Features
The most extreme hurricanes in history

Hurricane Melissa hit Jamaica with the strongest wind speeds the Caribbean nation has ever experienced. Here’s how it compares to other record-breaking storms.
In October 2025, category five Hurricane Melissa made landfall in south-western Jamaica, with winds of 185 mph [295 kmph], making it the strongest storm of the year in terms of wind speed and one of the most powerful Atlantic storms on record. The World Meteorological Organization described it as the ‘storm of the century’ for Jamaica and the National Hurricane Center warned that it would bring “catastrophic and life-threatening flash flooding”.
Here we look at some of history’s other powerful and destructive hurricanes.
The most lives lost: The Great Hurricane of 1780
On the night of 9 October 1780, after a balmy day on the Caribbean island of Barbados, rain began to fall. The next morning a breeze pickedup – and by 6pm a hurricane slammed into the island at full force. Known as the Great Hurricane, it remains the deadliest Atlantic hurricane ever recorded. Estimates of the death toll range between 20,000 and 27,500.
The hurricane whipped across the land, with winds of likely more than 200mph (322km/h) that were so loud people couldn’t hear their own voices. Little was left but nud, debris, dead cattle and rotting corpses.
Leaving Barbados, the Great Hurricane moved past Martinique, Saint Lucia, and Sint Eustatius. Waves reaching 25 ft [7m] high washed whole villages into the sea and entire fleets of British and French naval ships – along with the thousands of people aboard – were lost to the bottom of the ocean.

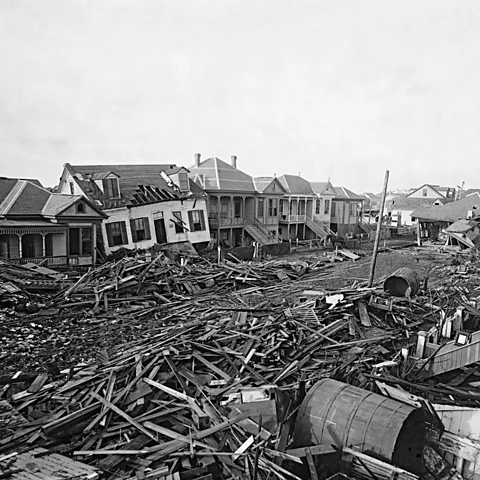
The deadliest storm in US history was the Galveston hurricane of 1900. It passed over the Gulf of Mexico in early September 1900, strengthening to a category four hurricane before slamming into Galvestone Texas, on 6 September.
“We kept running into so many dead bodies that I had to go forward with a pike and shove [them] out of the way… it was the most horrible thing I have ever seen,” a surviving fisherman is reported to have said. The storm is estimated to have caused between 6,000 and 8,000 deaths.

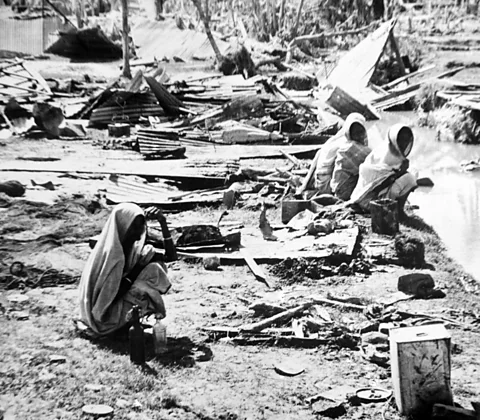
More deadly storms still have taken place outside the Atlantic basin, where these storms are known as cyclones or typhoons rather than hurricanes. The Bhola Cyclone of 1970 collided with north-east India and what was then East Pakistan (present-day Bangladesh). It brought with it a devastating storm surge of 35ft (10.5m). In total, as many as 500,000 people are thought to have been killed by cyclone.

The most destructive hurricanes: Katrina and Mitch
How you measure the damage caused by hurricanes is a matter of perspective. For the people who lose property, livelihoods and loved ones, the storm that has just swept over them was devastating. But if you examine it purely in terms of the number of properties destroyed, two hurricanes stand out – Katrina and Mitch.
The main reason why Hurricane Katrina ranks as the costliest hurricane in history is the sheer scale of the destruction it left in its wake across the south-east US. It is estimated that between 217,000 and 300,000 homes were destroyed or left uninhabitable by the storm. Wind speeds of up to 140mph [225kmph] careered into south-east Louisiana. The storm surge reached 25-28 ft[7.68.5m] above normal tide levels along the Mississippi coast and 10-20ft [3m-6.1m] above normal tide levels along the south-east Louisiana coast. In New Orleans, the driving waves and storm surge smashed through the levees intended to protect the city.

Overall, nearly 0% of the city was inundated with floodwater that reached 6m (20ft) deep while 59 tornadoes propagating from the storm spread further damage across eight states.
This damage made Hurricane Katrina the costliest hurricane on record to hit the US, resulting in a total of $201.3bn (£148.3bn) in damage, when adjusted for inflation to 2024 US dollars. After Katrina, the second costliest was Hurricane Harvey, which caused $160bn (£118bn) in damage when it made landfall in Texas and Louisiana.
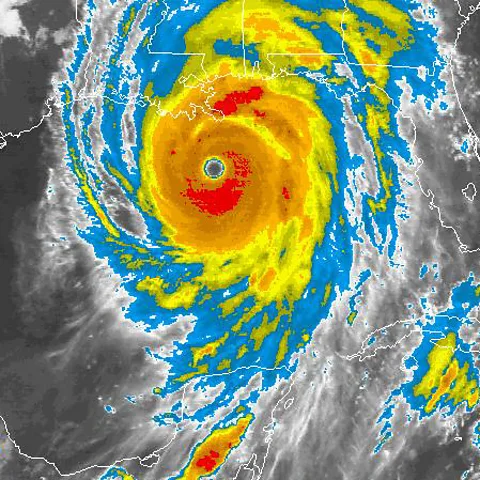
But nearly seven years earlier, another hurricane caused almost as much destruction as Katrina.
In the US, Hurricane Mitch left behind relatively minor damage – 645 homes in Florida were destroyed by the storm as it swept across the Gulf of Mexico from the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico in October 1998. By then, however, it had already done its worst.

A week earlier Mitch had slammed into Honduras, obliterating entire communities as it cut a swathe of destruction across Central America. This storm was a monster – a category five hurricane that still ranks as one of the most intense on record.
By the time it hit Honduras, it had weakened to a category one hurricane, but on making landfall it got stuck, hovering over Honduras and dumping huge amounts of rain. The flooding and landslides that followed left between 10,000 and 19,000 people dead across Honduras, Nicaragua, Guatemala, Belize and El Salvador. At least 200,000 homes were demolished or severly damaged by the storm. In Honduras alone, 70,000 homes and 92 bridges were destroyed, with whole villages being swallowed by rivers of mud that swept down mountainsides. The UN estimated that, in all, more than half a million people lost their homes.

Highest wind speeds
You could be forgiven for assuming that the most powerful storms are the ones that cause the most damage and take the most lives. That’s not always the case.
Hurricane Patricia was the 24th storm of the 2015 hurricane season, and formed near the Gulf of Tehuantepec off Mexico’s southern coast. Favourable conditions meant it grew from a tropical storm to a category five hurricane in just 24 hours.
On 23 October, Patricia’s highest wind speed sustained over 10 seconds was 221mph (356km/h), measured from an aircraft in flight (speeds of 210mph, or 338km/h, were measured at ground level). It was the highest speed ever recorded in the Western Hemisphere and as intense as one of the most powerful storms ever recorded, 1961’s Typhoon Nancy.

Patricia’s path cut through relatively unpopulated parts of Mexico, missing large cities, which limited its frath toll. It also dramatically weakened after it hit the Mexican coast, though it made landfall with recorded wind speeds as high as 265kmh [165mph]. The effect of Mexico’s mountainous terrain further weakened Patricia, and by 24 October it had dwindled to almost nothing.
Despite its intensity, Patricia’s death toll was surprisingly small – only two people died directly as a result of the storm, with four additional indirect deaths, according to the Us’s National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration.
Rapid intensification
This week, Hurricane Erin became the Atlantic’s first hurricane of 2025, skirting the US mainland leading forecasters to issue warnings to surfers about rip currents. It is thought to be one of the most rapidly intensifying hurricanes on record so early in the season. The strongest storms tend to occur later year, after 1 September. Erin went gtpm category one hurricanr to a category five in just over 24 hours, before weakening again to a category two storm.
Rapid intensification is an increase in the maximum sustained winds of a tropical cyclone of at least 30 knots (35 mph) in a 24 hour period, according to the US’s National Weather Service Such fast-intensifying hurricanes can be particularly dangerous, since people have less time to prepare for them.

Erin is not the only storm to rapidly intensify in recent years. In 2024, Hurricane Milton became the fastest Atlantic sorm ever to intensify from a tropical depression to a category five hurricane. The same year, Hurricane Beryl broke a record as the fastest ever Atlantic storm occurring in June or early July to intensify from a tropical depression to a hurricane. In 2023, meanwhile, Hurricane Lee and Hurricane Jova stunned scientists with their sudden intensification, especially considering they did so during an El Nino, which normally suppresses hurricane activity in the Atlantic.
Of course hurricanes have always intensified at different rates. Two other Atlantic hurricanes – Felix in 2007 and Wilma in 2005 – are also noteworthy for their especially rapid intensification. But research has shown overall intensification rates have significantly increased in recent years due to global warming, a trend which is set to continue. It’s all down to the warmer sea surfaces these storms pass over due to climate change – Erin, for example, passed over waters that were on average, 1.1C warmer due to climate change.
[This story was updated on 28.10.25 to include a reference to Hurricane Melissa].
[BBC
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
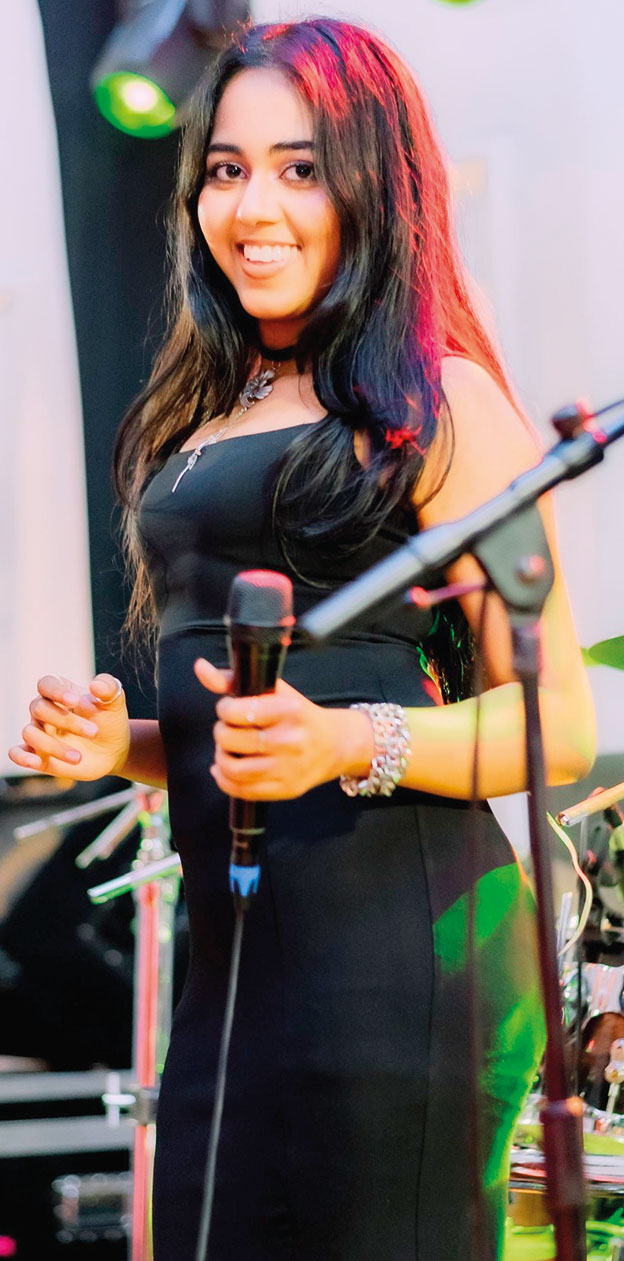
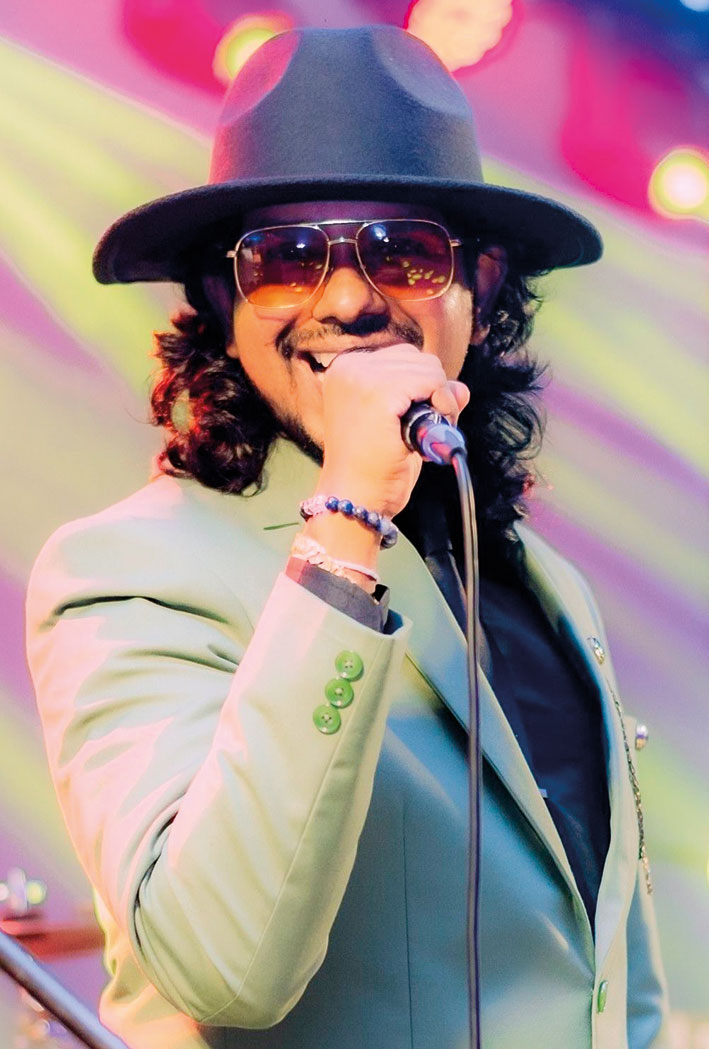
Talento … oozing with talent
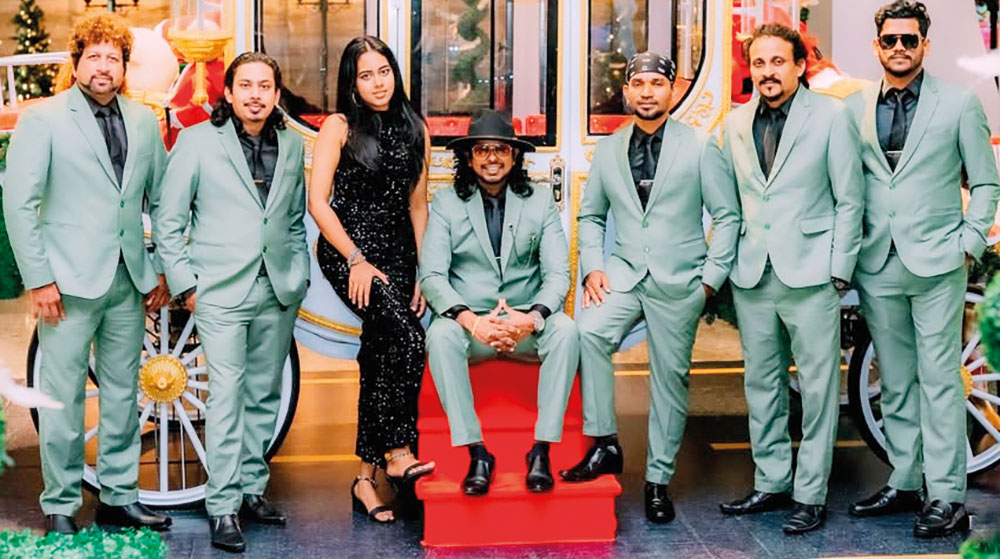

 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
Features
Special milestone for JJ Twins
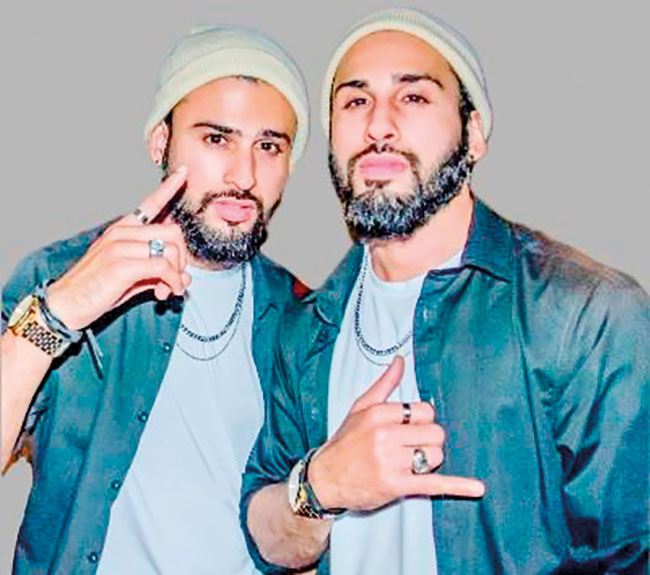

The JJ Twins, the Sri Lankan musical duo, performing in the Maldives, and known for blending R&B, Hip Hop, and Sri Lankan rhythms, thereby creating a unique sound, have come out with a brand-new single ‘Me Mawathe.’
In fact, it’s a very special milestone for the twin brothers, Julian and Jason Prins, as ‘Me Mawathe’ is their first ever Sinhala song!
‘Me Mawathe’ showcases a fresh new sound, while staying true to the signature harmony and emotion that their fans love.
This heartfelt track captures the beauty of love, journey, and connection, brought to life through powerful vocals and captivating melodies.
It marks an exciting new chapter for the JJ Twins as they expand their musical journey and connect with audiences in a whole new way.
Their recent album, ‘CONCLUDED,’ explores themes of love, heartbreak, and healing, and include hits like ‘Can’t Get You Off My Mind’ and ‘You Left Me Here to Die’ which showcase their emotional intensity.
Readers could stay connected and follow JJ Twins on social media for exclusive updates, behind-the-scenes moments, and upcoming releases:
Instagram: http://instagram.com/jjtwinsofficial
TikTok: http://tiktok.com/@jjtwinsmusic
Facebook: http://facebook.com/jjtwinssingers
YouTube: http://youtube.com/jjtwins
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-
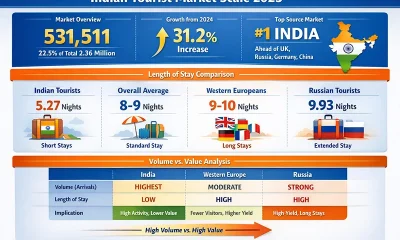
 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans















