Opinion
Red Alert: Need to quarantine imported organic fertilisers

By CHANDRE DHARMAWARDANA
Canada
When the government suddenly banned the import of fertilisers and pesticides in April 2021 and went ‘100 percent organic’, many scientists warned of dire danger ahead.
The hubris of becoming the world’s first to be free of alleged agricultural toxins made the government stand firm. Its rag-tag of ideologically motivated advisors pointed to roadside mounds of leaves, or Salvinia on rivers, and claimed that enough organic fertiliser can be produced, locally, to meet all needs. It was claimed falsely that Lanka’s ancients had even made it the ‘granary of the East’.
A decades-old ‘good food for health’ movement, among elite circles and fashionable eco-activists, gained a foothold among Sri Lankan nationalists as well. They falsely claimed that even the Chronic Kidney disease of Rajarata is caused by agrochemicals and that Lankans die of cancer due to the use of agrochemicals. According to one politicised doctor, the ancients ate toxin-free food and lived to 140 years, while modern Lankans have eaten poisoned food since 1970 (see https://dh-web.org/green/cdw-Padeniya18May2021.pdf, or Pethiyagoda: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qnmRk3BRtQc).
According to news reports, Sri Lanka is to import organic fertilisers costing Rs 3.8 billion, to cultivate 1.1 million hectares. This is alarming news. Organic fertilisers should not cross borders, as microbes, viruses and other components in them, benign in the local biosphere, may become harmful in a different biosphere.
More alarmingly, the organic fertilizer is from China! China is the country using the MOST amount of the harshest types of agrochemicals and industrial toxins. Its ‘organic fertiliser’ is made of urban waste, raw ‘night soil’, seaweeds or whatever, and processed for local use according to standards satisfactory for those ecosystems; but certainly ‘not’ for Sri Lankan ecosystems. Sri Lanka uses very low amounts per hectare of agrochemicals, even in the tea estates, as compared to most countries (see: The Island, 2021/05/6 ‘Political rhetoric, or sounding death knell for Sri Lanka’s agriculture?’ https://island.lk/political-rhetoric-or-sounding-death-knell-for-sri-lankas-agriculture/).
So, importing Chinese ‘organic fertilizer’ is like exporting bags of ‘processed’ Meethotamulla garbage to some country foolish enough to pay 3.8 billion rupees for it! While such humus is useful to the soil, the universally valid chemistry of proteins shows that such ‘organic fertiliser’ cannot contain significant amounts of nitrogen or phosphorus needed for plant growth. Claims of organic fertiliser, with unusually high nitrogen, content are pure propaganda.
Precautionary principle
Viruses, bacteria and other organisms in any imported product mutate and infect the host country rapidly. This danger is well understood and reflected in Sri Lanka’s import control standards.
Dr. Chris Panabokke, Director General of Agriculture some decades ago, strongly opposed suggestions to even ‘test’ the use of imported nitrogen-fixing bacteria, to enhance Sri Lanka’s relatively poor soils. A ‘good’ bacterium of a foreign ecosystem may become dangerous in a new ecosystem. Even an accidental release is a catastrophe. So the so-called ‘precautionary principle’ becomes relevant.
If a traveller had even visited a farm in a foreign country, or brought a mere twig of a plant, strict rules are applied at immigration, even though invasive pathogens and pests hitching a ride on imports is inevitable. Such invasions, including the invasion of the COVID-19 virus, are processes that countries have learnt to control as much as possible.
Importation of fertilisers and other agrochemicals, be they inorganic or organic, requires that the product be sterile, which means free of living organisms, and free of soils. Impurities like heavy metals and chemical residues should only occur at levels below the maximum allowed limits (MALs).
No country willingly imports potentially dangerous materials that can irreversibly implode a country’s food system and the health of its citizens. The organic fertiliser needed to cultivate 1.1 million hectares may be anywhere from 50-500 million metric tonnes, depending on the planted crops and soil conditions. No exporter of organic fertiliser, anywhere in the world, is set up to sterilise such large quantities of organic fertiliser or remove any residual soils from such fertilizer. So it is safe to distrust any large export.
Facing danger when much is at stake
No country can properly sample a huge amount, 30 to 500 million metric tonnes of a non-uniform material like organic fertiliser. Elementary statistical theory shows that for such non-uniform materials a fraction 1/e of the total, where “e=2.718” (the base of the Napierian logarithm) must be sampled. Even all the analytical chemistry labs of the whole world working for the President of Sri Lanka, cannot do the job!
However, a non-uniform material contaminated with pathogens has billions of pathogens. So even a few samples may show SOME pathogens, though not all types of pathogens, and that is the red alert.
News reports say that two advanced samples were found to be contaminated with Erwinia and Bacillus bacteria dangerous to crops, and also other pathogens harmful to humans. This is extremely alarming news. The food security of the country, the health of its residents, and prospects for generations are at stake. When so much is at stake, the precautionary principle must be applied.
Steps to take in facing the ‘Red Alert’
These so-called organic fertilizers are likely to arrive in Sri Lanka anytime soon. Drastic steps are needed to avert an irreversible tragedy. Humpty Dumpty cannot be put back on the wall, and his splinters should not spew havoc all over the island. Hence, here are the steps to take:
1.
Leading agricultural and health scientists should file a fundamental rights petition, based on the intrinsic impossibility of fulfilling the plant and biohazard quarantine rules at the scale of the planned imports.
2.
Require that the imported material on arrival be quarantined in an off-shore facility (an army-controlled island, for example) and sterilised to free it of pathogens.
3.
Once sterilised, the heavy metals content must be reduced below the Maximum Allowed Limits, as discussed below.
4.
The only technically viable option for the mass sterilisation of millions of tonnes of a metrical is via gamma-ray irradiation. An off-shore facility must be built where the foreign organic material is slowly and repeatedly rolled over a battery of gamma-ray sources (see, for example, N. Halis, Med Device Technol. 1992 Aug-Sep; 3(6):37-45.)
5. The sterilized organic fertiliser must then be freed of heavy metals such as Arsenic, Cadmium, Lead, Mercury that are extremely harmful to human and animal health.
Considering Cadmium (Cd) as an example, and the European average of 50 mg of Cd per kilogram of inorganic fertiliser as the MAL, the safe amount in organic fertiliser (applied in tonnes and not kilos) should be hundreds of times less. In fact, almost all the heavy metals have to be removed. Chemically removing all the heavy metals from millions of tonnes of fertiliser is impossible, and creates the bigger problem of disposing of the impurity. The only option is to render the heavy metals inert and ineffective using a cheap, non-poisonous but powerful chemical chelating agent that is also available in commercial quantities.
The only substance that fits the bill is glyphosate. It is known to promote the growth of earthworms and increase useful microorganisms when applied to contaminated soils (see: Environmental Toxicology, 2014 https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2683). The imported sterilised organic fertiliser must be mixed with the appropriate amount of glyphosate, in mixing vessels similar to cement mixers at each farming site.
6.
Alternatively, the import should be returned to China and Lanka suffers its loss, but avoids steps 1 to 5.
7.
The recent ambiguous gazette notification on limiting the import of agrochemicals should be challenged by importing a few kilos of urea and TPS as legal tests.
Once the first batch of organic fertilizer is handled according to the steps indicated above, no more organic fertiliser should be imported to avert irreversible tragedy.
Only locally made organic fertiliser must be used to provide ‘organic food’ for those who want it. Local composting must be technically controlled, to sequester dangerous greenhouse gases like methane and CO2 that should not be released into the atmosphere (see: R. Lal, https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/abs/10.1098/rstb.2007.2185). The major part of the market can be supplied via conventional agriculture, which is much safer from an environmental and human-health point of view than organic agriculture.
(The author was a professor of chemistry and a Vice-Chancellor of the Sri Jayewardenepura University in the 1970s, then known as the Vidyodaya University. Currently, he is affiliated with the National Research Council of Canada and the University of Montreal)
Opinion
Conference “Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill: Neither Here, Nor There”

January 21 | Olympus Auditorium, Bandaranaike Centre for International Studies (BCIS)
The National Collective of Community Savings and Credit Services Providers organised the conference “Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill: Neither Here, Nor There” on January 21 at the Olympus Auditorium, Bandaranaike Centre for International Studies (BCIS), BMICH, to foreground the community savings and credit services as an alternative credit practice to moneylending and microfinance. While underscoring the uniqueness of community credit practices, grounded in collective rights, solidarity, mutual aid, the non-hierarchical nature of organising and long years of practice, community credit providers opposed the Asian Development Bank (ADB)-Treasury-CBSL attempt to subsume the community credit model under moneylending and microfinance in the proposed Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill. Over 200 community credit practitioners from more than 50 community organisations from Mannar, Kilinochchi, Jaffna, Mullaitivu, Batticaloa, Anuradhapura, Polonnaruwa, Badulla, Rathnapura, and Hambanthota had gathered at the conference.
M. K. Jayathissa, a farmer leader from Hingurakgoda, Polonnaruwa, explained the microfinance crisis as resulting from the microfinancialisation of rural credit and the targeting of low-income women. He recalled his role in the farmers’ struggle against debt during the 1990s. Jayathissa linked the microfinance crisis among women and the farmers’ debt crisis to a wider crisis in food production.
Renuka Bhadrakanthi, chairperson of the Ekabaddha Praja Sanwardhana Kantha Maha Sangamaya, Weligepola, shared her three decades of experience as a community practitioner. She showed how the community credit framework helped women build assets and wealth through small savings. Unlike market-based initiatives such as microfinance and moneylending, community-controlled credit systems empowered women both with agency and material capabilities. Renuka also noted the regional diversity in organisational frameworks and credit purposes. She stressed the need for vigilance and action now, as globalisation and neoliberalism drive economic reforms aimed at capturing community wealth and making people dependent on the market.
Rajeswary Sritharan from Yuhashakthi, Mullaitivu, brought in experiences from war-torn societies. Yuhashakthi and Mahashakthi networks, operating in the Northern and Eastern provinces and comprising more than 10,000 women members, were created during the civil war to support women’s ability to control the household economy. These two networks have proven resilience against war-related dispossession and loss while also strengthening women. Rajeswary contended that self-help community credit groups are informal and unregulated, revealing that societies are governed by a collective ethos, community audits, and democratic decision-making, ensuring transparency and accountability. She pointed out that community groups do not have a history of bringing their members before the police or courts when they fail to service their debts, unlike microfinance companies. She also raised the significance of community groups such as Yuhashakthi and Mahashakthi as first responders in times of crisis, even as recently as with Ditwah, intervening and assisting affected communities much before the government could.
- Suneth Aruna Kumara
- Pubudu Manohara
- M K Jayathissa
Suneth Aruna Kumara, representing Vimukthi Gami Gowi Kantha Samithiya, Hingurakgoda, Polonnaruwa and also speaking on behalf of the microfinance-affected women, highlighted the creative space that collective forms of association have opened up for microfinance victims. “People who were hiding, afraid of debt collectors, are trying to rebuild their lives autonomously,” he said. In this journey, women are rethinking the meaning of credit, whether it is possible to create credit mechanisms that do not rely on interest income, and imaginative ways of decommodifying community relations. Suneth emphasised that women’s initiatives are emerging from their lived experiences as debtors, exploited by predatory interest rates and violent recovery practices. As a victim himself, Suneth criticised the proposed regulatory Bill for failing to adequately safeguard microfinance and credit consumers by providing legally binding safeguards. According to Suneth, the proposed Bill does not guarantee that the microfinance crisis will not recur.
Another highlight of the conference was the sharing of experiences by Malaihaya women, presented by Letchumanan Kamaleswary from the Centre for Equality and Justice. Kamaleswary described debt as ever-present in the Malaiyaha community. It forced migration from South India and kept people captive as plantation labour for over 200 years. Although the plantation management restricts all community associations within the plantations, microfinance companies can enter and operate freely. Debt is so severe that most Malaiyaha women work past their retirement age.
- Renuka Bhadrakanthi
- Rajeswary Sritharan
Pubudu Manohara, from the Rural Development Foundation in Hambanthota, traced the history of community credit projects to various state poverty alleviation programmes since 1977. These projects, affiliated with governments and supported by international groups such as the World Bank and UNDP, have survived many national and local crises. Over time, however, both the government and international organisations like the ADB have become wary of people’s ability to save. “They are afraid of our ability to create community funds,” he said.
The discussion emphasised that mobilising community groups and local political leaders is essential to oppose the Bill in its current form. Concerns arose about the negative impact of heavy regulations on community organisations and women’s resilience. “Domestic violence is rooted in economic violence. The destruction of community organisations will have a direct effect on local development and local economic activities. That will also burden the government,” said a Yuhashakthi representative from Mullathivu.
Community organisers urged the government to consult directly with them when developing regulations, emphasising that new rules should protect and strengthen community-based initiatives rather than respond to external pressures. They argued that the ADB, having promoted commercialisation of microfinance and contributed to the resulting crisis, lacks the legal and ethical standing to advocate for regulatory frameworks. Instead of receiving directives from the International Financial Institutions (IFIs), the government should converse with the grassroots communities, devising homegrown developmental solutions to regenerate local economies, empower the most vulnerable and build community wealth, the community organisers stressed.
Opinion
A puppet show?
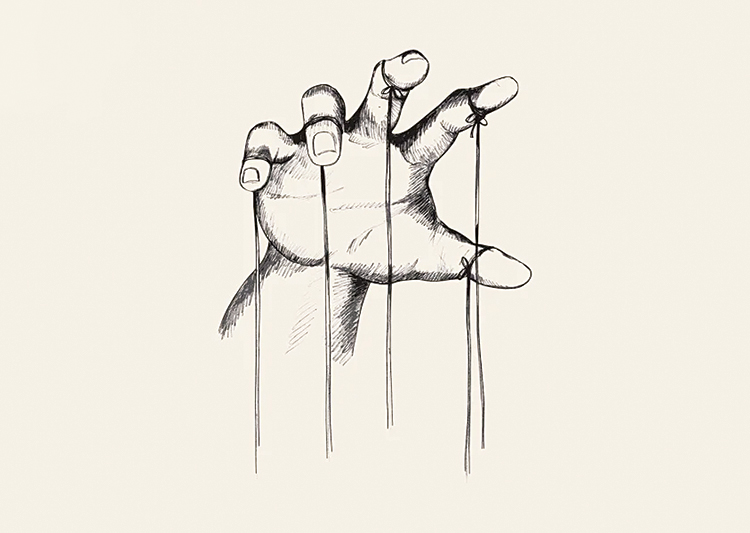
After jog for the camera, wearing shorts in Jaffna, thanks to the freedom gained by the country being liberated from the clutches of the Tigers by the valiant efforts led by Mahinda Rajapaksa, President Anura Kumara Dissanayaka, said: “Some come past Sri Maha Bodhi and other Buddhist temples all the way to Jaffna to observe Sil, not to spread compassion but hatred.” When the need of the hour is reconciliation what an outrageous statement that was, to be made by the head of state! Will he say that the people of the North and the East bypass many Kovils straddling the area and come to Kataragama to spread hate? Probably not! His claim has become a hot topic of conversation.
Having lost a majority of the votes garnered from the North at the presidential and parliamentary elections, to the Tamil nationalist parties at the local government elections, President Dissanayake’s claim may well have been a pitiful attempt to recover lost ground in the North. But at what cost?
It all started with AKD’s refusal to refer to those brave service personnel who saved the unity and the integrity of the country as Rana Viruwo. Interestingly, the most devastating rebuke for this came from a Tamil MP, who is an avowed admirer of Prabhakaran, stating in Parliament that a Sinhala Rana Viruwa saved his life when he was about to be washed off in the flood waters resulting from Cyclone Ditwah. He teased the government by asking in ‘raw’ Sinhala Ei umbalata lejjada unta Rana Viruwo kiyanna? (Are you shy to call them war heroes?)
In addition to slinging mud at MR and harassing service personnel, there is no doubt whatsoever that AKD’s government is trying to harass any Tamil politicians who helped eradicate the Tigers. This fact is borne out by the treatment meted out to Douglas Devananda. Shamindra Ferdinando has explained this in his article, “EPDP’s Devananda and missing weapons supplied by Army” (The Island, 7 January).
NPP ministers publicly insult Buddhist monks, but whenever they are in trouble, they rush to Kandy to meet the Maha Nayakas, the latest being Harini’s visit. Instead of admitting the mistake and trying to make amends, the government went on, until it realised the futility in trying to justify the ‘Buddy’ episode. Excuses given by Harini to the Maha Nayakas, to say the least, were laughable. She had the audacity to say that though the questionable web link was printed in the textbook there were no instructions to click on it! She may continue as Prime Minister but can anyone who does not know what to do with a link or who is trying to encourage ten-year-olds to have e-buddies when the rest of the world is heading towards banning 16-year-olds from social media, continue to be the Minister of Education?
Number of MOUs/pacts signed with India, including defence, have not yet been disclosed even to Parliament. The Cabinet Spokesman once stated that the contents of those MOUs/pacts could not be divulged without the consent of India. Interestingly, we have had very frequent visits from VVIP politicians and top government officials from India, some at very short notice. One of them referred to these as ‘usual’ ones! However, what is unusual is that a party that shed a lot of blood of Sri Lankans for even selling ‘Bombay’ onions, is now in government and seems under Indian command. Perhaps, its transformation occurred when India sponsored a visit by AKD in early 2024, which helped him secure the presidency. Among the NPP’s election pledges, the most touted one was to reveal the mastermind behind the Easter Sunday attacks. It has been alleged in some quarters that India was behind the attacks. The NPP government’s silence about this speaks volumes!
It has transpired recently that it was Indian High Commissioner Gopal Baglay who pressured Speaker Mahinda Yapa Abeywardena in July 2022 to take over the presidency after the elected President was toppled by protesters, but many believe that it was a joint effort by the Indian HC and the ‘Viceroy’ who just left, after an overstay! It is an illegal act as pointed out in the editorial “Conspiracy to subvert constitutional order” (The Island, 22 January) and may be investigated by a future government, if elections are not postponed forever!
We seem to be watching a puppet show where many puppeteers outside are pulling the strings! Are we paying the price for electing a bunch of inexperienced politicians?
By Dr Upul Wijayawardhana ✍️
Opinion
Remembering Cedric, who helped neutralise LTTE terrorism

Salute to a brave father-son
Cedric Martenstyn was a very affluent man. He owned a house in Colombo 7, valuable properties throughout the country, vehicles / speed boats and ran the lucrative business of importing Johnson and Evinrude Outboard Motors (OBM) and sold them to local fishermen and businessmen.
Cedric was the local agent for the OBMs, which were known for reliability and after-sales service, and among his customers were humble fishermen. He was fondly known as Sudu Mahattaya “(white Gentleman) by humble fishermen and he would often travel in his double cab across the country to meet his customers and solve their problems.
He had a loving wife and children. He was an excellent scuba diver, member of Sri Lanka Navy Practical Pistol Firing team and his knowledge of wildlife and reptiles was amazing.
A member of the Dutch Burgher community of Sri Lanka, he was a true patriot, who volunteered to protect country and people from terrorists. An old boy of S. Thomas’ College, Mount Lavinia, he was an excellent sportsman.
The founding father of Sri Lanka Army Commando Unit, Colonel Sunil Peris, was his classmate at S.Thomas’.
I first met Cedric when I was a very junior officer at Pistol Firing Range at Naval Base, Welisara. I helped him catch a poisonous snake in the Range. I think he carried that snake home in a bottle! That was the type of person Cedric was!
We became very close friends as we both loved “guns and fishing rods”. His experience and tactics in angling helped me catch much bigger Paraw (Trevallies) in the Elephant Rock area at the Trincomalee harbour. He was a dangerous man to live with at Trincomalee Naval Base wardroom (officers’ mess), because he had various live snakes kept in bottles and fed them with little frogs!
Even though he was a keen angler, he was keen to conserve endangered species both on land and in water. He spent days in Horton Plains and the Knuckles Mountain Range streams to identify freshwater species in Sri Lanka. Did you know there is an endangered freshwater fish species he found in Horton Plains and Knuckles Mountain Range has been named after him?
Feeding of snakes was an amusement to all our stewards at the wardroom at that time! They all gathered and watched carefully what Cedric was doing, keeping a safe distance to run away if the snake escaped. Our Navy stewards dare to enter Cedric’s cabin (room) at Trincomalee wardroom (officers’ mess), even keeping his tea on a stool outside his cabin door. One day pandemonium broke in the officers’ mess when Cedric announced that one snake escaped! We never found that snake, and that was the end of his hobby as the Commander Eastern Naval Area, at that time, ordered him to ” get rid of all snakes! Sadly, Cedric released all snakes to Sober Island that afternoon.
Cedric was a volunteer Navy officer, but still joined me (he was 47 years old then) to help SBS trainees (first and second batch) on boat handling and OBM maintenance in 1993, when I raised SBS. It was exactly 31 years ago!
The Arrow Boat
Being an excellent speed boat race driver and boat designer, he prepared the blueprint of the first “18-foot Arrow Boat” and supervised building it at a private Boat Yard in 1993. This 18- foot Arrow Boat was especially designed to be used in the shallow waters of the Jaffna lagoon, fitted 115 HP OBMs, and with two weapons he recommended; 40mm Automatic Grenade Launcher (AGL) and 7.62×51 mm General Purpose Machine Guns (GPMGs). In no time, we had highly trained and highly motivated four SBS men on board each Arrow Boat at Jaffna lagoon, and they were very effective.
Same hull (deep V hull) developed during the tenure of Admiral of the Fleet Wasantha Karannagoda, as Commander of the Navy, by Naval architects, with knowledge-gained through captured LTTE Sea Tiger boats, designed 23- foot Arrow Boats and implemented the “Lanchester Theory” (theory of battle of attrition at sea in littoral sea battles) to completely nullify LTTE’s superiority which it had gained with small craft and deadly suicide boats.
Thank you, the Admiral of the Fleet for understanding the importance of Arrow Boat design and mass production at our own boatyard at Welisara. Karannagoda, under whom I was fortunate to serve as Director Naval Operations, Director Maritime Surveillance and Director Naval Special Forces during the last stages (2006/7) of the Humanitarian Operations, always used to tell us “You cannot buy a Navy- you have to build one”! Thank you, Sir!

Cedric craft display at Naval Museum, Trincomalee
The Hero he was
When I was selected for my Naval War Course (Staff Course) conducted by the Pakistan Navy Staff College at Karachi, Pakistan, (now known as Pakistan Navy War College relocated at Lahore), Cedric took over the command (even though he was a VNF officer) as Commanding Officer of SBS.
Being one of the co-founders of this elite unit, he was the most suitable person to take over as CO SBS. He was loved by SBS officers and sailors. They were extremely happy to see him at Kilali or Elephant Pass, where SBS was deployed during a very difficult time of our recent history – fighting against terrorists during the 1996-97 period.
Motivated by father’s patriotism, his younger son, Jayson, who was a pilot working in the UK at that time, came back to Sri Lanka and joined the SLAF as an volunteer pilot to fly transport aircraft to keep an uninterrupted air link between Palaly (Jaffna) and Ratmalana (Colombo). Sometimes Jayson flew his beloved father on board from Palaly to Ratmalana. Cedric was extremely happy and proud of his son.
Tragically, young Jayson was killed in action in a suspected LTTE Surface-to-Air missile attack on his aircraft. Cedric was sad, but more determined to continue the fight against LTTE terrorists. He would also lead the rescue and salvage operation to identify the aircraft wreckage his son flew in. The then Navy Commander advised him to demobilise from VNF and look after his grieving family or join Naval Operations Directorate and work from Colombo which he vehemently refused. When I called him from Pakistan to convey my deepest condolences, he said, he would look after the “SBS boys”, he had no intention of leaving them alone at that difficult hour of our nation. That was Cedric. He was such a hero—a hero very few knew about!
The young officers, and sailors in SBS were of his sons’ age, and Cedric would not leave them even when he was facing a personal tragedy. He was a dedicated and courageous person.

Scientific name: Systomus Martenstyni
English name : Martenstyn’s Barb
Local name: Dumbara Pethiya
Sadly, like many who served our nation and stood against terrorists, Cedric would go on to be considered Missing In Action (MIA) following a helicopter crash off the seas of Vettalikani with Lt. Palihena (another brave SBS officer- KDU intake). He was returning to Point Pedro after visiting the SBS boys at Elephant Pass, Jaffna.
Cedric and his son, Jayson, will go down in history as a brave father-son duo who paid the supreme sacrifice for the motherland. MAY THEY REST IN PEACE ! Salute!
Commander Martenstyn was considered missing in action (MIA) on 22 January 1996 in the sea off Vettalaikerni, while returning to Palaly Air Force Base in an SLAF helicopter when it was lost to enemy fire. He was returning from visiting an SBS detachment in Elephant Pass near the Jaffna Lagoon. Considering his contribution to the war effort, his gallentry and valour in fighting the enemy, and his steadfast service to the Sri Lanka Navy in manufacturing Arrow Boats, and training the SBS, all SLN Arrow Boats were renamed ‘Cedric’ on his 70th Birthday.
(The writer is former Chief of Defence Staff and Commander of The Navy, and former Chairman of the Trincomalee Petroleum Terminals Ltd.)
By Admiral Ravindra
C Wijegunaratne
(Retired from Sri Lanka Navy)
Former Chief of Defence Staff and Commander of the Sri Lanka Navy,
Former Sri Lanka High Commissioner to Pakistan
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoExtended mind thesis:A Buddhist perspective
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoAmerican rulers’ hatred for Venezuela and its leaders
-

 Business13 hours ago
Business13 hours agoComBank advances ForwardTogether agenda with event on sustainable business transformation
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoCORALL Conservation Trust Fund – a historic first for SL
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoRemembering Cedric, who helped neutralise LTTE terrorism
-
 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoA puppet show?
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoHistory of St. Sebastian’s National Shrine Kandana
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoThe middle-class money trap: Why looking rich keeps Sri Lankans poor


















