Features
CEB Seeks 100% Tariff Increase but Blocks 4000 MW of Lower-Cost Renewable Energy Generation: What’s the Logic?
by Anil Cabraal, PhD
Power crisis worsened due to CEB favouring oil and coal power over lower-cost renewable energy
On 27 April 2022, the Renewable Energy Associations announced that 1,251 MW of Non-conventional Renewable Energy (NCRE) plants will have to cease operating, as the CEB owes them Rs.22 billion. NCRE includes mini-hydro, wind, solar, biomass and others that use renewable energy for power generation. The consequences will be severe – greater oil-fired generation, higher oil imports, increased CEB financial losses, depletion of foreign reserves, job losses for NCRE plant employees, default risk to banks holding Rs.60 billion in NCRE debt and NCRE investor losses.
Meanwhile, the CEB has blocked over 4,000 MW of new NCRE plant investments. According to the Auditor General’s 08 February 2022 report, the CEB had rejected signing power purchase agreements for 1,374 NCRE projects with an aggregate capacity of 4,015 MW, which the Sustainable Energy Authority (SEA) had approved from 2017 to 2019 [https://bit.ly/3rYiVPD]. Had these projects been approved by CEB and built, they could have supplied electricity at the prevailing Rs.16.07 to 25.09 per kWh tariff, far less than the cost of diesel electricity today.
On 30 April 2022, CEB Chairman stated that CEB is seeking a 100% tariff increase to pay for staff salaries, fuel imports and other liabilities [https://bit.ly/3s4ZWTv]. While seeking a tariff increase, is it not incumbent on the CEB to make sure they obtain electricity from the lowest cost suppliers?
Tariff update needed to revive NCRE development
Despite the potential for NCRE in Sri Lanka, the NCRE tariff offered by CEB ,under their Small Power Purchase (SPP) Program, has remained unchanged since 2012, thereby depressing the financial viability of such projects. A Cabinet-appointed Committee recommended a new NCRE tariff regime in December 2021 to the responsible State Minister. To update the tariffs to today’s economic reality, the author recalculated the tariffs using 2022 parameters for four sample NCRE technologies, using the 2012 PUCSL-approved methodology. For new NCRE power plants, Table 1 shows a comparison of the prevailing 2012 tariff, the 2021 Tariff Committee’s proposed tariff, and the author’s 2022 tariff for mini-hydro, solar, wind and biomass dendro (sustainably harvested biomass).
Table Comparison of NCRE 2022 Tariff with Prevailing 2012 Tariff and Tariff Committee’s Proposed 2021 Tariff
Notably, the Tariff Committee’s proposed 2021 NCRE tariff is lower than the prevailing 2012 tariff, despite exchange rate and other factors deteriorating from 2012 to 2021. On a positive note, US dollar investment costs of solar and wind technologies did decline significantly. NCRE which are financially nonviable in 2022 at the prevailing 2012 tariff, will be worse off under the 2021 tariff.
The severe economic shocks of 2022 are the principal reasons why the calculated 2022 tariffs are higher. Calculated higher tariffs in 2022 are due to: (a) The sharp rupee depreciation which makes investments costlier in rupee terms, as 70-80% of NCRE investment is foreign content. However, unlike oil or coal-powered generation, NCRE generation is immune to imported fuel rupee-price increases; (b) Credit has become more expensive. Even the author’s assumption of 18% interest rate may be too low. (2021 Tariff Committee assumed 9.85% interest). The one-year T-Bill rate is now more than 25%; (c) Inflation is higher; and (d) In the case of biomass-fuelled generation, fuelwood prices have risen sharply due to oil and LPG shortages and their price increases.
While the 2022 tariff may seem high, they are less costly than electricity from oil and coal today, as discussed below.
Is NCRE investment in 2022 worthwhile at these higher tariffs?
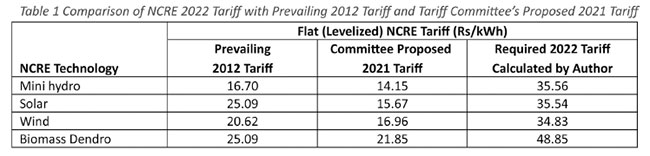
The answer is a Yes, as illustrated in Figure 1 which compares the flat (“levelized”) electricity cost, from NCRE, coal and oil under various conditions. Conservatively, the analysis assumed more favourable financing terms for CEB-owned coal and oil power plant investments, than for private sector NCRE or emergency diesel (Diesel IPP) investments.
NCRE electricity is cheaper than that from new oil-fired generation, even from efficient combined cycle plants. At today’s coal prices, NCRE electricity costs can be less than that from a new coal plant. The results are unsurprising as, once built, currency depreciation only marginally affects NCRE plants, unlike oil and coal plant operations. NCRE potential is very high in Sri Lanka.
Figure Comparison of Levelized Electricity Cost of NCRE, Oil and Coal Power Generation
What are the savings to CEB and to Sri Lanka from unblocking NCRE Investments?
The savings can be considerable to CEB by avoiding paying for higher cost electricity, and to the Nation from reduced fuel imports. As an example, implementing 800 MW (or 20% of the blocked projects) could supply about 1,800 GWh of NCRE electricity annually. In comparison, in 2020, oil thermal IPPs supplied 2,717 GWh of electricity and CEB oil thermals generated 1,462 GWh. Therefore 1,800 GWh of NCRE electricity could displace more expensive oil thermal generation, especially the more expensive IPP diesel generation. CEB may, however, need to upgrade its system control and operations to accommodate increased generation from variable solar and wind power.
The 800 MW of NCRE generation could offset about 400 million litres of diesel fuel annually. The net financial savings to CEB is Rs.37 billion per year (assumes paying flat 2022 tariff for NCRE, while avoiding paying for diesel fuel at US$0.75/litre, the price CEB paid for 40,000 MT in April 2022). The saving to Sri Lanka by avoiding diesel imports is about US$300 million for the year from these 800 MW of NCRE investments. The NCRE investment required is about US$1,000 million, giving a simple payback of 3.3 years in imported diesel fuel savings.
Special case of existing biomass power plants
Even if CEB pays the outstanding invoices for NCRE-supplied electricity, the existing biomass power plants (37 MW) are presently facing an existential threat to their financial survival due to the sharp rise in fuelwood prices (from about Rs.7/kg to Rs.12/kg for chipped fuelwood in 2022). Unless the Cabinet takes mitigatory actions immediately and approves an amendment to the existing Biomass Dendro Power Purchase Agreement to permit a higher tariff, these plants will cease operations and Sri Lanka will lose access to these 37 MW. Even at a fuelwood price of Rs.12/kg, electricity from these existing plants is far cheaper than CEB paying for diesel fuel. Paradoxically, unlike these biomass plants, oil-fired IPPs can pass-through the fuel cost to CEB and avoid the fuel price risk.
What must the Government and CEB do?
Given the significant benefits from investments in NCRE, the Government must direct the Ministry of Power and Energy, CEB, PUCSL and SEA to immediately undertake the following:
* Most urgently, CEB must settle its arrears of Rs.22 billion to NCRE producers.
*Tariff Committee must update the NCRE cost-reflective tariffs to 2022 conditions in consultation with technology and project finance specialists.
*PUCSL must approve, and CEB must adopt the tariff as soon as possible. The CEB and PUCSL must commit to updating the tariffs at least every 2 years.
*CEB must commit to accepting over 1,000 NCRE projects that they have hitherto blocked and invite other NCRE proposals.
*SEA should invite companies to revise feasibility studies and update their NCRE applications. Companies must respond quickly. SEA should, without delays or additional fees, review and approve the compliant proposals.
*CEB must issue letters of intent and sign Power Purchase Agreements without delay for compliant NCRE proposals.
*CEB must commit to providing necessary infrastructure and control systems upgrades required to connect these NCRE facilities to the CEB grid.
*SEA, with Ministry of Finance assistance, could mobilize financing from commercial banks and international financiers, particularly climate-friendly investors.
As Mr. Manjula Perera, CEO of Windforce Ltd., representing the renewable energy community, stated recently: “If the Power Ministry, CEB, SEA, and PUCSL work hand in hand and get the necessary policies in place, adding 1,000 MWs from NCRE within the next 2 years by local RE developers will not be a challenge”.
In conclusion, successfully accomplishing these actions will permit NCRE technologies and the private sector to help Sri Lanka address its near-term energy-sector and balance of payment challenges and to achieve the Government’s goal of 70% RE generation by 2030.
03 May 2022
Disclaimer: The views, data, assumptions, analyses, results interpretations, and opinions expressed in the text belong solely to the author, and not necessarily to any other group or individual, including those cited in the article.
The author is a former Lead Energy Specialist at the World Bank with specialization in renewable energy project development and financing in Asian and African countries, including in Sri Lanka. This article is based on his paper “Mobilizing Renewable Energy to Overcome the Energy and Financial Crisis: The Need for a Credible Renewable Electricity Tariff,” https://bit.ly/3Ltabsx
Features
The Venezuela Model:The new ugly and dangerous world order

 The US armed forces invading Venezuela, removing its President Nicolás Maduro from power and abducting him and his wife Cilia Flores on 3 January 2026, flying them to New York and producing Maduro in a New York kangaroo court is now stale news, but a fact. What is a far more potent fact is the pan-global impotent response to this aggression except in Latin America, China, Russia and a few others.
The US armed forces invading Venezuela, removing its President Nicolás Maduro from power and abducting him and his wife Cilia Flores on 3 January 2026, flying them to New York and producing Maduro in a New York kangaroo court is now stale news, but a fact. What is a far more potent fact is the pan-global impotent response to this aggression except in Latin America, China, Russia and a few others.
Colombian President Gustavo Petro described the attack as an “assault on the sovereignty” of Latin America, thereby portraying the aggression as an assault on the whole of Latin America. Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva referred to the attack as crossing “an unacceptable line” that set an “extremely dangerous precedent.” Again, one can see his concern goes beyond Venezuela. For Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum the attack was in “clear violation” of the UN Charter, which again is a fact. But when it comes to powerful countries, the UN Charter has been increasingly rendered irrelevant over decades, and by extension, the UN itself. For the French Foreign Minister, the operation went against the “principle of non-use of force that underpins international law” and that lasting political solutions cannot be “imposed by the outside.” UN Secretary General António Guterres said he was “deeply alarmed” about the “dangerous precedent” the United States has set where rules of international law were not being respected. Russia, notwithstanding its bloody and costly entanglement in Ukraine, and China have also issued strong statements.
Comparatively however, many other countries, many of whom are long term US allies who have been vocal against the Russian aggression in Ukraine have been far more sedate in their reaction. Compared to his Foreign Minister, French President Emmanuel Macron said the Venezuelan people could “only rejoice” at the ousting of Maduro while the German Chancellor Friedrich Merz believed Maduro had “led his country into ruin” and that the U.S. intervention required “careful consideration.” The British and EU statements have been equally lukewarm. India’s and Sri Lanka’s statements do not even mention the US while Sri Lanka’s main coalition partner the JVP has issued a strongly worded statement.
Taken together, what is lacking in most of these views, barring a negligible few, especially from the so-called powerful countries, is the moral indignation or outrage on a broad scale that used to be the case in similar circumstances earlier. It appears that a new ugly and dangerous world order has finally arrived, footprints of which have been visible for some time.
It is not that the US has not invaded sovereign countries and affected regime change or facilitated such change for political or economic reasons earlier. This has been attempted in Cuba without success since the 1950s but with success in Chile in 1973 under the auspices of Augusto Pinochet that toppled the legitimate government of president Salvador Allende and established a long-lasting dictatorship friendly towards the US; the invasion of Panama and the ouster and capture of President Manuel Noriega in 1989 and the 2003 invasion of Iraq both of which were conducted under the presidency of George Bush.
These are merely a handful of cross border criminal activities against other countries focused on regime change that the US has been involved in since its establishment which also includes the ouster of President of Guyana Cheddi Jagan in 1964, the US invasion of the Dominican Republic in 1965 stop the return of President Juan Bosch to prevent a ‘communist resurgence’; the 1983 US invasion of Grenada after the overthrow and killing of Prime Minister Maurice Bishop purportedly to ensure that the island would not become a ‘Soviet-Cuban’ colony. A more recent adventure was the 2004 removal and kidnapping of the Haitian President Jean-Bertrand Aristide, which also had French support.
There is however a difference between all the earlier examples of US aggression and the Venezuelan operation. The earlier operations where the real reasons may have varied from political considerations based on ideological divergence to crude economics, were all couched in the rhetoric of democracy. That is, they were undertaken in the guise of ushering democratic changes in those countries, the region or the world irrespective of the long-term death and destruction which followed in some locations. But in Venezuela under President Donald Trump, it is all about controlling natural resources in that country to satisfy US commercial interests.
The US President is already on record for saying the US will “run” Venezuela until a “safe transition” is concluded and US oil companies will “go in, spend billions of dollars, fix the badly broken infrastructure, the oil infrastructure, and start making money” – ostensibly for the US and those in Venezuela who will tag the US line. Trump is also on record saying that the main aim of the operation was to regain U.S. oil rights, which according to him were “stolen” when Venezuela nationalized the industry. The nationalization was obviously to ensure that the funds from the industry remained in the country even though in later times this did lead to massive internal corruption.
Let’s be realistic. Whatever the noise of the new rhetoric is, this is not about ‘developing’ Venezuela for the benefit of its people based on some unknown streak of altruism but crudely controlling and exploiting its natural assets as was the case with Iraq. As crude as it is, one must appreciate Trump’s unintelligent honesty stemming from his own unmitigated megalomania. Whatever US government officials may say, the bottom line is the entire operation was planned and carried out purely for commercial and monetary gain while the pretext was Maduro being ‘a narco-terrorist.’ There is no question that Maduro was a dictator who was ruining his own country. But there is also no question that it is not the business of the US or any other country to decide what his or Venezuela’s fate is. That remains with the Venezuelan people.
What is dangerous is, the same ‘narco-terrorist’ rhetoric can also be applied to other Latin American countries such as Columbia, Brazil and Mexico which also produce some of the narcotics that come into the US consumer markets. The response should be not to invade these countries to stem the flow, but to deal with the market itself, which is the US. In real terms what Trump has achieved with his invasion of Venezuela for purely commercial gain and greed, followed by the abject silence or lukewarm reaction from most of the world, is to create a dangerous and ugly new normal for military actions across international borders. The veneer of democracy has also been dispensed with.
The danger lies in the fact that this new doctrine or model Trump has devised can similarly be applied to any country whose resources or land a powerful megalomaniac leader covets as long as he has unlimited access to military assets of his country, backed by the dubius remnants of the political and social safety networks, commonsense and ethics that have been conveniently dismantled. This is a description of the present-day United States too. This danger is boosted when the world remains silent. After the success of the Venezuela operation, Trump has already upended his continuing threats to annex Greenland because “we need Greenland from the standpoint of national security.” Greenland too is not about security, but commerce given its vast natural resources.
Hours after Venezuela, Trump threatened the Colombian President Gustavo Petro to “watch his ass.” In the present circumstances, Canadians also would not have forgotten Trump’s threat earlier in 2025 to annex Canada. But what the US President and his current bandwagon replete with arrogance and depleted intelligence would not understand is, beyond the short-term success of the Venezuela operation and its euphoria, the dangerous new normal they have ushered in would also create counter threats towards the US, the region and the world in a scale far greater than what exists today. The world will also become a far less safe place for ordinary American citizens.
More crucially, it will also complicate global relations. It would no longer be possible for the mute world leaders to condemn Russian action in Ukraine or if China were to invade Taiwan. The model has been created by Trump, and these leaders have endorsed it. My reading is that their silence is not merely political timidity, but strategic to their own national and self-interest, to see if the Trump model could be adopted in other situations in future if the fallout can be managed.
The model for the ugly new normal has been created and tested by Trump. Its deciding factors are greed and dismantled ethics. It is now up to other adventurers to fine tune it. We would be mere spectators and unwitting casualties.
Features
Beyond the beauty: Hidden risks at waterfalls

Sri Lanka is blessed with a large number of scenic waterfalls, mainly concentrated in the central highlands. These natural features substantially enhance the country’s attractiveness to tourists. Further, these famous waterfalls equally attract thousands of local visitors throughout the year.
While waterfalls offer aesthetic appeal, a serene environment, and recreational opportunities, they also pose a range of significant hazards. Unfortunately, the visitors are often unable to identify these different types of risks, as site-specific safety information and proper warning signs are largely absent. In most locations, only general warnings are displayed, often limited to the number of past fatalities. This can lead visitors to assume that bathing is the sole hazard, which is not the case. Therefore, understanding the full range of waterfall-related risks and implementing appropriate safety measures is essential for preventing loss of life. This article highlights site-specific hazards to raise public awareness and prevent people from putting their lives at risk due to these hidden dangers.
Flash floods and resultant water surges
Flash floods are a significant hazard in hill-country waterfalls. According to the country’s topography, most of the streams originate from the catchments in the hilly areas upstream of the waterfalls. When these catchments receive intense rainfalls, the subsequent runoff will flow down as flash floods. This will lead to an unexpected rise in the flow of the waterfall, increasing the risk of drowning and even sweeping away people. Therefore, bathing at such locations is extremely dangerous, and those who are even at the river banks have to be vigilant and should stay away from the stream as much as possible. The Bopath Ella, Ravana Ella, and a few waterfalls located in the Belihul Oya area, closer to the A99 road, are classic examples of this scenario.
Water currents
The behaviour of water in the natural pool associated with the waterfall is complex and unpredictable. Although the water surface may appear calm, strong subsurface currents and hydraulic forces exist that even a skilled swimmer cannot overcome. Hence, a person who immerses confidently may get trapped inside and disappear. Water from a high fall accelerates rapidly, forming hydraulic jumps and vortices that can trap swimmers or cause panic. Hence, bathing in these natural pools should be totally avoided unless there is clear evidence that they are safe.
Slipping risks
Slipping is a common hazard around waterfalls. Sudden loss of footing can lead to serious injuries or fatal falls into deep pools or rock surfaces. The area around many waterfalls consists of steep, slippery rocks due to moisture and the growth of algae. Sometimes, people are overconfident and try to climb these rocks for the thrill of it and to get a better view of the area. Further, due to the presence of submerged rocks, water depths vary in the natural pool area, and there is a chance of sliding down along slippery rocks into deep water. Waterfalls such as Diyaluma, Bambarakanda, and Ravana Falls are likely locations for such hazards, and caution around these sites is a must.
Rockfalls
Rockfalls are a significant hazard around waterfalls in steep terrains. Falling rocks can cause serious injuries or fatalities, and smaller stones may also be carried by fast-flowing water. People bathing directly beneath waterfalls, especially smaller ones, are therefore exposed to a high risk of injury. Accordingly, regardless of the height of the waterfall, bathing under the falling water should be avoided.
Hypothermia and cold shock
Hypothermia is a drop in body temperature below 35°C due to cold exposure. This leads to mental confusion, slowed heartbeat, muscle stiffening, and even cardiac arrest may follow. Waterfalls in Nuwara Eliya district often have very low water temperatures. Hence, immersing oneself in these waters is dangerous, particularly for an extended period.
Human negligence
Additional hazards also arise from visitors’ own negligence. Overcrowding at popular waterfalls significantly increases the risk of accidents, including slips and falls from cliffs. Sometimes, visitors like to take adventurous photographs in dangerous positions. Reckless behavior, such as climbing over barriers, ignoring warning signs, or swimming in prohibited zones, amplifies the risk.
Mitigation and safety
measures
Mitigation of waterfall-related hazards requires a combination of public awareness, engineering solutions, and policy enforcement. Clear warning signs that indicate the specific hazards associated with the water fall, rather than general hazard warnings, must be fixed. Educating visitors verbally and distributing bills that include necessary guidelines at ticket counters, where applicable, will be worth considering. Furthermore, certain restrictions should vary depending on the circumstances, especially seasonal variation of water flow, existing weather, etc.
Physical barriers should be installed to prevent access to dangerous areas by fencing. A viewing platform can protect people from many hazards discussed above. For bathing purposes, safer zones can be demarcated with access facilities.
Installing an early warning system for heavily crowded waterfalls like Bopath Ella, which is prone to flash floods, is worth implementing. Through a proper mechanism, a warning system can alert visitors when the upstream area receives rainfall that may lead to flash floods in the stream.
At present, there are hardly any officials to monitor activities around waterfalls. The local authorities that issue tickets and collect revenue have to deploy field officers to these waterfalls sites for monitoring the activities of visitors. This will help reduce not only accidents but also activities that cause environmental pollution and damage. We must ensure that these natural treasures remain a source of wonder rather than danger.
(The writer is a chartered Civil Engineer specialising in water resources engineering)
By Eng. Thushara Dissanayake ✍️
Features
From sacred symbol to silent victim: Sri Lanka’s elephants in crisis

The year 2025 began with grim news. On 1st January, a baby elephant was struck and killed by a train in Habarana, marking the start of a tragic series of elephant–train collisions that continued throughout the year. In addition to these incidents, the nation mourned the deaths of well-known elephants such as Bathiya and Kandalame Hedakaraya, among many others. As the year drew on, further distressing reports emerged, including the case of an injured elephant that was burnt with fire, an act of extreme cruelty that ultimately led to its death. By the end of the year, Sri Lanka recorded the highest number of elephant deaths in Asia.
This sorrowful reality stands in stark contrast to Sri Lanka’s ancient spiritual heritage. Around 250 BCE, at Mihintale, Arahant Mahinda delivered the Cūḷahatthipadopama Sutta (The Shorter Discourse on the Simile of the Elephant’s Footprint) to King Devanampiyatissa, marking the official introduction of Buddhism to the island. The elephant, a symbol deeply woven into this historic moment, was once associated with wisdom, restraint, and reverence.
Yet the recent association between Mihintale and elephants has been anything but noble. At Mihintale an elephant known as Ambabo, already suffering from a serious injury to his front limb due to human–elephant conflict (HEC), endured further cruelty when certain local individuals attempted to chase him away using flaming torches, burning him with fire. Despite the efforts of wildlife veterinary surgeons, Ambabo eventually succumbed to his injuries. The post-mortem report confirmed severe liver and kidney impairment, along with extensive trauma caused by the burns.
Was prevention possible?
The question that now arises is whether this tragedy could have been prevented.
To answer this, we must examine what went wrong.
When Ambabo first sustained an injury to his forelimb, he did receive veterinary treatment. However, after this initial care, no close or continuous monitoring was carried out. This lack of follow-up is extremely dangerous, especially when an injured elephant remains near human settlements. In such situations, some individuals may attempt to chase, harass, or further harm the animal, without regard for its condition.
A similar sequence of events occurred in the case of Bathiya. He was initially wounded by a trap gun—devices generally intended for poaching bush meat rather than targeting elephants. Following veterinary treatment, his condition showed signs of improvement. Tragically, while he was still recovering, he was shot a second time behind the ear. This second wound likely damaged vital nerves, including the vestibular nerve, which plays a critical role in balance, coordination of movement, gaze stabilisation, spatial orientation, navigation, and trunk control. In effect, the second shooting proved far more devastating than the first.
After Bathiya received his initial treatment, he was left without proper protection due to the absence of assigned wildlife rangers. This critical gap in supervision created the opportunity for the second attack. Only during the final stages of his suffering were the 15th Sri Lanka Artillery Regiment, the 9th Battalion of the Sri Lanka National Guard, and the local police deployed—an intervention that should have taken place much earlier.
Likewise, had Ambabo been properly monitored and protected after his injury, it is highly likely that his condition would not have deteriorated to such a tragic extent.
It should also be mentioned that when an injured animal like an elephant is injured, the animal will undergo a condition that is known as ‘capture myopathy’. It is a severe and often fatal condition that affects wild animals, particularly large mammals such as elephants, deer, antelope, and other ungulates. It is a stress-induced disease that occurs when an animal experiences extreme physical exertion, fear, or prolonged struggle during capture, restraint, transport, or pursuit by humans. The condition develops when intense stress causes a surge of stress hormones, leading to rapid muscle breakdown. This process releases large amounts of muscle proteins and toxins into the bloodstream, overwhelming vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, and liver. As a result, the animal may suffer from muscle degeneration, dehydration, metabolic acidosis, and organ failure. Clinical signs of capture myopathy include muscle stiffness, weakness, trembling, incoordination, abnormal posture, collapse, difficulty breathing, dark-coloured urine, and, in severe cases, sudden death. In elephants, the condition can also cause impaired trunk control, loss of balance, and an inability to stand for prolonged periods. Capture myopathy can appear within hours of a stressful event or may develop gradually over several days. So, if the sick animal is harassed like it happened to Ambabo, it does only make things worse. Unfortunately, once advanced symptoms appear, treatment is extremely difficult and survival rates are low, making prevention the most effective strategy.
What needs to be done?
Ambabo’s harassment was not an isolated incident; at times injured elephants have been subjected to similar treatment by local communities. When an injured elephant remains close to human settlements, it is essential that wildlife officers conduct regular and continuous monitoring. In fact, it should be made mandatory to closely observe elephants in critical condition for a period even after treatment has been administered—particularly when they remain in proximity to villages. This approach is comparable to admitting a critically ill patient to a hospital until recovery is assured.
At present, such sustained monitoring is difficult due to the severe shortage of staff in the Department of Wildlife Conservation. Addressing this requires urgent recruitment and capacity-building initiatives, although these solutions cannot be realised overnight. In the interim, it is vital to enlist the support of the country’s security forces. Their involvement is not merely supportive—it is essential for protecting both wildlife and people.
To mitigate HEC, a Presidential Committee comprising wildlife specialists developed a National Action Plan in 2020. The strategies outlined in this plan were selected for their proven effectiveness, adaptability across different regions and timeframes, and cost-efficiency. The process was inclusive, incorporating extensive consultations with the public and relevant authorities. If this Action Plan is fully implemented, it holds strong potential to significantly reduce HEC and prevent tragedies like the suffering endured by Ambabo. In return it will also benefit villagers living in those areas.
In conclusion, I would like to share the wise words of Arahant Mahinda to the king, which, by the way, apply to every human being:
O’ great king, the beasts that roam the forest and birds that fly the skies have the same right to this land as you. The land belongs to the people and to all other living things, and you are not its owner but only its guardian.
by Tharindu Muthukumarana ✍️
tharinduele@gmail.com
(Author of the award-winning book “The Life of Last Proboscideans: Elephants”)
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoInterception of SL fishing craft by Seychelles: Trawler owners demand international investigation
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoBroad support emerges for Faiszer’s sweeping proposals on long- delayed divorce and personal law reforms
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoThe minstrel monk and Rafiki, the old mandrill in The Lion King – II
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoThe Venezuela Model:The new ugly and dangerous world order
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoPrez seeks Harsha’s help to address CC’s concerns over appointment of AG
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPrivate airline crew member nabbed with contraband gold
-

 Business16 hours ago
Business16 hours agoSevalanka Foundation and The Coca-Cola Foundation support flood-affected communities in Biyagama, Sri Lanka
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoIndian Army Chief here













