Business
Geographical Indications for Sri Lankan products: The need to expand local registration
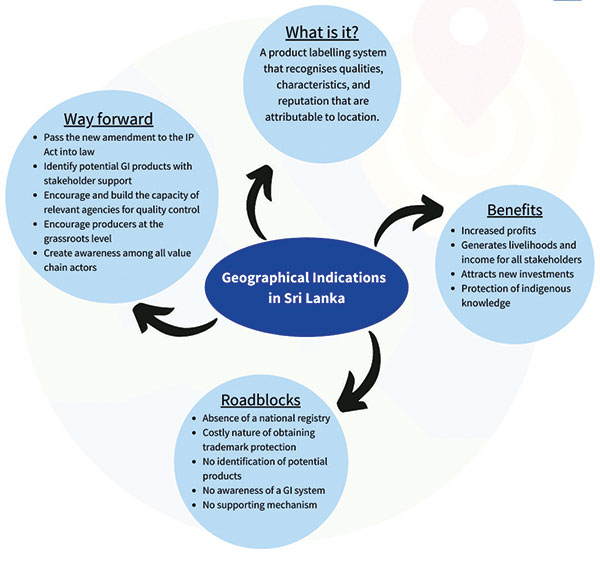
Sri Lanka obtained its first-ever Geographical Indication (GI) certification on 02 February 2022 for ‘Ceylon Cinnamon’ from the European Union due to untiring efforts during the last nine years. Ceylon Cinnamon is now in the register of Protected Designations of Origin and Protected Geographical Indications (PGI) and it was published in the Official Journal of the European Union. Can we similarly market and protect distinctive Sri Lankan products such as Ceylon Tea, Ceylon Blue Sapphire, Ruhunu Curd, Dumbara Mats, Ambalangoda Masks and so on? Yes, marketing and protecting geographically unique products are possible by implementing a robust GI system with local registration to support obtaining international registration and protection.

What is a GI?
GI is a labelling system that identifies a product originating from a specific geographical area. It recognises qualities, characteristics, or the product’s reputation that are importantly linked or attributable to its location. The environmental and human factors in such areas help create a high-quality product. An Intellectual Property Right (IPR), GIs protect producers in the identified geographical location who meet the specific standards listed in the GI registration. More than 160 countries have already implemented GI systems for agriculture, handicrafts, food, and wine products. India, Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, and Cambodia are some of Sri Lanka’s Asian neighbours which enjoy GI’s economic and social benefits. For example, India introduced GI in 2003 and has registered nearly 400 products, of which more than 100 products are in agriculture. Thailand also introduced GIs in 2003, and by 2019, there were about 100 GI-protected products covering rice, vegetables, fruits, wine, and spirits.
Economic and Social Benefits of GIs
Both developed and developing countries have identified GIs as a potential tool to improve the agriculture and traditional handicrafts sectors by assuring the quality of the products. As in other forms IPRs, GIs also attempt to solve market failures such as information asymmetry. The economic benefits of GIs for producers are similar to the benefits of protecting trademarks and patents. It rewards producers from a geographical area and prevents outside producers who do not meet the production requirement from using such benefits.
Producers receive increased profits by obtaining a price premium for their geographically specific, high-quality products. Studies have shown that the price premium for GI products increase from 20% to 50% compared to non-GI products. For example, in the European Union (EU), the price of a GI product has been estimated to be 2.23 times higher than that of a comparable non-GI product (on average, 1.5 times more for agro-food products). As a policy instrument, GIs have positive implications for protecting indigenous knowledge and generating livelihoods and income for all stakeholders in the value chain. A strong GI eco-system will also attract new investments to the selected regions, thereby boosting the socio-economic development of rural areas. Thus, the country will gain several socio-economic benefits with a GI system.
GI in Sri Lanka: Slow Progress of Local Registration
According to Sri Lanka’s existing IP law, GIs can be protected in three methods. First, as a trademark law in the form of certification mark or a collective mark; second, as a mode of business practice which prevents unfair competition and provides consumer protection; and third, as a sui generis system – i.e. a system of its own. The World Trade Organization’s (WTOs), Trade-Related Intellectual Property Rights Agreement ( TRIPs) agreement does not impose any method and it is based on the country’s legal system. Some countries may have two or three protection systems, and there are pros and cons in each system. It is said that the sui generis system offers the most comprehensive protection for GIs. Internationally most of the countries that use sui generis protection system have a registration system where GIs are registered in a national registry governed by the national authorities.
Sri Lanka obtained certification marks for ‘Ceylon Tea’ in 2010 and ‘Ceylon Cinnamon’ in 2013 which provide local registration for these goods. However, Sri Lanka has not been able to expand local protection for several other similarly unique products yet due to several reasons. The absence of a national registry in the sui generis system and the costly nature of obtaining trademark protection, which require annual renewals, are among the most salient reasons. Added to this, the relevant authorities are not actively identifying potential products and encouraging stakeholders to protect their unique products. Furthermore, stakeholders, especially producers, are not aware of the GI system and there is no mechanism to support stakeholders to obtain local GI registration. The delay in local registration hinders the international registration as it is a prerequisite to go for international registration.
In 2018, as an initial step to create a national registry system for Sri Lanka, an amendment to the existing IP Act was introduced. The amendment confers power to the Minister to prescribe geographical indication in respect of any goods or products. However, as several legal and academic practitioners highlighted, the selection criteria, application procedure, and the modalities of how the GI is prescribed were not specified in the 2018 amendment. A new amendment on the GI registration system which introduces the procedure was tabled in the Parliament this year, the quick passage of which would be beneficial for Sri Lankan producers looking at securing GIs for their products.
Way Forward
A strong GI eco-system motivates all stakeholders in the value chain to protect the uniqueness of their products. This can significantly boost economic development. Therefore, Sri Lanka needs to swiftly pass the new amendment to the IP Act to enable the implantation of a local GI registration system. Equally, it is necessary to identify potential GI products with stakeholders’ support, encourage and build the capacity of relevant agencies for quality control, and encourage producers at the grassroots level to work towards securing GI certification. Further, it is essential to create a mechanism to link stakeholders with the relevant government agencies to obtain local registration initially and then go for international registration. Most importantly, creating awareness among all value chain actors is crucial as they are – finally – the intellectual property owners of their products.
Link to the full Talking Economics blog: https://www.ips.lk/talkingeconomics/2022/03/07/geographical-indications-gis-for-sri-lankan-products-the-need-to-expand-local-registration/
Dilani Hirimuthugodage is a Research Economist at IPS with research interests in Agriculture and Agribusiness Development, Environment, Natural Resources and Climate Change, and Intellectual Property. She holds a BA in Economics with a Second Class (Upper) and Masters in Economics (Distinction Pass) from the University of Colombo. In addition, she is a part-qualified candidate of CIMA-UK. (Talk with Dilani: dilani@ips.lk).
Piyumi Rasangi was a Project Intern at IPS’ Agriculture & Agribusiness Development team.
Business
SL’s construction sector ‘bleeding billions’ due to weak cost-control mechanisms

Sri Lanka’s construction sector one of the country’s largest economic drivers, continues to bleed billions due to weak cost-control mechanisms, ad-hoc estimating practices and the absence of internationally recognised methodologies, warns veteran Chartered Quantity Surveyor Mafahir Shuhood, a global authority in building economics whose work has shaped industry standards across continents.
A member of IQS (Sri Lanka), AIQS (Australia), ASAC (USA) and CIRB (UK), Shuhood is widely considered a pioneer of modern cost management. His first book, How to Estimate for Building Works, written in 1978, became one of the region’s earliest structured guides on controlling construction expenditure.
His subsequent publications—Cost Control Methodology and Costing Guide, authored in Qatar—today form part of the reference material used by universities, engineers and international contractors from Doha to London and Sydney.
“My methodologies are being used worldwide. Sri Lanka must now bring the same discipline and scientific approach if it wants financial stability in its construction sector, Shuhood told The Island Financial Review.
At the recent BMICS Exhibition in Colombo, all available copies of his books were sold within hours, signalling the growing demand among local professionals for structured, globally aligned cost-control knowledge.
According to Shuhood, Sri Lanka’s project inefficiencies stem from the lack of a unified national system to estimate, monitor and analyse costs. He argues that building economics is not merely a technical discipline,
it is a national economic safeguard.
“Before constructing anything—a house, a building or a public infrastructure project—you must assess materials, labour, wastage, inflation, time and value. Without a scientific system, cost overruns are inevitable, he said.
He believes that the country’s persistent budget blowouts in major infrastructure projects could be avoided with proper cost-control frameworks and independent monitoring.
“Sri Lanka cannot afford imprecision. Every unnecessary cost ultimately affects the national economy.”
Shuhood revealed that he recently met the Prime Minister and shared his recommendations, including copies of his internationally used publications.
“I told the Prime Minister that my advice is not for money. I am prepared to support Sri Lanka purely as a service. This is my profession since childhood, and I want to contribute meaningfully, he said.
He maintains that the introduction of a national cost-control discipline—developed using proven international best practices—could save the country billions in project overruns and miscalculations.
By Ifham Nizam
Business
InsureMe debuts on CSE Empower Board

InsureMe Insurance Brokers Ltd successfully completed its Equity Introduction and subsequent listing on the Empower Board of the CSE recently marking a significant milestone for a local digital-first enterprise.
InsureMe Insurance Brokers Ltd (InsureMe) rang the market opening bell at a market opening ceremony, held at the CSE’s iconic Trading Floor, to commemorate its landmark listing on the Empower Board. highlighting InsureMe’s commitment to digital transformation and its success as a rapidly growing Insure-Tech firm leveraging the capital market for growth.
Founded in 2016 as startup, InsureMe is a digital insurance aggregator and a fully licensed broker regulated by the Insurance Regulatory Commission of Sri Lanka (IRCSL) with a digital-first operating model supported by online assistance and end-to-end digital claims support, operating with advanced platforms such as DigiEye (Motor Claims Automation), DigiMed (Medical Claims Automation), and DigiEx (Corporate Expense & Reimbursement Automation).
Delivering the welcome address at the event, Rajeeva Bandaranaike, CEO of the Colombo Stock Exchange, congratulated InsureMe on their successful listing. Remarking upon the occasion and InsureMe’s role as successful startup leveraging the capital market, he stated: “InsureMe is one of the very few startups in Sri Lanka making a debut on the Stock Exchange and as the sixth company on the Empower Board and is an innovator in the technology start up space. We are happy to see companies such as InsureMe involved in the IT sector making use of the capital market. When we set up the Empower Board, this is precisely what we had in mind.”
Prajeeth Balasubramaniam Chairman of InsureMe Insurance Brokers Ltd also remarked the companies list, remarking: “This listing represents far more than a financial achievement; it signals strong confidence in Sri Lanka’s burgeoning startup ecosystem and urges us all to aim higher. It demonstrates how visionary teams, armed with essential resources and guidance, can reshape industries and alter the national narrative. “
Also speaking the event Vipula Dharmapala, CEO and Director of InsureMe Insurance Brokers Ltd discussed the companies’ journey, stating: “InsureMe began almost a decade ago when my co-founders and I set out to give Sri Lankan customers the same transparent and convenient digital insurance experience enjoyed in other markets. Guided by our vision of ‘Insurance Made Easy’, we have grown through continuous innovation, digitising policy access, enabling online insurance claims, and developing advanced claims-automation solutions now being deployed in Sri Lanka and overseas.”
The capital raised through the listing is expected to strengthen InsureMe’s capital base and support its strategic expansion into cutting-edge technology adoption, product diversification, and enhancing its digital platform for seamless customer service. These initiatives are aligned with its goal of becoming the most preferred digital insurance intermediary in the country, fostering greater insurance penetration through easy-to-use digital channels.
Business
JXG awarded top honour for Parent-Inclusive Workplace practices 2024/2025

JXG (Janashakthi Group) was recently recognised with the Parent-Inclusive Workplace of the Year 2024/25 Award at the Parent-Inclusive Workplaces Summit 2025. Held at the Courtyard by Marriott, Colombo, the recognition reflects JXG’s commitment to fostering a supportive, empowering, and inclusive environment for working parents.
Positioning JXG as a benchmark for parent-friendly workplace practices in Sri Lanka, the award aligned with global diversity, equality and inclusion (DEI) and family-friendly workplace standards, recognising JXG’s achievements with the highest score in all five sub-categories of the Parent-Inclusive Workplaces Summit 2025. The categories included Best CEO/Leadership Initiatives for Working Parents, Best HR Policies Empowering Working Parents, Best Workplace Culture for Parents, Best Well-being Initiative for Working Parents, and Most Innovative Initiative Supporting Working Parents.
Discussing the award, Wasanthi Stephen, Group Chief Human Resources Officer at JXG said, “Family is at the heart of our policies, culture, and infrastructure. We recognise the importance of dedicating time to family and how it strengthens talent retention while encouraging workplace loyalty. This award not only reaffirms our efforts to meet the emotional and practical needs of our JXG families but renews our commitment to helping our employees thrive professionally while cultivating their personal lives.”
JXG’s progressive HR policies, culture-building efforts, and well-being initiatives demonstrate a comprehensive and sustained approach to parent inclusivity. The initiatives include up to twelve weeks of fully paid maternity leave with the option of a two-month extension on half pay. Similarly, fathers can apply for two weeks of fully paid paternity leave with additional paid leave upon request. JXG also offers parents versatile arrangements including remote work, flexible scheduling, and permission for parents to attend school and family events without having to take leave.
-
News7 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
 News6 days ago
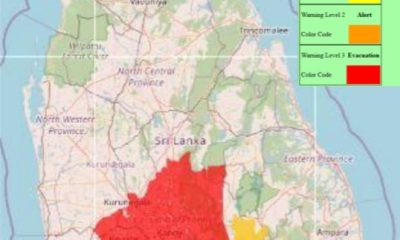
News6 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Midweek Review7 days ago
Midweek Review7 days agoHouse erupts over Met Chief’s 12 Nov unheeded warning about cyclone Ditwah













