Features
The recovery has begun

by Jehan Perera
Downtown Colombo and especially its upmarket commercial areas sparkled, and will continue to do so, in the night this Christmas season until the grand finale on New Year’s Eve. There is little indication that this city of night lights had experienced dire economic collapse just three years ago. The long lines of vehicles that once queued up for fuel outside petrol stations are overshadowed the much longer lines of traffic crawling on the way to the centre of celebrations at Galle Face Green, once the epicentre of the Aragalaya protests that brought down the government and had the president fleeing the country.
The hotels and nightclubs at the higher end have been packed to capacity. The cost of celebrating in them is steep but there seem to be a large number of people who can afford this expenditure, at least once in a while. New hotels such as ITC Ratnadeepa and City of Dreams overlooking water fronts create an image of Dubai at night. The ever-rising stock market is evidence for the new found confidence in the economic management of the country. There is a sense of political stability that comes not only from the 2/3 majority that the government enjoys in parliament but also from the inability of the opposition to make suggestions or proposals that are significantly different from the policies being followed by the government.
The desire to be part of the festivities was visible also in the large number of people who participate in them at different levels. They enjoyed themselves at the expensive buffets of five star hotels and in the open spaces of Galle Face Green, where there was a carnival and mobile eateries or in the big shopping malls where they might have a bite at Pizza Hut or engage in window shopping. The high costs of restaurants and consumer items relative to income are manifest in the struggle of the government to bring down the cost of living but with little success. The ongoing battle of the government with the so-called “Rice Mafia” has yielded positive results after the import of rice. But the price of coconuts remains high along with everything else that went up in price three years ago and did not come down.
SPREAD DEVELOPMENT
Outside of Colombo the Christmas celebrations were more muted if they existed at all. Christian churches were the focus of such initiatives. The big celebrations outside of Colombo would take place during the traditional Sinhala and Tamil New Year in April. Some of the provincial capitals like Jaffna had their own displays of festive lights and decorations, but they were not on the scale of Colombo. The difference in purchasing power of Colombo, the national capital, and the provincial capitals was reflected in this disparity.
One of the key justifications for the devolution of power is that there needs to be equitable development across the country and not only in the region of the capital city. Power and wealth tend to go together as those with power to decide will tend to make decisions that benefit themselves and the area they live in. The devolution of power to the provinces is to provide engines of development to the provincial capitals, ensuring wider distribution of the fruits of development. This aspect of devolution of power needs to be explained to the general population who see the concept as being a foreign-driven one meant to resolve the ethnic conflict. Devolved systems of governance have existed in Sri Lanka from the times of the kings due to the impracticalities of centralized rule.
So far the devolution of power in Sri Lanka has been seen in the context of resolving the ethnic conflict. But it can also be justified in a broader perspective as befits the “System Change” that was the main slogan of the Aragalaya protest movement that finally propelled the present government to power. The present system of devolution has been brought into operation through the 13th Amendment to the constitution which came at the height of the ethnic war in 1987 and was facilitated by the external intervention of India. It is not surprising, therefore, that the devolution of power under the 13th Amendment should be seen in that context and as having a bearing on the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the country. Its implementation has been resisted by all successive governments, including the one that brought it into law. This may account for the government’s commitment to devolve power with the passage of a new constitution, but on a different basis to that which exists at present.
CHANGED BEHAVIOURS
The progress of the economy, which is expected to grow by 4 percent this year, and higher than anticipated by international financial institutions, will be due in part to the stability in the polity, which is reflected in increased investor confidence. This positive growth factor will be supplemented by the government’s promise of non-corrupt governance. Unlike in the past, the first 100 days of the new government have not given rise to any major corruption scandal involving government leaders. The issue of the PhD degree of the Speaker of Parliament which led to the resignation of the Speaker has been a new practice when compared to the practices of the recent past. Those in power have not stepped down or been asked to step down when found out for things done which were much more detrimental to the country’s reputation and economy.
The non-ostentatious, non-extravagant and non-corrupt attitude that comes from the president and his top team appears to be seeping down to the bottom. During the holiday season a visit to the local government office to obtain a Grama Niladari certificate of local residence bore this out. The concerned officer was at his desk at the time of the visit, gave information about the application procedure and delivered the required document without any fuss or delay. He explained that he was following all the formalities including getting the signatory to sign in his presence. He explained his supervisor would be checking for this. He also volunteered the information that the change in behaviour at the top of the government was influencing those at the bottom to follow the rules in performing their duties.
Another point he made was that his area was a multi ethnic and multi religious one. The previous person he had attended to was from the Diaspora, a dual citizen, and asking for a national identity card. As that person had all the proper documentation, he had issued the relevant certificate even though he had no personal knowledge of this person who had lived abroad for the past twenty years. He said that person was a citizen and needed to be treated as an equal. In response to the query whether this too was part of the positive influence from the new government, the Grama Niladari said no, it was a message that he had picked up during the period of the Yahapalana government. The new government has inherited not only the bad but also the good from the past and is taking the good alone, to build on it in the year to come and beyond. This gives hope for the future.
Features
Meet the women protecting India’s snow leopards
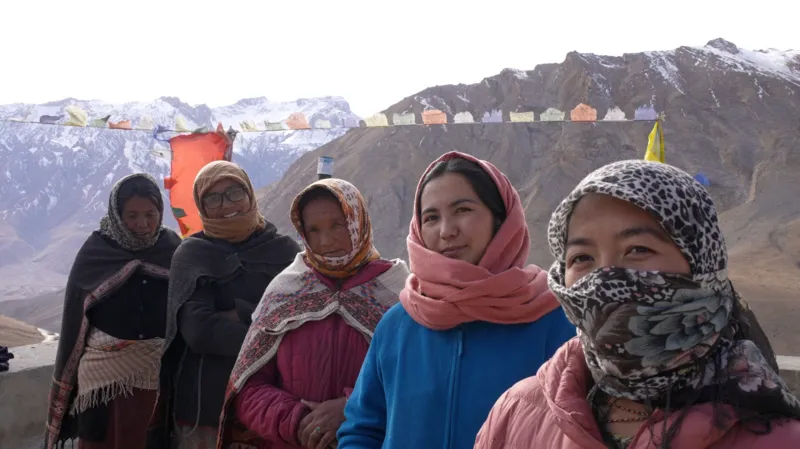

In one of India’s coldest and most remote regions, a group of women have taken on an unlikely role: protecting one of Asia’s most elusive predators, the snow leopard.
Snow leopards are found in just 12 countries across Central and South Asia. India is home to one of the world’s largest populations, with a nationwide survey in 2023 – the first comprehensive count ever carried out in the country – estimating more than 700 animals, .
One of the places they roam is around Kibber village in Himachal Pradesh state’s Spiti Valley, a stark, high-altitude cold desert along the Himalayan belt. Here, snow leopards are often called the “ghosts of the mountains”, slipping silently across rocky slopes and rarely revealing themselves.
For generations, the animals were seen largely as a threat, for attacking livestock. But attitudes in Kibber and neighbouring villages are beginning to shift, as people increasingly recognise the snow leopard’s role as a top predator in the food chain and its importance in maintaining the region’s fragile mountain ecosystem.
Nearly a dozen local women are now working alongside the Himachal Pradesh forest department and conservationists to track and protect the species, playing a growing role in conservation efforts.
Locally, the snow leopard is known as Shen and the women call their group “Shenmo”. Trained to install and monitor camera traps, they handle devices fitted with unique IDs and memory cards that automatically photograph snow leopards as they pass.
“Earlier, men used to go and install the cameras and we kept wondering why couldn’t we do it too,” says Lobzang Yangchen, a local coordinator working with a small group supported by the non-profit Nature Conservation Foundation (NCF) in collaboration with the forest department.
Yangchen was among the women who helped collect data for Himachal Pradesh’s snow leopard survey in 2024, which found that the state was home to 83 snow leopards – up from 51 in 2021.

The survey documented snow leopards and 43 other species using camera traps spread across an area of nearly 26,000sq km (10,000sq miles). Individual leopards were identified by the unique rosette patterns on their fur, a standard technique used for spotted big cats. The findings are now feeding into wider conservation and habitat-management plans.
“Their contribution was critical to identifying individual animals,” says Goldy Chhabra, deputy conservator of forests with the Spiti Wildlife Division.
Collecting the data is demanding work. Most of it takes place in winter, when heavy snowfall pushes snow leopards and their prey to lower altitudes, making their routes easier to track.
On survey days, the women wake up early, finish household chores and gather at a base camp before travelling by vehicle as far as the terrain allows. From there, they trek several kilometres to reach camera sites, often at altitudes above 14,000ft (4,300m), where the thin air makes even simple movement exhausting.
The BBC accompanied the group on one such trek in December. After hours of walking in biting cold, the women suddenly stopped on a narrow trail.
Yangchen points to pugmarks in the dust: “This shows the snow leopard has been here recently. These pugmarks are fresh.”

Along with pugmarks, the team looks for other signs, including scrapes and scent‑marking spots, before carefully fixing a camera to a rock along the trail.
One woman then carries out a “walk test”, crawling along the path to check whether the camera’s height and angle will capture a clear image.
The group then moves on to older sites, retrieving memory cards and replacing batteries installed weeks earlier.
By mid-afternoon, they return to camp to log and analyse the images using specialised software – tools many had never encountered before.
“I studied only until grade five,” says Chhering Lanzom. “At first, I was scared to use the computer. But slowly, we learned how to use the keyboard and mouse.”
The women joined the camera-trapping programme in 2023. Initially, conservation was not their motivation. But winters in the Spiti Valley are long and quiet, with little agricultural work to fall back on.
“At first, this work on snow leopards didn’t interest us,” Lobzang says. “We joined because we were curious and we could earn a small income.”
The women earn between 500 ($5.46; £4) and 700 rupees a day.
But beyond the money, the work has helped transform how the community views the animal.
“Earlier, we thought the snow leopard was our enemy,” says Dolma Zangmo, a local resident. “Now we think their conservation is important.”
Alongside survey work, the women help villagers access government insurance schemes for their livestock and promote the use of predator‑proof corrals – stone or mesh enclosures that protect animals at night.
Their efforts come at a time of growing recognition for the region. Spiti Valley has recently been included in the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve, a Unesco-recognised network aimed at conserving fragile ecosystems while supporting local livelihoods.
As climate change reshapes the fragile trans-Himalayan landscape, conservationists say such community participation will be crucial to safeguarding species like the snow leopard.
“Once communities are involved, conservation becomes more sustainable,” says Deepshikha Sharma, programme manager with NCF’s High Altitudes initiative.
“These women are not just assisting, they are becoming practitioners of wildlife conservation and monitoring,” she adds.
As for the women, their work makes them feel closer to their home, the village and the mountains that raised them, they say.
“We were born here, this is all we know,” Lobzang says. “Sometimes we feel afraid because these snow leopards are after all predatory animals, but this is where we belong.”
[BBC]
Features
Freedom for giants: What Udawalawe really tells about human–elephant conflict

If elephants are truly to be given “freedom” in Udawalawe, the solution is not simply to open gates or redraw park boundaries. The map itself tells the real story — a story of shrinking habitats, broken corridors, and more than a decade of silent but relentless ecological destruction.
“Look at Udawalawe today and compare it with satellite maps from ten years ago,” says Sameera Weerathunga, one of Sri Lanka’s most consistent and vocal elephant conservation activists. “You don’t need complicated science. You can literally see what we have done to them.”
What we commonly describe as the human–elephant conflict (HEC) is, in reality, a land-use conflict driven by development policies that ignore ecological realities. Elephants are not invading villages; villages, farms, highways and megaprojects have steadily invaded elephant landscapes.
Udawalawe: From Landscape to Island
Udawalawe National Park was once part of a vast ecological network connecting the southern dry zone to the central highlands and eastern forests. Elephants moved freely between Udawalawe, Lunugamvehera, Bundala, Gal Oya and even parts of the Walawe river basin, following seasonal water and food availability.
Today, Udawalawe appears on the map as a shrinking green island surrounded by human settlements, monoculture plantations, reservoirs, electric fences and asphalt.
“For elephants, Udawalawe is like a prison surrounded by invisible walls,” Sameera explains. “We expect animals that evolved to roam hundreds of square nationakilometres to survive inside a box created by humans.”
Elephants are ecosystem engineers. They shape forests by dispersing seeds, opening pathways, and regulating vegetation. Their survival depends on movement — not containment. But in Udawalawa, movement is precisely what has been taken away.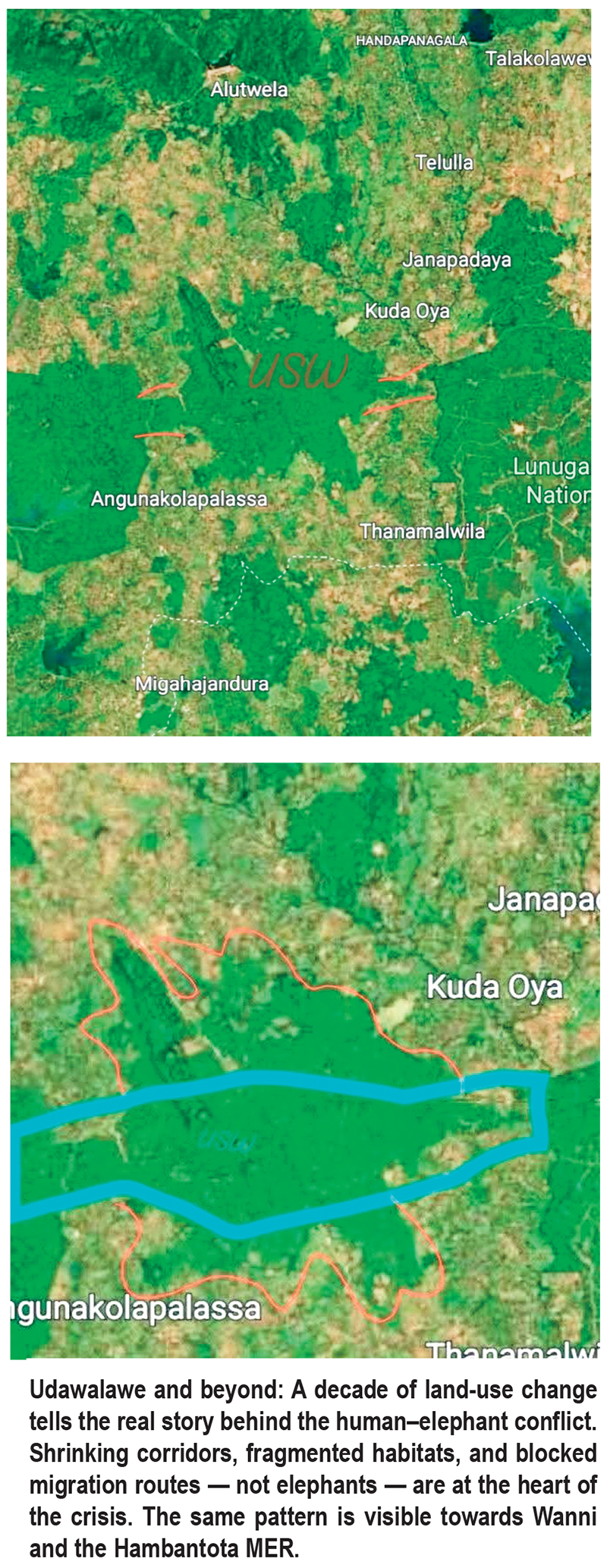
Over the past decade, ancient elephant corridors have been blocked or erased by:
Irrigation and agricultural expansion
Tourism resorts and safari infrastructure
New roads, highways and power lines
Human settlements inside former forest reserves
“The destruction didn’t happen overnight,” Sameera says. “It happened project by project, fence by fence, without anyone looking at the cumulative impact.”
The Illusion of Protection
Sri Lanka prides itself on its protected area network. Yet most national parks function as ecological islands rather than connected systems.
“We think declaring land as a ‘national park’ is enough,” Sameera argues. “But protection without connectivity is just slow extinction.”
Udawalawe currently holds far more elephants than it can sustainably support. The result is habitat degradation inside the park, increased competition for resources, and escalating conflict along the boundaries.
“When elephants cannot move naturally, they turn to crops, tanks and villages,” Sameera says. “And then we blame the elephant for being a problem.”
The Other Side of the Map: Wanni and Hambantota
Sameera often points to the irony visible on the very same map. While elephants are squeezed into overcrowded parks in the south, large landscapes remain in the Wanni, parts of Hambantota and the eastern dry zone where elephant density is naturally lower and ecological space still exists.
“We keep talking about Udawalawe as if it’s the only place elephants exist,” he says. “But the real question is why we are not restoring and reconnecting landscapes elsewhere.”
The Hambantota MER (Managed Elephant Reserve), for instance, was originally designed as a landscape-level solution. The idea was not to trap elephants inside fences, but to manage land use so that people and elephants could coexist through zoning, seasonal access, and corridor protection.
“But what happened?” Sameera asks. “Instead of managing land, we managed elephants. We translocated them, fenced them, chased them, tranquilised them. And the conflict only got worse.”
The Failure of Translocation
For decades, Sri Lanka relied heavily on elephant translocation as a conflict management tool. Hundreds of elephants were captured from conflict zones and released into national parks like Udawalawa, Yala and Wilpattu.
The logic was simple: remove the elephant, remove the problem.
The reality was tragic.
“Most translocated elephants try to return home,” Sameera explains. “They walk hundreds of kilometres, crossing highways, railway lines and villages. Many die from exhaustion, accidents or gunshots. Others become even more aggressive.”
Scientific studies now confirm what conservationists warned from the beginning: translocation increases stress, mortality, and conflict. Displaced elephants often lose social structures, familiar landscapes, and access to traditional water sources.
“You cannot solve a spatial problem with a transport solution,” Sameera says bluntly.
In many cases, the same elephant is captured and moved multiple times — a process that only deepens trauma and behavioural change.
Freedom Is Not About Removing Fences
The popular slogan “give elephants freedom” has become emotionally powerful but scientifically misleading. Elephants do not need symbolic freedom; they need functional landscapes.
Real solutions lie in:
Restoring elephant corridors
Preventing development in key migratory routes
Creating buffer zones with elephant-friendly crops
Community-based land-use planning
Landscape-level conservation instead of park-based thinking
“We must stop treating national parks like wildlife prisons and villages like war zones,” Sameera insists. “The real battlefield is land policy.”
Electric fences, for instance, are often promoted as a solution. But fences merely shift conflict from one village to another.
“A fence does not create peace,” Sameera says. “It just moves the problem down the line.”
A Crisis Created by Humans
Sri Lanka loses more than 400 elephants and nearly 100 humans every year due to HEC — one of the highest rates globally.
Yet Sameera refuses to call it a wildlife problem.
“This is a human-created crisis,” he says. “Elephants are only responding to what we’ve done to their world.”
From expressways cutting through forests to solar farms replacing scrublands, development continues without ecological memory or long-term planning.
“We plan five-year political cycles,” Sameera notes. “Elephants plan in centuries.”
The tragedy is not just ecological. It is moral.
“We are destroying a species that is central to our culture, religion, tourism and identity,” Sameera says. “And then we act surprised when they fight back.”
The Question We Avoid Asking
If Udawalawe is overcrowded, if Yala is saturated, if Wilpattu is bursting — then the real question is not where to put elephants.
The real question is: Where have we left space for wildness in Sri Lanka?
Sameera believes the future lies not in more fences or more parks, but in reimagining land itself.
“Conservation cannot survive as an island inside a development ocean,” he says. “Either we redesign Sri Lanka to include elephants, or one day we’ll only see them in logos, statues and children’s books.”
And the map will show nothing but empty green patches — places where giants once walked, and humans chose. roads instead.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
Challenges faced by the media in South Asia in fostering regionalism

 SAARC or the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation has been declared ‘dead’ by some sections in South Asia and the idea seems to be catching on. Over the years the evidence seems to have been building that this is so, but a matter that requires thorough probing is whether the media in South Asia, given the vital part it could play in fostering regional amity, has had a role too in bringing about SAARC’s apparent demise.
SAARC or the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation has been declared ‘dead’ by some sections in South Asia and the idea seems to be catching on. Over the years the evidence seems to have been building that this is so, but a matter that requires thorough probing is whether the media in South Asia, given the vital part it could play in fostering regional amity, has had a role too in bringing about SAARC’s apparent demise.
That South Asian governments have had a hand in the ‘SAARC debacle’ is plain to see. For example, it is beyond doubt that the India-Pakistan rivalry has invariably got in the way, particularly over the past 15 years or thereabouts, of the Indian and Pakistani governments sitting at the negotiating table and in a spirit of reconciliation resolving the vexatious issues growing out of the SAARC exercise. The inaction had a paralyzing effect on the organization.
Unfortunately the rest of South Asian governments too have not seen it to be in the collective interest of the region to explore ways of jump-starting the SAARC process and sustaining it. That is, a lack of statesmanship on the part of the SAARC Eight is clearly in evidence. Narrow national interests have been allowed to hijack and derail the cooperative process that ought to be at the heart of the SAARC initiative.
However, a dimension that has hitherto gone comparatively unaddressed is the largely negative role sections of the media in the SAARC region could play in debilitating regional cooperation and amity. We had some thought-provoking ‘takes’ on this question recently from Roman Gautam, the editor of ‘Himal Southasian’.
Gautam was delivering the third of talks on February 2nd in the RCSS Strategic Dialogue Series under the aegis of the Regional Centre for Strategic Studies, Colombo, at the latter’s conference hall. The forum was ably presided over by RCSS Executive Director and Ambassador (Retd.) Ravinatha Aryasinha who, among other things, ensured lively participation on the part of the attendees at the Q&A which followed the main presentation. The talk was titled, ‘Where does the media stand in connecting (or dividing) Southasia?’.
Gautam singled out those sections of the Indian media that are tamely subservient to Indian governments, including those that are professedly independent, for the glaring lack of, among other things, regionalism or collective amity within South Asia. These sections of the media, it was pointed out, pander easily to the narratives framed by the Indian centre on developments in the region and fall easy prey, as it were, to the nationalist forces that are supportive of the latter. Consequently, divisive forces within the region receive a boost which is hugely detrimental to regional cooperation.
Two cases in point, Gautam pointed out, were the recent political upheavals in Nepal and Bangladesh. In each of these cases stray opinions favorable to India voiced by a few participants in the relevant protests were clung on to by sections of the Indian media covering these trouble spots. In the case of Nepal, to consider one example, a young protester’s single comment to the effect that Nepal too needed a firm leader like Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi was seized upon by the Indian media and fed to audiences at home in a sensational, exaggerated fashion. No effort was made by the Indian media to canvass more opinions on this matter or to extensively research the issue.
In the case of Bangladesh, widely held rumours that the Hindus in the country were being hunted and killed, pogrom fashion, and that the crisis was all about this was propagated by the relevant sections of the Indian media. This was a clear pandering to religious extremist sentiment in India. Once again, essentially hearsay stories were given prominence with hardly any effort at understanding what the crisis was really all about. There is no doubt that anti-Muslim sentiment in India would have been further fueled.
Gautam was of the view that, in the main, it is fear of victimization of the relevant sections of the media by the Indian centre and anxiety over financial reprisals and like punitive measures by the latter that prompted the media to frame their narratives in these terms. It is important to keep in mind these ‘structures’ within which the Indian media works, we were told. The issue in other words, is a question of the media completely subjugating themselves to the ruling powers.
Basically, the need for financial survival on the part of the Indian media, it was pointed out, prompted it to subscribe to the prejudices and partialities of the Indian centre. A failure to abide by the official line could spell financial ruin for the media.
A principal question that occurred to this columnist was whether the ‘Indian media’ referred to by Gautam referred to the totality of the Indian media or whether he had in mind some divisive, chauvinistic and narrow-based elements within it. If the latter is the case it would not be fair to generalize one’s comments to cover the entirety of the Indian media. Nevertheless, it is a matter for further research.
However, an overall point made by the speaker that as a result of the above referred to negative media practices South Asian regionalism has suffered badly needs to be taken. Certainly, as matters stand currently, there is a very real information gap about South Asian realities among South Asian publics and harmful media practices account considerably for such ignorance which gets in the way of South Asian cooperation and amity.
Moreover, divisive, chauvinistic media are widespread and active in South Asia. Sri Lanka has a fair share of this species of media and the latter are not doing the country any good, leave alone the region. All in all, the democratic spirit has gone well into decline all over the region.
The above is a huge problem that needs to be managed reflectively by democratic rulers and their allied publics in South Asia and the region’s more enlightened media could play a constructive role in taking up this challenge. The latter need to take the initiative to come together and deliberate on the questions at hand. To succeed in such efforts they do not need the backing of governments. What is of paramount importance is the vision and grit to go the extra mile.
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoHayleys Mobility ushering in a new era of premium sustainable mobility
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoSLIM-Kantar People’s Awards 2026 to recognise Sri Lanka’s most trusted brands and personalities
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoAdvice Lab unveils new 13,000+ sqft office, marking major expansion in financial services BPO to Australia
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoArpico NextGen Mattress gains recognition for innovation
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoAltair issues over 100+ title deeds post ownership change
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoGovt. provoking TUs
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoSri Lanka opens first country pavilion at London exhibition
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoAll set for Global Synergy Awards 2026 at Waters Edge















