Features
The altar on which we sacrifice our children

By Dr. Ranil Senanayake
It is stated that Cuba, “is a small country which has for almost 50 years refused to relinquish its national sovereignty to the greatest superpower on the planet”. Sri Lanka is the opposite; ‘it is a small country which has for almost 50 years worked to relinquish its national sovereignty for loans from any superpower on the planet”. The most fundamental cause of becoming such a loser, was the linking of ‘development’ to the consumption of fossil energy. Thus, Sri Lanka can serve as a classic case study on how to become addicted to external inputs and loose independence.
In Sri Lanka, in December 1979, an official communiqué was issued by the Government and displayed in the nation’s newspapers stating, “No oil means no development, and less oil, less development. It is oil that keeps the wheels of development moving”. This defines with clarity what is to be considered development by the policy makers of that Nation. Here was a fundamental and fateful decision that cast a deadly policy framework for the nation. The energy source that was to drive the national economy would be fossil. The increasing addiction to fossil fuels (Coal, Oil, Gas) is clearly seen in the growth of oil and gas imports. Even today, that same policy framework and its adherents continue. The public discussions on the irrationality of clinging to coal, oil and gas for the development of our power needs in the face of the modern technologies, clearly demonstrate serious flaws in the current energy policy.
After the heat energy of biomass used for the hearth and local industry, electrical energy is the fundamental force that drives modern civilisation. While the sources of this energy were many, the political/industrial nexus ensured that the energy source was restricted to fossil fuels. The planetary crisis with climate change has forced us to look at developing technologies that reduce our reliance on fossil fuels as source of energy to generate electricity. Today there is a choice of from a multitude of other sources, hydro, solar, wind, bio, tidal, etc. All of them being ultimately driven by the power of the Sun.
With such developments, the old arguments that ‘economies need to industrialise in order to reduce poverty, but industrialisation leads to emissions’ rings hollow. Industrialisation, if so desired, need not lead to emissions, if modern technologies are used and a caring government is in place. A vision of development based on the profligate use of fossil fuel, may never be attainable. However, a vision of power for our homes and industry, based on ‘renewable’ sources of energy, is attainable. Indeed, one indicator of ‘development’ could be ‘the per capita consumption of power’ if that consumption of power is non fossil in generation sustainable development goals could be reached easily.
The consumption of power is a double-edged sword. While it will improve the quality of life, it will like a drug, create dependency on that level of input to maintain that quality of life. This relationship has been exploited by politicians and salesmen to promise an increasing supply of power, without considering the cost to the future. To a nation that is rapidly modernizing, there is a great danger of investing in fossil fuel dependent infrastructure and centralised, energy production.
It is commonsense that, as the demand accelerates and price increases, allowing fossil energy-based power production to move to more expensive, ever more problematical and polluting sources such as coal, fracking or high sulphur oils.
The fact that all fossil fuel dependent countries are in deep trouble is indicated by two trends. One is that the cost of fossil fuel is a driving factor of inflation. The other is that, in a warming world, the call for punitive taxes on the use of fossil fuel will get stronger with each climate crisis. At such a time, if development policy focuses on fossil energy based acquisitive consumerism, there lies a recipe for ‘the perfect storm’ of debt, suffering and despair, in a resource hungry world.
For all the commitments on paper, the inequality of health, wealth and trade the world over, continue to rise. The ethic of ‘He/She who consumes the most is the best’ still rules the world and propels us, blindly, to a frightening future.
Commenting on the bright displays of advertising lights of consumerist London 1920, A.M. Hocart Ceylon’s Archaeological Commissioner observed that, ” Every one of them has been placed there in chaotic confusion by a cold calculating purpose. Each one is designed to make a gaping crowd desire what they never dreamt of desiring before and what they had been perfectly happy not to desire. It is intended to destroy that happiness and take away from the soul its rest until it has satisfied the newborn desire.” The creation of desire has not slowed any and inequality not lessened. It is this model of development has brought us to this precarious present.
Develop we must, but cautiously – with the full awareness of the long-term consequences of each process accepted.
Development must be determined by protecting the fundamental rights of the people and of the future generations. Clean air, clean water, access to food and freedom from intoxication, are some of these fundamental rights. Any activity that claims to be part of a development process must address these, among other social and legal fundamental needs.
The toxic substance used in electricity generation is one half of the altar, the toxins used in the production of our foods, fibre and medicines is the other.
Agriculture
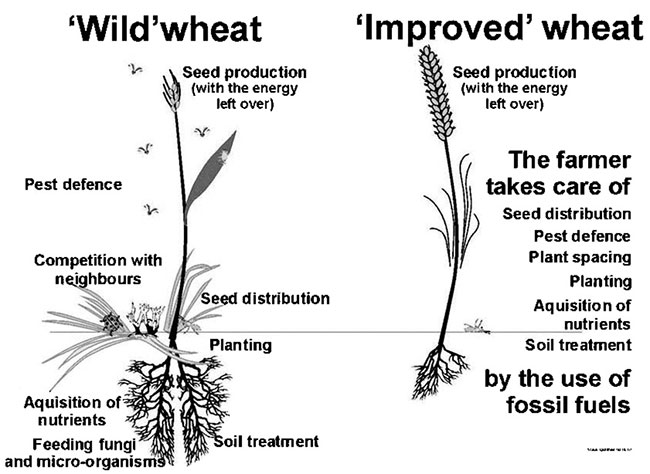
Much has been written about the pros and cons of ‘modern agriculture’ the focus always being on the levels of crop production or on the ‘feeding the hungry’. Irrespective of the global scandal of feeding much of the crop to livestock and industry, when people still go hungry. It is salutary to examine the basis of the crop increase gained by the so-called ‘Green Revolution’ (fig 1). The natural defences and modes of feeding of the plant have been done away with, these needs now being supplied by the farmer through the use of fossil fuels. Competition and predation by pests are taken care of by chemicals and the roots and shots made small so that there will be much energy left over for seed production. Traditionally ‘improved’ seeds perform well without such high fossil based inputs, but a problem with modern agriculture is that farmers are forced to use ‘modern’ varieties and methods where increases in productivity are only made possible by a high input of fossil energy.
Fig 1. Traditional Wheat and Improved Wheat
The ecological impact of increasing energy input into a system has been well documented. It is an ecological axiom that ; In any ecosystem, an increase in the flow of energy tends to organize and simplify that ecosystem, with the destruction of many homeostatic mechanisms of the original system. Field studies on identified ecosystems at various levels of organization have confirmed the loss of original stability following a large influx of energy into those systems. A good example is provided by experiments which looked at the effects of sewage (as an energy source) as it was added to a stream whose biotic composition was known. The effect was to drastically reduce the number of species in the original community, producing a new community made up of large populations
of very few of the original species. Studies of insect communities, have shown that pest outbreaks are characteristic of systems with lowered species diversity. The application of fertilizer or the use of mechanical energy in a field situation produces the similar ecological effects.
An increase in the input of energy to an ecosystem often provides a useful measure by which ecosystem modification can be addressed. Thus in a heavily energy dependent agricultural system the natural or biological system has been dispensed with and an artificial environment has been created to allow production (fig 1) . Such a system of production is sustainable only as long as the inputs are provided, it also raises many biological questions, for this system is clearly not sustainable in a biological sense. It also raises economic questions, especially in regard to input costs and subsidies. Further, this process has been demonstrated to be increasingly dependent on a steadily increasing quantum of energy input to produce a unit of output. It is estimated that for US agriculture, fossil energy based production input, accounts for over twice the amount of energy gained by eating a potato. The dependence on fossil energy for food production increases with an increase of fossil led, industrial agriculture. The demand for tractors, transport and processing, all based on fossil energy will grow. As this process keeps increasing, the fossil carbon footprint of the food we eat will also enlarge.
So, much the same as in the area of power for the generation of electricity, power to ensure sustainable food production has also fallen prey to fossil fuel. It is in this context that we should examine the role of fossil fuels in today’s development vision.
What are the assumptions and costs?
“It is oil that keeps the wheels of development moving” says the Government of Sri Lanka who have no oil of their own and has to depend on imports for every drop.
“Oil represents the spirits of the dead, to ask it for power you sacrifice your children” says the Shuar, an Amazonian tribe under whose feet lie reservoirs of oil that they will not allow drilling for.
Indeed, the reality of climate change and acceleration of development diseases would seem to justify the concern of the Shuar that, “to ask it for power means sacrificing the future of our children”. Are the unlettered Shuar more sensitive to global and human needs than the wicked Governments throughout the world, who profit from extracting, promoting and selling fossil fuels as the path to development ?
The bottom-line question is “Is the current development policy increasing the national dependency on fossil fuels? “. If the answer is yes, and everything we see about us seems to confirm that reality, we are being herded into an ‘Energy Trap’ where we will become totally reliant on fossil fuels to sustain our society. Totally dependent on whoever supplies those fuels. Not the way to develop into an independent nation !
The price of addiction is to neglect of the well being of the public, in pursuit of power. In the rush to establish dirty coal fired power plants, they have been sited where the maximum damage to public health and our national heritage could be compromised. Perhaps India’s health experience with coal-fired power plants will make us think twice. So-called ‘natural gas’ is no panacea either, it comes from the same toxic ‘fossil carbon’ source. While it produces a lower volume of toxic outputs, the total output from burning it produces the same impact on climate change. Fossil fuels are biospheric toxins, they reduce the ability of living things to have a stable environment to live in. The Shuar are right, even now oil is demanding the health and well being of our children. Is the current development processes the altar on which we will sacrifice our children? Are the compliant politicians and corporate heads of fossil companies, promoting this myth of ‘development’ facilitated through fossil energy, the high priests at the altar who justify and facilitate this horrendous sacrifice ?
Features
The invisible crisis: How tour guide failures bleed value from every tourist

 (Article 04 of the 04-part series on Sri Lanka’s tourism stagnation)
(Article 04 of the 04-part series on Sri Lanka’s tourism stagnation)
If you want to understand why Sri Lanka keeps leaking value even when arrivals hit “record” numbers, stop staring at SLTDA dashboards and start talking to the people who face tourists every day: the tour guides.
They are the “unofficial ambassadors” of Sri Lankan tourism, and they are the weakest, most neglected, most dysfunctional link in a value chain we pretend is functional. Nearly 60% of tourists use guides. Of those guides, 57% are unlicensed, untrained, and invisible to the very institutions claiming to regulate quality. This is not a marginal problem. It is a systemic failure to bleed value from every visitor.
The Invisible Workforce
The May 2024 “Comprehensive Study of the Sri Lankan Tour Guides” is the first serious attempt, in decades, to map this profession. Its findings should be front-page news. They are not, because acknowledging them would require admitting how fundamentally broken the system is. The official count (April 2024): SLTDA had 4,887 licensed guides in its books:
* 1,892 National Guides (39%)
* 1,552 Chauffeur Guides (32%)
* 1,339 Area Guides (27%)
* 104 Site Guides (2%)
The actual workforce: Survey data reveals these licensed categories represent only about 75% of people actually guiding tourists. About 23% identify as “other”; a polite euphemism for unlicensed operators: three-wheeler drivers, “surf boys,” informal city guides, and touts. Adjusted for informal operators, the true guide population is approximately 6,347; 32% National, 25% Chauffeur, 16% Area, 4% Site, and 23% unlicensed.
But even this understates reality. Industry practitioners interviewed in the study believe the informal universe is larger still, with unlicensed guides dominating certain tourist hotspots and price-sensitive segments. Using both top-down (tourist arrivals × share using guides) and bottom-up (guides × trips × party size) estimates, the study calculates that approximately 700,000 tourists used guides in 2023-24, roughly one-third of arrivals. Of those 700,000 tourists, 57% were handled by unlicensed guides.
Read that again. Most tourists interacting with guides are served by people with no formal training, no regulatory oversight, no quality standards, and no accountability. These are the “ambassadors” shaping visitor perceptions, driving purchasing decisions, and determining whether tourists extend stays, return, or recommend Sri Lanka. And they are invisible to SLTDA.
The Anatomy of Workforce Failure
The guide crisis is not accidental. It is the predictable outcome of decades of policy neglect, regulatory abdication, and institutional indifference.
1. Training Collapse and Barrier to Entry Failure
Becoming a licensed National Guide theoretically requires:
* Completion of formal training programmes
* Demonstrated language proficiency
* Knowledge of history, culture, geography
* Passing competency exams
In practice, these barriers have eroded. The study reveals:
* Training infrastructure is inadequate and geographically concentrated
* Language requirements are inconsistently enforced
* Knowledge assessments are outdated and poorly calibrated
* Continuous professional development is non-existent
The result: even licensed guides often lack the depth of knowledge, language skills, or service standards that high-yield tourists expect. Unlicensed guides have no standards at all. Compare this to competitors. In Mauritius, tour guides undergo rigorous government-certified training with mandatory refresher courses. The Maldives’ resort model embeds guide functions within integrated hospitality operations with strict quality controls. Thailand has well-developed private-sector training ecosystems feeding into licensed guide pools.
2. Economic Precarity and Income Volatility
Tour guiding in Sri Lanka is economically unstable:
* Seasonal income volatility: High earnings in peak months (December-March), near-zero in low season (April-June, September)
* No fixed salaries: Most guides work freelance or commission-based
* Age and experience don’t guarantee income: 60% of guides are over 40, but earnings decline with age due to physical demands and market preference for younger, language-proficient guides
* Commission dependency: Guides often earn more from commissions on shopping, gem purchases, and restaurant referrals than from guiding fees
The commission-driven model pushes guides to prioritise high-commission shops over meaningful experiences, leaving tourists feeling manipulated. With low earnings and poor incentives, skilled guides exist in the profession while few new entrants join. The result is a shrinking pool of struggling licensed guides and rising numbers of opportunistic unlicensed operators.
3. Regulatory Abdication and Unlicensed Proliferation
Unlicensed guides thrive because enforcement is absent, economic incentives favour avoiding fees and taxes, and tourists cannot distinguish licensed professionals from informal operators. With SLTDA’s limited capacity reducing oversight, unregistered activity expands. Guiding becomes the frontline where regulatory failure most visibly harms tourist experience and sector revenues in Sri Lanka.
4. Male-Dominated, Ageing, Geographically Uneven Workforce
The guide workforce is:
* Heavily male-dominated: Fewer than 10% are women
* Ageing: 60% are over 40; many in their 50s and 60s
* Geographically concentrated: Clustered in Colombo, Galle, Kandy, Cultural Triangle—minimal presence in emerging destinations
This creates multiple problems:
* Gender imbalance: Limits appeal to female solo travellers and certain market segments (wellness tourism, family travel with mothers)
* Physical limitations: Older guides struggle with demanding itineraries (hiking, adventure tourism)
* Knowledge ossification: Ageing workforce with no continuous learning rehashes outdated narratives, lacks digital literacy, cannot engage younger tourist demographics
* Regional gaps: Emerging destinations (Eastern Province, Northern heritage sites) lack trained guide capacity
1. Experience Degradation Lower Spending
Unlicensed guides lack knowledge, language skills, and service training. Tourist experience degrades. When tourists feel they are being shuttled to commission shops rather than authentic experiences, they:
* Cut trips short
* Skip additional paid activities
* Leave negative reviews
* Do not return or recommend
The yield impact is direct: degraded experiences reduce spending, return rates, and word-of-mouth premium.

2. Commission Steering → Value Leakage
Guides earning more from commissions than guiding fees optimise for merchant revenue, not tourist satisfaction.
This creates leakage: tourism spending flows to merchants paying highest commissions (often with foreign ownership or imported inventory), not to highest-quality experiences.
The economic distortion is visible: gems, souvenirs, and low-quality restaurants generate guide commissions while high-quality cultural sites, local artisan cooperatives, and authentic restaurants do not. Spending flows to low-value, high-leakage channels.
3. Safety and Security Risks → Reputation Damage
Unlicensed guides have no insurance, no accountability, no emergency training. When tourists encounter problems, accidents, harassment, scams, there is no recourse. Incidents generate negative publicity, travel advisories, reputation damage. The 2024-2025 reports of tourists being attacked by wildlife at major sites (Sigiriya) with inadequate safety protocols are symptomatic. Trained, licensed guides would have emergency protocols. Unlicensed operators improvise.
4. Market Segmentation Failure → Yield Optimisation Impossible
High-yield tourists (luxury, cultural immersion, adventure) require specialised guide-deep knowledge, language proficiency, cultural sensitivity. Sri Lanka cannot reliably deliver these guides at scale because:
* Training does not produce specialists (wildlife experts, heritage scholars, wellness practitioners)
* Economic precarity drives talent out
* Unlicensed operators dominate price-sensitive segments, leaving limited licensed capacity for premium segments
We cannot move upmarket because we lack the workforce to serve premium segments. We are locked into volume-chasing low-yield markets because that is what our guide workforce can provide.
The way forward
Fixing Sri Lanka’s guide crisis demands structural reform, not symbolic gestures. A full workforce census and licensing audit must map the real guide population, identify gaps, and set an enforcement baseline. Licensing must be mandatory, timebound, and backed by inspections and penalties. Economic incentives should reward professionalism through fair wages, transparent fees, and verified registries. Training must expand nationwide with specialisations, language standards, and continuous development. Gender and age imbalances require targeted recruitment, mentorship, and diversified roles. Finally, guides must be integrated into the tourism value chain through mandatory verification, accountability measures, and performancelinked feedback.
The Uncomfortable Truth
Can Sri Lanka achieve high-value tourism with a low-quality, largely unlicensed guide workforce? The answer is NO. Unambiguously, definitively, NO. Sri Lanka’s guides shape tourist perceptions, spending, and satisfaction, yet the system treats them as expendable; poorly trained, economically insecure, and largely unregulated. With 57% of tourists relying on unlicensed guides, experience quality becomes unpredictable and revenue leaks into commission-driven channels.
High-yield markets avoid destinations with weak service standards, leaving Sri Lanka stuck in low-value, volume tourism. This is not a training problem but a structural failure requiring regulatory enforcement, viable career pathways, and a complete overhaul of incentives. Without professionalising guides, high-value tourism is unattainable. Fixing the guide crisis is the foundation for genuine sector transformation.
The choice is ours. The workforce is waiting.
This concludes the 04-part series on Sri Lanka’s tourism stagnation. The diagnosis is complete. The question now is whether policymakers have the courage to act.
For any concerns/comments contact the author at saliya.ca@gmail.com
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT, Malabe. The views and opinions expressed in this article are personal.)
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
Talento … oozing with talent

 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoAn efficacious strategy to boost exports of Sri Lanka in medium term
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoOverseas visits to drum up foreign assistance for Sri Lanka
















