Features
Sixty-five years after entry to university of Ceylon, Peradeniya – II

We, as undergraduates were very fortunate to have two to share a room, and in the older two halls, Arunachalam and Jayathilaka they had a washbasin inside the room so that the occupants did not have to go to the common washrooms for their early morning ablutions such as shaving and washing the face. We were also fortunate to have all three meals in the hall. For breakfast we were served different varieties such as bread with eggs, pulses, milk rice, hoppers, etc. Lunch was always rice and curry which was not served on plates but kept in dishes for self-service. These dishes were replenished as soon as they were empty. Whereas, for dinner we had courses, and rice and curry once a week.
by HM NISSANKA WARAKAULLE
(First part of this article appeared on Friday (12)
Situated between the Hanthana Hill on one side and the Mahaweli River on the other the university campus was extraordinary. The landscaping of the campus had been done according to a meticulous plan. In April and May, the flowering trees and creepers were in bloom with flowers of vivid colours, right along the Galaha Road and with the creepers laden with yellow flowers hanging down from the mara tree at the “kissing bend” was really a sight one could not easily forget. The workmen who attended to the garden had to cut the grass, trim the hedges, etc., from one end of the campus and when they reached the other end, they had to start all over again, so that it was a never-ending task. Wonder whether it still happens that way.
Now having entered the portals of the hallowed university which was to be “more open than usual” (according to the late Duke of Edinburgh as indicated on the plaque at the entrance to the Senate building) the new entrants settled down in their allotted rooms and got to know the roommate, whom some of us were meeting for the first time, as they were from two different schools. Some undergraduates were fortunate to get classmates as their roommates. Gradually all the freshers arrived in their respective halls before lunch time on the first day, having used various modes of transport, such as the train, bus, hiring cars and private family cars.
The times the meals were ready were announced by a bell being rung by a hall servant. We met all the freshers who were assigned rooms in the same hall in the dining hall for the first time. And for one week it was only the freshers who were on the campus. Before the seniors arrived, we had a wonderful week, mixing up with batchmates from the other halls, playing netball, going on hikes to Hanthana and attending socials.
The period that all freshers dreaded was the following week. However, at the end of the week we found that the rag was not as bad as we had envisaged. In our hall there were only a handful of seniors who were able to rag. The reason for this we found out later was that the senior batch immediately before ours had not been ragged, and if one does not face a rag, one cannot rag. Anyway, the rag that we underwent was not at all humiliating or frightening as what happens in universities at present. In fact, we enjoyed the rag, and it also helped us to get to know the seniors and become friends for the rest of our stay on the campus.
We, as undergraduates were very fortunate to have two to share a room, and in the older two halls, Arunachalam and Jayathilaka they had a washbasin inside the room so that the occupants did not have to go to the common washrooms for their early morning ablutions such as shaving and washing the face. We were also fortunate to have all three meals in the hall. For breakfast we were served different varieties such as bread with eggs, pulses, milk rice, hoppers, etc. Lunch was always rice and curry which was not served on plates but kept in dishes for self-service. These dishes were replenished as soon as they were empty. Whereas, for dinner we had courses, and rice and curry once a week. At that time all provisions, including dry rations, eggs and chicken were imported from India through the University Supplies Organisation.
Once a month we used to have a high table dinner, when someone from outside was invited to address the undergraduates on a current topic. At this dinner, the Warden and the sub-Wardens, the President of the Hall Society and the Secretary occupied seats at the high table along with the invited guest.
The undergraduates of one hall could go to another hall with prior arrangement with friends to have dinner in that hall, which a few of us used to do on a day when there was rice and curry for dinner.
The university had medical facilities with a Health Centre with three doctors, namely Dr. Wijetunge as the Chief Medical Officer, and Dr. Uduwela as a full-time Medical Officer (MO) and Dr. (Mrs.) Ram Aluvihare as a part-time MO (as she was the Warden of Sangamitta Hall). There were two nurses and two attendants for the Male and Female wards. Believe it or not these facilities were available for the undergraduates for a paltry sum of Rs. 10 for the year!
Every week the dhoby used to come in his Morris Minor car bringing the washed and ironed clothes and to take the soiled ones. He used to visit the campus almost every day as he had to serve all the halls of residence. And here again we were charged Rs. 10 for the whole year for this luxury!
In respect of sports, the facilities available were unbeatable. The sports arena extended from the Galaha Road (which ran through the campus) down to the railway line near the Sarasavi Uyana station. The tennis courts and the volleyball court abutted the Galaha Road. Then it was the athletics field with a cinder track (may have been the only one in Sri Lanka at that time) which had been laid around the hockey field. Beyond that on a lower level was the circular cricket ground and at the far end the soccer and rugby playing field. In addition to these outdoor playing areas, there was a huge gymnasium for all indoor games such as basketball, netball, boxing, wrestling, weightlifting, table tennis and badminton. There was also a billiard table. During our time all these facilities were made use of very well. It is a pity to hear that most of those who have graduated recently from that university have not participated in any sports activities at all.
The Peradeniya hockey team in our final year won the Inter-Club hockey tournament conducted by the Kandy District Hockey Association undefeated. This was the first time the university had won this championship. It was only after a lapse of a decade or so that this feat was accomplished by the university again.
It was also during that year that four players from the Peradeniya hockey team were selected to participate as members of the University of Ceylon team in the All-India inter University Hockey tournament which was conducted in Ahmedabad in Uttar Pradesh. The team spent about a month playing matches in Ahmedabad, Mumbai and Pune, having travelled by ship both ways.
While on the subject of sports, I would like to mention one cricket match we played against a leading school in Kandy from which there were three colours men in the university team (all three from our batch). When we won the toss, some of our teammates had got hold of a car and gone to the city. When they came back, we had been dismissed for a humiliating 37 runs! However, we were able to stave off defeat and return to the campus though not very happy.
While on sports in Peradeniya, it is noteworthy that almost all sports were handled by the undergraduates. As the captain of a team, it was his/her responsibility to arrange matches, the transport if the matches were played away from the campus, provide the meals if required, and conduct the practices too. The captain had to obtain the money from the Director of Physical Education (DPE) for the expenses. On completion of the match, he/she had to submit the balance to the DPE with the receipts of payments made. At present all these are handled by the Instructors of Physical Education (IPE) in charge of the respective sport. There are coaches from outside to train the undergraduates in their respective sport.
The captains and the vice-captains formed the Sports Council, and the office bearers were elected by them. All matters pertaining to sports were handled by the Sports Council, which included the election of the captains and vice captains, conducting the Colours Nite and Colours dance. Several of our batchmates were captains and vice-captains of various sports. They were- Athletics-Captain N. Puvimanasinghe, Badminton- Captain N De Silva, Cricket-Captain M Kurukulasooriya, Vice-captain A Rambukpotha, Football Vice-captain GS Hidelarachchi, Netball- Captain Miss Ranee Saverimuttu, Hockey- Captain N Warakaulle, Vice-captain SB Ekanayake, Swimming Captain A Muttucumaraswamy, Volleyball Captain AB Wijepala, Wrestling Vice Captain PA Senaratne. Many of our batchmates were awarded university colours in various sports.
The university was not devoid of cultural activities. There were dramas staged in the open-air theatre (now referred to as the wala) below Hilda Obeyekera Hall, in which the actors were all undergraduates. The charge to watch a drama was 50 cents. There were weekly film shows in the Arts Theatre and some of the reputed films were screened for the benefit of the undergraduates. The cost of a ticket for a film show was also 50 cents. In addition to the dramas and films, we also had debates, in English and Sinhala. These were between two teams of undergraduates or between two teams of Teachers. These are rare or not heard of now as no one is interested in this type of activity.
Politics on the campus at that time was a different kettle of fish. It was only the male undergraduates who were involved in politics, and some to the extent of failing their final examination, and earning the prefix “pol” to their names. The students who were interested joined one of three groups available at that time. The groups affiliated to the LSSP were called Trotskyites, the MEP group and the Communist group, referred to as “Commies”. Many of the undergraduates joined a group because their friends were there and not that they were really interested in politics. In our final year, the Demsoc group was formed, which was aligned to the UNP. One can imagine how the politics of the undergraduates were when we found that some ardent Trotskyites were holding important positions in the then UNP government and the pioneers of the Demsoc group joined an SLFP government.
Annual elections for the positions in the Student Union were very interesting depending on candidates pitted against each other. Our batch had the best contested election for the top post of President when Ille and Nihal (both from our batch) contested for the top post in the second term of 1961-62 academic year. A few of our batchmates were elected to the posts of President(P) and Vice President (VP). They were: TAL Fernando as VP in the first term in 1960-61, Sirimega Wijeratne as P and Kamini Wickramasinghe as VP in the second term of that year; Mohan Edirisooriya as P in the first term of 1961-62, Punya Illayperuma as P and Piyaseeli Samaranayake as VP in the 2nd term and Jackson Karunasekera as P in third term of that year. The election of the office bearers of the Student Union was conducted after the elections to the Hall Societies. At the end of the election of office bearers of the Student Union, they were invited by the Vice-Chancellor to tea at the Lodge. This was the only chance an undergraduate had an opportunity to visit the Lodge.
The most noteworthy things to mention were that the undergraduates never pasted any posters nor drew any graffiti on the walls and there were protests like what happens at present, except for one protest march to Kandy when Patrice Lumumba was assassinated.
The men undergraduates wore long trousers and shirts with shoes to attend lectures and the women were dressed in either saree or dress. It was a pleasant sight during the day when the ladies went to attend lectures and returned to their halls of residence as they were dressed in colourful attire and almost all having coloured umbrellas opened out so that it was a colourful parasol parade along the Galaha Road.
The four-storied Library was just opened when we entered the university, and it was the best library in Sri Lanka at that time. Many undergraduates made use of the facilities in the library, some even after dinner as the library was open till 8.00pm. There were some who stayed on during the vacations to do their reading in the library.
There were seven First Classes in our batch. After graduation a large number held very important positions, both in the public and the private sectors. Of those who did Law, there was a Judge of the Supreme Court, and two in the Court of Appeal, and a few eminent lawyers in the private Bar. A fair number joined the Sri Lanka Administrative Service and ended up as Secretaries of Ministries whilst one was the Secretary to the Prime Minister. We had five ambassadors, four from within the service and one from outside. The other important positions held were Commissioner-General of Inland Revenue, Commissioner-General of Immigration and Emigration, Chairman of Corporations, Chairman of a State Bank, and Principals of schools (both government and private), Professors of Universities (both local and foreign),Deans of Faculties, Chancellor of a university and Senior Deputy Inspectors-General of police and a Registrar of a University. A large number emigrated to seek greener pastures and did well in the countries they were domiciled in.
In 1959, a few of us got together and organized a function to celebrate fifty years after entry. It was not an easy task to contact batchmates most of whom we had lost touch with. This was held at the 80 Club, attended by about 166 batchmates both from abroad and here. A souvenir was published with several of the batchmates contributing articles reminiscing of their stay in Peradeniya. Those who were fortunate to attend the get together were very happy to renew the camaraderie we had while at Peradeniya, and all enjoyed the fun.
These were indeed the best times in the University of Ceylon, and we had the privilege of enjoying it. It is very doubtful that undergraduates in Sri Lankan universities at present or in the future, will ever get an opportunity to enjoy the university life as we did. Those three or four years of luxury, so to speak, spent in the salubrious surroundings at Peradeniya and the friendships cultivated whilst there will never be erased from our minds. (Concluded)
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
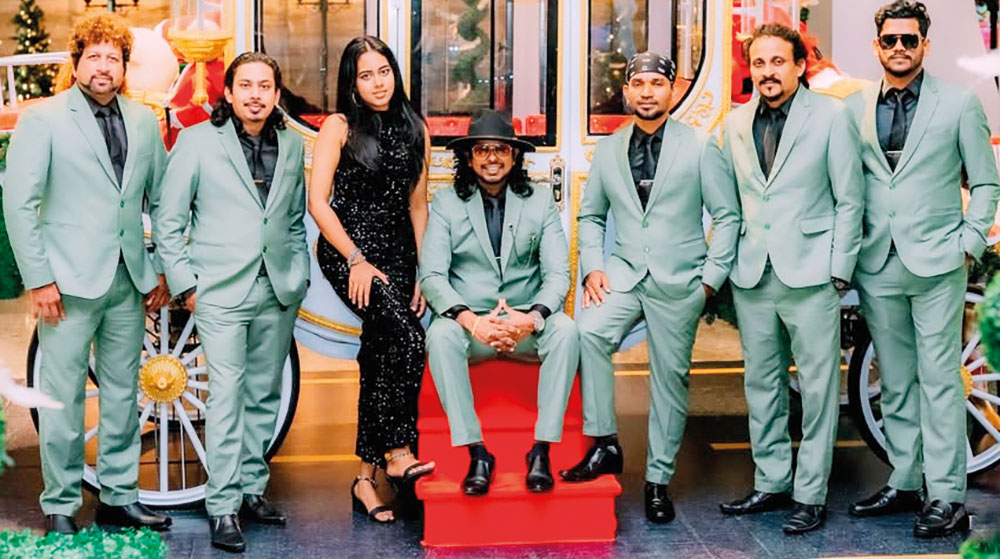
Talento … oozing with talent

 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
Features
Special milestone for JJ Twins
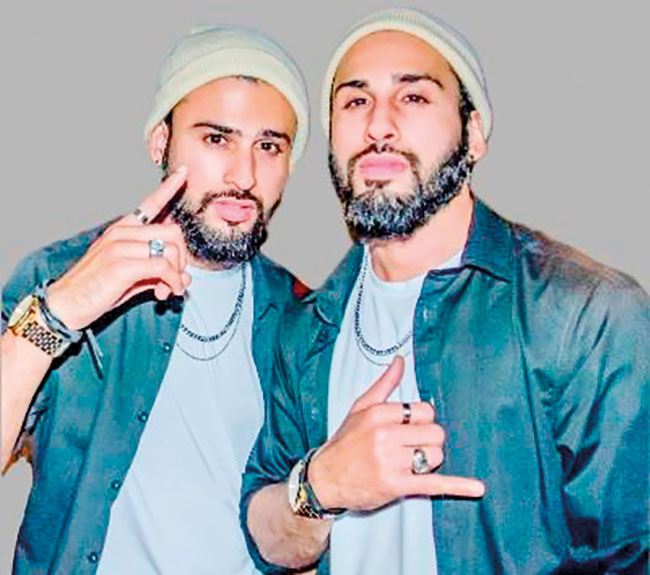

The JJ Twins, the Sri Lankan musical duo, performing in the Maldives, and known for blending R&B, Hip Hop, and Sri Lankan rhythms, thereby creating a unique sound, have come out with a brand-new single ‘Me Mawathe.’
In fact, it’s a very special milestone for the twin brothers, Julian and Jason Prins, as ‘Me Mawathe’ is their first ever Sinhala song!
‘Me Mawathe’ showcases a fresh new sound, while staying true to the signature harmony and emotion that their fans love.
This heartfelt track captures the beauty of love, journey, and connection, brought to life through powerful vocals and captivating melodies.
It marks an exciting new chapter for the JJ Twins as they expand their musical journey and connect with audiences in a whole new way.
Their recent album, ‘CONCLUDED,’ explores themes of love, heartbreak, and healing, and include hits like ‘Can’t Get You Off My Mind’ and ‘You Left Me Here to Die’ which showcase their emotional intensity.
Readers could stay connected and follow JJ Twins on social media for exclusive updates, behind-the-scenes moments, and upcoming releases:
Instagram: http://instagram.com/jjtwinsofficial
TikTok: http://tiktok.com/@jjtwinsmusic
Facebook: http://facebook.com/jjtwinssingers
YouTube: http://youtube.com/jjtwins
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-
 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans




