Opinion
Wind Power – why ignore Little Basses?

Dr. Tilak Siyambalapitiya’s essay on “Wind Power in Mannar, now a reality”, in The Island (22/12) is very convincing and will encourage businessmen to invest on wind energy, dispelling the view of present day promoters and guardians of renewable sources of energy who dared not to venture, as they considered wind power too expensive, and that there is no wind in Sri Lanka, but doldrums or trade winds. I remember, there was a Consultant from Denmark, attached to the Energy Division, of the Ministry for Power and Energy, whose name sounded ‘KNIFE’, who also did not encourage wind energy. I 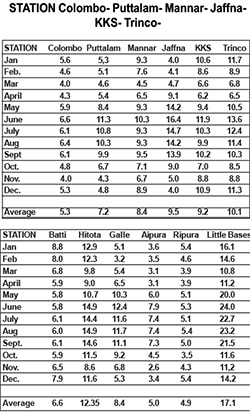 also remember there was an experimental station at Pattiyapola, near Matara, funded by UNDP, to study and take steps to promote solar, wind , biogas energy, but after the demise of that enthusiastic Engineer, activities virtually came to a halt. If this station is yet functioning, it is best to up-grade same to an Advisory and Experimental Organisation, where even the public could seek advice and guidance.
also remember there was an experimental station at Pattiyapola, near Matara, funded by UNDP, to study and take steps to promote solar, wind , biogas energy, but after the demise of that enthusiastic Engineer, activities virtually came to a halt. If this station is yet functioning, it is best to up-grade same to an Advisory and Experimental Organisation, where even the public could seek advice and guidance.
He also speaks of an engineer who went to Mannar in 2002 to set up a wind measuring system. However, I believe, the Meteorological Department makes periodical studies, as seen in the statement given below:
“Now that a serious step has been taken, as seen by commissioning a 100 Mw. wind plant at Mannar, it is presumed the Ministry for Power has already taken action to secure land as stated in the Gazette Extraordinary 2135/61 of 9th August 2019 which says – 3.9.2…. Best sites to locate large scale renewable energy infrastructure such as wind and solar farms would be identified in advance and marked on a master plan so that they can be developed as large concentrated facilities in phases.”
If such lands are advertised or given publicity, the land owners would not undertake buildings or other developments in such areas.
Mean Monthly Wind Speeds at the Coastal and Inland stations in Ceylon [Miles per Hour] Source – Wind Energy Unit, Hydraulic Research Lab
Station Colombo Puttalam Mannar Jaffna Kankesanthurai Trinco Batticaloa Hambantota, Galle Anuradhapura Ratnapura Little Bases
It will be seen from the above statement, that the best station for harnessing wind power are Little Bases islands, four miles off Hambantota, having an average speed of 17.1 Mph, the best months being from May to August, having a wind speed of over 20 Mph, followed by Hambantota 12.35 Mph, Trinco 10.1Mph, Jaffna 9.5 Mph and Kankesanthurai 9.2. and Mannar 8.4 Mph.
It is strange, going by the above statement, unless the wind patterns have changed drastically, why CEB decided to start the Wind Energy programme from Mannar, which has the lowest wind speed. My fear is, if the performance is not up to expectation, then investors may be reluctant to invest. The other question is why was not Little Basses Island not given priority. Was it the fear of disturbing the Yala wildlife?
It is hoped that a young enthusiastic State Minister for Solar Power will encourage domestics to go for Solar Power and relieve the CEB and also lure the private sector, too, in his effort to popularise renewable sources of energy and make his dream come true to supply our neighbour India.
G. A. D. SIRIMAL
Boralesgamuwa
Opinion
Why Sri Lanka needs a National Budget Performance and Evaluation Office

Sri Lanka is now grappling with the aftermath of the one of the gravest natural disasters in recent memory, as Cyclone Ditwah and the associated weather system continue to bring relentless rain, flash floods, and landslides across the country.
In view of the severe disaster situation, Speaker Jagath Wickramaratne had to amend the schedule for the Committee Stage debates on Budget 2026, which was subsequently passed by Parliament. There have been various interpretations of Budget 2026 by economists, the business community, academics, and civil society. Some analyses draw on economic expertise, others reflect social understanding, while certain groups read the budget through political ideology. But with the country now trying to manage a humanitarian and economic emergency, it is clear that fragmented interpretations will not suffice. This is a moment when Sri Lanka needs a unified, responsible, and collective “national reading” of the budget—one that rises above personal or political positions and focuses on safeguarding citizens, restoring stability, and guiding the nation toward recovery.
Budget 2026 is unique for several reasons. To understand it properly, we must “read” it through the lens of Sri Lanka’s current economic realities as well as the fiscal consolidation pathway outlined under the International Monetary Fund programme. Some argue that this Budget reflects a liberal policy orientation, citing several key allocations that support this view: strong investment in human capital, an infrastructure-led growth strategy, targeted support for private enterprise and MSMEs, and an emphasis on fiscal discipline and transparency.
Anyway, it can be argued that it is still too early to categorise the 2026 budget as a fully liberal budget approach, especially when considering the structural realities that continue to shape Sri Lanka’s economy. Still some sectors in Sri Lanka restricted private-sector space, with state dominance. And also, we can witness a weak performance-based management system with no strong KPI-linked monitoring or institutional performance cells. Moreover, the country still maintains a broad subsidy orientation, where extensive welfare transfers may constrain productivity unless they shift toward targeted and time-bound mechanisms. Even though we can see improved tax administration in the recent past, there is a need to have proper tax rationalisation, requiring significant simplification to become broad-based and globally competitive. These factors collectively indicate that, despite certain reform signals, it may be premature to label Budget 2026 as fully liberal in nature.
Overall, Sri Lanka needs to have proper monitoring mechanisms for the budget. Even if it is a liberal type, development, or any type of budget, we need to see how we can have a budget monitoring system.
Establishing a National Budget Performance and Evaluation Office
Whatever the budgets presented during the last seven decades, the implementation of budget proposals can always be mostly considered as around 30-50 %. Sri Lanka needs to have proper budget monitoring mechanisms. This is not only important for the budget but also for all other activities in Sri Lanka. Most of the countries in the world have this, and we can learn many best practices from them.
Establishing a National Budget Performance and Evaluation Office is essential for strengthening Sri Lanka’s fiscal governance and ensuring that public spending delivers measurable value. Such an office would provide an independent, data-driven mechanism to track budget implementation, monitor programme outcomes, and evaluate whether ministries achieve their intended results. Drawing from global best practices—including India’s PFMS-enabled monitoring and OECD programme-based budgeting frameworks—the office would develop clear KPIs, performance scorecards, and annual evaluation reports linked to national priorities. By integrating financial data, output metrics, and policy outcomes, this institution would enable evidence-based decision-making, improve budget credibility, reduce wastage, and foster greater transparency and accountability across the public sector. Ultimately, this would help shift Sri Lanka’s budgeting process from input-focused allocations toward performance-oriented results.
There is an urgent need for a paradigm shift in Sri Lanka’s economy, where export diversification, strengthened governance, and institutional efficiency become essential pillars of reform. Establishing a National Budget Performance and Evaluation Office is a critical step that can help the country address many long-standing challenges related to governance, fiscal discipline, and evidence-based decision-making. Such an institution would create the mechanisms required for transparency, accountability, and performance-focused budgeting. Ultimately, for Sri Lanka to gain greater global recognition and move toward a more stable, credible economic future, every stakeholder must be equipped with the right knowledge, tools, and systems that support disciplined financial management and a respected national identity.
by Prof. Nalin Abeysekera ✍️
Opinion
Comfort for some, death for others: The reality of climate change

The recent Cyclone Ditwah struck South and Southeast Asia in an unprecedented way, causing floods, landslides, deaths, displacement of thousands, and severe soil degradation. For many in Sri Lanka, the disaster is seen as a natural event that the government should have anticipated. Yet, the reality is that small countries like ours have little power to prevent disasters of this scale. Despite contributing minimally to global carbon emissions, we are forced to bear the consequences of ecological harm caused largely by wealthier nations. Excessive consumption and profit-driven production in capitalist economies fuel climate change, while the Global South suffers the resulting losses in lives, homes, and livelihoods. The dead, the disappeared, and the displaced from Cyclone Ditwah demand climate justice—a justice that addresses structural inequality, exploitation of nature for profit, and the failure of global powers to take responsibility.
The Role of Excessive Consumption
The environmental crisis is driven by excessive consumption, particularly in developed countries. Cars, electronics, clothing, and other consumer goods require immense energy to produce, much of it from fossil fuels such as coal, gas, and oil. The transportation of raw materials and finished products adds further emissions, while waste from overconsumption ends up in landfills, releasing methane, a potent greenhouse gas. This cycle of consumption, production, and waste underscores a systemic problem: climate change is not merely an environmental issue, but a symptom of an economic system built on profit, not sustainability.
Market-Based “Solutions” and Greenwashing
Neoliberal economies are not silent in the face of climate change—they perform “sustainability” while offering superficial solutions. Many corporations engage in green branding to appear environmentally responsible, even as their practices remain unchanged. Carbon trading, for example, allows companies to buy and sell the right to emit CO₂ under a capped system. While intended to reduce emissions, it often commodifies pollution rather than eliminating it, enabling wealthy actors to continue environmentally harmful practices. Since many developing countries do not strictly enforce carbon caps, wealthy corporations often relocate their factories to these regions. Meanwhile, the burden of “reductions” is shifted to marginalised communities, turning these areas into pollution havens that endure the worst effects of climate disasters despite contributing the least to the problem. Market-based solutions, therefore, frequently reinforce existing inequalities rather than addressing the structural causes of climate change.
International Agreements and Structural Limitations
The global community has reached multiple climate agreements, including the UNFCCC (1992), the Kyoto Protocol (1997), and the Paris Agreement (2015). Yet these agreements remain constrained by capitalist agendas and weak enforcement mechanisms. Most rely on voluntary national commitments, peer pressure, and reporting transparency rather than legally binding obligations. Countries can submit inadequate Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and remain technically compliant, rendering the agreements more symbolic than transformative. While not entirely ineffective, international agreements often prioritise narrative performance over real structural change, allowing wealthy nations to avoid meaningful responsibility for emissions and ecological harm.
Climate Justice and Social Inequalities
Climate change is inseparable from social injustice. Marginalised communities—those affected by poverty, colonial histories, racial discrimination, or gender inequality—face the greatest risks from environmental disasters. These populations generally lack safe housing, and even when warned to evacuate, they have few resources or means to recover from disasters. General climate policies, which have been influcned by capitalist agendas, that focus solely on emissions reduction or “green” initiatives fail to address these deeper inequalities. True climate action must empower communities, redistribute wealth, and integrate social justice with environmental sustainability. Only by tackling the structural drivers of both inequality and ecological harm can we move toward genuine climate justice.
Conclusion
Cyclone Ditwah and other climate disasters are reminders that the effects of environmental degradation are unevenly distributed. The Global South pays a heavy price for the consumption patterns and industrial practices of the Global North. Market-based solutions, superficial sustainability initiatives, and weak international agreements are insufficient to address the systemic roots of climate change. Achieving climate justice requires a fundamental rethinking of economic priorities, social structures, and global responsibility—placing people and the planet above profit.
The author is a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard Divinity School.
by Anushka Kahandagamage ✍️
Opinion
Ditwah wake-up call demands a national volunteer community service for rebuilding Sri Lanka

The Tsunami of 2004 struck our coasts, but the recent Cyclone Ditwah has delivered an unprecedented blow, devastating and traumatising the entire country. President Anura Kumara Dissanayake rightly called it the “largest and most challenging natural disaster” in Sri Lanka’s history.
The toll is staggering: Over 600 people were confirmed dead, with hundreds still missing. More than 2 million citizens – nearly one in ten people—have been affected. 41,000 to 86,000 houses are damaged or completely destroyed. The damage is widespread, with 22 of the island’s 25 districts declared disaster-affected areas. A provisional economic damage estimate reaching up to USD 7 billion—a figure that instantly consumes about 7% of our national GDP. This was not merely a natural disaster; it was a crisis amplified by systemic failure, culminating in a catastrophe that now demands a radical, long-term policy response.
Unlike the Tsunami, the destruction to our vital inland infrastructure—roads, bridges, railway lines, and power networks—has been colossal, crippling the nation’s ability to recover. Over 25,000 members of the tri-forces have been mobilised, and the nation rightly hails their courageous and relentless efforts in rescue and relief. They should now be graduated from ‘Rana Viruvo’ to RUN VIRUVO considering the efforts they are still putting into the relief operations in this unprecedented calamity. But the scale of the rebuilding effort requires a permanently sustained unified national mechanism, perhaps learning from their rich experiences.
Why did devastation reach this cataclysmic level?
Unlike a sudden earthquake/Tsunami, a cyclone’s path is largely traceable. Yet, the “post-mortem” on Ditwah reveals a horrifying truth: the storm’s devastation was amplified by our own institutional failures.
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) which runs the Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre (RMSC) monitors the oceans in this region and issues alerts for cyclones. It serves all the regional countries — Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Thailand. The RMSC first predicted the formation of a depression as early as November 13 and issued an alert over the possibility of a cyclone forming on November 20. From November 23 onwards, IMD/RMSC had been routinely sharing frequent weather updates with Sri Lanka.
Robust models from the India Meteorological Department and the RMSC provided ample warnings of the depression and subsequent cyclonic intensification. Some of these predictions by the RMC and even the BBC forecasted rainfall over 300- 400 mm which could go up to even half a meter per day. True to their forecasts, Matale tragically received unprecedented rainfall of around 520 mm, triggering fatal landslides. Ditwah’s impact was worsened by its unusually slow movement over the island which sustained heavy rainfall over several days.
The Governance Gap
The critical breakdown occurred between the scientific prediction and the state’s executive arm. Warnings, if not taken seriously or acted upon, become meaningless data points. The core issue is a fragmented disaster management system that lacks the “unified command structure” required for real-time data sharing and rapid deployment. As one analyst noted, the disaster delivered a hard lesson: we entered one of our worst natural disasters in decades without a functioning national strategy and with a severe deficit in “adaptive capacity.
Scientific forecasts were not translated into an appropriate, urgent disaster preparedness program by the Sri Lankan state apparatus. Public reports indicate that national preparedness was woefully short of what was needed. The warnings failed to translate into a coherent, proactive response into an appropriate disaster preparedness action program on the island. This failure points directly to long-standing institutional deficits.
The Strategic Imperative: Dedicated Workforce for a $7B Recovery
President Anura Kumara Dissanayake rightly emphasised that restoring public life requires a unified operational mechanism that goes beyond normal state administration. To tackle this immense task, the Government has established a ‘Rebuilding Sri Lanka Fund’ to finance the medium- and long-term recovery, including essential infrastructure and public health issues.
This newly established ‘Rebuilding Sri Lanka Fund’ addresses the financial cost, but it does not solve the fundamental manpower crisis which is a key bottleneck in retarding the progress of this formidable undertaking. Rebuilding 247 kilometers of impacted roads, restoring two-thirds of unusable railway lines, clearing hundreds of landslides, and repairing crucial irrigation systems demands a sustained, disciplined, and massive workforce that normal state administration simply cannot provide. Furthermore, with the changing climate, events of this nature and magnitude may be more frequent in the future.
As such, there is a moral call to a strategic imperative. The immediate, ad-hoc spontaneous public volunteerism is commendable, but the scale of the task ahead requires a permanent, non-partisan national investment in human resources. The time for piecemeal recovery programs is over. Ditwah has forced the issue of structural accountability and national capacity onto the policy agenda.
A Call for Mandatory National Service
One of the most responsible paths forward is to utilise this crisis to institutionalise a robust National Service System, transforming a generation of youth into a standing army for climate resilience and nation-building. To fail to do so would be to guarantee that the next storm will bring an even higher price.
Sri Lanka cannot afford to be unprepared again. The solution is to immediately mobilise and, for the long term, institutionalise the patriotic energy of our youth into a robust, structured National Service System. This service should be more than just disaster relief; it is a long-term investment that will:
i) Build the Nation: Provide a rapid-response labour force for future disasters, infrastructure projects, and conservation efforts.
ii) Forge Character: Instill essential skills like discipline, leadership, accountability, and responsibility in our youth, thereby contributing to lower rates of substance abuse and crime.
iii) Strengthen Unity: Promote social cohesion and reinforce national identity by having youth from all backgrounds work together for a common cause.
The legal framework for such a move already exists. The Mobilisation and Supplementary Forces Act, No. 40 of 1985, already gives the government the powers to issue a National Service Order to enlist people in a National Armed Reserve. This mechanism can be adapted to establish a non-military, civilian-focused service.
Sri Lanka already has a government supported National Volunteer Service affiliated to her Social Services Department. It coordinates volunteers, develops management systems, and works with partners like the UN volunteers. This service can be improved and upgraded to tackle challenges in natural and/or human induced disasters which are going to be more frequent with greater intensity, at times.
In the immediate term, the large number of existing volunteers dispersed all over the island need to be engaged as understudy groups, working directly alongside the armed forces and government departments in the recovery process which is already happening in a number of instances.
Ditwah is our wake-up call for longer-term strategic planning and policy reforms. Alongside reacting to catastrophes in a piecemeal manner in the short-term, we must systematically start building a resilient nation with a vision for the future. Investing in a structured, mandatory Civilian National Service is the only way to safeguard our future against the inevitable challenges of climate change and to truly rebuild Sri Lanka.
Globally over 60 countries have national service portfolios mostly of military nature. Both Germany and France have recently reintroduced their national services to meet their own specific needs. In the US, the National Community Service centers around the Corporation for National and Community Service (CNCS), a federal agency that runs programs like AmeriCorps and Senior Corps, mobilising millions of Americans in service to address needs in education, disaster relief, environment, and more, fostering civic duty and offering educational awards for service.
Incorporate National Service into Educational Reforms
We must mobilize our youthful energy into a national service portfolio unique to our own needs giving due recognition to our history, geography and culture. As a long-term investment, this should be initiated while children are still in school, preparing them mentally and physically to contribute to nation-building.
A well-designed National Volunteer Community Service would instill discipline and foster essential skills like leadership, responsibility, and mutual respect, while contributing at the same time to national development. We can tailor this service to tackle our unique challenges in public safety, disaster relief, and environment conservation.
Existing school programmes like scouting and cadeting can be innovatively transformed to lay a sound foundation for this life-changing National Service for all schoolchildren. According to the initial estimates of UNICEF, over 275,000 children are among the 1.4 million people affected both physically and mentally who need careful rehabilitation.
The current educational reforms are an ideal platform to impart crucial values in patriotism and introduce essential skills like time management, discipline, and accountability. This system could not only build successful individuals but also help decrease social issues like substance abuse and crime among youth.
In the immediate future, to meet the demands of the recovery effort now, currently available volunteers should be engaged as understudy groups, working alongside the armed forces and government departments involved in the rebuilding process. The long-term investment in a Mandatory National Service, on the other hand, will strengthen our national identity and contribute to the “unified operational mechanism” the President has called for.
The author can be contacted at nimsavg@gmail.com
by Emeritus Professor
Nimal Gunatilleke
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoFinally, Mahinda Yapa sets the record straight
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoCyclone Ditwah leaves Sri Lanka’s biodiversity in ruins: Top scientist warns of unseen ecological disaster
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoThe Catastrophic Impact of Tropical Cyclone Ditwah on Sri Lanka:
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoHandunnetti and Colonial Shackles of English in Sri Lanka
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCabinet approves establishment of two 50 MW wind power stations in Mullikulum, Mannar region
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoSri Lanka betting its tourism future on cold, hard numbers