Opinion
Save Parakrama Samudraya!

By Bandula Kendaragama, Dam Safety Consultant, Melbourne, Australia
This article is written based on information collated through consultations that were submitted as a technical report recently to President Gotabaya Rajapaksa and other relevant government authorities. The consultations were among those who had been interested in dam safety and directly involved in managing the “Narrowly-Missed” breach and in the reconstruction of the Parakrama Samudraya bund after the Cyclone in 1978. They considered it appropriate in sharing concerns and acquired knowledge with the public at this crucial juncture of decision-making on the safety of the aging irrigation infrastructures in Sri Lanka.
The Parakrama Samudraya Reservoir was built by King Parakramabahu the Great, during his reign (1153-1186 AD) and it has a reservoir capacity of 116,000 acre-feet, feeding approximately 25,000 acres of paddy cultivation. This reservoir has a bund 52 feet high and 10 miles long.
The study on the Parakrama Samudraya bund was undertaken owing to information and misinformation that had been widely shared and debated in the formal media, and especially in the social media, concerning the Parakrama Samudraya bund being proposed as a site to construct an 8-feet wide walking path. Further, it is noted that similar walking paths will be constructed on bunds of other reservoirs such as Kantale, Udukirala Wewa, etc.,
Cyclone in 1978
The 1978 Cyclone started with the onset of the storm formed on 20 November 1978 over the southwest Bay of Bengal. It intensified gradually, reaching Super Cyclonic Storm Status Category 4 Cyclone on 23 November with a gusty wind speed of 220 kmph. The 1978 Cyclone was the second strongest Super Cyclonic Storm to strike Sri Lanka’s Eastern Province since modern records began. The cyclone attained peak intensity on November 23, before making landfall in Batticaloa. The Eastern Province was heavily affected by the cyclone.
The cyclone had devastating impacts in Sri Lanka, killing about 915 people and an unaccounted number of cattle and other animals. An estimated more than one million people were affected, with over 250,000 buildings damaged, and one-fifth of Batticaloa’s fishing fleet destroyed. Nine of the 11 paddy stores were destroyed and 90 % of the coconut plantation (about 28,000 acres) in the Batticaloa district were destroyed. Also, in Polonnaruwa District, the public and private infrastructure, paddy, and rice stored in Food Commissioners and Cooperatives, coconut cultivation, etc., were devastated.
Cyclone 1978 and Parakrama Samudraya
The Cyclone reached the Parakrama Samudraya bund at about 6:30 pm on 23 November and lasted till about 4:00 am on 24 November. According to eyewitnesses, the height of the waves was 10 to 12 feet. Knowing the imminent catastrophic danger of overtopping leading to a breach of the bund, the Irrigation Engineer in charge of Polonnaruwa A. D. S. Gunawardana, the Government Agent Polonnaruwa Austin Fernando, and a few other officials, on duty, decided to be ready with a few bulldozers and retain them standby at strategic locations such as at the sluice and spillway, to breach the bund at these locations if the need arises.
The idea behind this decision was if the predicted overnight rainfall occurred and the anticipated inflow to the Parakrama Samudraya did really eventuate, the inflow would have been greater than the outflow with all 10 radial gates and the sluice gates kept open. Then there was a risk of overtopping and breaching the bund. Hence, an artificially introduced breach of the bund to discharge floods along the existing channels would prevent a haphazard catastrophic breach at an unknown and unwanted location, which could inundate the heavily populated downstream areas. Such an emergency rapid drawdown is the standard practice to prevent a dam breach. Fortunately, predicted overnight rainfall was low. However, the drawdown of the reservoir continued overnight.
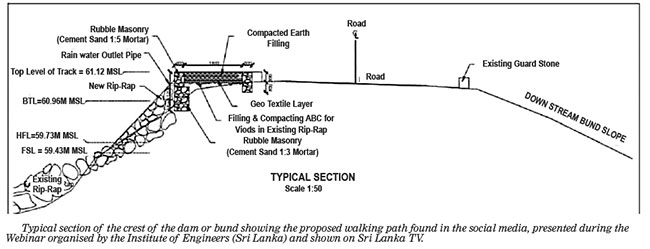
Following the overnight drawdown, about 2/3 of the 12-feet wide bund top road and a fair portion of the upstream shoulder were found to be slipped into the reservoir, leaving only about 1/3 of the bund top road intact. There were widespread such slips along the full length of the bund. The damaged areas were repaired with earthfill and Ralapanawa reinstated as a short-term risk reduction measure. The upstream face of the Ralapanawa was not flattened to improve the safety margin (i.e., Factor of Safety) of the bund in case of future similar drawdowns as it was a long-term risk reduction measure to be implemented by the Government Authorities. Therefore, consideration should be given to implementing appropriate long-term risk reduction measures.
Walking Track Proposal
Based on information available to date, the proposed walking path will be constructed on the upstream side of the bitumen surfaced bund top road where there was a sliding failure during the 1978 cyclone and floods (See Figure above 1).
Several long tension cracks, sealed with tar, are present on the bitumen surfaced bund top road as seen in videos of Sri Lanka media. Most of them are located along (parallel) the bund top road, thus increasing the risk of sliding failures similar to those that occurred during the 1978 floods. Additional loads due to the construction of a walking path would widen and deepen those tension cracks, compromising the safety of the bund, which is not known.
Therefore, it is the considered view that additional loading on top of the 1978 sliding mass for construction of the walking path would increase the risk of reactivating the 1978 slides during a future rapid drawdown, similar to in 1978.
It is understood and appreciated that the Irrigation Department is currently undertaking geotechnical investigations to assess the safety margin of the bund.
The highest concern is dam-safety
Based on information available, it is understood that there is a period of 741-years (i.e., from 1159 to 1900), where the performance of the bund is not documented and unknown. However, it is reported that the bund was totally breached during the colonial era. According to R L Brohier, the bund and the reservoir were abandoned for more than a century.
Given that the population at risk in case of a dam break is extremely high, it appears that the consequence category of this bund is “Extreme” as per the current international dam safety guidelines. Therefore, the proposed walking path at Parakrama Samudraya cannot be compared to that of the Kurunegala Wewa, Boralesgamuwa Lake, etc., constructed along the reservoir rim, and the walking paths constructed around water bodies in the suburbs of Colombo.
It is understood that the Parakrama Samudraya is formed by combining three reservoirs of unknown history. Therefore, the bund may have been raised in several stages during the 741-years associated with unknown performance. It is not known whether dam safety-related defects of the bund such as slips or slides, cracks, animal burrows, sinkholes, soft areas, root bowls, zones of desiccation cracking, zones of residual shear strength because of historical failures, etc., were repaired to satisfactory standards, or not.
The aging of dams constructed of earth and rockfill material is due to time-related changes in the properties of the materials of the structure and its foundation. As reported in a technical paper published in May 2010 by the United States Society of Dams, the aging or deterioration of embankment dams and their foundations are of concern. These concerns extend throughout the entire life of the dam until safe abandonment or demolition.
Recent interventions on dam-safety
Given the dam safety issues associated with this controversial walking path project, the Water Forum of the Institute of Engineers in Sri Lanka conducted a Webinar on 09 September 2021 on “Usage of Inland Water Bodies for Recreation”. More than 280 personnel, mainly engineers, participated in this Webinar and raised over 100 questions related to the safety of the bund. Several questions were raised on fundamental errors and potential failure modes associated with the proposed walking path. It appears that ad hoc decisions have been taken for reasons unknown. The lack of laws and dam safety regulations in Sri Lanka could be one of the reasons for such ad hoc decisions taken by various individuals and organisations.
As far as dam safety regulations are concerned, India is well ahead of Sri Lanka. Even Ghana in Africa has introduced Dam Safety Regulations to ensure the safe design, construction, operation, and maintenance as well as decommissioning of dams.
Based on statistics of embankment dam failures and accidents, 48% of dam failures are related to overtopping and failures of appurtenant structures, and 46.5% are due to internal erosion. Due to the absence of an internal filter system in this bund, not only the slope instability, but the internal erosion is also likely to be a prominent potential failure mode.
It is understood that planning is underway to construct several fast-food outlets, toilet facilities (including a “changing room”) at the toe of the bund, i.e., within the reservation area of the bund located immediately downstream of it. It is to be stressed that this stretch of land along the bund is a critical area to ensure the safety of the bund. Identification of dam safety features such as heaving the ground, cracks, wet areas, springs, seepage locations, etc., in this area, is critical. Digging of lavatory pits, trenches, etc., could intercept permeable layers in the foundation and may trigger “backward erosion tunnels” leading to piping, which is a major failure mode in embankment dams (or, bunds). Excavations in this area could lead to sides of the downstream face of the bund, compromising its safety margin.
Should there be a need to improve the safety margin of the bund, additional stabilizing fills are to be constructed in this area over the downstream face of the existing bund. An access road along the downstream toe of the bund is an essential item for repairs and routine maintenance of the bund. Given the proximity to the dam, this reservation area should be used to stockpile materials to be used during dam emergencies such as filter sand, crushed rock, rockfill, etc., and movement of construction machinery for maintenance and repairs. This area is an integral part of the bund, hence should not be used for either permanent or temporary constructions. Therefore, consideration should be given to providing these facilities at an alternate suitable location, perhaps close to the Government Agent’s residence, or thereabouts.
Recommendations to maintain dam safety
Based on dam safety concerns and consequences discussed, it is recommended that,
1) the crest of the bund is reserved for routine maintenance, including replacement of displaced Ralapanawa if necessary, placement of additional boulders if required, and for construction of temporary overtopping protection bund using ‘Sandbags”, as and when required.
2) the stretch between the Ralapanawa and bitumen road be reserved for the construction of a wave wall to meet the dam safety requirements of future hydrological reviews to be undertaken during the service life of the reservoir and bund.
3) a safe “Load Capacity” be imposed on the bund top road, and arrangements are made to stop all heavy trucks plying on the bund top road as the bund has not been designed for such traffic loads.
4) the bund top road is completely closed for all traffic, say from 5:30 am to 7:30 am and then from 6:00 pm to 9:00 pm or as agreed by local authorities, in the preferred 2km long stretch, and then the existing bitumen surfaced bund top road to be used as the walking path (Alternatively, only the upstream-half of the bitumen surfaced bund top road to be used as the walking path while the downstream-half of the bitumen surfaced bund top road to be kept open for one-way light traffic only, subject to nominated maximum speed to ensure the safety of people using the walking path).
5) an alternative walking path (For example, in the reservoir rim), be investigated which will not compromise the safety of the dam.
6) the reservation area located immediately downstream of the bund is not used for developments that are been planned by the Urban Development Authority as this area is very sensitive to dam safety issues.
7) the reservation area located immediately downstream of the bund, which is an integral component of the dam, be a property of the Irrigation Department for inspection and monitoring of critical dam safety features, construction of a toe access road, construction of stabilizing fills if required, stockpiling of construction materials required during dam emergencies, etc.,
8) a potential failure modes analysis and Risk Assessment be undertaken in accordance with international dam safety standards.
9) a Design and Safety Review of the dam and appurtenant structures be undertaken in accordance with the international dam safety standards incorporating review of geotechnical parameters of the bund and foundation, hydrology, wave run-up, seismicity, flood handling capacity, reliability of gates and instrumentation, etc.,
10) sufficient funds must be allocated to undertake Design and Safety Reviews of all “Extreme” consequence category dams in Sri Lanka.
11) sufficient funds must be allocated to routine maintenance of dams (Note: Depending on their nature, some maintenance items, if not addressed in a systematic and timely manner, may eventually become dam safety issues, eventually leading to failure of dams).
12) early arrangements must be made to implement the recommendations of the Cabinet Memorandum No. 11-2020 dated 26 October 2020 on the Establishment of a Dam Safety Consultation Centre and a Dam Safety Regulatory Mechanism.
(The author can be contacted on email: bandula.kendaragama@gmail.com)
Opinion
Assisting solar power debate in Cabinet

Authors: Directors of Solar Village SDG CIC
www.solarvilllagesdg.org
I.M. Dharmadasa (Emeritus Professor), Nilmini Roelens (Solicitor) and Saroj Pathirana (Journalist)
The purpose of this article is to inform the Cabinet discussion on Solar Power proposed by the Ceylon Electricity Board (CEB)
Net metering and the Prosumer
The CEB has put forward a motion to the Sri Lankan Cabinet which proposes to reduce the unit price payable under the various net metering schemes to the “prosumer” (the owner of a solar panel system).
A prosumer is a blend of producer and consumer, referring to individuals who both create and consume. This is based on the notion that most producers of electricity through self-owned solar panels generate more than double their own needs as consumers. It thus enables the prosumer to connect to the national grid and receive money on a pay back scheme from the CEB for the excess electricity they produce.
What is this debate about?
Currently there are four schemes.
The Public Utilities Commission of Sri Lanka explains the various schemes involving roof -top solar solutions thus under a heading published in October 2023 – Rooftop Solar PV Connection Schemes. The two most noteworthy schemes are the Net plus and the Net plus plus schemes.
https://www.pucsl.gov.lk/rooftop-solar-pv-connection-schemes/
Through the NET Plus Plus Scheme CEB regards the prosumer as a mini power plant holder which maximises roof top generation well beyond the prosumer’s own needs making maximum use of extra roof space. This would work well for schools and companies with large buildings. CEB used to pay Rs. 37 per unit to the prosumer for up to 500kW. This unit price was available between 26 October 2022 to 1 July 2024. However, as of 1 July 2024 the unit price was reduced to Rs. 27.
We understand the new CEB proposal to the cabinet is to scrap this scheme altogether.
In relation to the Net Plus scheme which is the more accessible and popular scheme for ordinary householders the current CEB proposal is to reduce the unit price even further to Rs. 19 for solar power systems generating less than 20 kW, whilst for those generating between 20 – 100 kW the unit pay back will be Rs.17 and those generating between 100 – 500 kW will receive Rs.15 per unit.
The installation costs of a 5-kW solar panel is now around Rs 1.0 million. The cost of solar panels has in fact come down over the years and the units are recyclable. The lifespan of a solar unit is expected to be in the region of 22 to 25 years. There are now over 300 active solar companies in Sri Lanka. This is a rapidly growing sector with the prospect of generating employment for tens of thousands of young Sri Lankans for many years to come as technicians, administrators and entrepreneurs. The potential advantages for the economy are extensive Sri Lanka’s growth of the renewable energy sector using freely available sunshine available virtually all year-round given the geographical proximity to the equator
It is not just about reducing the electricity bills of the prosumer. This green energy solution would also mean we avoid the heavy annual cost of the import of fossil fuels into Sri Lanka which very seriously affects its balance of payments each year. The unwarranted need for environmentally damaging energy sources like coal, diesel and nuclear (with its inherent dangers and enormous costs), etc., will lead to a meaningless downward spiral of more debt, enhanced climate risk and pollution.
The intermittency argument
The argument of intermittency of renewables is a misguided premise. Some may argue that seasonal variations of renewables such as solar or hydro power may make them unreliable. This can very easily be remedied by investment in a smart grid. This can be done by upgrading the existing transformers and grid lines. A policy decision would be required at cabinet level to advise the CEB to reinvest any profits for this purpose.
Green Hydrogen is the future
Solar generated power can be harnessed to invest in Green Hydrogen solutions which could mean that rather being an importer of fossil fuels, that the rest of the world is turning away from, Sri Lanka becomes an exporter of green hydrogen to countries in the northern hemisphere where sunshine is scarcer.
Picture what it could do to the Sri Lankan economy if, rather than being dependent on imports of polluting and expensive fuel which can exacerbate the climate crisis, we transform our island into an eco-tourist paradise and become an exporter of clean green hydrogen.
Green hydrogen is created by splitting water molecules into its components of Hydrogen and Oxygen. The hydrogen gas can be compressed and stored for export. The minimum voltage required for splitting the water molecule is about 1.50 Volts DC and scaling up and commercialisation is happening throughout the world currently.
Rebranding Sri Lanka as a renewable energy island
To limit imports of fossil fuels for automobiles, a policy decision at governmental level could provide concessions for electric cars for solar roof owners and encourage the use of solar powered charging stations. The annual cost of imports of petrol and diesel would reduce overtime as Sri Lanka encourages clean and green electric cars.
Whilst the rest of the world is turning to renewable energy with alacrity, Sri Lanka ought not turn to fossil fuel imports in breach of its commitments to the international community.
In 2015 Sri Lanka signed up to the United Nations 2030 Agenda. Ahead of the Paris Summit Sri Lanka set out its climate action plan which the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) stated “Countries have agreed that there will be no back-tracking in these national climate plans, meaning that the level of ambition to reduce emissions will increase over time.”
(https://unfccc.int/news/sri-lanka-submits-its-climate-action-plan-ahead-of-2015-paris-agreement)
Sri Lanka has a real opportunity to rebrand itself as a renewable energy island. This means moving towards the commitments made at UNFCC – COP25, Sri Lanka Country Statement in Madrid in December 2019:
“Sri Lanka recognises the importance of the role of COP and highlights the need to take effective and definitive steps for finalising the follow up actions of the Paris Agreement.
The rise of the global mean temperature and the resulting changes have created adverse impacts on key sectors of Sri Lanka, such as agriculture, forestry, biodiversity, marine and fisheries, tourism and energy (hydro power) sectors, leading to disastrous effects on its people, ecosystems and economy. According to official statistics from 2008 to 2018, droughts, floods and landslides have affected over 15 million people, and losses and damages resulting from these calamities have been borne by Sri Lanka’s national budget… Sri Lanka is committed to inclusive and participatory climate actions to ensure that affirmative actions are taken to address the vulnerabilities of climate change.“https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/resource/SRILANKA_cop25cmp15cma2_HLS_EN.pdf
Why is reduction of the unit price a very regressive, harmful measure?
The reduction will discourage the use of clean renewable energy in favour of higher imports and a move towards dangerous and expensive sources of energy.
The consequences of a reduction of unit price will thus be far reaching beyond the loss to the prosumer.
Lithium battery storage options mean that even when the sun stops shining at night or in the wet season the solar panel produced energy can continue to be used. It is very likely that current solar companies will need to diversify to survive and move towards lithium battery storage solutions and inverters so that year long, 24-hour access to energy is available without recourse to the national grid for their customers. As individuals and institutions go off grid CEB’s income will dwindle in the long run as the private sector takes over.
Recommendations to the cabinet
We make the following recommendations to the Government of Sri Lanka:
(i) At present we have a fragile grid, and the CEB should strenuously endeavour to minimise energy leakages and improve the grid by replacing weak transformers and grid lines. Such continuous improvements will enable us to move towards a “Smart Grid” enabling absorption of large amounts of intermittent renewable energies like wind and solar.
(ii) At present we have ~1500 MW of renewables installed, comparable to hydroelectricity. When solar power is plentiful during the daytime, hydro power can be reduced simply by controlling the water flow without any technical difficulties. This is one way of assuring energy storage while balancing the grid energy.
(iii) Another solution for this is pumped-water storage plants. It is important to follow through with such measures which have now been under discussion for some time.
(iv) The future energy carrier is green hydrogen (GH) produced by electrolysing water using both wind and solar. A global Green Hydrogen revolution is taking place, and GH can be used to run vehicles using fuel cell technology. Trains and buses are being run with GH technology in Europe. GH can also be converted into ammonia and methanol to produce fertilizer and be applied for other industrial uses. Sri Lanka must not be left behind.
(v) GH can be stored and burned whenever energy is needed, especially during nighttime. Only water vapour is produced during the burning of hydrogen without any air pollution. Sri Lanka already has the Sobhadanavi LNG plant which is almost ready to use. Since we must import LNG to run this power plant, we should be able to reduce the LNG import bill by half by mixing the natural gas (methane) with the locally produced GH. See here:
(vi) Local solar energy companies should install high quality solar energy systems and provide “after sale services” in accordance with their guarantees.
(vii) PV companies should also be encouraged to collaborate with local electronics departments to manufacture accessories like inverters and other components needed for these systems, creating new jobs, and reducing the total cost of the systems.
(viii) In addition to grid tied solar roofs, the PV companies should also market hot water systems and water pumping systems. As a country reliant mainly on agriculture, solar water pumping and drip irrigation systems, especially in the dry zone, provide a huge potential for increasing food production.
(ix) Battery capacities are improving, and costs are coming down. This can be encouraged pending replacing grid infrastructure.
(x) It is important to increase public awareness through government funded campaigns. The public should recognise the dangers of using imported and expensive fossil fuel and the importance of using renewables.
(xi) The public should also recognise the advantages of having a clean environment, health benefits and enhanced living conditions.
(xii) A community development project called “Solar Village” to empower needy communities, accelerate their sustainable development, reduce poverty and take climate action has been developed over the past two decades. Seven solar villages have been established and funding for three more solar villages have been obtained.
Solar Village SDG, a UK based community interest company has been established to encourage the use of renewables and to pilot programmes which will support sustainable development goals. This includes providing access to a quality education for all via smart rooms which will be set up alongside solar villages in rural schools. Such initiatives could be encouraged and supported.
Opinion
How monks practice Buddhism in Sri Lanka

Time was when we had to observe the five precepts chanting in front of the omnipresent Buddha statue in every Buddhist household, and pay homage to parents straight afterwards. Attend mandatory Sunday schools, trek about 6 miles (return) to Moratu Vidyalaya’s main hall together as a family on Fridays to listen to a sermon by erudite visiting monks from the Vajiraramaya and elsewhere.
Having been settled in the UK for half a century, I can only go by what I read and hear from Sri Lankan friends and families. All those practices seem to have changed for the worse, sadly! Living in luxury, temples are run on business models nowadays! Monks ask what they wish to eat at alms-givings, including pork, etc., tell how much it costs the laypeople to invite them, etc! Unbelievable to say the least! I dare say it seems to start from the top of the hierarchy – the Kandy Temples, where the prelates live and are patronised by all politicians from Presidents, Prime Ministers and others! Some monks engaging in politics is not uncommon! For example, a recent statement made by Ven. Dodampahala Rahula Thera during a religious ceremony held to bless former President Ranil Wickremesinghe on his birthday has sparked widespread discussion on social media.
Speaking at the event, Ven. Rahula Thera had claimed that he had advised then-President Wickremesinghe not to import fuel ahead of the 2024 Presidential Election. However, the Thera has since clarified that the remark was made in error due to the pressure of the moment. Pertinent question is why did he choose such intervention?
All these are in such sharp contrast to Buddhist monks in the Western world and South East Asia where they shun luxury to lead a truly monastic lifestyle in order to practise what they preach.
Respected and loved in his own country as a man of great wisdom, Ajahn Cha was also instrumental in establishing Theravada Buddhism in the West. Beginning in 1979 with the founding of Cittaviveka commonly known as Chithurst Buddhist Monastery) in the United Kingdom, the Forest Tradition of Ajahn Chah has spread throughout Europe, the United States and the British Commonwealth. The dhamma talks of Ajahn Chah have been recorded, transcribed and translated into several languages.
More than one million people, including the Thai Royal Family attended Ajahn Chah’s funeral in January 1993 held a year after his death due to the “hundreds of thousands of people expected to attend”. He left behind a legacy of dhamma talks, students, and monasteries. The little I know of Buddhism teaches me to practice His Noble Teachings. It follows therefore the importance of listening to practising Buddhist monks who actually command respect, not by their titles! They don’t mean anything to me. Not familiar with various Nikayas, I think Buddhist monks should have both their shoulders properly covered in the interests of propriety! Though not a vegetarian, I believe in Ahimsa as even little spiders feel pain. Though my wife is scared of them, I tell her they are scared of her, more to the point! So, I catch the innocent crawly creatures by hand to throw them out of harm’s way! We have stopped the practice of throwing inevitable food waste into Council provided bins, instead collect them on a regular basis to feed wildlife we have in abundance around rural Wales we live in. They are all gone the following day including old marrow bones after our two little dogs finish with them! It gives us great pleasure! In the end, it all boils down to respecting Mother Nature! It’s Mother’s Day today to remember Mother Nature and how proud I am of my surname!
Sunil Dharmabandhu
Wales, UK
Opinion
East awaits PM Modi’s visit

Former Vice Chancellor, Eastern University
President, Batticaloa District Chamber of Commerce, Industries, and Agriculture (BDCCIA)
It has been announced that Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi will be visiting Sri Lanka this week
It is also understood that the Prime Minister will meet the Sri Lankan leaders and hold formal meetings for discussion and action. There will likely be many issues on the agenda.
However, in a country with centuries-old ties to India and a significant population with strong affiliations to the Indian people, it will be a pity if the Prime Minister were to limit his engagements to government representatives alone. While parliamentarians may be an obvious choice for meetings, they have already engaged with Indian counterparts frequently. It would be more relevant for the Prime Minister to meet with representatives from business sectors, trade unions, and chambers of commerce to gain a broader and more practical understanding of Sri Lanka’s economic landscape and its relations with India.
The Eastern Province, in particular, has a special claim for attention. The Indian government has previously indicated its commitment to developing the East, and it is crucial to have direct discussions with communities in the Eastern Province to understand their issues and the agreements India is willing to pursue in relation to development. If this does not happen, the Eastern Province risks being, once again, misled by promises that never materialise—a mirage that keeps its people hopeful but ultimately unfulfilled. The East has long remained in the blind spot of development, acknowledged but never truly engaged, resulting in rising poverty and unemployment. It desperately needs a concrete programme for meaningful restoration and growth.
Batticaloa, in particular, lacks both the political backing that Ampara enjoys and the economic advantage of Trincomalee, which benefits from its harbour. Without targeted intervention, Batticaloa and other underserved areas in the East will continue to lag behind.
India needs to be more aware of the Eastern Province’s potential if it is to play a constructive role in its development. The region is naturally gifted with abundant resources, making it highly suitable for agriculture, fisheries, dairy farming, and tourism. It has vast lagoons, water bodies (Thonas) that connect to the sea, forests, and coastal ecosystems—elements that create immense economic potential. India has expertise in all these sectors, and tourism, in particular, could thrive with increased engagement, given the presence of Hindu temples of cultural and religious significance to the Indian population.
The dry zone, which dominates the North and East, shares similarities with Indian landscapes, making it ideal for cultivating crops and flowers with mutual trade agreements. Expanding fisheries within the 200-mile exclusive economic zone in the East, as well as harnessing ocean floor resources, presents a valuable opportunity for both India and the Eastern Province. Additionally, the large cattle population in the region could greatly benefit from India’s expertise in dairy production, as India is the world’s largest milk producer. The vast lagoons in the East rival those of Kerala, offering significant potential for inland tourism with boat services and associated activities.
The scope for development is clear, but what remains uncertain is India’s real commitment as a development partner, as stated by the Sri Lankan government. The Prime Minister’s visit must engage with all communities to ensure transparency and assurance that the East will not be left behind.
It is also crucial for the Eastern Province to be treated with the same level of importance as the North. The North has its own dedicated branch of the Indian High Commission, and the Malayagam community has established formal links with India. However, the Eastern Province appears to be the forgotten limb in this equation, and this neglect must be addressed.
The Eastern Province also continues to grapple with unresolved issues from the past conflict, including physical and cultural encroachments. The region was separated from the North through a court ruling two decades after the Indo-Sri Lanka Agreement’s merger of the North and East, yet it has never had the referendum required by law. India’s interests in Trincomalee and its harbour are well known, but the larger population of the Eastern Province is still awaiting India’s engagement in the region’s overall development. The people in the East want India to be truly committed to facilitating progress in their region, and will eagerly look to see that its actions reflect that commitment.
Let us hope that this visit brings a mirror of true reflection and action, rather than be another mirage of unfulfilled promises.
by Prof. Emeritus Thangamuthu Jayasingam
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoSri Lanka’s eternal search for the elusive all-rounder
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoGnanasara Thera urged to reveal masterminds behind Easter Sunday terror attacks
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoAIA Higher Education Scholarships Programme celebrating 30-year journey
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoBid to include genocide allegation against Sri Lanka in Canada’s school curriculum thwarted
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoComBank crowned Global Finance Best SME Bank in Sri Lanka for 3rd successive year
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoSanctions by The Unpunished
-

 Latest News1 day ago
Latest News1 day agoIPL 2025: Rookies Ashwani and Rickelton lead Mumbai Indians to first win
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoMore parliamentary giants I was privileged to know











