Latest News
Thailand names third prime minister in two years
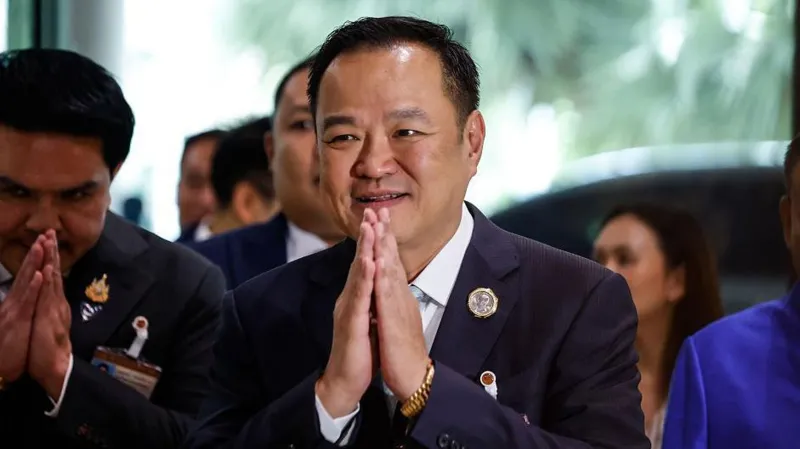

Thailand’s parliament has chosen business tycoon Anutin Charnvirakul as the country’s prime minister – the third in two years, after yet another leader was removed from office.
Paetongtarn Shinawatra, who belongs to Thailand’s most powerful political dynasty, was removed by the constitutional court last week for ethical violations over her handling of the border dispute with Cambodia.
Anutin’s Bhumjaithai party broke from the coalition led by the Shinawatras’ Pheu Thai, and secured enough support in parliament to win the premiership.
But the uncertainty may not be over for Thailand which has seen multiple administrations deposed by court interventions and military coups in the recent past.
Anutin’s rise to the premiership deals a significant blow to the Shinawatra family, which has dominated Thai politics since 2001, when Paetongtarn’s father Thaksin became PM.
On Thursday night there was intense scrutiny in Thailand of a private jet carrying Thaksin out of the country.
Early on Friday he posted on social media saying that he had flown to Dubai for medical treatment and that he intends to return in time for a 9 September hearing for a court case that could put him back in jail.
His Pheu Thai party, which emerged as a major player in the 2023 election, is now on the sidelines. It had one last remaining candidate for PM, Chaikasem Nitisiri, who has little public profile and is in poor health.
In the past the Shinawatras’ populist policies gave them wide support among lower-income Thais, but put them at odds with Bangkok’s conservative-royalist elite.
Both Thaksin, and his sister Yingluck, who served as prime minister after him, were ousted by military coups in 2006 and 2014 respectively.
When Paetongtarn became the PM, it was seen as a comeback for the family – but her dismissal suggests they have again lost favour with the conservative-royalist elite.

Paetongtarn was the fifth Thai prime minister to be removed from office by the Constitutional Court, all of them from administrations backed by her father Thaksin.
She herself took office after her predecessor was dismissed by the same court, also for an ethics violation.
And the Pheu Thai-led coalition formed the government only after the reformist party that won the election was prevented from doing so – before it was then dissolved by the Constitutional Court, and some of its leaders banned from politics for the next 10 years.
Its successor, the People’s Party, is among those currently supporting Anutin. It has the most number of seats in parliament but it is still barred from forming a government.
[BBC]
Latest News
Gold tops $5,000 for first time ever, adding to historic rally

The price of gold has risen above $5,000 (£3,659) an ounce for the first time, extending a historic rally that saw the precious metal jump by more than 60% in 2025.
It comes as tensions between the US and NATO over Greenland have added to growing concerns about financial and geopolitical uncertainty.
US President Donald Trump’s trade policies have also worried markets. On Saturday he threatened to impose a 100% tariff on Canada if it strikes a trade deal with China.
Gold and other precious metals are seen as a so-called safe-haven assets that investors buy in times of uncertainty.
Demand for gold has also been driven by a range of other factors including higher-than-usual inflation, the weak US dollar, buying by central banks around the world and as the US Federal Reserve is expected to cut interest rates again this year.
Wars in Ukraine and Gaza, as well as Washington seizing Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro, have also helped push up the price of gold.
On Friday, silver topped $100 an ounce for the first time, building on its almost 150% rise last year.
[BBC]
Latest News
U – 19 World Cup: Andrew, McKenzie deliver West Indies comfortable win
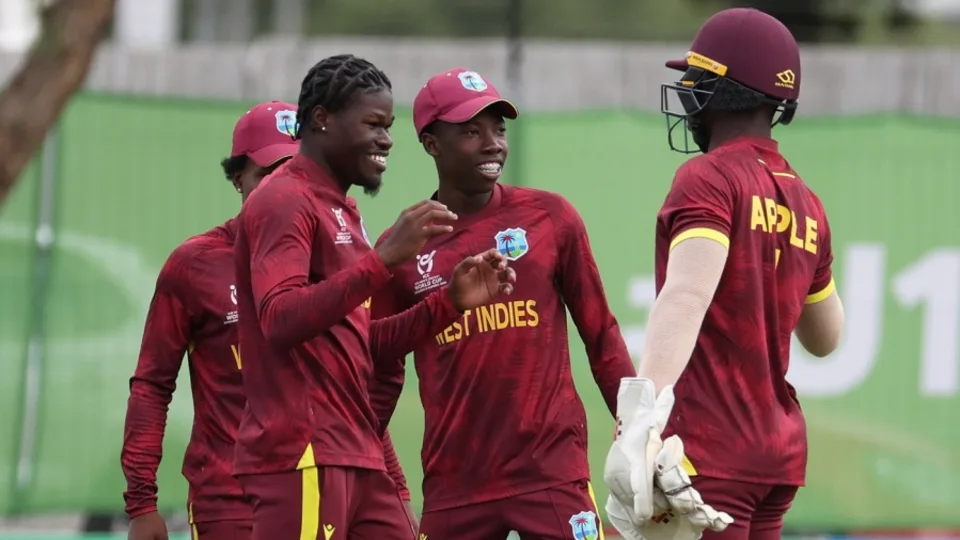

West Indies wristspinners, Micah McKenzie and Vitel Lawes, combined to take six wickets on a surface that had plenty of turn and bite to close out a rain shortned contest against Ireland. Opting to bat first, the West Indies innings had earlier been held together by keeper-batter Jewel Andrew at No. 3 – his 66 off 82 consisted of four fours and four sixes, the majority of which came in the company of Jonathan van Lange,, during their fourth-wicket partnership of 67.
Jewel departed just six overs after van Lange, in the 33rd, and the rest of the batters struggled. No one besides him managed to cross the 30-run mark. Reuben Wilson scalped up van Lange, before returning to take out two lower-order batters to finish with figures of 3 for 50, closing out the innings with West Indies bowled out for 226.
His effort, complemented by James West’s economical 2 for 24 off seven overs, gave Ireland a realistic chance at chasing down the total. West also opened the batting for Ireland and top-scored for them, hitting a 55-ball 45 that was littered with eight boundaries. By the time he was Lawes’ first victim of the innings, in the 18th over, Ireland sat at a comfortable 82 for 2.
However, the going just got worse from there: Ireland lost four wickets to McKenzie, who spun his way through the middle order. Lawes held back his best over for his final one of the match, fizzing out Oliver Riley with its first ball, and then turning the ball prodigiously against Wilson and Bruce Whaley.
Ireland were on 164 for 7 by the time they played out Lawes’ over, needing an unlikely 62 off the final ten overs. The rain had the final say when it interrupted the match and delivered the final blow to Ireland’s hopes. The DLS par score had shot way past Ireland’s total, and when no further play was possible, West Indies walked away with a convincing spin display and a 25-run win to boost their chances in the Super Sixes.
Brief scores:
West Indies Under 19s 226 in 46.5 overs (Jewel Andrew 66; Reuben Wilson 3-50, Luke Murray 2-37, James West 2-24) beat Ireland Under 19s 164 for 7 in 40 overs (James West 45; Mica McKenzie 4-36, Vitel Lawes 2-41)by 25 runs (DLS method)
[Cricinfo]
Latest News
U – 19 World Cup: Bowlers, Hogan help Australia breeze past South Africa
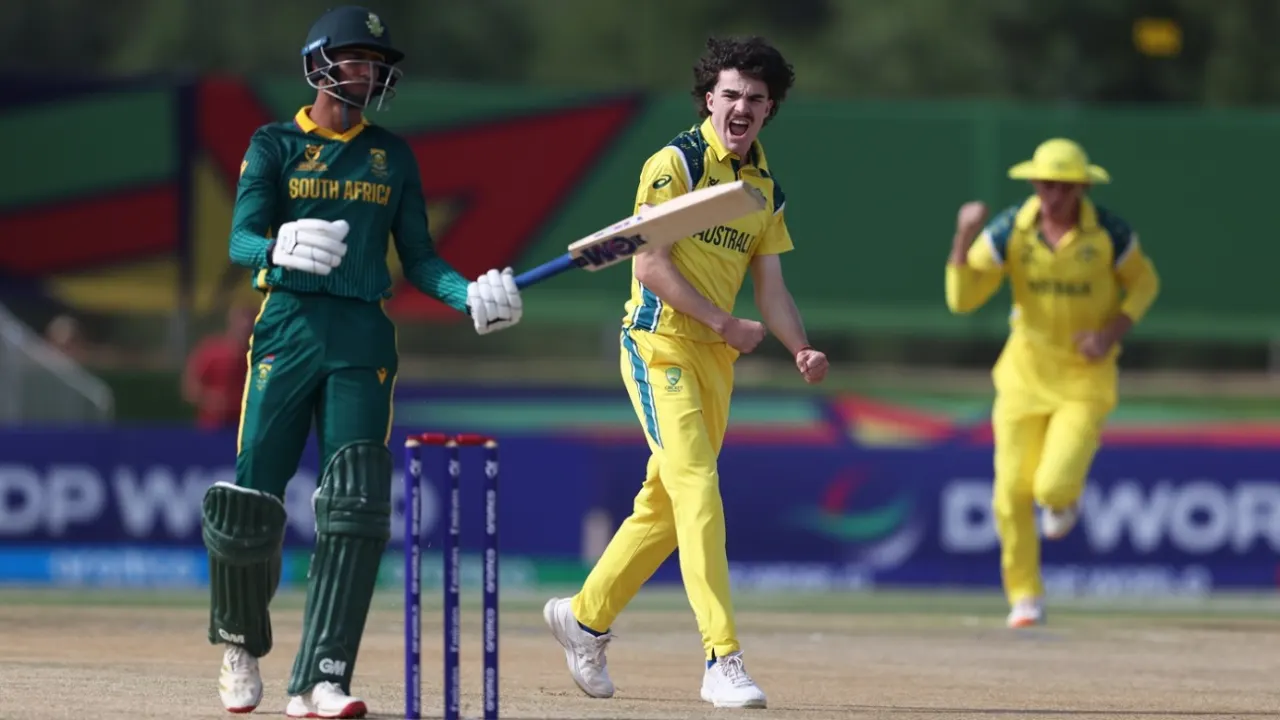

It took Australia U19s 32.5 overs, going at just around 3.5 runs an over for the majority of a belaboured chase against an excellent South Africa U-19 bowling effort. But they had that liberty after Charles Lachmond’s 3 for 29, and two wickets each from Will Byrom and Aryan Sharma, had bowled South Africa out for 118 all but ensuring the result of the match was in little doubt even at the halfway stage.
South Africa had been reduced to 37 for 4 inside the powerplay, failing to find answers against the raw pace and movement that Lachmund and Byrom found off the surface. Opener Jorich Van Schalkwyk was the sole bright spot for them, battling his way through this period and putting together a 30-run stand with Paul James, even as he was pinged on the helmet off a brutal Kasey Barton delivery.
Spinner Aryan proved to be particularly troublesome to face, as he kept spinning the ball away from the outside edge of the right-handers. He dropped two catches at point before coming into the attack, but made up for his fielding by scalping up two wickets of his own.
James kept one end steady once Schalkwyk was run out for a 26 off 55, but wickets kept falling at the other. He would eventually be the last batter out, for a 60-ball 34 .
In response, JJ Basson led a South Africa bowling attack that was incisive and economical. His spell of 3 for 41 was the highlight of a bowling effort that kept the Australia batters defensive, and also ensured that the Australia line-up lost three wickets for the first time in this tournament – in their fourth match of the tournament.
Steven Hogan never looked comfortable during his 73-ball 43, but timed short deliveries well while cutting late, and mowed down more than a third of the target by himself. He was the last Australian wicket to fall, as Basson’s third wicket. Alex Lee Young and Jayden Draper got together at the crease, and the latter smacked two fours in the 33rd over of the contest to bring it to a close.
Brief scores:
Australia 122 for 4 in 32.5 overs (Steven Hogan 43, Jayden Draper 21*, Alex Lee Young 21*; JJ Basson 3-41) beat South Africa Under 19s 118 in 32.1 overs (Paul James 34; Charles Lachmund 3-29, Will Byrom 2-16, Aryan Sharma 2-27) by six wickets
[Cricinfo]
-

 Business21 hours ago
Business21 hours agoComBank, UnionPay launch SplendorPlus Card for travelers to China
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoComBank advances ForwardTogether agenda with event on sustainable business transformation
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoAmerican rulers’ hatred for Venezuela and its leaders
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoRemembering Cedric, who helped neutralise LTTE terrorism
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoCORALL Conservation Trust Fund – a historic first for SL
-
 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoA puppet show?
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoConference “Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill: Neither Here, Nor There”
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoHistory of St. Sebastian’s National Shrine Kandana













