thriving democracies and occupy a strategic geographical location which enhances their appeal for other states of the region and enables them to relate to the latter with a degree of equableness. Their strategic location makes it possible for ‘Swing States’ to even mediate in resolving conflicts among states.
More recently, countries such as Indonesia, South Africa and South Korea have qualified, going by the above criteria, to enter the fold.
For us in South Asia, India’s special merit as a successful democracy resides, among other positives, in its constitutionally guaranteed fundamental rights. Of principal appeal in this connection is India’s commitment to secularism. In accordance with these provisions the Indian federal government and all other governing entities, at whatever level, are obliged to adhere to the principle of secularism in governance.
That is, governing bodies are obliged to keep an ‘equidistance’ among the country’s religions and relate to them even-handedly. They are required to reject in full partiality towards any of the country’s religions. Needless to say, practitioners of minority religions are thus put at ease that the Indian judiciary would be treating them and the adherents of majority religions as absolute equals.
To be sure, some politicians may not turn out to be the most exemplary adherents of religious equality but in terms of India’s constitutional provisions any citizen could seek redress in the courts of law confidently for any wrongs inflicted on her on this score and obtain it. The rest of South Asia would do well to take a leaf from India’s Constitution on the question of religious equality and adopt secularism as an essential pillar of governance. It is difficult to see the rest of South Asia settling its religious conflicts peacefully without making secularism an inviolable principle of governance.
The fact is that the Indian Constitution strictly prohibits discriminatory treatment of citizens by the state on religious, racial, caste, sex or place of birth grounds, thus strengthening democratic development. The Sri Lankan governing authorities would do well to be as unambiguous and forthright as their Indian counterparts on these constitutional issues. Generally, in the rest of South Asia, there ought to be a clear separation wall, so to speak, between religion and politics.
As matters stand, not relating to India on pragmatic and cordial terms is impossible for almost the rest of the world. The country’s stature as a global economic heavyweight accounts in the main for this policy course. Although it may seem that the US is in a position to be dismissive of India’s economic clout and political influence at present, going forward economic realities are bound to dictate a different policy stance.
India has surged to be among the first four of global economic powers and the US would have no choice but to back down in its current tariff strife with India and ensure that both countries get down to more friction-free economic relations.
In this connection the EU has acted most judiciously. While it is true that the EU is in a diplomatic stand-off of sorts with the US over the latter’s threat to take over Greenland and on questions related to Ukraine, it has thought it best to sew-up what is described as an historic free trade agreement with India. This is a truly win-win pact that would benefit both parties considering that together they account for some 25 percent of global GDP and encompass within them 3 billion of the world’s population.
The agreement would reduce trade tariffs between the states and expand market access for both parties. The EU went on record as explaining that the agreement ‘would support investment flows, improve access to European markets and deepen supply chain integration’.
Besides, the parties are working on a draft security and defence partnership. The latter measure ought to put the US on notice that India and the EU would combine in balancing its perceived global military predominance. The budding security partnership could go some distance in curbing US efforts to expand its power and influence in particularly the European theatre.
Among other things, the EU-India trade agreement needs to be seen as a coming together of the world’s foremost democracies. In other words it is a notable endorsement of the democratic system of government and a rebuffing of authoritarianism.
However, the above landmark agreement is not preventing India from building on its ties with China. Both India and China are indicating in no uncertain terms that their present cordiality would be sustained and further enriched. As China’s President Xi observed, it will be a case of the ‘dragon and the elephant dancing together.’
Here too the pragmatic bent in Indian foreign policy could be seen. In economic terms both countries could lose badly if they permit the continuation of strained ties between them. Accordingly, they have a common interest in perpetuating shared economic betterment.
It is also difficult to see India rupturing ties with the US over Realpolitik considerations. Shared economic concerns would keep the US and India together and the Trump administration is yet to do anything drastic to subvert this equation, tariff battles notwithstanding.
Although one would have expected the US President to come down hard on India over the latter’s continuing oil links with Russia, for instance, the US has guarded against making any concrete and drastic moves to disrupt this relationship.
Accordingly, we are left to conclude from the foregoing that all powers that matter, whether they be from the North or South, perceive it to be in their interests to keep their economic and other links with India going doubly strong. There is too much to lose for them by foregoing India’s friendship and goodwill. Thus does India underscore its ‘Swing State’ status.
Features
Securing public trust in public office: A Christian perspective – Part III

Professor, Dept of Public & International Law, Faculty of Law, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka and independent member, Constitutional Council of Sri Lanka (January 2023 to January 2026)
This is an adapted version of the Bishop Cyril Abeynaike Memorial Lecture delivered on 14 June 2025 at the invitation of the Cathedral Institute for Education and Formation, Colombo, Sri Lanka.
(Continued from yesterday)
Conviction
I now turn to my third attribute, which is conviction. We all know that we can have different types of convictions. Depending on our moral commitments, we may think of convictions as good or bad. From the Bible, the convictions of Saul and the contrasting convictions of Paul (Saul was known as Paul after his conversion) provide us with an excellent illustration of the different convictions and value commitments we may have. As Christians we are required to be convinced about the values of the Kingdom of God, such as truthfulness and rationality, the first and second attributes that I spoke of. We are also called to act, based on our convictions in all that we do.
I used to associate conviction with fearlessness, courage or boldness. But in the last two to three years of my own life, I have had the opportunity to think more deeply about the idea of conviction and, increasingly, I am of the view that conviction helps us to stand by certain values, despite our fears, anxieties or lack of courage. Conviction forecloses possibilities of doing what we think is the wrong thing or from giving up. Recall here the third example I referred to, of Lord Wilberforce and his efforts at abolishing the slave trade and slavery. He had to persevere, despite numerous failures, which he clearly did. In my own experiences, whether at the university or at the Constitutional Council, failures, hopelessness, fear or anxiety are real emotions and states of mind that I have had to deal with. In Sri Lanka, if convictions about truth, rationality and justice compel a public official to speak truth to power and act rationally, chances are that such public official has gone against the status quo and given people with real human power, reason to harm them. Acting out of conviction, therefore, can easily give rise to a very human set of reactions – of fear for oneself and for one’s family’s safety, anxiety about grave consequences, including public embarrassment and, sometimes, even regret about taking on the responsibilities that one has taken on. In such situations, such public officials, from what I have noticed, do not ever regret acting out of conviction, but rather struggle with the implications and the consequences that may follow.
When we consider the work of Lord Wilberforce, Lalith Ambanwela and Thulsi Madonsela we can see the ways in which their convictions helped them to persist in seeking the truth, in remaining rational and in seeking justice. They demonstrate to us that conviction about truth and justice pushes and even compels us to stand by those ideals and discharge our responsibilities in a principled and ethical way. Convictions help us to do so, even when the odds are stacked against us and when the status quo seems entrenched and impossible to change. This is well illustrated in how Wilberforce persisted with his attempts at law reform, despite the successive failures.
Importantly, some public officials saw the results of acting out of conviction in their lifetime, but others did not. Wilberforce saw the results of his work in his lifetime. Dietrich Bonhoeffer, a German theologian who opposed Hitler’s rule, was executed, by hanging, by the Nazi German state, a couple of weeks before Hitler committed suicide. Paul spent the last stage of his life as a prisoner of the Romans and was crucified. These examples suggest that conviction compels us to action, regardless of our chances of success, and for some of us, even unto death. Yet, conviction gives us hope about the unknown future. Conviction, indeed, is a very powerful human attribute.
I will not go into this, but the Christian faith offers much in terms of how a public official may survive in such difficult situations, as has been my own experience thus far.
Critical Introspection
I chose critical introspection as the fourth attribute for two reasons. One, I think that the practice of critical introspection by public officials is a way of being mindful of our human limitations and second it is a way in which we can deepen and renew our commitment to public service. Critical introspection, therefore, in my view, is essential for securing public trust and it is an attribute that I consider to be less and less familiar among public officials.
In Jesus, and in the traditions of the Church, we find compelling examples of a commitment to critical introspection. During his Ministry, he was unapologetic about taking time off to engage in prayer and self-reflection. He intentionally went away from the crowds. His Ministry was only for three years and he was intentional about identifying and nurturing his disciples. These practices may have made Jesus less available, perhaps less ‘productive’ and perhaps even less popular. However, this is the approach that Jesus role-modelled and I would like to suggest to you today, that there is value in this approach and much to emulate. Similarly, the Biblical concept of the Sabbath has much to offer to public officials even from a secular perspective in terms of rest, stepping away from work, of refraining from ‘doing’ and engaging with the spiritual realm.
Importantly, critical introspection helps us to anticipate that we are bound to make mistakes. no matter how diligent we may be and of our blind spots. Critical introspection creates space for truth, rationality and conviction to continue to form us into public officials who can secure public trust and advance it.
In contrast, I have found, in my work, that many embrace, without questioning, a relentless commitment to working late hours and over the weekends. This is, of course, at the cost of their personal well-being, and, equally importantly, of the well-being of their families. Relentless hard work, at the cost of health and personal relationships, is commonly valorised, rather than questioned, from what I can see, ironically, even in the Church.
One of the greatest risks of public officials not engaging in critical introspection is that they may lose the ability to see how power corrupts them or they may end up taking themselves too seriously. I have seen these risks manifest in some public officials that I work with – power makes them blind to their own abuse of power and they consider themselves to be above others and beyond reproach.
Where a public official does not practice critical introspection, the trappings of public office can place them at risk of taking themselves too seriously and losing their ability to remain service-oriented. Recall the trappings of high constitutional office – the security detail, the protocol and sometimes the kowtowing of others. It is rare for us to see public officials who respond to these trappings of public office lightly and with grace. Unfortunately for us, we have seen many who thrive in it. In my own work, I have come across public officials who are extremely particular about their titles and do not hesitate to reprimand their subordinates if they miss addressing them by one of their titles. Thankfully, I also know and work with public officials who are most uncomfortable with the trappings of public office and suffer it while preserving their attitude of humility and service.
Permit me to add a personal note here. In April 2022 a group of Christians and Catholics decided to celebrate Maundy Thursday by washing the feet of some members of the public. I was invited to come along. On that hot afternoon, in one corner of public place where people were milling about, the few of us washed the feet of some members of the public, including those who maintain the streets of Colombo. I do not know what they thought of our actions but I can tell you how it made me feel. The simple act of kneeling before a stranger and one who was very obviously very different to me, and washing their feet, had a deep impact on me. Many months later, when I was called, most unexpectedly, to be part of Sri Lanka’s Constitutional Council and had to struggle through that role for the better part of my term, that experience of washing feet of member of the public became a powerful and personal reminder to me of the nature of my Christian calling in public service. I do think that the Christian model of servant leadership has much to offer the world in terms of what we require of our public officials.
Compassion
Due to limitations of time, I will speak to the fifth attribute only briefly. It is about compassion – an aspect of love. Love is a complex multi-dimensional concept in Christianity and for today’s purposes, I focus on compassion, an idea that is familiar to our society more generally in terms of Karuna or the ability to see suffering in oneself and in others. The Gospels, at one point, record that when Jesus saw the crowds that he was ministering to, that he had compassion on them.
Of course, we know that the people are not always mere innocent victims of the abuse of power but can be active participants of the culture of patronage and corruption in our society. Nevertheless, for public officials to secure public trust, I think compassion, is essential. Compassion, however, is not about bending the rules, arbitrarily, or about showing favouritism, based on sympathy. In Sri Lanka we are hard pressed to find examples of compassion by public officials, at high levels, despite the horrors we have experienced in this land. However, in the everyday and at lower layers of public service, I do think there are powerful acts of compassion. An example that has stayed with me is about an unnamed police officer who is mentioned in the case of Yogalingam Vijitha v Wijesekera SC(FR) 186/2001 (SC Minutes 28 August 2002). In 2001, Yogalingam Vijitha was subject to severe forms of sexual torture by the police. After one episode of horrific torture, including the insertion of the tip of a plaintain-flower dipped in chilli to her vagina, the torturers left her with orders that she should not be given any water. This unnamed police officer, however, provided her with the water that she kept crying out for. In a case which records many horrific details about how Yogalingam Vijitha was tortured, this observation by the Court, about the unnamed police office, stands out as a very powerful example of compassion in public office.
Compassion for those who seek our services whether at university, at courts or at the kachcheri, should be an essential attribute for public officials.
Aspects not explored
There is much more that can be said about what a Christian perspective has to offer in terms of securing public trust in public office but due to limitations of time, I have only spoken about truthfulness, rationality, conviction, critical introspection and compassion – and that, too, in a brief way. I have not explored today several other important attributes, such as the Christian calling to prioritise the vulnerable and the Christian perspectives on confession, forgiveness and mercy that offers us a way of dealing with any mistakes that we might make as public officials. I have also not spoken of the need for authenticity – public officials ought to maintain harmony in the values that they uphold in their public lives with the values that they uphold their personal lives, too. Finally, I have not spoken of how these attributes are to be cultivated, including about the responsibility of the Church in cultivating these attributes, practice them and about how the Church ought to support public officials to do the same.
Securing Public Trust
Permit me to sum up. I have tried to suggest to you that cultivating a commitment to truthfulness, rationality, conviction about the values of public service, critical introspection and compassion – are essential if public officials are to secure public trust.
The crisis of 2022 is a tragic illustration of the pressing need in our society to secure trust in public office. In contrast, the examples of Thulsi Madonsela, former Public Protector of South Africa, of late Lalith Ambanwela, former Audit Superintendent from Sri Lanka and Lord Wilberforce illustrate that individual public officials who approach public service can and have made a significant difference, but, of course, at significant personal cost. Given the mandate of this memorial lecture, I drew from the Christian faith to justify and describe these five attributes. However, I do think that a similar secular justification is possible. Ultimately, secular or faith-based, we urgently need to revive a public and dynamic discourse of our individual responsibilities towards our collective existence, including about the ways in which can secure public trust in public office. I most certainly think that the future of our democracy depends on generating such a discourse and securing the trust of the public in public office.
If any of you here have been wondering whether I am far too idealistic or, as some have tried to say, ‘extreme’ in the standard that I have laid out for myself and others like me who hold public office – I will only say this. Most redeeming or beautiful aspects of our human existence have been developed mostly because individuals and collectives dared to dream of a better future, for themselves and for others. Having gone through what has easily been the toughest two-three years of my life, I know that, here in Sri Lanka, too, we have among us, individuals and collectives who dare to dream of a better future for this land and its peoples – and they are making an impact. Three years ago, you could have dismissed what I have had to say as being the musings of an armchair academic – but today, given my own experiences in public office with such individuals who have dared to dream of a better future for us, I can confidently tell you – these are not mere musings of an armchair academic but rather insights drawn from what I have been witness to.
(Concluded)
by Dinesha Samararatne
Features
High-end tourists or budget-friendly visitors!

 According to the Sri Lanka Tourism Development Authority (SLTDA), over 130,000 tourists have arrived in the country during the first 15 days of this year.
According to the Sri Lanka Tourism Development Authority (SLTDA), over 130,000 tourists have arrived in the country during the first 15 days of this year.
Impressive, indeed, but how many of them make up the big spending list, or were the majority backpackers?
Of course, we need both – the big spenders and the backpackers – but, as one knowledgeable source said, it’s better to have 10 tourists spending 1000 dollars (per day) than 1000 tourists spending 10 dollars (per day)!
When it comes to tourism, countries often prioritise big spenders over high numbers. Why? Because big spenders bring in more revenue.
A smaller number of high-spending tourists can generate more income for local businesses, infrastructure, and communities, compared to a large number of low-spending visitors.
For example, luxury travellers tend to spend more on accommodation, dining, and activities, boosting the local economy.
Yes, Sri Lanka’s got the potential to attract both – high-end tourists and a steady flow of budget-friendly visitors.
One would say that with our rich culture, stunning beaches, and wildlife, Sri Lanka is a gem for tourism – the high-end tourists, in particular – but, at the same time, the question crops up: how come lots of big spenders visit the Maldives, and the Maldives have no nightlife, wildlife, etc.?
The big spenders, I’m told, visit the Maldives for total relaxation…to check out the beaches and the beautiful resorts, and that’s because they seek exclusivity, luxury, and relaxation.
They’re drawn to stunning beaches, high-end resorts, privacy and exclusivity, world-class amenities (spas, fine dining), unique experiences (sunset cruises, snorkeling).
And, guess what! Anant Ambani, son of Indian businessman Mukesh Ambani, and his wife Radhika Merchant, have arrived in the Maldives for a holiday.
Ambani’s Boeing 737 private jet landed in the Maldives on Saturday (17) and they are currently staying at Waldorf Astoria Maldives Ithaafushi’s private island.
The Ambani family has previously spent holidays in the Maldives. Last year, other members of the family spent the Christmas and New Year period at Waldorf Astoria Maldives Ithaafushi.
In fact, even singer Madonna went to the Maldives, a few years ago, for a $32,000-a-week Maldives holiday, with her family – cycling, sunset picnics on private beaches, infinity pools, luxury spas, etc.
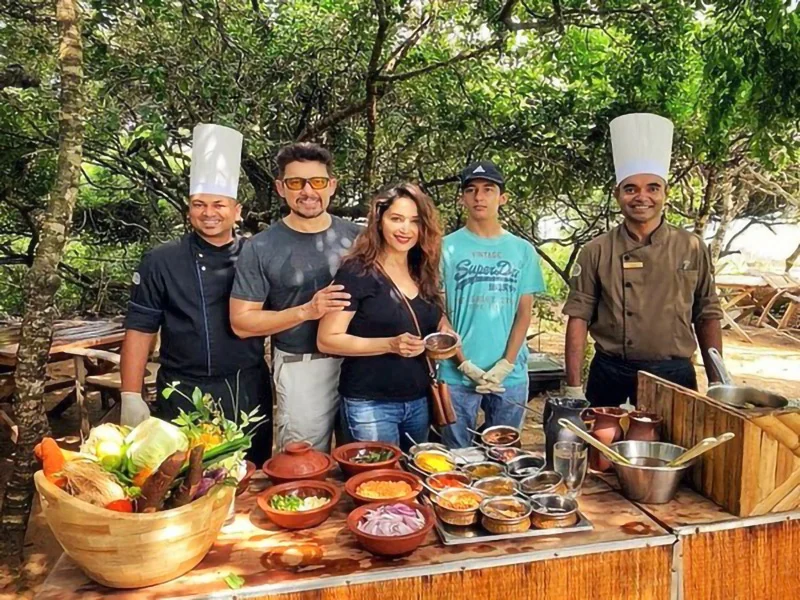

Madhuri Dixit’s cooking scene in Sri Lanka
In early 2020, Bollywood actress Madhuri Dixit visited Sri Lanka for a family vacation, during which she explored local culture, nature, and cuisine.
She took a local cooking class during her visit, which, she later mentioned, was helpful during the 2020 COVID-19 lockdown.
Dixit described a tour of a local tea factory as “intricate and interesting”.
Perhaps, we should introduce Tea Plantations Retreats – High-end bungalows in tea estates with tea-tasting sessions.
Dixit’s trip also included visits to scenic spots in the mountains.
No doubt, Sri Lanka’s got the natural beauty, rich culture, and warm hospitality but we need to package it into luxury experiences that big spenders crave; Think boutique hotels, private villas, and curated experiences.
We should tap more into this luxury relaxation vibe – maybe we could add some more sparkle by introducing Gourmet Food Trails: Exclusive culinary tours with private chefs, wine tastings, and farm visits; Festival Experiences: VIP access to Esala Perahera or Vesak festivals with cultural performances; Island Hopping: Luxury yacht cruises to untouched islands, like Pigeon Island or coral reefs; Adventure Sports: Private surfing lessons in Arugam Bay or hot air balloon rides over Ella.
I believe Sri Lanka could become the ultimate luxury destination if the SLTDA works diligently towards that goal.
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoComBank, UnionPay launch SplendorPlus Card for travelers to China
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoComBank advances ForwardTogether agenda with event on sustainable business transformation
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoConference “Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill: Neither Here, Nor There”
-
 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoA puppet show?
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoLuck knocks at your door every day
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog Brings the ICC Men’s T20 Cricket World Cup 2026 Closer to Sri Lankans
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days ago‘Building Blocks’ of early childhood education: Some reflections
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoRising climate risks and poverty in focus at CEPA policy panel tomorrow at Open University














