Features
The Year of Darkness

BY SUMI MOONESINGHE
narrated to Savitri Rodrigo
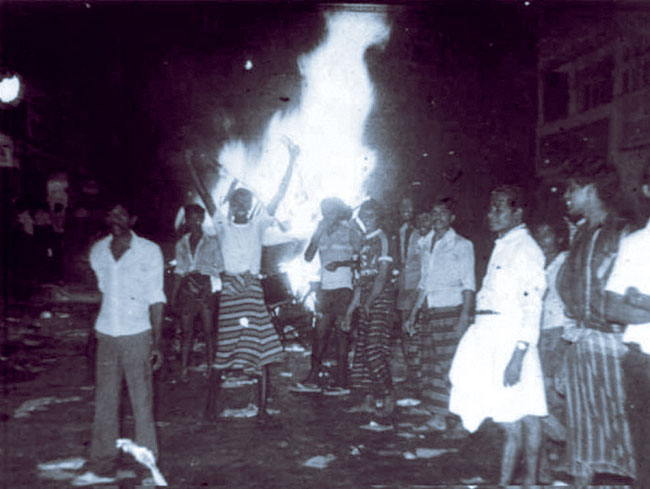
July 1983 was one of the darkest months this country has ever experienced. It was then that I saw my countrymen turn on each other and where barbarism outweighed every Buddhist precept upon which the country had built its foundations. Black July is what it came to be known as – or Kalu Juliya –the anti-Tamil pogrom that was triggered by a deadly ambush in Jaffna by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE), which resulted in the deaths of 13 army soldiers. Believed to have been orchestrated by some members of the UNP, by July 24, anti-Tamil rioting had spread across the city of Colombo and quickly to other parts of the country.
The day the riots began, Susil and I had been on holiday in Nuwara Eliya and were driving back. Going past the junction of Kanatte, the main cemetery in Colombo, we noticed a large crowd gathered but didn’t take too much notice of it. When we got home, we heard that the bodies of the 13 soldiers killed by the LTTE had been brought to Colombo for interment. The Government made a colossal mistake with that decision.
The LTTE had been founded way back in 1976 with the aim of securing an independent Tamil Eelam, or separate in north-eastern Sri Lanka as a response to what was was widely considered successive governments being discriminatory towards the minority Tamils. There had been anti-Tamil pogroms in 1956 and 1958, carried out by the majority Sinhalese, and oppressive action which caused the eventual genesis of the LTTE leading to yet another anti-Tamil pogrom in 1977. The subsequent burning of the Jaffna Public Library in 1981 added to the woes and was widely believed to be sanctioned by the incumbent government.
But it was with the deaths of these 13 soldiers and the anti-Tamil pogrom carried out by Sinhalese mobs in July 1983 that fuelled a full-scale escalation of violence that would ruin the country for nearly three decades.
When Susil heard about the mass funeral being held in Kanatte, he predicted problems for the country. There were rumbles of impending riots and on hearing these, we phoned some of our friends and told them to be vigilant as trouble may be brewing. In fact, I remember Susil asking them not to stay in their homes but to move to safe places.
We were too worried to go to sleep and for good reason. Because by 4 am, the whole of Colombo seemed to be burning. My bosses, Maha and Killi were Tamil, and I knew they were at risk. By 12 noon, the mobs had already attacked and burned most of the Maharaja properties starting with Berec, our battery factory, our Group Head Office, Maha’s home at Coniston Place and every factory the Maharajas owned.
Before the attackers had made it to Maha’s home however, we quickly transported Maha and Ruki as well as our friends Thanchi and Vasanta Coomaraswamy into our home.
Transporting Tamils to safe places also became hazardous. The mobs were uncontrollable and were fanned out across all the main roads. They had lists bearing the addresses of the Tamils and were strategically searching for those homes, to loot, bum and kill. I remember the beautiful house belonging to K. Gunaratnam down Bullers Road where mobs pulled down massive crystal chandeliers from their sockets, brought these onto the road and dashed them into smithereens. Vasanta’s mother’s house was also burned. I remember walking into the smouldering house looking for his niece who was pregnant.
She was nowhere to be found and I prayed nothing had happened to her. I was near to tears by this time because I was imagining the worst and was quite relieved to hear that she had jumped over the wall and managed to save herself. My astrologer Mr. Arulpragasam’s house was set on fire and Susil and I brought him to our home and kept him with us.
Until his immigration papers to Australia were approved, we rented out an annexe for him to stay. We also brought the Food Commissioner Mr Pullendian and his wife to stay with us. Their home in Wellawatte had also been razed to the ground.
Then there was Potato Shanmugam, named thus because he was the biggest potato importer in Pettah, in addition to being the biggest sugar buyer from Jones Overseas. Over the years, I had forged a strong bond of friendship with him and his Finance Director Mr. Sangarasivam. This bond was so strong that each morning, Mr. Sangarasivam would come to our home after going to the kovil and place a vibhuti on three-year-old Aushi’s forehead before he made his way to work in the Pettah. Such was their closeness to us.
When the riots began I remembered Potato Shanmugam having taken out a number of bank loans to finance a huge stock of sugar in his go-downs. Susil anticipated problems for the man, and pulled some strings to place a quick board at Shanmugam’s stores stating ‘Property of the Food Department’. This was to ensure the mobs won’t attack the property assuming it was government property.
In the week of the riots with anti-Tamil sentiments fully fueled into unimaginable proportions, Mr. Sangarasivam had bravely visited the banks to assure them that their collateral was safe_ He called me from there saying, “Madam, don’t worry. We are fine. The stock will not fall into the hands of the mobs nor will we get burnt because you put up that board. Nobody touched the place.”
I spoke to the Bank Manager as well, assuring them that the stock and as a result their money was safe.
That was the last time I spoke with Mr. Sangarasivam. He was driving back from the bank that morning when he was stopped by the mobs at the Pettah Clock Tower, pulled out of his car, shoved into the boot, the car doused with petrol and set on fire.
The insane killing of Mr. Sangarasivam was the turning point for me. I completely collapsed. This was the man who came to our house every morning and would bless my child before he left for work. How are human beings capable of such brutality? I was truly shattered.
When I heard of Mr. Sangarasivan’s death, I just bent over and cried. It seemed a never-ending nightmare and I was hoping against hope that I would wake up from this bad dream. I had come to that point when I wanted to pack up everything and leave. But how could 1, when our friends were feeling the deadly brunt of a racial riot that our country had never experienced before? I couldn’t possibly abandon them now!
Susil and I spent an inordinate amount of time on the road trying our best to get whomever we knew to safety. The country was seething and tempers were rife. I even took a policeman in the car with me to 4th Cross Street to bring the cash in the safe belonging to Potato Shanmugam. I couldn’t bear to open my eyes when I got to the Pettah. The whole area was burning.
The moment the news hit the international news wires, our foreign partners began calling me to find out how we were doing. I really didn’t know what to say. I was so ashamed of my countrymen, the majority Sinhalese who were now known all over the world as murderers. The images spread around the world showed the Sinhalese as brutal, cruel people carrying out barbaric actions that had never been seen in the civilised world in modern history.
By this time, our home was filled with Tamil friends taking refuge. There were so many cars parked outside that even the neighbours figured it was not a good sign and refused to let us park. Hema Premadasa, the wife of the Prime Minister Ranasinghe Premadasa, dropped in to see Maha; and I think word got around that we were sheltering Tamil people in our house, which also spelled danger for us.
My Tamil staff including my Finance Director had been taken to an Internally Displaced Camp came because they had lost everything they owned. I wanted to do whatever I could to make their pain go away. We visited the camps, took food and other necessities for them, but this -just didn’t seem sufficient for the pain and indignity they suffered.
The riots began. on a Monday early morning and went on unabated until Friday. As Susil and I watched helplessly, one aspect became very clear. Our good friend J R had all the power in the world to stop the riots and reinstate sanity in the country, but he never did. In that week, Susil and I made multiple trips see J R, pleading with him to stop the massacre that was now totally out of hand.
I still remember Satyendra, Maha’s brother-in-law, calling J R during one of those visits, asking him to do something. Not once did J R come out publicly and ask the mobs to stop the attacks or express sympathy for those killed and displaced.
The riots however did simmer to an uneasy halt on the Friday of that week which was named ‘Kotiya Day’ – the day of the Tigers. And it was not the Government’s apathy that did it. The rumour mills had begun churning out unsubstantiated statements which fortunately, for once, worked as an advantage. The rumour that the Tigers were in Colombo and murdering people indiscriminately began spreading like wildfire and the rioting petered out.
But in those five days of the Government’s procrastination and indecisiveness, over 4,000 Tamils and some Muslims who were mistaken for Tamils had been killed, with even those injured and those in hospitals killed. Over 300,000 were displaced, homes, vehicles and over 2,500 businesses destroyed. Such was the blanket of hate that had descended on this country.
An uneasy calm descended over the city and gradually, those who yet had places to go to, moved out of our home. Maha moved to Guildford Crescent as did the other families at home. But we were still on tenterhooks. We were so attuned to unusual noises due to the fear that had enveloped us that one night when Susil heard what he thought was a strange noise, he said, “We can’t bring up our family this way. The children are living in fear and are traumatized. We have to leave.”
Susil called the Manager of Swiss Air whom we had met in Singapore and taken out to dinner on one of our trips, and requested four tickets to London. Apologizing profusely, the manager said there were only three seats left on the next flight and if we could keep Aushi on our laps, which was against IATA rules but since these were unusual circumstances, we could go. We left for London that night.
Even though I agreed to leave Sri Lanka on Susil’s incisive reasoning, I regret leaving Sri Lanka that day. It was the worst decision I made. I had so much confidence in Susil and would never question anything he did or said. But I left Killi and Maha, when they needed me the most. I was a Director of Jones Overseas, one of the biggest companies in The Maharaja Group, and it was my responsibility to stay and weather the storm with them. The factories had been burned to the ground and our people were in camps. While I mulled over this conundrum in my head and had many a misgiving, I knew in my heart that neither Killi nor Maha ever held my decision to leave against me.
We returned to Colombo after a month. There still remained that uneasy calm but on the surface, it seemed like it was ‘back to business’ in Colombo.’ While we adults have the ability to delete unsavoury details from our minds and carry on, the horrific scenes we had left behind had been ingrained in little Aushi’s mind. On the way back from the airport, Aushi, in all her innocence asked me, “Are those things still burning?” That was her last memory of Sri Lanka because when we left that fateful night, all she saw was fire everywhere. Anarkali however, was old enough to understand and didn’t quite express herself with that kind of innocence.
(Excerpted from Sumi Moonesinghe’s recently published Memoirs)
Features
Trump’s Interregnum
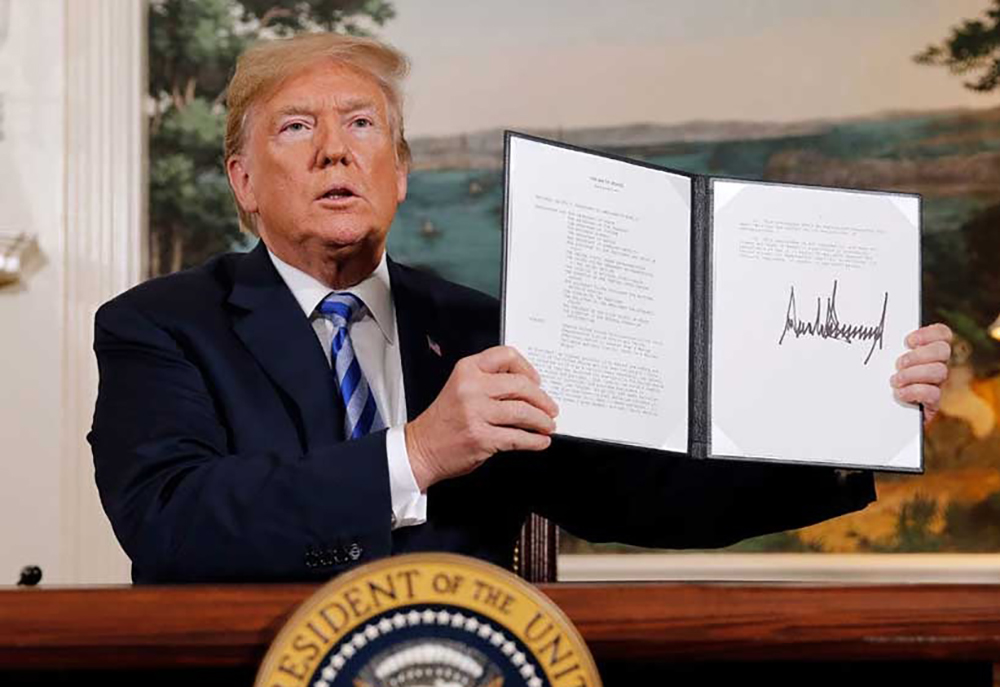

Trump is full of surprises; he is both leader and entertainer. Nearly nine hours into a long flight, a journey that had to U-turn over technical issues and embark on a new flight, Trump came straight to the Davos stage and spoke for nearly two hours without a sip of water. What he spoke about in Davos is another issue, but the way he stands and talks is unique in this 79-year-old man who is defining the world for the worse. Now Trump comes up with the Board of Peace, a ticket to membership that demands a one-billion-dollar entrance fee for permanent participation. It works, for how long nobody knows, but as long as Trump is there it might. Look at how many Muslim-majority and wealthy countries accepted: Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Egypt, Jordan, Qatar, Pakistan, Indonesia, and the United Arab Emirates are ready to be on board. Around 25–30 countries reportedly have already expressed the willingness to join.
The most interesting question, and one rarely asked by those who speak about Donald J. Trump, is how much he has earned during the first year of his second term. Liberal Democrats, authoritarian socialists, non-aligned misled-path walkers hail and hate him, but few look at the financial outcome of his politics. His wealth has increased by about three billion dollars, largely due to the crypto economy, which is why he pardoned the founder of Binance, the China-born Changpeng Zhao. “To be rich like hell,” is what Trump wanted. To fault line liberal democracy, Trump is the perfect example. What Trump is doing — dismantling the old façade of liberal democracy at the very moment it can no longer survive — is, in a way, a greater contribution to the West. But I still respect the West, because the West still has a handful of genuine scholars who do not dare to look in the mirror and accept the havoc their leaders created in the name of humanity.
Democracy in the Arab world was dismantled by the West. You may be surprised, but that is the fact. Elizabeth Thompson of American University, in her book How the West Stole Democracy from the Arabs, meticulously details how democracy was stolen from the Arabs. “No ruler, no matter how exalted, stood above the will of the nation,” she quotes Arab constitutional writing, adding that “the people are the source of all authority.” These are not the words of European revolutionaries, nor of post-war liberal philosophers; they were spoken, written and enacted in Syria in 1919–1920 by Arab parliamentarians, Islamic reformers and constitutionalists who believed democracy to be a universal right, not a Western possession. Members of the Syrian Arab Congress in Damascus, the elected assembly that drafted a democratic constitution declaring popular sovereignty — were dissolved by French colonial forces. That was the past; now, with the Board of Peace, the old remnants return in a new form.
Trump got one thing very clear among many others: Western liberal ideology is nothing but sophisticated doublespeak dressed in various forms. They go to West Asia, which they named the Middle East, and bomb Arabs; then they go to Myanmar and other places to protect Muslims from Buddhists. They go to Africa to “contribute” to livelihoods, while generations of people were ripped from their homeland, taken as slaves and sold.
How can Gramsci, whose 135th birth anniversary fell this week on 22 January, help us escape the present social-political quagmire? Gramsci was writing in prison under Mussolini’s fascist regime. He produced a body of work that is neither a manifesto nor a programme, but a theory of power that understands domination not only as coercion but as culture, civil society and the way people perceive their world. In the Prison Notebooks he wrote, “The crisis consists precisely in the fact that the old world is dying and the new cannot be born; in this interregnum a great variety of morbid phenomena appear.” This is not a metaphor. Gramsci was identifying the structural limbo that occurs when foundational certainties collapse but no viable alternative has yet emerged.
The relevance of this insight today cannot be overstated. We are living through overlapping crises: environmental collapse, fragmentation of political consensus, erosion of trust in institutions, the acceleration of automation and algorithmic governance that replaces judgment with calculation, and the rise of leaders who treat geopolitics as purely transactional. Slavoj Žižek, in his column last year, reminded us that the crisis is not temporary. The assumption that history’s forward momentum will automatically yield a better future is a dangerous delusion. Instead, the present is a battlefield where what we thought would be the new may itself contain the seeds of degeneration. Trump’s Board of Peace, with its one-billion-dollar gatekeeping model, embodies this condition: it claims to address global violence yet operates on transactional logic, prioritizing wealth over justice and promising reconstruction without clear mechanisms of accountability or inclusion beyond those with money.
Gramsci’s critique helps us see this for what it is: not a corrective to global disorder, but a reenactment of elite domination under a new mechanism. Gramsci did not believe domination could be maintained by force alone; he argued that in advanced societies power rests on gaining “the consent and the active participation of the great masses,” and that domination is sustained by “the intellectual and moral leadership” that turns the ruling class’s values into common sense. It is not coercion alone that sustains capitalism, but ideological consensus embedded in everyday institutions — family, education, media — that make the existing order appear normal and inevitable. Trump’s Board of Peace plays directly into this mode: styled as a peace-building institution, it gains legitimacy through performance and symbolic endorsement by diverse member states, while the deeper structures of inequality and global power imbalance remain untouched.
Worse, the Board’s structure, with contributions determining permanence, mimics the logic of a marketplace for geopolitical influence. It turns peace into a commodity, something to be purchased rather than fought for through sustained collective action addressing the root causes of conflict. But this is exactly what today’s democracies are doing behind the scenes while preaching rules-based order on the stage. In Gramsci’s terms, this is transformismo — the absorption of dissent into frameworks that neutralize radical content and preserve the status quo under new branding.
If we are to extract a path out of this impasse, we must recognize that the current quagmire is more than political theatre or the result of a flawed leader. It arises from a deeper collapse of hegemonic frameworks that once allowed societies to function with coherence. The old liberal order, with its faith in institutions and incremental reform, has lost its capacity to command loyalty. The new order struggling to be born has not yet articulated a compelling vision that unifies disparate struggles — ecological, economic, racial, cultural — into a coherent project of emancipation rather than fragmentation.
To confront Trump’s phenomenon as a portal — as Žižek suggests, a threshold through which history may either proceed to annihilation or re-emerge in a radically different form — is to grasp Gramsci’s insistence that politics is a struggle for meaning and direction, not merely for offices or policies. A Gramscian approach would not waste energy on denunciation alone; it would engage in building counter-hegemony — alternative institutions, discourses, and practices that lay the groundwork for new popular consent. It would link ecological justice to economic democracy, it would affirm the agency of ordinary people rather than treating them as passive subjects, and it would reject the commodification of peace.
Gramsci’s maxim “pessimism of the intellect, optimism of the will” captures this attitude precisely: clear-eyed recognition of how deep and persistent the crisis is, coupled with an unflinching commitment to action. In an age where AI and algorithmic governance threaten to redefine humanity’s relation to decision-making, where legitimacy is increasingly measured by currency flows rather than human welfare, Gramsci offers not a simple answer but a framework to understand why the old certainties have crumbled and how the new might still be forged through collective effort. The problem is not the lack of theory or insight; it is the absence of a political subject capable of turning analysis into a sustained force for transformation. Without a new form of organized will, the interregnum will continue, and the world will remain trapped between the decay of the old and the absence of the new.
by Nilantha Ilangamuwa ✍️
Features
India, middle powers and the emerging global order

Designed by the victors and led by the US, its institutions — from the United Nations system to Bretton Woods — were shaped to preserve western strategic and economic primacy. Yet despite their self-serving elements, these arrangements helped maintain a degree of global stability, predictability and prosperity for nearly eight decades. That order is now under strain.
This was evident even at Davos, where US President Donald Trump — despite deep differences with most western allies — framed western power and prosperity as the product of a shared and “very special” culture, which he argued must be defended and strengthened. The emphasis on cultural inheritance, rather than shared rules or institutions, underscored how far the language of the old order has shifted.
As China’s rise accelerates and Russia grows more assertive, the US appears increasingly sceptical of the very system it once championed. Convinced that multilateral institutions constrain American freedom of action, and that allies have grown complacent under the security umbrella, Washington has begun to prioritise disruption over adaptation — seeking to reassert supremacy before its relative advantage diminishes further.
What remains unclear is what vision, if any, the US has for a successor order. Beyond a narrowly transactional pursuit of advantage, there is little articulation of a coherent alternative framework capable of delivering stability in a multipolar world.
The emerging great powers have not yet filled this void. India and China, despite their growing global weight and civilisational depth, have largely responded tactically to the erosion of the old order rather than advancing a compelling new one. Much of their diplomacy has focused on navigating uncertainty, rather than shaping the terms of a future settlement. Traditional middle powers — Japan, Germany, Australia, Canada and others — have also tended to react rather than lead. Even legacy great powers such as the United Kingdom and France, though still relevant, appear constrained by alliance dependencies and domestic pressures.
st Asia, countries such as Saudi Arabia and the UAE have begun to pursue more autonomous foreign policies, redefining their regional and global roles. The broader pattern is unmistakable. The international system is drifting toward fragmentation and narrow transactionalism, with diminishing regard for shared norms or institutional restraint.
Recent precedents in global diplomacy suggest a future in which arrangements are episodic and power-driven. Long before Thucydides articulated this logic in western political thought, the Mahabharata warned that in an era of rupture, “the strong devour the weak like fish in water” unless a higher order is maintained. Absent such an order, the result is a world closer to Mad Max than to any sustainable model of global governance.
It is precisely this danger that Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney alluded to in his speech at Davos on Wednesday. Warning that “if great powers abandon even the pretense of rules and values for the unhindered pursuit of their power and interests, the gains from transactionalism will become harder to replicate,” Carney articulated a concern shared by many middle powers. His remarks underscored a simple truth: Unrestrained power politics ultimately undermine even those who believe they benefit from them.
Carney’s intervention also highlights a larger opportunity. The next phase of the global order is unlikely to be shaped by a single hegemon. Instead, it will require a coalition — particularly of middle powers — that have a shared interest in stability, openness and predictability, and the credibility to engage across ideological and geopolitical divides. For many middle powers, the question now is not whether the old order is fraying, but who has the credibility and reach to help shape what comes next.
This is where India’s role becomes pivotal. India today is no longer merely a balancing power. It is increasingly recognised as a great power in its own right, with strong relations across Europe, the Indo-Pacific, West Asia, Africa and Latin America, and a demonstrated ability to mobilise the Global South. While India’s relationship with Canada has experienced periodic strains, there is now space for recalibration within a broader convergence among middle powers concerned about the direction of the international system.
One available platform is India’s current chairmanship of BRICS — if approached with care. While often viewed through the prism of great-power rivalry, BRICS also brings together diverse emerging and middle powers with a shared interest in reforming, rather than dismantling, global governance. Used judiciously, it could complement existing institutions by helping articulate principles for a more inclusive and functional order.
More broadly, India is uniquely placed to convene an initial core group of like-minded States — middle powers, and possibly some open-minded great powers — to begin a serious conversation about what a new global order should look like. This would not be an exercise in bloc-building or institutional replacement, but an effort to restore legitimacy, balance and purpose to international cooperation. Such an endeavour will require political confidence and the willingness to step into uncharted territory. History suggests that moments of transition reward those prepared to invest early in ideas and institutions, rather than merely adapt to outcomes shaped by others.
The challenge today is not to replicate Bretton Woods or San Francisco, but to reimagine their spirit for a multipolar age — one in which power is diffused, interdependence unavoidable, and legitimacy indispensable. In a world drifting toward fragmentation, India has the credibility, relationships and confidence to help anchor that effort — if it chooses to lead.
(The Hindustan Times)
(Milinda Moragoda is a former Cabinet Minister and diplomat from Sri Lanka and founder of the Pathfinder Foundation, a strategic affairs think tank. this article can read on
https://shorturl.at/HV2Kr and please contact via email@milinda.org)
by Milinda Moragoda ✍️
For many middle powers, the question now is not whether the old order is fraying,
but who has the credibility and reach to help shape what comes next
Features
The Wilwatte (Mirigama) train crash of 1964 as I recall
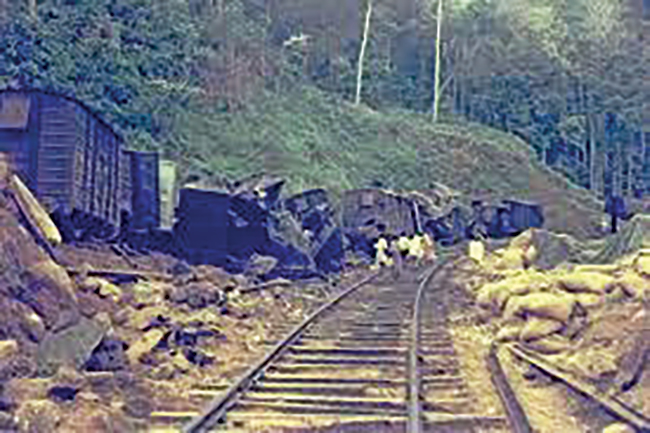

Back in 1964, I was working as DMO at Mirigama Government Hospital when a major derailment of the Talaimannar/Colombo train occurred at the railway crossing in Wilwatte, near the DMO’s quarters. The first major derailment, according to records, took place in Katukurunda on March 12, 1928, when there was a head-on collision between two fast-moving trains near Katukurunda, resulting in the deaths of 28 people.
Please permit me to provide details concerning the regrettable single train derailment involving the Talaimannar Colombo train, which occurred in October 1964 at the Wilwatte railway crossing in Mirigama.
This is the first time I’m openly sharing what happened on that heartbreaking morning, as I share the story of the doctor who cared for all the victims. The Health Minister, the Health Department, and our community truly valued my efforts.
By that time, I had qualified with the Primary FRCS and gained valuable surgical experience as a registrar at the General Hospital in Colombo. I was hopeful to move to the UK to pursue the final FRCS degree and further training. Sadly, all scholarships were halted by Hon. Felix Dias Bandaranaike, the finance minister in the Bandaranaike government in 1961.
Consequently, I was transferred to Mirigama as the District Medical Officer in 1964. While training as an emerging surgeon without completing the final fellowship in the United Kingdom, I established an operating theatre in one of the hospital’s large rooms. A colleague at the Central Medical Stores in Maradana assisted me in acquiring all necessary equipment for the operating theatre, unofficially. Subsequently, I commenced performing minor surgeries under spinal anaesthesia and local anaesthesia. Fortunately, I was privileged to have a theatre-trained nursing sister and an attendant trainee at the General Hospital in Colombo.
Therefore, I was prepared to respond to any accidental injuries. I possessed a substantial stock of plaster of Paris rolls for treating fractures, and all suture material for cuts.
I was thoroughly prepared for any surgical mishaps, enabling me to manage even the most significant accidental incidents.
On Saturday, October 17, 1964, the day of the train derailment at the railway crossing at Wilwatte, Mirigama, along the Main railway line near Mirigama, my house officer, Janzse, called me at my quarters and said, “Sir, please come promptly; numerous casualties have been admitted to the hospital following the derailment.”
I asked him whether it was an April Fool’s stunt. He said, ” No, Sir, quite seriously.
I promptly proceeded to the hospital and directly accessed the operating theatre, preparing to attend to the casualties.
Meanwhile, I received a call from the site informing me that a girl was trapped on a railway wagon wheel and may require amputation of her limb to mobilise her at the location along the railway line where she was entrapped.
My theatre staff transported the surgical equipment to the site. The girl was still breathing and was in shock. A saline infusion was administered, and under local anaesthesia, I successfully performed the limb amputation and transported her to the hospital with my staff.
On inquiring, she was an apothecary student going to Colombo for the final examination to qualify as an apothecary.
Although records indicate that over forty passengers perished immediately, I recollect that the number was 26.
Over a hundred casualties, and potentially a greater number, necessitate suturing of deep lacerations, stabilisation of fractures, application of plaster, and other associated medical interventions.
No patient was transferred to Colombo for treatment. All casualties received care at this base hospital.
All the daily newspapers and other mass media commended the staff team for their commendable work and the attentive care provided to all casualties, satisfying their needs.
The following morning, the Honourable Minister of Health, Mr M. D. H. Jayawardena, and the Director of Health Services, accompanied by his staff, arrived at the hospital.
I did the rounds with the official team, bed by bed, explaining their injuries to the minister and director.
Casualties expressed their commendation to the hospital staff for the care they received.
The Honourable Minister engaged me privately at the conclusion of the rounds. He stated, “Doctor, you have been instrumental in our success, and the public is exceedingly appreciative, with no criticism. As a token of gratitude, may I inquire how I may assist you in return?”
I got the chance to tell him that I am waiting for a scholarship to proceed to the UK for my Fellowship and further training.
Within one month, the government granted me a scholarship to undertake my fellowship in the United Kingdom, and I subsequently travelled to the UK in 1965.
On the third day following the incident, Mr Don Rampala, the General Manager of Railways, accompanied by his deputy, Mr Raja Gopal, visited the hospital. A conference was held at which Mr Gopal explained and demonstrated the circumstances of the derailment using empty matchboxes.
He explained that an empty wagon was situated amid the passenger compartments. At the curve along the railway line at Wilwatte, the engine driver applied the brakes to decelerate, as Mirigama Railway Station was only a quarter of a mile distant.
The vacant wagon was lifted and transported through the air. All passenger compartments behind the wagon derailed, whereas the engine and the frontcompartments proceeded towards the station without the engine driver noticing the mishap.
After this major accident, I was privileged to be invited by the General Manager of the railways for official functions until I left Mirigama.
The press revealed my identity as the “Wilwatte Hero”.
This document presents my account of the Wilwatte historic train derailment, as I distinctly recall it.
Recalled by Dr Harold Gunatillake to serve the global Sri Lankan community with dedication. ✍️
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoExtended mind thesis:A Buddhist perspective
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoAmerican rulers’ hatred for Venezuela and its leaders
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoCORALL Conservation Trust Fund – a historic first for SL
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoRemembering Cedric, who helped neutralise LTTE terrorism
-

 Business12 hours ago
Business12 hours agoComBank advances ForwardTogether agenda with event on sustainable business transformation
-
 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoA puppet show?
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoHistory of St. Sebastian’s National Shrine Kandana
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoThe middle-class money trap: Why looking rich keeps Sri Lankans poor













