Features
Travels in Xinjiang Province, China

by Jayantha Perera
At the Urumqi Airport in Xinjiang Province, China, I did not expect to face any immigration formalities. I had travelled from Guangzhou in southern China to Urumqi on a local flight. I was with an ADB team, on a mission to examine how several projects funded by ADB in Xinjiang Province, particularly those aimed at improving infrastructure and livelihoods, would impact local ethnic minorities. An officer with two stars on his jacket lapel stopped me before I reached the immigration desk. Nandia, the ADB translator, told me that the officer wanted my passport. A few minutes later, he shouted at Nandia when she tried to explain something. The officer led us into an unheated dark room. He sat on the only chair in the room, studied my passport for a few minutes, and walked out of the room with it.
After half an hour, a man in civil attire came with the officer who had taken my passport. They discussed something with Nandia. She told me he was the chief Inspector. He examined my passport page by page while questioning me:
“Why do you live in the Philippines?” Nandia translated.
“Because I work in Manila at the Asian Development Bank,” I replied.
“Why do you come to Urumqi?” the chief queried.
“Asian Development Bank assists several projects in western Xinjiang, and I have come to meet project officials with a team of experts from ADB,” I responded.
“But the infrastructure ministry did not inform us about your coming,” he shouted.
Another 10 minutes passed before the chief Inspector read the official invitation letter in Mandarin and English. He first read the Mandarin letter and then tried to read its English translation. The Inspector opened a fat ledger pulled from a dusty cupboard and flipped through pages looking for something. He shook his head and muttered something. Nandia tried to avoid his gaze, but her unease was apparent.
“The chief can’t find any entry about your arrival,” Nandia whispered in a strained voice.
“But we have official invitation letters,” I told her.
“Could you please stop talking to me? They suspect us when we talk in English.” Nandia sounded angry. I tried to avoid her eyes, too.
A few minutes later, two jovial young security guards came running in their black uniforms with long lances. A lance is a long, black, rod-like weapon with a trigger at one end and a long, sharp blade at the other. The two escorted me to another dark room. They switched on the light and directed me to sit. I waited for the Chief Inspector and the officer who had taken my passport. I knew I was under arrest. I was mentally prepared to spend the night in this dingy room with the two guards. I did not know what happened to my ADB colleague who travelled with me and Nandia. Twenty minutes later, the chief Inspector returned. He said, “Okay, bye,” and returned my passport and the invitation letter. The relief was palpable as I regained my freedom.
A middle-aged man with a short beard and rimmed glasses awaited me with my ADB colleague and Nandia in the ‘Visitors Area.’ I guessed he was the ADB’s contact person in Urumqi. Nandia introduced me to him. He was a shy man and spoke a few words in English. He was a professor of economics at a local university. The two young women with him helped us load our suitcases into a large van. One woman told us the outside temperature was minus 25 Celsius. The professor apologetically informed us he would not join our mission because his mother was ill. He said he was taking us to a hotel. I saw an elegant hotel near the airport and asked the professor whether we would stay there. He told us only foreign journalists were accommodated there and all other visiting foreigners stay at designated hotels in the city for security reasons.
The hotel the professor booked for us was an old building. It looked grandiose but was in a state of disrepair. The van driver directed us to walk through the police barricade in the hotel lobby. Two uniformed policemen checked our bags manually first, then x-rayed them. They used hand-held detectors to search our bodies. One examined me roughly as if he were determined to find suspicious objects on me. He was huge, smelly, and unfriendly. He grabbed my passport after baggage examination and went through its pages. He then disappeared with passports, leaving us at the barrier.
The hotel’s lobby manager was agitated because he was waiting for the local authority’s approval to allocate rooms for us. After 30 minutes, the professor told us we could stay at the hotel that night. Then, the manager told us to wait in the lounge for room keys. A hotel employee led us to our rooms through a narrow, dimly lit corridor. My room was large with huge curtains. The room lights were dim, and I could hardly see my bed.
A few minutes later, I left the room to find my way to the lounge, where I hoped to have dinner. There was no dinner, so I headed back to my room. I realised it was a mistake to roam in the hotel without a local colleague. The policeman at the hotel entrance raised his head and saw me in the lounge. He recognised me and waved me back to my room. I was hungry. I had tea bags and a few cookies. There was no kettle in the room. I ate the cookies and drank cold water from the tap, feeling the stark loneliness of the unfamiliar surroundings.
The following day, I bundled up in all my warm clothes and headed to the hotel restaurant. The large, dimly lit banquet room was a stark contrast to the breakfast spread, which consisted of a simple meal of thick rice soup, boiled eggs, and black tea, with no coffee in sight.
The professor came to see us off to Alashankou City. He advised Nandia what she should tell guards at checkpoints. He introduced the vehicle driver as a senior project official who would safely take us to our destination. The driver did not speak English, but his assistant, who sat beside him, tried talking to us in English. He was a civil servant.
We could see only the snow for many hours, and the road ahead was barely visible. We travelled for about six hours, and the civil servant told us we would soon reach a critical checkpoint. Before we arrived there, we saw a large concrete display board that stated, “Border Area.” We could see high barbed-wire fences and low buildings on both sides of the road, partially covered with snow. After collecting our passports and official invitation letters, the civil servant told us to stay in the van and ran to a small office about 25 metres from the road in a heavy snowstorm. He returned within a few minutes, distributed our passports, and asked us to follow him, leaving our bags behind in the van.
We stood in an open area outside the building and waited for the civil servant to accompany us. There were several police officers, and sliding steel barricades blocked the entrance. I could hardly breathe and felt dizzy. The civil servant talked to a policeman and told us to follow him through an electrical gate. He disappeared again. A young Chinese policeman shouted at us, showed us the entrance, and waved us to go through the gate. A policewoman beckoned me to the gate and indicated I should leave my wallet and reading glasses beside the gate counter. Someone else directed me to empty my pockets and remove my trouser belt.
After that, I went through a box-like structure without knowing it was an X-ray machine. Before I collected my belongings, including the passport, from the gate, I was told to enter a tunnel-like concrete structure. I did not know what had happened to my passport, reading glasses, and the wallet. When I resurfaced from the tunnel, a young policewoman gave them to me. She then directed me into another building, where several locals waited for security clearance. I soon realised they were bus passengers from the border area between Xinjiang Province and Kazakhstan. Several buses were waiting for them on the road under heavy security and snowfall.
I tried to find a corner in the foyer to avoid the cold wind. I was curious to watch what the young, enthusiastic policemen and women in dark uniforms were doing inside the glass cubicle. The cubicle had three front windows. Several computers were below the windows, and the young policemen sat before them. Behind them, there were several rooms. And I guessed some were to detain those who could not prove their bona fide travel purposes. The young police officers were more enthusiastic about checking those locals who had arrived from the border area than clearing us for travel. Our driver, the project officer or the civil servant who travelled with us could not do anything to rescue us.
Local travellers handed their cell phones to police officers. Two officers checked each cell phone’s telephone messages, photos, and internet downloads under the scrutiny of a senior officer. Checking each cell phone for suspicious material took about 15 minutes. Out of about 20 persons, the police detained three. They pleaded in their languages, but the officers ignored them.
An officer with several stars on his coat lapel arrived and checked with his colleagues what we, foreigners, were doing in the lobby. He entered the cubicle, chased two young police officers away from a computer and occupied it. Our driver forced himself into the front and handed our passports to the officer. The driver told us to give the officer our invitation letters and pose our faces to a mirror-like gadget on the wall. The officer carefully observed what he had seen on the computer and matched our facial images with our passport photographs. He handed over our passports and talked to the driver. The driver saluted him and took us to our vehicle.
The saga of security clearance took about 90 minutes. I could not feel my legs when I walked to the van because of the nasty cold wind. The driver gave us hot tea from his large flask. The unexpected delay at the border checkpoint made our journey difficult and precarious. The sun had set about an hour before, and fresh snow covered the unlit, slippery road. The driver drove fast as if he knew each nook and corner of the road. We reached Alashankou City at 8.30 pm.
Unlike in Urumqi, in Alashankou, checking into the hotel was easy. It was a modern four-star hotel. Its furniture and internal décor were artistic and minimalist. The staff at the counter spoke English. Two policemen appeared from nowhere and beckoned us back to the security gate at the hotel entrance. They were polite and wanted to X-ray our handbags.
My room was large and had modern furniture and amenities. There was a TV on the wall facing the cosy double bed. When I removed my shoes and socks, my feet felt warm, and I was elated to walk barefoot in my room. Hot water was flowing under the room floor, warming the room. We had dinner in the hotel dining room. A hot vegetable soup and spicy meat dishes were tasty and lifted my spirit.
I could not sleep because of some loud shouting outside the hotel. A group of people shouted slogans as if they were in an army regiment. I suspected the regimented roar came from a police training centre or a workers’ camp. I did not ask Nandia about the uproar because I did not want to embarrass her by asking about things she might not want to discuss with me.
Several Project Management Office (PMO) officials picked us up from the hotel lobby the following morning. They took us to their office, and we walked through several barriers without any hindrance. After a brief, cordial conversation on ethnic minority issues in project areas, the PMO chief told us there were no ethnic minorities in Xinjiang province!
After lunch at our hotel, I watched the main public road from my room’s balcony. It was a four-lane road with a concrete partition in the middle. I saw several small white police cars of the same make crawling on the road at a human pace. The vehicles had tinted dark windows. It would be eerie to walk on the road if such a car accompanied me at my speed. My strange feeling graduated to a sense of fear. I counted
three such cars moving north and three cars south all the time on the road. Although it was a working day, the road was largely empty. Two armoured vehicles parked at a street corner were waiting for trouble to break out on the road. A compact police station with deep blue walls on a slightly elevated platform was at each street corner. It had small windows and bright blinking blue lights hanging from the roof.
On our second day in Alashankou, we lunched at a family-run Muslim restaurant. A middle-aged man served grilled lamb chunks on long skewers, unleavened bread as big as a standard pizza, and boiled vegetables. The soup came in a separate bowl. The food was tasty and was enough for three or four people. Several police officers were also having lunch at the restaurant. They were jovial but curiously observed us from their table.
On the following day, when we were at the restaurant for breakfast, we saw a platoon of young police officers in their black uniforms and with lances. They secured each floor’s hotel entrances, exits, elevators, and staircases. They opened room doors as if they knew the layout of the building. Two came to us, smiled, and went away.
Twenty policemen came down with a local young couple. The bearded man was wearing ethnic attire. The woman looked like a young teenager draped in a Muslim wedding dress. They talked with a middle-aged police officer and shook hands. Soon, the police platoon disappeared from the hotel. I checked the road and saw several young officers joking with each other while crossing the street. I wanted to ask the hotel manager what had happened. But the golden rule in Xinjiang – not publicly discussing government activities – stopped me from talking to him.
At Horgos City, we were mesmerised by distant snow-capped mountains and frozen lakes. The road was winding, and we drove slowly, absorbing the breathtaking beauty. The bright sun gave us a sense of warmth as the heating device of the van quit working. We saw several skiing kiosks where local people gathered. We stopped at a kiosk to use the toilet. An old woman managed the toilet and gave a piece of paper for a few cents. The bathroom was clean and modern. Its floor was dry. We talked to a few people at the resort through our driver and the translator. The locals came to ski on the lake and stayed at local hotels.
The civil servant took us to a restaurant where foreigners could have Chinese, Uyghur, and halal meals and consume liquor. Halfway to the restaurant, there was a large police station. Several police officers were smoking and chatting on the side road. I could see stone plates of the pavement under a layer of fresh snow. When I reached the officers, they did not move for me to pass, and I had to wade through fresh snow by the path to continue my walk.
When we returned to the hotel from the restaurant, I saw many police officers on the side walk in front of the police Station. They were smoking and joking with each other. Snow piled up to about two feet on both sides of the side walk. When I reached them, they ignored me. They expected me to circumvent them and continue through the snow. I told them, “Excuse me.” They moved away from the side walk and stared at me. I walked a few yards and waited for my colleagues. I watched how they walked without disturbing the police officers.
At the hotel, I talked to Nandia about the episode. She said she saw how I had walked through the police officers’ circle. She was scared as the police officers would have harassed me for disturbing their conversation. She told me never to anger a police officer in Xinjiang: they were powerful, arrogant, and quick-tempered, although they pretended to be cheerful and helpful. They probably did not stop me because I was a foreigner, and they did not know any English to accost me. Or perhaps they did not want to spoil their relaxing evening over a minor incident.
The inter-country dry port at the border of Kazakhstan and Xinjiang Province is a thriving business centre. I saw hundreds of Kazaks in colourful clothes and with large empty suitcases, coming to shop at warehouses and shopping malls across the border. The central bus stand displayed a list of bus numbers for different Kazakhstani cities. Some went to large, covered markets to buy Russian goods. They brought clothes, leather hats, dried fruits such as dates, pistachios, and sliced dry bananas. The dry port area looked like a heavily guarded fort, and surveillance cameras observed the movements and transactions of visitors.
The PMO officer invited us to visit the free trade zone. We went through several security searches; the final was verifying our identities. The officer could not tally the information on the computer with my passport information. An alarm bell went off, and two smiling policemen appeared from nowhere. They escorted me to a room. They asked me to sit on a bench and studied me. Suddenly, one guard spoke to me in English. “Hi, what is your name? American? We like to talk English.” I smiled; they smiled. I said “Jayantha, a Sri Lankan.” But they could not go further, so they repeated ‘Jantha,’ ‘Jantha.’ Again, they smiled; I smiled. After 20 minutes, two senior officials interviewed me in the room and returned my passport.
The following day, we visited Yining City. We checked into a palace-like hotel where we were the only guests. The rooms were enormous and well-appointed. The professor had arranged with three friends in Yining to take us sightseeing. A woman and two men in their forties met us at the hotel. They took us to the Xibo Ethnic Minority Exhibition Village. Zibo was a civilisation in medieval times, but with the arrival of marauding bands, the Zibo state collapsed and became a collection of ethnic communities spread over a vast area.
When we returned to the exit gate, some officers showed us two policemen in black with a white strip glued to their chest, “SWAT.” The SWAT officers directed us to follow their vehicle and sped away. Our friends followed the police vehicle with us. After travelling for 15 minutes, the police officers signalled us to get out of the car. The two policemen went through several barriers and waited for us to follow them. Nandia joined my ADB colleague and me. Our friends stayed in their vehicle. As we passed through each barrier, its gate closed with a loud bang behind us. After going through the three barriers, we found ourselves in the compound of the large building, where puppies were playing with several young men.
Nandia introduced us to a man in jeans who was the chief of the police station. A few minutes later, he asked me, and Nandia translated: “You are a Sri Lankan. Why do you live in Manila”?
“I have been in Manila because I work for the Asian Development Bank,” I replied.
“Show me your invitation letter from Beijing,” he demanded.
He read the Mandarin portion of the letter and phoned someone. Then he said, “Bye”.
The three friends took us for dinner. They ordered a roasted baby lamb with boiled potatoes and vegetables. In addition, they selected a local steamed fish dish. Our hosts were a very close group of buddies from their school days. They travelled together and often met for drinks and dinner without their spouses. They were a cheerful group; one man tried to sing a song, and the other two politely stopped him.
At the dinner, I commented that the lamb roast was excellent. That triggered a discussion among our hosts. The woman sent the lamb’s head to the kitchen. Before the dessert, a plate arrived with cut pieces of the lamb head. The host invited me to eat the cooked brain in the skull and said that it would be a great honour for them if I ate a piece of the brain. I told them that I could not eat lamb brain. My ADB colleague came to my rescue and ate the baked brain on my behalf. She told me later that it would have insulted them if we had refused to eat the brain. The hosts were sad to leave us. Before leaving, they called a taxi to send us back to our hotel so we could catch the earliest flight to Urumqi the following day.
Features
The US-China rivalry and challenges facing the South

 The US-China rivalry could be said to make-up the ‘stuff and substance’ of world politics today but rarely does the international politics watcher and student of the global South in particular get the opportunity of having a balanced and comprehensive evaluation of this crucial relationship. But such a balanced assessment is vitally instrumental in making sense of current world power relations.
The US-China rivalry could be said to make-up the ‘stuff and substance’ of world politics today but rarely does the international politics watcher and student of the global South in particular get the opportunity of having a balanced and comprehensive evaluation of this crucial relationship. But such a balanced assessment is vitally instrumental in making sense of current world power relations.
Thanks to the Regional Centre for Strategic Studies (RCSS), Colombo the above window of opportunity was opened on December 8th for those sections of the public zealously pursuing an understanding of current issues in global politics. The knowledge came via a forum that was conducted at the RCSS titled, ‘The US-China Rivalry and Implications for the Indo-Pacific’, where Professor Neil DeVotta of the Wake Forest University of North Carolina in the US, featured as the speaker.
A widely representative audience was present at the forum, including senior public servants, the diplomatic corps, academics, heads of civil society organizations, senior armed forces personnel and the media. The event was ably managed by the Executive Director of the RCSS, retired ambassador Ravinatha Aryasinha. Following the main presentation a lively Q&A session followed, where many a point of interest was aired and discussed.
While there is no doubt that China is fast catching up with the US with regard to particularly military, economic, scientific and technological capability, Prof. DeVotta helped to balance this standard projection of ‘China’s steady rise’ by pointing to some vital facts about China, the omission of which would amount to the observer having a somewhat uninformed perception of global political realities.
The following are some of the facts about contemporary China that were highlighted by Prof. DeVotta:
* Money is steadily moving out of China and the latter’ s economy is slowing down. In fact the country is in a ‘ Middle Income Trap’. That is, it has reached middle income status but has failed to move to upper income status since then.
* People in marked numbers are moving out of China. It is perhaps little known that some Chinese are seeking to enter the US with a view to living there. The fact is that China’s population too is on the decline.
* Although the private sector is operative in China, there has been an increase in Parastatals; that is, commercial organizations run by the state are also very much in the fore. In fact private enterprises have begun to have ruling Communist Party cells in them.
* China is at its ‘peak power’ but this fact may compel it to act ‘aggressively’ in the international sphere. For instance, it may be compelled to invade Taiwan.
* A Hard Authoritarianism could be said to characterize central power in China today, whereas the expectation in some quarters is that it would shift to a Soft Authoritarian system, as is the case in Singapore.
* China’s influence in the West is greater than it has ever been.
The speaker was equally revelatory about the US today. Just a few of these observations are:
* The US is in a ‘Unipolar Moment’. That is, it is the world’s prime power. Such positions are usually not longstanding but in the case of the US this position has been enjoyed by it for quite a while.
* China is seen by the US as a ‘Revisionist Power’ as opposed to being a ‘Status Quo Power.’ That is China is for changing the world system slowly.
* The US in its latest national security strategy is paying little attention to Soft Power as opposed to Hard Power.
* In terms of this strategy the US would not allow any single country to dominate the Asia-Pacific region.
* The overall tone of this strategy is that the US should step back and allow regional powers to play a greater role in international politics.
* The strategy also holds that the US must improve economic ties with India, but there is very little mention of China in the plan.
Given these observations on the current international situation, a matter of the foremost importance for the economically weakest countries of the South is to figure out how best they could survive materially within it. Today there is no cohesive and vibrant collective organization that could work towards the best interests of the developing world and Dr. DeVotta was more or less correct when he said that the Non-alignment Movement (NAM) has declined.
However, this columnist is of the view that rather being a spent force, NAM was allowed to die out by the South. NAM as an idea could never become extinct as long as economic and material inequalities between North and South exist. Needless to say, this situation is remaining unchanged since the eighties when NAM allowed itself to be a non-entity so to speak in world affairs.
The majority of Southern countries did not do themselves any good by uncritically embracing the ‘market economy’ as a panacea for their ills. As has been proved, this growth paradigm only aggravated the South’s development ills, except for a few states within its fold.
Considering that the US would be preferring regional powers to play a more prominent role in the international economy and given the US’ preference to be a close ally of India, the weakest of the South need to look into the possibility of tying up closely with India and giving the latter a substantive role in advocating the South’s best interests in the councils of the world.
To enable this to happen the South needs to ‘get organized’ once again. The main differences between the past and the present with regard to Southern affairs is that in the past the South had outstanding leaders, such as Jawaharlal Nehru of India, who could doughtily stand up for it. As far as this columnist could ascertain, it is the lack of exceptional leaders that in the main led to the decline of NAM and other South-centred organizations.
Accordingly, an urgent task for the South is to enable the coming into being of exceptional leaders who could work untiringly towards the realization of its just needs, such as economic equity. Meanwhile, Southern countries would do well to, indeed, follow the principles of NAM and relate cordially with all the major powers so as to realizing their best interests.
Features
Sri Lanka and Global Climate Emergency: Lessons of Cyclone Ditwah
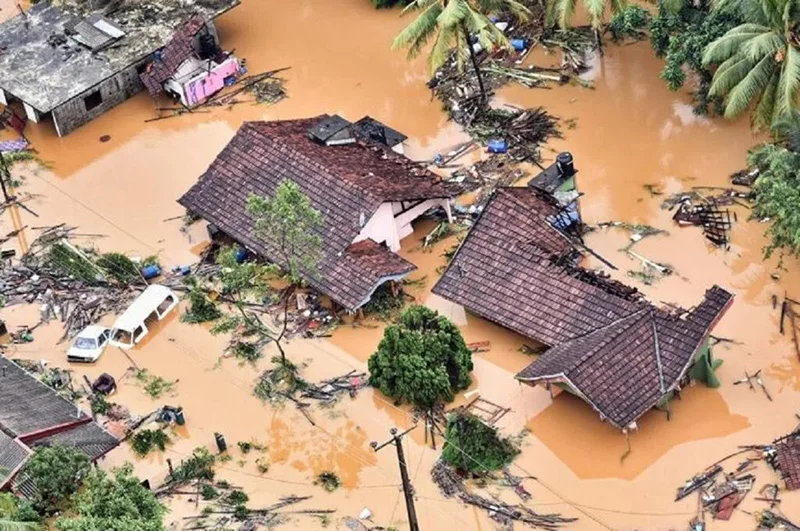

Tropical Cyclone Ditwah, which made landfall in Sri Lanka on 28 November 2025, is considered the country’s worst natural disaster since the deadly 2004 tsunami. It intensified the northeast monsoon, bringing torrential rainfall, massive flooding, and 215 severe landslides across seven districts. The cyclone left a trail of destruction, killing nearly 500 people, displacing over a million, destroying homes, roads, and railway lines, and disabling critical infrastructure including 4,000 transmission towers. Total economic losses are estimated at USD 6–7 billion—exceeding the country’s foreign reserves.
The Sri Lankan Armed Forces have led the relief efforts, aided by international partners including India and Pakistan. A Sri Lanka Air Force helicopter crashed in Wennappuwa, killing the pilot and injuring four others, while five Sri Lanka Navy personnel died in Chundikkulam in the north while widening waterways to mitigate flooding. The bravery and sacrifice of the Sri Lankan Armed Forces during this disaster—as in past disasters—continue to be held in high esteem by grateful Sri Lankans.
The Sri Lankan government, however, is facing intense criticism for its handling of Cyclone Ditwah, including failure to heed early warnings available since November 12, a slow and poorly coordinated response, and inadequate communication with the public. Systemic issues—underinvestment in disaster management, failure to activate protocols, bureaucratic neglect, and a lack of coordination among state institutions—are also blamed for avoidable deaths and destruction.
The causes of climate disasters such as Cyclone Ditwah go far beyond disaster preparedness. Faulty policymaking, mismanagement, and decades of unregulated economic development have eroded the island’s natural defenses. As climate scientist Dr. Thasun Amarasinghe notes:
“Sri Lankan wetlands—the nation’s most effective natural flood-control mechanism—have been bulldosed, filled, encroached upon, and sold. Many of these developments were approved despite warnings from environmental scientists, hydrologists, and even state institutions.”
Sri Lanka’s current vulnerabilities also stem from historical deforestation and plantation agriculture associated with colonial-era export development. Forest cover declined from 82% in 1881 to 70% in 1900, and to 54–50% by 1948, when British rule ended. It fell further to 44% in 1954 and to 16.5% by 2019.
Deforestation contributes an estimated 10–12% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Beyond removing a vital carbon sink, it damages water resources, increases runoff and erosion, and heightens flood and landslide risk. Soil-depleting monocrop agriculture further undermines traditional multi-crop systems that regenerate soil fertility, organic matter, and biodiversity.
In Sri Lanka’s Central Highlands, which were battered by Cyclone Ditwah, deforestation and unregulated construction had destabilised mountain slopes. Although high-risk zones prone to floods and landslides had long been identified, residents were not relocated, and construction and urbanisation continued unchecked.
Sri Lanka was the first country in Asia to adopt neoliberal economic policies. With the “Open Economy” reforms of 1977, a capitalist ideology equating human well-being with quantitative growth and material consumption became widespread. Development efforts were rushed, poorly supervised, and frequently approved without proper environmental assessment.
Privatisation and corporate deregulation weakened state oversight. The recent economic crisis and shrinking budgets further eroded environmental and social protections, including the maintenance of drainage networks, reservoirs, and early-warning systems. These forces have converged to make Sri Lanka a victim of a dual climate threat: gradual environmental collapse and sudden-onset disasters.
Sri Lanka: A Climate Victim
Sri Lanka’s carbon emissions remain relatively small but are rising. The impact of climate change on the island, however, is immense. Annual mean air temperature has increased significantly in recent decades (by 0.016 °C annually between 1961 and 1990). Sea-level rise has caused severe coastal erosion—0.30–0.35 meters per year—affecting nearly 55% of the shoreline. The 2004 tsunami demonstrated the extreme vulnerability of low-lying coastal plains to rising seas.
The Cyclone Ditwah catastrophe was neither wholly new nor surprising. In 2015, the Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) identified Sri Lanka as the South Asian country with the highest relative risk of disaster-related displacement: “For every million inhabitants, 15,000 are at risk of being displaced every year.”
IDMC also noted that in 2017 the country experienced seven disaster events—mainly floods and landslides—resulting in 135,000 new displacements and that Sri Lanka “is also at risk for slow-onset impacts such as soil degradation, saltwater intrusion, water scarcity, and crop failure”.
Sri Lanka ranked sixth among countries most affected by extreme weather events in 2018 (Germanwatch) and second in 2019 (Global Climate Risk Index). Given these warnings, Cyclone Ditwah should not have been a surprise. Scientists have repeatedly cautioned that warmer oceans fuel stronger cyclones and warmer air holds more moisture, leading to extreme rainfall. As the Ceylon Today editorial of December 1, 2025 also observed:
“…our monsoons are no longer predictable. Cyclones form faster, hit harder, and linger longer. Rainfall becomes erratic, intense, and destructive. This is not a coincidence; it is a pattern.”
Without urgent action, even more extreme weather events will threaten Sri Lanka’s habitability and physical survival.
A Global Crisis
Extreme weather events—droughts, wildfires, cyclones, and floods—are becoming the global norm. Up to 1.2 billion people could become “climate refugees” by 2050. Global warming is disrupting weather patterns, destabilising ecosystems, and posing severe risks to life on Earth. Indonesia and Thailand were struck by the rare and devastating Tropical Cyclone Senyar in late November 2025, occurring simultaneously with Cyclone Ditwah’s landfall in Sri Lanka.
More than 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions—and nearly 90% of carbon emissions—come from burning coal, oil, and gas, which supply about 80% of the world’s energy. Countries in the Global South, like Sri Lanka, which contribute least to greenhouse gas emissions, are among the most vulnerable to climate devastation. Yet wealthy nations and multilateral institutions, including the World Bank, continue to subsidise fossil fuel exploration and production. Global climate policymaking—including COP 30 in Belém, Brazil, in 2025—has been criticised as ineffectual and dominated by fossil fuel interests.
If the climate is not stabilised, long-term planetary forces beyond human control may be unleashed. Technology and markets are not inherently the problem; rather, the issue lies in the intentions guiding them. The techno-market worldview, which promotes the belief that well-being increases through limitless growth and consumption, has contributed to severe economic inequality and more frequent extreme weather events. The climate crisis, in turn, reflects a profound mismatch between the exponential expansion of a profit-driven global economy and the far slower evolution of human consciousness needed to uphold morality, compassion, generosity and wisdom.
Sri Lanka’s 2025–26 budget, adopted on November 14, 2025—just as Cyclone Ditwah loomed—promised subsidised land and electricity for companies establishing AI data centers in the country.
President Anura Kumara Dissanayake told Parliament: “Don’t come questioning us on why we are giving land this cheap; we have to make these sacrifices.”
Yet Sri Lanka is a highly water-stressed nation, and a growing body of international research shows that AI data centers consume massive amounts of water and electricity, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
The failure of the narrow, competitive techno-market approach underscores the need for an ecological and collective framework capable of addressing the deeper roots of this existential crisis—both for Sri Lanka and the world.
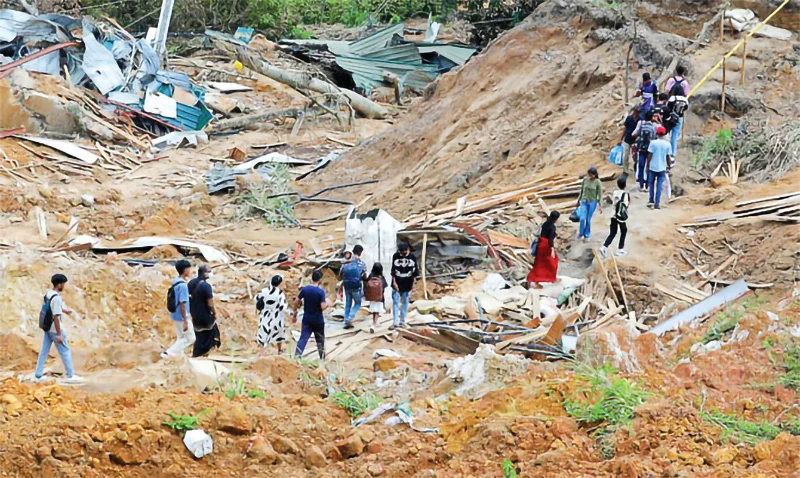

A landslide in Sri Lanka (AFP picture)
Ecological and Human Protection
Ecological consciousness demands
recognition that humanity is part of the Earth, not separate from it. Policies to address climate change must be grounded in this understanding, rather than in worldviews that prize infinite growth and technological dominance. Nature has primacy over human-created systems: the natural world does not depend on humanity, while humanity cannot survive without soil, water, air, sunlight, and the Earth’s essential life-support systems.
Although a climate victim today, Sri Lanka is also home to an ancient ecological civilization dating back to the arrival of the Buddhist monk Mahinda Thera in the 3rd century BCE. Upon meeting King Devanampiyatissa, who was out hunting in Mihintale, Mahinda Thera delivered one of the earliest recorded teachings on ecological interdependence and the duty of rulers to protect nature:
“O great King, the birds of the air and the beasts of the forest have as much right to live and move about in any part of this land as thou. The land belongs to the people and all living beings; thou art only its guardian.”
A stone inscription at Mihintale records that the king forbade the killing of animals and the destruction of trees. The Mihintale Wildlife Sanctuary is believed to be the world’s first.
Sri Lanka’s ancient dry-zone irrigation system—maintained over more than a millennium—stands as a marvel of sustainable development. Its network of interconnected reservoirs, canals, and sluices captured monsoon waters, irrigated fields, controlled floods, and even served as a defensive barrier. Floods occurred, but historical records show no disasters comparable in scale, severity, or frequency to those of today. Ancient rulers, including the legendary reservoir-builder King Parākramabāhu, and generations of rice farmers managed their environment with remarkable discipline and ecological wisdom.
The primacy of nature became especially evident when widespread power outages and the collapse of communication networks during Cyclone Ditwah forced people to rely on one another for survival. The disaster ignited spontaneous acts of compassion and solidarity across all communities—men and women, rich and poor, Buddhists, Christians, Muslims, and Hindus. Local and international efforts mobilized to rescue, shelter, feed, and emotionally support those affected. These actions demonstrated a profound human instinct for care and cooperation, often filling vacuums left by formal emergency systems.
Yet spontaneous solidarity alone is insufficient. Sri Lanka urgently needs policies on sustainable development, environmental protection, and climate resilience. These include strict, science-based regulation of construction; protection of forests and wetlands; proper maintenance of reservoirs; and climate-resilient infrastructure. Schools should teach environmental literacy that builds unity and solidarity, rather than controversial and divisive curriculum changes like the planned removal of history and introduction of contested modules on gender and sexuality.
If the IMF and international creditors—especially BlackRock, Sri Lanka’s largest sovereign bondholder, valued at USD 13 trillion—are genuinely concerned about the country’s suffering, could they not cancel at least some of Sri Lanka’s sovereign debt and support its rebuilding efforts? Addressing the climate emergency and the broader existential crisis facing Sri Lanka and the world ultimately requires an evolution in human consciousness guided by morality, compassion, generosity and wisdom. (Courtesy: IPS NEWS)
Dr Asoka Bandarage is the author of Colonialism in Sri Lanka: The Political Economy of the Kandyan Highlands, 1833-1886 (Mouton) Women, Population and Global Crisis: A Politico-Economic Analysis (Zed Books), The Separatist Conflict in Sri Lanka: Terrorism, Ethnicity, Political Economy, ( Routledge), Sustainability and Well-Being: The Middle Path to Environment, Society and the Economy (Palgrave MacMillan) Crisis in Sri Lanka and the World: Colonial and Neoliberal Origins, Ecological and Collective Alternatives (De Gruyter) and numerous other publications. She serves on the Advisory Boards of the Interfaith Moral Action on Climate and Critical Asian Studies.
Features
Cliff and Hank recreate golden era of ‘The Young Ones’

 Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin’s reunion concert at the Riverside Theatre in Perth, Australia, on 01 November, 2025, was a night to remember.
Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin’s reunion concert at the Riverside Theatre in Perth, Australia, on 01 November, 2025, was a night to remember.
The duo, who first performed together in the 1950s as part of The Shadows, brought the house down with their classic hits and effortless chemistry.
The concert, part of Cliff’s ‘Can’t Stop Me Now’ tour, featured iconic songs like ‘Summer Holiday’, ‘The Young Ones’, ‘Bachelor Boy’, ‘Living Doll’ and a powerful rendition of ‘Mistletoe and Wine.’
Cliff, 85, and Hank, with his signature red Fender Stratocaster, proved that their music and friendship are timeless.
According to reports, the moment the lights dimmed and the first chords of ‘Move It’ rang out, the crowd knew they were in for something extraordinary.
Backed by a full band, and surrounded by dazzling visuals, Cliff strode onto the stage in immaculate form – energetic and confident – and when Hank Marvin joined him mid-set, guitar in hand, the audience erupted in applause that shook the hall.
Together they launched into ‘The Young Ones’, their timeless 1961 hit which brought the crowd to its feet, with many in attendance moved to tears.
The audience was treated to a journey through time, with vintage film clips and state-of-the-art visuals adding to the nostalgic atmosphere.
Highlights of the evening included Cliff’s powerful vocals, Hank’s distinctive guitar riffs, and their playful banter on stage.
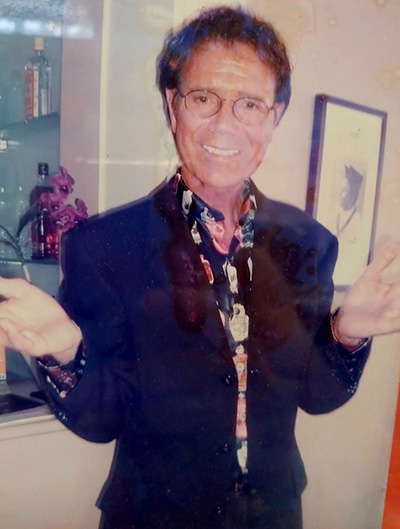

Cliff posing for The Island photographer … February,
2007
Cliff paused between songs to reflect on their shared journey saying:
“It’s been a lifetime of songs, memories, and friendship. Hank and I started this adventure when we were just boys — and look at us now, still up here making noise!”
As the final chords of ‘Congratulations’ filled the theatre, the crowd rose for a thunderous standing ovation that lasted several minutes.
Cliff waved, Hank gave a humble bow, and, together, they left the stage, arm-in-arm, to the refrain of “We’re the young ones — and we always will be.”
Reviews of the show were glowing, with fans and critics alike praising the duo’s energy, camaraderie, and enduring talent.
Overall, the Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin reunion concert was a truly special experience, celebrating the music and friendship that has captivated audiences for decades.
When Cliff Richard visited Sri Lanka, in February, 2007, I was invited to meet him, in his suite, at a hotel, in Colombo, and I presented him with my music page, which carried his story, and he was impressed.
In return, he personally autographed a souvenir for me … that was Cliff Richard, a truly wonderful human being.
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoFinally, Mahinda Yapa sets the record straight
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCyclone Ditwah leaves Sri Lanka’s biodiversity in ruins: Top scientist warns of unseen ecological disaster
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoThe Catastrophic Impact of Tropical Cyclone Ditwah on Sri Lanka: