Features
Challenges in meeting President’s target

Development of renewable energy projects II –
By Dr Janaka Ratnasiri
The comments made by the President at the meeting he had on 15.12.2020 to discuss the development of renewable energy (RE) projects were highlighted in recent media reports, as described in the writer’s earlier write-up which appeared in The Island of 28.12.2020 under the same heading. However, there was no reference in these reports to any feedback that would have been made by officials present. The purpose of this write-up is to discuss likely issues that would have been of concern to institution officials and the challenges they may have to face in meeting the President’s target.
FEARS OF DESTABILIZING THE SYSTEM
The first challenge is to change the mindset of professionals concerned. Energy experts both within the Ceylon Electricity Board (CEB) and outside have been saying for years that connecting too many of RE plants such as wind and solar power systems to the grid will cause its destabilization, not being able to maintain the voltage and the frequency within permitted limits. The output of these RE supplies keep fluctuating momentarily, hourly and diurnally and the problem is how to balance the supply and load under such dynamic conditions. It was also said that excess harmonics generated during conversion of direct current (DC) output from solar systems or from DC wind turbines into alternating current (AC) for feeding into the grid could degrade the quality of the supply.
According to a website on RE systems, “Impacts caused by high penetration levels of intermittent renewable distributed generation can be complex and severe and may include voltage increase, voltage fluctuation, interaction with voltage regulation and control equipment, reverse power flows, temporary overvoltage, power quality and protection concerns, and current and voltage unbalance, among others. The uncertainty and intermittency of wind and solar generation are major complications that must be addressed before the full potential of these renewables can be reached”. These challenges require advanced control strategies to solve the problems effectively.
PROBLEMS ASSOCIATED WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS
One problem associated with RE systems is that they are not considered dispatchable, which means that their output is not available as and when necessary, unlike in the case of thermal power plants. Wind power output is available only when wind blows which keeps changing in a stochastic manner hourly, diurnally and seasonally. In Sri Lanka, wind is generally strong during the second half of the year than in the first half. In the case of solar panels, their output is available only during the daytime peaking at noon and declining with the increasing solar angle. Even during daytime, the output would drop if there is cloud cover or rainfall. If there is extended periods of bad weather, a consumer has to depend on some back-up power.
According to the CEB Chairman’s Review given in its 2018 Annual Report, “a study on Integration of Renewable Based Generation into Sri Lankan Grid 2020-2030 was conducted during the year (2018) with the objective of investigating the main challenges faced in renewable energy-based generation and determining the optimum level of renewable energy generation”. However, there is no report of this study available in the CEB’s website.
STORAGE SYSTEMS FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY PLANTS
In order to make use of solar energy that is generated during the day, at night time, it is necessary to store the electricity by suitable means. This also applies to wind energy to even out the fluctuating output into a steady output. If the system is connected to the grid, energy generated by solar systems during the day or by wind systems when the wind blows can be fed into the grid and the grid provides the electricity to the consumer during night time or when there is no wind blowing. Hence, there is no need for a separate storage facility with grid-connected systems.
For large scale solar systems, one method of storage is to make use of exiting hydro power reservoirs by saving the water which would have been used for generating an equivalent amount of energy generated by solar panels during the day, and using the water saved during night time. This does not require any additional expenditure on building extra facilities. Another is to build pump-storage facilities comprising two sets of reservoirs at two elevations connected via a penstock with a generator/pump system at the bottom. Already one such system is being planned at Aranayaka.
Any surplus energy generated during the day from solar panels or when wind blows is made use of to pump water from the lower reservoir to the upper reservoir. At night time or when there is no wind, the pumped water is allowed to flow down the penstock driving the pump in the reverse mode to generate electricity. In the West, such pump-storage systems have been used for many decades for peaking purposes. One good example is the system installed at the Niagara Falls.
HYDROGEN SYSTEMS FOR STORAGE
Another method available is to feed the solar panel output to a set of electrolyzers, which are available commercially today, to generate hydrogen by splitting water. Hydrogen generated is stored and fed to a bank of fuel-cells to generate electricity in the form of direct current (DC) and later inverted to AC. After filtering out harmonics, this steady output is fed to the grid as and when necessary, day or night, using the stored hydrogen which makes it dispatchable. Each solar or wind or hybrid energy park that is being planned could be supplemented by such hydrogen storage system accompanied by a bank of fuel cells, enabling the output from these RE parks dispatchable.
There is much interest among developed countries to develop hydrogen energy systems. European Union has set out plans which could require up to € 470 billion (USD 570 billion) of investment in green hydrogen by 2050. Germany alone is targeting 5,000 MW of electrolysis capacity by 2030. Japan, a front-runner along with South Korea, is looking to sharply increase a target to import 300,000 tonnes a year of hydrogen in 2030. U.S. President Joe Biden wants to fund research into technology, including large-scale electrolyzers, to help make green hydrogen costs match conventional hydrogen within a decade. (https://energy.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/renewable/explainer-why-green-hydrogen-is-finally-getting-its-day-in-the-sun/79672523).
PROPOSAL FOR ROOF-TOP SOLAR INSTALLATIONS
The 2021 Budget Speech states that a capacity of 500 MW will be added to the grid, by providing solar panels each generating 5 kW, to 100,000 houses of low-income families. At the meeting the President had on 15.12.2020 with the two Ministers and Ministry officials, he has said that the Government would bear the cost of LKR. 800,000 per house for installing solar cell panels under this project. This means the expenditure on this project will be about LKR 80 billion. The question arises who will be responsible for implementing this project? The SLSEA Act grants powers to it for “entertainment of applications for carrying on of on-grid and off-grid renewable energy projects”. It also has powers for “the development of guidelines on renewable energy projects and disseminating them among prospective investors”. Hence, the SLSEA may be assigned the task of coordinating the project.
The purchase of 100,000 roof-top panels and getting them installed is a challenge by itself. There is a large number of local companies, numbering about 200, involved in supplying and installing roof-top solar panels. The government should call for expressions of interest (EOI) from these companies to undertake this assignment requesting information on their track record and proof of their ability and competency. Next, bids need to be invited from selected companies after announcing detailed specifications for the panels.
It is important to specify in the bid document itself the limiting values for key parameters with tolerances that need to be met by the panel offered, without just saying that panels offered should conform to international standards, as normally done by the CEB. The evaluation of the bids would be much simpler and faster then. It is best if the supply is distributed among as many vendors as possible, after agreeing on a fixed price, to expedite the implementation of the project and avoid complaints from unsuccessful bidders.
POOR PLANNING FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY PROJECTS
Though the Cabinet of Ministers since 2016 has been taking decisions to introduce RE projects including solar power systems at both domestic level and utility scale, their follow up by the two implementing agencies, viz. SLSEA and the CEB has been rather slow, possibly due to divided responsibility. According to the SLSEA Act, any RE project needs the approval of the SLSEA before commencing any work.
The Electricity Act also requires accepting projects selected only after calling for tenders except those recommended by the SLSEA. The misinterpretation of the Electricity has resulted in projects recommended by the SLSEA getting held up by the CEB for extended periods. The CEB’s draft LTGE Plan for 2020-39 prepared in May 2019, plans to add only 165 MW of mini-hydro systems, 555 MW of wind systems, 880 MW of solar systems and 55 MW of biomass systems up to 2030. Even the SLSEA has failed to come out with a plan to develop RE systems in an optimal manner as highlighted in the Writer’s article in the Island of 28.12.2020.
This is despite the fact that the previous Cabinet decisions had wanted about 2,000 MW of solar power added within a shorter time frame, comprising 1000 MW of roof-top systems and 1000 MW of utility systems. As mentioned in the previous article, even the SLSEA has failed to come up with a plan to develop RE systems though it is a requirement given in its Act. So, another challenge is to get the CEB and SLSEA to enhance their plans for RE generation and fall in line with the Government policy. If they do not comply, the solution is not closing down of the PUCSL as highlighted in writer’s article in The Island of 25.12.2020. (See https://island.lk/cabinet-discussion-on-public-utilities-commission/)
INCOMPATIBILITY OF NEW COAL POWER PLANTS WITH INCREASED RE SHARE
One problem possibly encountered in increasing the RE share is the incorporation of several new coal power plants in the system by 2030. This increases the share of fossil fuel share leaving only a small fraction to be filled by RE systems. For example, the draft Plan for 2020-39 shows the demand in 2030 as 31,740 GWh, out of which 20,640 GWh (65%) will be from fossil fuels and 11,100 GWh (35%) from RE sources. Out of the 20,640 GWh expected from fossil fuel plants, 7,721 GWh (24%) will be from the two new coal power plants to be built at Norochcholai (600 MW) and Trincomalee (300 MW). Another 4,781 GWh (15%) will be from the existing coal power plant at Norochcholai.
This means by 2030, 12,502 GWh (39%) of the demand will be met from coal while another 8,140 GWh (26%) will be from oil or jointly 20,640 GWh (65%) from fossil fuels. If 70% of total demand is to be met from renewables, then only 30% could be generated from fossil fuels. This means that the RE contribution has to be 48,160 GWh if the fossil fuel contribution is to be maintained at 20,640 GWh, making the total supply to be 68,800 GWh, which is more than double the forecasted demand in 2030. In order to make achieving of 70% share from RE sources feasible, it is therefore imperative to limit the fossil fuel contribution to 9,520 GWh in order to maintain the total supply at 31,740 GWh.
The easiest way to achieve this target is to stop building the two new coal power plants at Norochcholai and at Trincomalee, and retire the 20-year-old existing coal plant at Norochcholai. Hence, building new coal power plants is not compatible with President’s target on RE share of 70% in electricity generation. The President should therefore give a clear directive to CEB to discontinue planning of new coal power plants disregarding what its Unions say.
It is reported in the media that a former Army Officer has been appointed as Vice-Chairman of CEB to help CEB “to achieve President Gotabaya Rajapaksa’s of goal promoting renewable energy and providing electricity at a minimal cost” (Island of 22.12.2020). Perhaps the new Vice-Chairman will keep those within CEB who oppose President’s move at bay, including the trade unions.
IMPROVING RESEARCH CAPABILITY OF CEB
According to the CEB Act of 1969, CEB has powers to conduct research into matters affecting the generation, distribution, transmission, supply and use of electricity (Article 12h). However, CEB’s Annual Reports do not refer to any research being done within the CEB. Students in the Physical Science stream having the highest scores at GCE (A level) examination get admitted to engineering courses and those who follow electrical engineering ending up in institutions like CEB.
It is a pity that the CEB management does not make use of this talented graduates to undertake research to seek solutions to such problems such as integrating RE systems into the grid, develop new storage systems and to provide other research and development support for RE systems. In 2019, the CEB has spent about LKR 97 Billion on importing fuel for thermal power plants (SD 2019).
With the introduction of large scale RE systems, part of this expenditure could be saved which could be utilized to set up a Research and Development (R&D) Division in CEB as provided for in its Act.
Perhaps, a senior academic with research experience in RE systems could be invited to set up the R&D Division and provide him with a team of young engineers comprising both electrical and ICT engineers with aptitude for research to undertake studies on how to make the grid smart as described above.
THE WAY FORWARD
If the full potential of the country’s RE resources is exploited, it will be possible to achieve the entire electricity generation from RE sources. It will also save hundreds of Billions of Rupees annually on importing fuel required for operating thermal power plants. However, there are many problems to surmount before this could be achieved. Among these are the following:
a. Change the mindset of senior officials controlling the power sector that changing from fossil fuels to RE sources to meet the base load requirements is technically feasible.
b. Discontinue building new coal power plants and retire the existing coal power plant by 2030 as their presence will exceed the 30% share from fossil fuels.
c. Introduce mechanisms for energy storage at utility scale through utilizing existing hydro power reservoirs or building pump-storage systems or adding large batteries or adding electrolyzer-fuel cell systems which are commercially available now.
d. Set up a R&D Division within CEB to seek solutions for problems associated with integration of utility scale RE systems into the grid.
e. Entertain investors directly for RE projects on build, own, operate and transfer (BOOT) basis by providing efficient, clear and transparent mechanism for accepting proposals and guaranteeing security of their investments.
f. Publish a set of guidelines prepared jointly by SLSEA, CEB and PUCSL for accepting and approving candidate RE projects proposed by investors on BOOT basis.
CONCLUSION
It is important for decision makers to take a wholistic view of the power sector in the country and take evidence-based decisions rather than taking a piecemeal approach. It is not possible to build more coal power plants on one hand and fix targets for increased RE share on the other. While the President wants more renewable energy projects, the Ministry and CEB want more coal power plants. The President should decide on his priorities. If his priority is to have more renewable energy share by 2030, then he should get CEB to give up building more coal power plants. He cannot have both. It is his biggest challenge.
Features
Lasting solutions require consensus

Problems and solutions in plural societies like Sri Lanka’s which have deep rooted ethnic, religious and linguistic cleavages require a consciously inclusive approach. A major challenge for any government in Sri Lanka is to correctly identify the problems faced by different groups with strong identities and find solutions to them. The durability of democratic systems in divided societies depends less on electoral victories than on institutionalised inclusion, consultation, and negotiated compromise. When problems are defined only through the lens of a single political formation, even one that enjoys a large electoral mandate, such as obtained by the NPP government, the policy prescriptions derived from that diagnosis will likely overlook the experiences of communities that may remain outside the ruling party. The result could end up being resistance to those policies, uneven implementation and eventual political backlash.
A recent survey done by the National Peace Council (NPC), in Jaffna, in the North, at a focus group discussion for young people on citizen perception in the electoral process, revealed interesting developments. The results of the NPC micro survey support the findings of the national survey by Verite Research that found that government approval rating stood at 65 percent in early February 2026. A majority of the respondents in Jaffna affirm that they feel safer and more fairly treated than in the past. There is a clear improving trend to be seen in some areas, but not in all. This survey of predominantly young and educated respondents shows 78 percent saying livelihood has improved and an equal percentage feeling safe in daily life. 75 percent express satisfaction with the new government and 64 percent believe the state treats their language and culture fairly. These are not insignificant gains in a region that bore the brunt of three decades of war.
Yet the same survey reveals deep reservations that temper this optimism. Only 25 percent are satisfied with the handling of past issues. An equal percentage see no change in land and military related concerns. Most strikingly, almost 90 percent are worried about land being taken without consent for religious purposes. A significant number are uncertain whether the future will be better. These negative sentiments cannot be brushed aside as marginal. They point to unresolved structural questions relating to land rights, demilitarisation, accountability and the locus of political power. If these issues are not addressed sooner rather than later, the current stability may prove fragile. This suggests the need to build consensus with other parties to ensure long-term stability and legitimacy, and the need for partnership to address national issues.
NPP Absence
National or local level problems solving is unlikely to be successful in the longer term if it only proceeds from the thinking of one group of people even if they are the most enlightened. Problem solving requires the engagement of those from different ethno-religious, caste and political backgrounds to get a diversity of ideas and possible solutions. It does not mean getting corrupted or having to give up the good for the worse. It means testing ideas in the public sphere. Legitimacy flows not merely from winning elections but from the quality of public reasoning that precedes decision-making. The experience of successful post-conflict societies shows that long term peace and development are built through dialogue platforms where civil society organisations, political actors, business communities, and local representatives jointly define problems before negotiating policy responses.
As a civil society organisation, the National Peace Council engages in a variety of public activities that focus on awareness and relationship building across communities. Participants in those activities include community leaders, religious clergy, local level government officials and grassroots political party representatives. However, along with other civil society organisations, NPC has been finding it difficult to get the participation of members of the NPP at those events. The excuse given for the absence of ruling party members is that they are too busy as they are involved in a plenitude of activities. The question is whether the ruling party members have too much on their plate or whether it is due to a reluctance to work with others.
The general belief is that those from the ruling party need to get special permission from the party hierarchy for activities organised by groups not under their control. The reluctance of the ruling party to permit its members to join the activities of other organisations may be the concern that they will get ideas that are different from those held by the party leadership. The concern may be that these different ideas will either corrupt the ruling party members or cause dissent within the ranks of the ruling party. But lasting reform in a plural society requires precisely this exposure. If 90 percent of surveyed youth in Jaffna are worried about land issues, then engaging them, rather than shielding party representatives from uncomfortable conversations, is essential for accurate problem identification.
North Star
The Leader of the Lanka Sama Samaja Party (LSSP), Prof Tissa Vitarana, who passed away last week, gave the example for national level problem solving. As a government minister he took on the challenge the protracted ethnic conflict that led to three decades of war. He set his mind on the solution and engaged with all but never veered from his conviction about what the solution would be. This was the North Star to him, said his son to me at his funeral, the direction to which the Compass (Malimawa) pointed at all times. Prof Vitarana held the view that in a diverse and plural society there was a need to devolve power and share power in a structured way between the majority community and minority communities. His example illustrates that engagement does not require ideological capitulation. It requires clarity of purpose combined with openness to dialogue.
The ethnic and religious peace that prevails today owes much to the efforts of people like Prof Vitarana and other like-minded persons and groups which, for many years, engaged as underdogs with those who were more powerful. The commitment to equality of citizenship, non-racism, non-extremism and non-discrimination, upheld by the present government, comes from this foundation. But the NPC survey suggests that symbolic recognition and improved daily safety are not enough. Respondents prioritise personal safety, truth regarding missing persons, return of land, language use and reduction of military involvement. They are also asking for jobs after graduation, local economic opportunity, protection of property rights, and tangible improvements that allow them to remain in Jaffna rather than migrate.
If solutions are to be lasting they cannot be unilaterally imposed by one party on the others. Lasting solutions cannot be unilateral solutions. They must emerge from a shared diagnosis of the country’s deepest problems and from a willingness to address the negative sentiments that persist beneath the surface of cautious optimism. Only then can progress be secured against reversal and anchored in the consent of the wider polity. Engaging with the opposition can help mitigate the hyper-confrontational and divisive political culture of the past. This means that the ruling party needs to consider not only how to protect its existing members by cloistering them from those who think differently but also expand its vision and membership by convincing others to join them in problem solving at multiple levels. This requires engagement and not avoidance or withdrawal.
by Jehan Perera
Features
Unpacking public responses to educational reforms

 As the debate on educational reforms rages, I find it useful to pay as much attention to the reactions they have excited as we do to the content of the reforms. Such reactions are a reflection of how education is understood in our society, and this understanding – along with the priorities it gives rise to – must necessarily be taken into account in education policy, including and especially reform. My aim in this piece, however, is to couple this public engagement with critical reflection on the historical-structural realities that structure our possibilities in the global market, and briefly discuss the role of academics in this endeavour.
As the debate on educational reforms rages, I find it useful to pay as much attention to the reactions they have excited as we do to the content of the reforms. Such reactions are a reflection of how education is understood in our society, and this understanding – along with the priorities it gives rise to – must necessarily be taken into account in education policy, including and especially reform. My aim in this piece, however, is to couple this public engagement with critical reflection on the historical-structural realities that structure our possibilities in the global market, and briefly discuss the role of academics in this endeavour.
Two broad reactions
The reactions to the proposed reforms can be broadly categorised into ‘pro’ and ‘anti’. I will discuss the latter first. Most of the backlash against the reforms seems to be directed at the issue of a gay dating site, accidentally being linked to the Grade 6 English module. While the importance of rigour cannot be overstated in such a process, the sheer volume of the energies concentrated on this is also indicative of how hopelessly homophobic our society is, especially its educators, including those in trade unions. These dispositions are a crucial part of the reason why educational reforms are needed in the first place. If only there was a fraction of the interest in ‘keeping up with the rest of the world’ in terms of IT, skills, and so on, in this area as well!
Then there is the opposition mounted by teachers’ trade unions and others about the process of the reforms not being very democratic, which I (and many others in higher education, as evidenced by a recent statement, available at https://island.lk/general-educational-reforms-to-what-purpose-a-statement-by-state-university-teachers/ ) fully agree with. But I earnestly hope the conversation is not usurped by those wanting to promote heteronormativity, further entrenching bigotry only education itself can save us from. With this important qualification, I, too, believe the government should open up the reform process to the public, rather than just ‘informing’ them of it.
It is unclear both as to why the process had to be behind closed doors, as well as why the government seems to be in a hurry to push the reforms through. Considering other recent developments, like the continued extension of emergency rule, tabling of the Protection of the State from Terrorism Act (PSTA), and proposing a new Authority for the protection of the Central Highlands (as is famously known, Authorities directly come under the Executive, and, therefore, further strengthen the Presidency; a reasonable question would be as to why the existing apparatus cannot be strengthened for this purpose), this appears especially suspect.
Further, according to the Secretary to the MOE Nalaka Kaluwewa: “The full framework for the [education] reforms was already in place [when the Dissanayake government took office]” (https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2025/08/12/wxua-a12.html, citing The Morning, July 29). Given the ideological inclinations of the former Wickremesinghe government and the IMF negotiations taking place at the time, the continuation of education reforms, initiated in such a context with very little modification, leaves little doubt as to their intent: to facilitate the churning out of cheap labour for the global market (with very little cushioning from external shocks and reproducing global inequalities), while raising enough revenue in the process to service debt.
This process privileges STEM subjects, which are “considered to contribute to higher levels of ‘employability’ among their graduates … With their emphasis on transferable skills and demonstrable competency levels, STEM subjects provide tools that are well suited for the abstraction of labour required by capitalism, particularly at the global level where comparability across a wide array of labour markets matters more than ever before” (my own previous piece in this column on 29 October 2024). Humanities and Social Sciences (HSS) subjects are deprioritised as a result. However, the wisdom of an education policy that is solely focused on responding to the global market has been questioned in this column and elsewhere, both because the global market has no reason to prioritise our needs as well as because such an orientation comes at the cost of a strategy for improving the conditions within Sri Lanka, in all sectors. This is why we need a more emancipatory vision for education geared towards building a fairer society domestically where the fruits of prosperity are enjoyed by all.
The second broad reaction to the reforms is to earnestly embrace them. The reasons behind this need to be taken seriously, although it echoes the mantra of the global market. According to one parent participating in a protest against the halting of the reform process: “The world is moving forward with new inventions and technology, but here in Sri Lanka, our children are still burdened with outdated methods. Opposition politicians send their children to international schools or abroad, while ours depend on free education. Stopping these reforms is the lowest act I’ve seen as a mother” (https://www.newsfirst.lk/2026/01/17/pro-educational-reforms-protests-spread-across-sri-lanka). While it is worth mentioning that it is not only the opposition, nor in fact only politicians, who send their children to international schools and abroad, the point holds. Updating the curriculum to reflect the changing needs of a society will invariably strengthen the case for free education. However, as mentioned before, if not combined with a vision for harnessing education’s emancipatory potential for the country, such a move would simply translate into one of integrating Sri Lanka to the world market to produce cheap labour for the colonial and neocolonial masters.
According to another parent in a similar protest: “Our children were excited about lighter schoolbags and a better future. Now they are left in despair” (https://www.newsfirst.lk/2026/01/17/pro-educational-reforms-protests-spread-across-sri-lanka). Again, a valid concern, but one that seems to be completely buying into the rhetoric of the government. As many pieces in this column have already shown, even though the structure of assessments will shift from exam-heavy to more interim forms of assessment (which is very welcome), the number of modules/subjects will actually increase, pushing a greater, not lesser, workload on students.

A file photo of a satyagraha against education reforms
What kind of education?
The ‘pro’ reactions outlined above stem from valid concerns, and, therefore, need to be taken seriously. Relatedly, we have to keep in mind that opening the process up to public engagement will not necessarily result in some of the outcomes, those particularly in the HSS academic community, would like to see, such as increasing the HSS component in the syllabus, changing weightages assigned to such subjects, reintroducing them to the basket of mandatory subjects, etc., because of the increasing traction of STEM subjects as a surer way to lock in a good future income.
Academics do have a role to play here, though: 1) actively engage with various groups of people to understand their rationales behind supporting or opposing the reforms; 2) reflect on how such preferences are constituted, and what they in turn contribute towards constituting (including the global and local patterns of accumulation and structures of oppression they perpetuate); 3) bring these reflections back into further conversations, enabling a mutually conditioning exchange; 4) collectively work out a plan for reforming education based on the above, preferably in an arrangement that directly informs policy. A reform process informed by such a dialectical exchange, and a system of education based on the results of these reflections, will have greater substantive value while also responding to the changing times.
Two important prerequisites for this kind of endeavour to succeed are that first, academics participate, irrespective of whether they publicly endorsed this government or not, and second, that the government responds with humility and accountability, without denial and shifting the blame on to individuals. While we cannot help the second, we can start with the first.
Conclusion
For a government that came into power riding the wave of ‘system change’, it is perhaps more important than for any other government that these reforms are done for the right reasons, not to mention following the right methods (of consultation and deliberation). For instance, developing soft skills or incorporating vocational education to the curriculum could be done either in a way that reproduces Sri Lanka’s marginality in the global economic order (which is ‘system preservation’), or lays the groundwork to develop a workforce first and foremost for the country, limited as this approach may be. An inextricable concern is what is denoted by ‘the country’ here: a few affluent groups, a majority ethno-religious category, or everyone living here? How we define ‘the country’ will centrally influence how education policy (among others) will be formulated, just as much as the quality of education influences how we – students, teachers, parents, policymakers, bureaucrats, ‘experts’ – think about such categories. That is precisely why more thought should go to education policymaking than perhaps any other sector.
(Hasini Lecamwasam is attached to the Department of Political Science, University of Peradeniya).
Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.
Features
Chef’s daughter cooking up a storm…
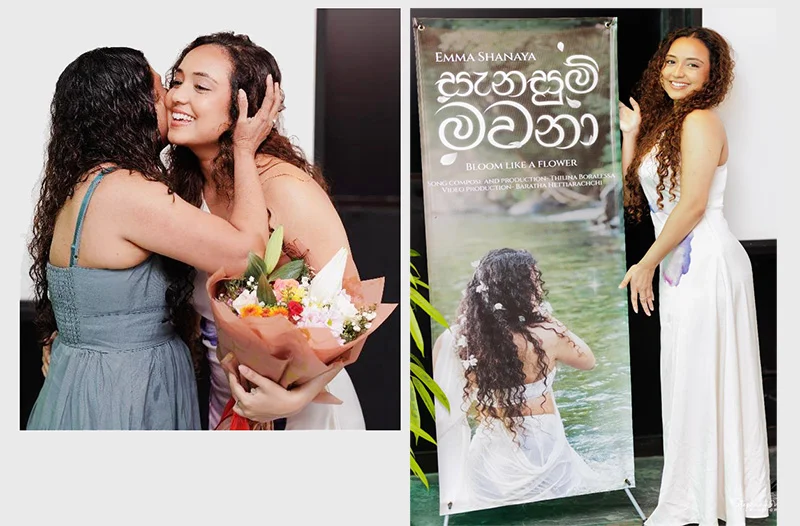
 Don Sherman was quite a popular figure in the entertainment scene but now he is better known as the Singing Chef and that’s because he turns out some yummy dishes at his restaurant, in Rajagiriya.
Don Sherman was quite a popular figure in the entertainment scene but now he is better known as the Singing Chef and that’s because he turns out some yummy dishes at his restaurant, in Rajagiriya.
However, now the spotlight is gradually focusing on his daughter Emma Shanaya who has turned out to be a very talented singer.
In fact, we have spotlighted her in The Island a couple of times and she is in the limelight, once gain.
When Emma released her debut music video, titled ‘You Made Me Feel,’ the feedback was very encouraging and at that point in time she said “I only want to keep doing bigger and greater things and ‘You Made Me Feel’ is the very first step to a long journey.”
Emma, who resides in Melbourne, Australia, is in Sri Lanka, at the moment, and has released her very first Sinhala single.
“I’m back in Sri Lanka with a brand new single and this time it’s a Sinhalese song … yes, my debut Sinhala song ‘Sanasum Mawana’ (Bloom like a Flower).
“This song is very special to me as I wrote the lyrics in English and then got it translated and re-written by my mother, and my amazing and very talented producer Thilina Boralessa. Thilina also composed the music, and mix and master of the track.”
Emma went on to say that instead of a love song, or a young romance, she wanted to give the Sri Lankan audience a debut song with some meaning and substance that will portray her, not only as an artiste, but as the person she is.
Says Emma: “‘Sanasum Mawana’ is about life, love and the essence of a woman. This song is for the special woman in your life, whether it be your mother, sister, friend, daughter or partner. I personally dedicate this song to my mother. I wouldn’t be where I am right now if it weren’t for her.”
On Friday, 30th January, ‘Sanasum Mawana’ went live on YouTube and all streaming platforms, and just before it went live, she went on to say, they had a wonderful and intimate launch event at her father’s institute/ restaurant, the ‘Don Sherman Institute’ in Rajagiriya.
It was an evening of celebration, good food and great vibes and the event was also an introduction to Emma Shanaya the person and artiste.
Emma also mentioned that she is Sri Lanka for an extended period – a “work holiday”.
“I would like to expand my creativity in Sri Lanka and see the opportunities the island has in store for me. I look forward to singing, modelling, and acting opportunities, and to work with some wonderful people.
“Thank you to everyone that is by my side, supporting me on this new and exciting journey. I can’t wait to bring you more and continue to bloom like a flower.”
-

 Life style3 days ago
Life style3 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Midweek Review7 days ago
Midweek Review7 days agoA question of national pride
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoWill computers ever be intelligent?
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:



















