Features
Proposed Penal Code amendmentand threat of promotion of sexual abuse of children – IV

by Kalyananda Tiranagama
Executive Director
Lawyers for Human Rights and Development
(The third part of this article appeared in The Island of 13 June 2023)
Joining the discussion, Freedom People’s Congress MP Prof. Charitha Herath has said that they would support decriminalization of same-sex relations, if and when the Bill is presented to Parliament.
‘‘We must engage with two domains to achieve the desired results. One is the political domain and the other is the cultural domain. We can change old fashioned political and cultural establishments through constant engagement. ‘’
‘’The technical approach alone will not usher in a meaningful change. That is why I highlight the importance of cultural discussions, as well, to overcome the existing barriers. Sometimes, I feel that these cultural platforms are forgotten by the younger generation,’’ Prof. Herath explained.
Minister Jeevan Thondaman countered the argument that culture was a barrier in achieving non-discrimination for the LGBTQ community in SL. He said ‘’ There is more than enough evidence from ancient history that same sex relations existed and they were very much embraced many, many centuries ago.’’ Thondaman pledged support to legislative reforms decriminalizing same-sex relations.
(E) Existing Penal Code provisions compared with Proposed Amendments
S. 365 of the original Penal Code: ‘’ Whoever voluntarily has carnal intercourse against the order of nature with any man, woman, or animal shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to 10 years and shall also be liable to fine.’’
In the Penal Code there is no definition as to what is meant by carnal intercourse against the order of nature. According to Indian cases, acts of anal sex and oral sex were considered as carnal intercourse against the order of nature. The Police had no idea as to what is meant by it. Only where there was a complaint of a person having anal or vaginal sex with an animal, like a cow, goat or a bitch, they acted on it. This happened very, very seldom and this provision remained almost unenforced.
However, with the promotion of tourism in the 1980s, many incidents of foreign tourists having anal sex with male children were reported. The Police used to produce the suspects in courts for committing an offence not under this Section but under S. 365A of the Penal Code, carrying a much less penalty.
By 1995 Amendments, S. 365 was amended by adding a clause making it explicitly applicable to punish sexual abusers of children.
1995 Amendment of S. 365 of the Penal Code –
‘’ Whoever voluntarily has carnal intercourse against the order of nature with any man, woman, or animal shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to 10 years and shall also be punished with fine and where the offence is committed by a person over 18 years of age in respect of a person under 16 years of age, the offender shall be punished with rigorous imprisonment for a term not less than 10 years and not exceeding 20 years and with fine and shall also be ordered to pay compensation of an amount determined by court to the person in respect of whom the offence was committed for injuries caused to such person.’’
The new Bill proposes to repeal S. 365 and substitute it with the following section:
‘’Whoever voluntarily has carnal intercourse against the order of nature with an animal, shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to 10 years and shall also liable to fine.’’
Under the proposed Bill, anal or oral sex with any man, woman or child will no longer be considered as carnal intercourse against the order of nature; it will be considered as normal human sexual behaviour, not an offence punishable under the law.
This new Bill proposes to totally repeal S. 365A of the Penal Code, without any substitution.
S. 365A of the original Penal Code:
‘’Any male person who, in public or private, commits or is a party to the commission of, or procures or attempts to precure the commission by any male person, of any act of gross indecency with another male person shall be guilty of an offence and shall be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend up to two years or with fine or both, and shall also be liable to be punished with whipping.’’
This provision covered offences committed by male persons only. 1995 Amendment made it applicable to cover offences committed by both male and female persons and made provision for imposing deterrent penalties for offences committed on children.
1995 Amendment of S. 365A of the Penal Code –
‘’Any person who, in public or private, commits or is a party to the commission of, or procures or attempts to precure the commission by any person, of an act of gross indecency with another person is guilty of an offence punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend up to two years or with fine or both and where the offence is committed by a person over 18 years of age in respect of any person under 16 years of age shall be punished with rigorous imprisonment for a term not less than 10 years and not exceeding 10 years and with fine and shall also be ordered to pay compensation of an amount determined by court to the person in respect of whom the offence was committed for injuries caused to such person.’’
The Supreme Court Determination on the Bill…
Three persons had filed an application – SC SD No. 13 / 2023 – in the Supreme Court challenging the constitutionality of this Bill. Fourteen petitions have been filed by persons seeking Court’s permission to intervene in the Application and the Court has allowed their applications. Out of the 14 intervenient applications, intervenient petitioners only in two applications have supported the petitioners opposing the Bill. Intervenient petitioners in 12 intervenient applications have supported the Bill, opposing the petitioners.
Among the Intervenient petitioners who supported the Bill, there were representatives of four foreign-funded NGOs that have played a leading role in the anti-Sri Lanka campaign carried on in the UN HRC in Geneva making wild allegations against the Govt.
of Sri Lanka since 2006; representatives of 3 or 4 LGBTQ groups; a former Professor in the Faculty of Law, University of Colombo; a leading NGO figure who has served as the President and two other women who have served as members of the Human Rights Commission of Sri Lanka; a women who has served as the President of the National Child Protection Authority; the person who moderated the discussion at the Canadian High Commission and a major activist in the LGBTQ movement in Sri Lanka.
Having examined and analysed the arguments and submissions of the Counsels for the petitioners, intervenient petitioners, respondents and the Attorney General, the Court has made its determination in a lengthy a Judgement. As mentioned in the Judgement:
This Bill proposes to repeal S. 365A in its entirety. ‘‘It must be reiterated that the cumulative effect of the Bill, as captured in Clause (2) (iii), is that sexual orientation of a person shall no longer be a punishable offence, and any consensual conduct between two adult persons of the same sex, irrespective of whether it takes place in private or public, shall no longer be an offence.’’ – P. 10
‘‘The Counsels who appeared for the petitioners opposing the Bill have presented four arguments in support of their position that the provisions of the Bill are violative of Articles 1,3, 4d, 9, 12(1), 13(4), 27(1), 27(2)(d) and 27(13) of the Constitution…It must, perhaps, be stated at the outset that in our view, ex facie, none of the four arguments impinge upon the provisions of Articles 1, 3, 4d, 12(1) and 13(4) of the Constitution….
‘‘The first argument was that the safeguards provided in Ss. 365 and 365A for the protection of children and those under 16 years of age will be taken away by the amendments proposed by the Bill, thereby creating space for exploitation of children and leaving a lacuna in the enforcement of the law relating to offences against children.
‘‘In this connection it was further submitted that:
exposure to lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) programmes in schools could impact upon the free decision-making power of children and give rise to transgender children;
the enactment of the Bill would be contrary to the provisions in Article 27(13) which provides that ‘The state shall promote with special care the interests of children and youth, so as to ensure their full development, physical, mental, moral, religious and social, and protect them from exploitation and discrimination.’;
the protection presently afforded to children would be removed, if Ss. 365 and 365A are amended as proposed by the Bill, and that even a person under 16 years of age could engage in sexual activity with a person over 18 years of age.
‘‘ It is in this background that this Court was urged as the upper guardian of children to act in the best interests of the child and declare that the Bill is violative of Article 12(1).
The Stand taken by the State…
‘‘The learned Additional Solicitor General Haripriya Jayasundara, PC, submitted that women and children were the focus of the amendments introduced to the PC in 1995, and that while Ss. 365 and 365A were amended by increasing the punishment where one party was a person below the age of sixteen, S. 365B introduced a new offence titled ‘grave sexual abuse.’ It was further submitted by the Additional Solicitor General that the amendment introduced to S, 365B by the Penal Code Amendment Act No. 29 of 1998 specifically provides that consent with regard to any sexual conduct constituting grave sexual abuse is immaterial where the offence is committed in respect of a child below the age of 16. – vide S. 365B(1)(aa). It was her position that in the event the conduct of any person does not fall within the definition contained in S. 365B, S. 345 of the PC which deals with sexual harassment could be resorted to in order to protect children against any unwelcome sexual advances by words or action. Thus, the contention of the petitioners is unfounded and without any legal basis.’’
It appears that the Court has come to this conclusion on the basis of the submission made by the learned Additional Solicitor General. However, her submission is far from correct. It does not appear from the Judgement as to whether the Counsels of the petitioners made any attempt to show the fallacy of the submissions made by the learned ASG.
‘‘The second argument of the Counsels of the petitioners was that the impugned amendment will dilute the Rule of the Law and result in the life and liberty of the citizens being at risk. This argument is even more tenuous and the petitioners have not been able to connect passing of this Bill to any violation of the Rule of the Law.
‘‘The third argument was that a majority of those with HIV and Aids have history of male or bisexual exposure and that decriminalization of same-sex relationships will give rise to an increase in the number of persons infected with HIV and Aids. It was further submitted that this would have an adverse impact on national security by destroying individuals, families, communities, economic and socio-political institutions, and the military police forces, and that the protection granted by the Chapter on fundamental rights cannot be truly enjoyed without the provision of a safe, secure and protective environment in which a citizen of Sri Lanka may realize the full potential of his existence.
‘‘However, little to nothing has been submitted to this court in support of this proposition other than a singular point that HIV and Aids affect those engaging in same-sex intercourse more than those engaging in hetero-sexual intercourse. Hence, the material placed before this Court by the petitioners does not support their position that HIV and Aids are only prevalent in homo-sexuals or that the proposed amendment will result in an increase in the number of persons afflicted with HIV and Aids.
‘‘Counsels for some of the intervenient petitioners presented three important arguments. The first was that it is not only homo-sexual males who contract HIV, but female sex workers, returnee migrant workers and those who use or inject drugs. The second is that criminalization of homo-sexual conduct between two consenting adult males has only resulted in such persons being marginalised from society and thereby being deprived to access of proper health care which if available would address the spread of HIV and Aids among those persons. The third is that the amendment of S. 365 and S, 365A would facilitate the outreach to individuals and groups at a heightened risk of infection. The intervenient petitioners and the ASG agree on the point that the perception that HIV is disproportionately higher in homo-sexuals is due to the social stigma caused by the criminalization of their relationships…..The Counsels of petitioners did not adduce any scientifically acceptable evidence in support of this line of thinking.
The fourth and final argument was that ‘‘homo-sexual activity is contrary to the principles of Buddhism and therefore violates Article 9 of the Constitution…. The petitioners did not explain the manner in which the decriminalization of one’s sexual orientation derogates from the State’s duty protect and foster Buddha Sasana nor the point of how the proposed amendments are prohibited by or contrary to Buddha Sasana, except to state that it is an offence (parajika) for a Buddhist priest to have sexual relations with another, irrespective of whether the other person is of the same sex or opposite sex.
‘‘On the contrary, Mr. Sanjeewa Jayawardana, PC and Mr. Prasantha Lal de Alwis, PC, appearing for some of the intervenient petitioners submitted that: (a) Bhikkus and Bhikkunis have a separate code of conduct (Vinaya rules) and lay persons are not governed by the rules in the said code; (b) none of the ‘sutras’ focussed on the conduct of lay persons condemn homo-sexuality; (c) while the basic tenets of all religions are that all human beings should be treated fairly and equally irrespective of their circumstances, the fundamental teachings of Buddhism includes tolerance towards and equal treatment of all human beings and that Buddhism does not discriminate persons whose sexual orientation is anything other than hetero-sexual; (d) from whatever parity of reasoning, it would be outrageous for the petitioners to allege that a law which decriminalises homosexuality would result in the undermining of the Buddha Sasana.
‘’We are of the view that the final argument of the petitioners too lacks merit.
‘‘Most of the arguments put forward by and in support of the petitioners are largely based on speculation and may be disposed of summarily. For instance, the argument that children would be harmed by the passing of this Bill or the argument that there shall be an increase in the number of those afflicted with HIV and Aids is specious.’’ – P. 17 (To be continued)
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
Talento … oozing with talent
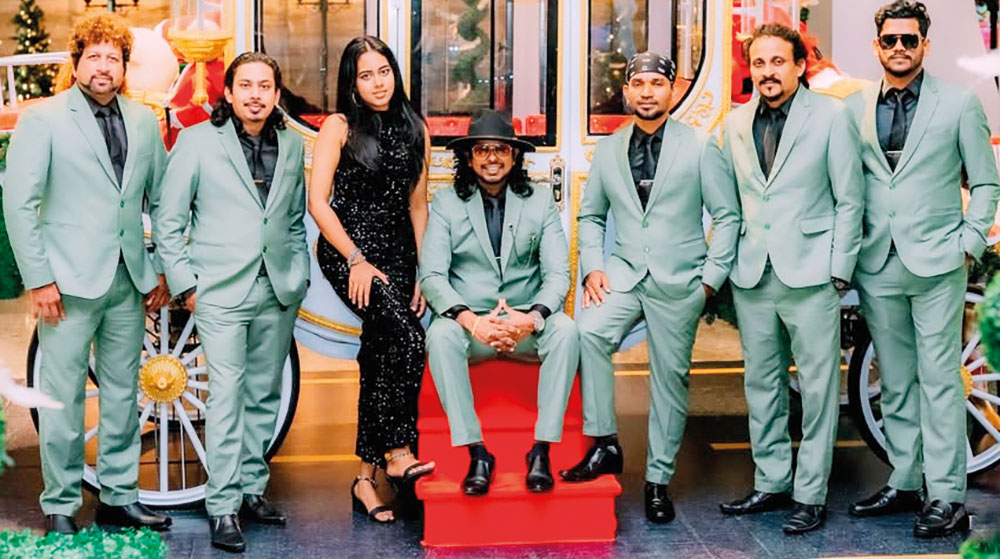

 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
Features
Special milestone for JJ Twins
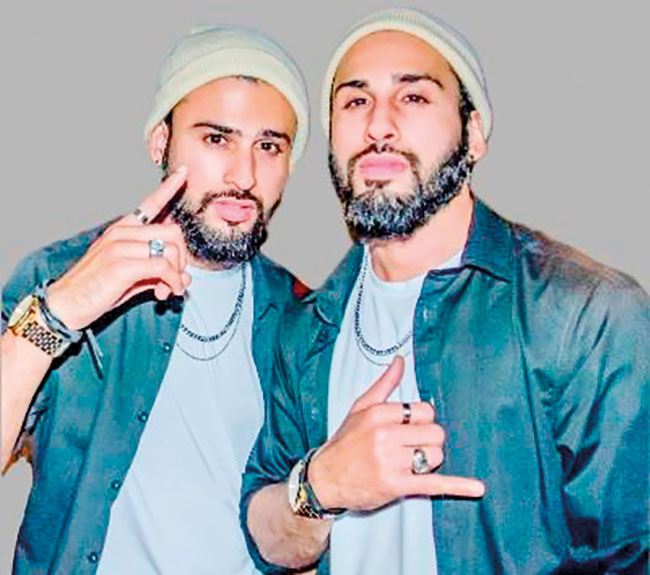

The JJ Twins, the Sri Lankan musical duo, performing in the Maldives, and known for blending R&B, Hip Hop, and Sri Lankan rhythms, thereby creating a unique sound, have come out with a brand-new single ‘Me Mawathe.’
In fact, it’s a very special milestone for the twin brothers, Julian and Jason Prins, as ‘Me Mawathe’ is their first ever Sinhala song!
‘Me Mawathe’ showcases a fresh new sound, while staying true to the signature harmony and emotion that their fans love.
This heartfelt track captures the beauty of love, journey, and connection, brought to life through powerful vocals and captivating melodies.
It marks an exciting new chapter for the JJ Twins as they expand their musical journey and connect with audiences in a whole new way.
Their recent album, ‘CONCLUDED,’ explores themes of love, heartbreak, and healing, and include hits like ‘Can’t Get You Off My Mind’ and ‘You Left Me Here to Die’ which showcase their emotional intensity.
Readers could stay connected and follow JJ Twins on social media for exclusive updates, behind-the-scenes moments, and upcoming releases:
Instagram: http://instagram.com/jjtwinsofficial
TikTok: http://tiktok.com/@jjtwinsmusic
Facebook: http://facebook.com/jjtwinssingers
YouTube: http://youtube.com/jjtwins
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-
 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans

























