Features
My Cricketing Journey, From Big Dreams To Big Matches

Michael Wille died in Australia a few days ago and his funeral will take place on Dec. 6
By Michael Wille
I have been asked to write an article about my cricketing journey from Colombo to Melbourne. I have some reservations about how relevant my article will be. However, I trust that it will serve essentially as an insight to the exhilarating schoolboy cricketing era of the 1950s.I debuted for Royal in ’54 and captained in ’57. A couple of weeks after the Royal-Thomian I migrated to Australia, and was the first Sri Lankan to play District (Grade) cricket in Melbourne.
In the ‘50s, Sri Lanka was far from attaining test status. Sri Lanka possessed great players such Mahadevan Sathasivam, F C de Saram, C I Gunasekera, Vernon Prins, and Mike Tissera, et al. The only exposure to international cricket that Sri Lanka had was a one-day friendly played when the English or Australian teams passed through Colombo on their way to Australia or England every two years.
In Australia at that time the game was purely amateur. Today, Sri Lanka has achieved test status and cricket is professional in both countries and the standard of cricket is considerably higher, particularly fielding.
Maybe my article should be regarded as no more than providing some insights into specific schoolboy cricketing encounters in the ‘50s, magnificent experiences that have now become wonderful memories of glorious days in the sun among some incredibly talented and sporting cricketers.
From the time I can remember, Sri Lanka was cricket mad. It was the only game in town, with the Royal-Thomian (RT), Josephian-Peterite and Ananda-Nalanda big matches being the centrepiece of the island’s sporting calendar. I attended my first RT at the iconic Colombo Oval in 1947 at the age of nine, I will never forget the experience. The flags waved by the supporters of the rival schools, the gaily coloured dresses of the girls, the raucous singing from the Mustang tent and the beating of rabanas (the papare band) gave the match a carnival atmosphere. Records show the Royalists won the game and a happy nine-year-old went home dreaming that one day he would be playing in the match.
I joined Royal in 1951, the RT of that year was one of the most exciting in the history of the game and was described as “the impossible finish of ‘51”. Royal, the underdogs snatched victory in the dying moments of the game. The Thomians had Roger Inman, Jayalingam and P I Pieris but the cool head of Vairavanathan (the Royal captain) saved the day for Royal. I left the ground with an even stronger desire to play in this great match.
I came a step closer of achieving my dreams when, as a 15-year-old, I was selected to join the First XI squad in the third term of ‘53. Nirmalingam was captain and we had a very strong squad with ten coloursmen, including Ubaya de Silva, “Frecko” Kreltzsheim, Ranjit de Silva and Fitzroy Crozier. The freshers were Brendon Gunaratne, Selvi Perinpanayagam and I. Dr Barney Gunasekera was the coach, and Harold Samaraweera the cricket master.
I interrupt my narrative to pay homage to two men who have had a massive influence on my cricket and my life, namely Barney and Harold.
In Sri Lanka, we tended to idolize and hold in awe men who had outstanding sporting success. In 1930, Barney playing in the big match, broke the record by scoring 130 runs and taking nine wickets. This match went down in history as Barney’s Match.
Barney was not really a cricket coach in a technical sense. He was more a philosopher with an interest in the mental aspects of the game. I cannot recall him talking to me about batting technique. One afternoon he said to me: “Michael, just play your normal game and don’t look at the scoreboard. I guarantee that if you do that and bat for three hours you will score a century.” I did just that in the RT of 1957, when captain, and scored a century.
Barney was a self-effacing man with a whimsical sense of humour and he treated everyone with respect. Barney had coached for many years and was highly respected by all of us. We would have walked over hot coals for him.Harold was my under-14 coach, my form master in Form 3 and now the cricket master of the First XI so I knew him very well. Harold was an enthusiastic and happy guy who wore his heart on his sleeve. At Royal, we were a bit elitist and because Harold had not played for one of the big schools we tended to underestimate his advice. He was very knowledgeable on cricket and was a great help to me when I was captain. Harold and Barney have passed on and I often think of them with love and gratitude.
After the first practice session, Barney addressed the squad. He said he believed that to play for Royal was an honour, he believed it was essential that we played as a team, and he believed it was important that we played within the rules and the spirit of the game. He said that if anyone did not believe in these three pillars than he did not want that boy in the squad. Very inspirational stuff!
To a Royalist (or Thomian) the RT is the Holy Grail but there were some other matches that also had a long tradition of fierce competition. One of these was the Wesley encounter. In 1954, Wesley had a strong side – the Fuard brothers, the Adhihetty brothers, Samsudeen, Chapman and Neil Gallagher to name a few.
Nirma won the toss, we batted and made about 200. M. Wille ct Chapman b Fuard 1. Abu was too good for me.
Miraculously we dismissed Wesley for 39. Unfortunately, I cannot recall who took the wickets. Nirma enforced the follow on and the Wesleyites did better in their second dig, avoiding an innings defeat, but leaving us with about 40 to win. It should have been a piece of cake but Lou Adhihetty and Samsudeen had other ideas and made us earn every run.
I understand that in later life Lou became heavily involved in the Christian church. But he showed no Christian brotherly love that afternoon. Samsudeen and Lou subjected us to a barrage of bouncers, one of which hit Rabindran in the face. Rabindran dropped like a sack of potatoes and there was blood all over the place. I was padded up and trembling in my boots. I prayed to all the gods Christian, Hindu, Buddhist, Muslim and a few others that I invented that I would not have to go in. My prayers were answered as our early batsmen weathered the storm and we won a hard-fought game by a comfortable margin.
Later on I was awarded my “colours” along with Brendon and Selvi. There is nothing more satisfying than to realise a dream one has worked very hard to achieve. The ‘54 RT, unfortunately, like the four I played in, ended in a draw.
Off the first ball of the match their star batsman, Tyrell Gauder, was given not out to a catch behind the wicket. You could hear the snick at the Borella junction. It was a shocking decision. Nirma looked at the umpire and walked back to his mark. Tyrell shrugged his shoulder as if to say, “What can I do.” We got on with the game. No histrionics. The other highlights were a brilliant 69 by Nirma before he ran himself out and a rearguard action from the Thomians to save the match, including a fighting 48 from Michael Tissera giving an indication of things to come.
After the match, the Principal of Royal and the Warden of S. Thomas’ hosted a dinner for the two teams. We could not wait for this to be over so that, according to custom and practice, we could paint the town red. First stop the Liberty cinema, owned by the Cader family. Zacroff was playing for S. Thomas’, and everything, bar included, was on the house. The teams then adjourned to the CR & FC as guests of some reprobate old boys of both schools. Last stop, Galle Face Green for a sing-song and a few bottles of beers. Home at about 5am.
I really believe that this bonding led to a great spirit of camaraderie between the teams and was the start of many lifelong friendships, which was a hallmark of schoolboy team sport at that time.
Ranjit de Silva captained in ‘55. In ‘54 I had batted at No. 6, and I was hoping to talk Ranjit into letting me bat at No. 4. After the first practice and after Barney had made his speech he turned to what he termed “housekeeping matters”. He called for a volunteer to open batting with Selvi. Nobody spoke. I took a great interest in my boots and avoided eye contact with everybody. Suddenly a voice pipes up, “Michael used to open in the under-14s”. I could have killed him. Quick as a flash, Barney said, “Thanks Michael, that’s settled then.” So began my career as an opening batsman.
The ‘55 season started poorly as we were comprehensively beaten by St Anthony’s at Katugastota, ACM Lafir, who was playing for Ceylon at the time, made a century, Another superstar we encountered was Clive Inman. Clive was captain of St Peter’s and after leaving school followed Stanley Jayasinghe to England to play as a professional in the Lancashire League.
We played Wesley at Reid Avenue. Lou was captain of Wesley and obviously had not forgiven us for beating them the previous year. We batted first and faced some terrific bowling plus some chatter from Lou and Samsudeen. It was hard to score runs. I called Selvi for a stupid single. “Yes, no, sorry”. Selvi was run out by half the length of the pitch and he departed staring daggers at me.
I made up my mind to stay in the middle as long as possible (a) to make up for running Selvi out and, (b) to avoid Harold who I knew would be breathing fire. Alas, the best-laid plans. A couple of overs later Lou bowled me a full toss. I thought all my Christmases had come at once. I lifted my head, hit across the line and the ball thudded into the stumps. When I got to the dressing room, Harold closed the door and gave me an unmerciful tongue lashing. He was livid and said inter alia “What is the matter with you? Not only do you run Selvi out you get out to a cock shot. You are a bloody menace.”
I didn’t say a word because he was right. I sought out Selvi, who was rightfully furious with me, and apologized. He accepted my apology and we shook hands and moved on. We lost the match and next week I entered college from a side entrance to avoid the Kadlay man and Cobra man, legendary street hawkers who had, for years, peddled their wares at the gate of the school and who were our strongest supporters and our most stringent critics.
Later in the season, I scored a century against Trinity. Centuries were pretty rare and Harold was over the moon. He grabbed me by the shoulders and, beaming like a cat who had eaten all the cream, said: “Well done Michael, terrific performance, I knew you could do it and, by the way, you are not really a bloody menace.” We had a bit of a laugh.
The RT was a battle between two equally balanced sides which on a scale of 1 to 10, would probably have been rated at 7. When stumps were drawn, we were three wickets away from victory. There were no outstanding performances, with Brendon doing best for us top-scoring with 48 and taking four wickets in the Thomian first innings
The ‘57 side, captained by Fitzroy Crozier was the strongest I played in and arguably was the strongest side in the competition that year. We had four fourth year players, three third year players, one second year player and four very talented “Freshers” in Lorenz Pereira, the Samarasinghe brothers R K and S C and Pat Poulier. We were going to give the Thomians hell, maybe we were over-confident.
Barney announced that this year would be his last year as coach. We breezed through the early matches hardly ever being put to the test.
Life was great, the only cloud in the sky was the political situation. SWRD Bandaranaike had resigned from the UNP and had formed his own party and was going to challenge the government at the next election on a policy of “Sinhala only”. I was 17 years old and politics meant nothing to me. Although, my dad was very concerned and said that the “Sinhala only” policy would be a disaster for Sri Lanka, and if Bandaranaike won the election he advised me to follow my two brothers to Australia.
I had opened the batting with Selvi for two seasons. For one and a half of those seasons, I scored faster than Selvi. That changed on the day we played St Joseph’s at Darley Rd. We won the toss and Selvi and I walked out together, nothing appeared different except that when we got to the middle Selvi cut and hooked the Josephian bowlers like there was no tomorrow. He left me for dead and made 99.
The rumour in the market place was that Selvi had a secret girlfriend to whom he used to write and on the morning of the game he had a received a “Dear Selvi” letter and decided to take his anger out on the Josephian bowlers. We played Nalanda the following week. We batted second and with Selvi still in a swashbuckling mood we put on over 50 for the first wicket, with Selvi scoring most of the runs.
I went home, had a shower, and went to give my Dad a report on the day’s play. While I was talking to him he told me he was not feeling well and, to cut the long story short, he died within the next 48 hours. His death was a devastating blow as I loved him very much. The immediate result was that the family decided to migrate to Australia as soon as possible as Bandaranaike had won the election.
About three days after my Dad’s funeral, Dudley de Silva, the Principal of Royal asked for an appointment to meet my Mum. He said that he was aware of our plans to migrate and asked if we would postpone them as he wanted me to captain in ‘57. I declined the offer because I was grieving for my father and wanted to make a fresh start in Australia as soon as possible. Also, I never had any aspirations to captain Royal. When my older brother Peter heard of my refusal he applied immense emotional pressure, saying that my Dad would have been proud to see me captain. It was emotional blackmail and I gave in after a week. In the interim Selvi completed a century against Nalanda.’
Features
Meet the women protecting India’s snow leopards
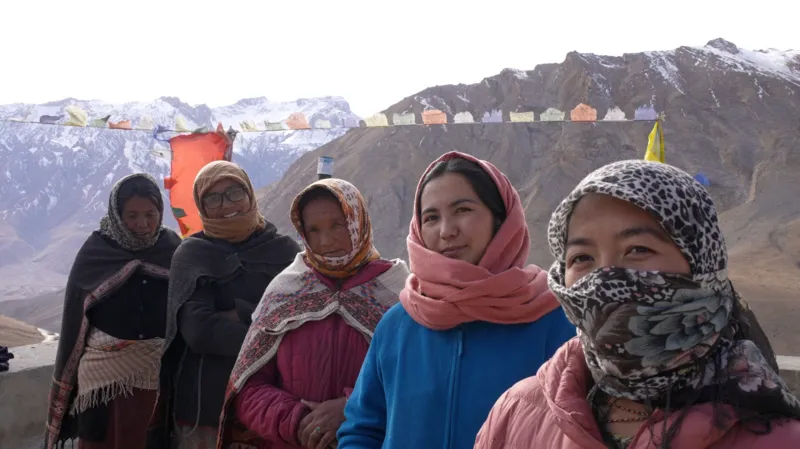

In one of India’s coldest and most remote regions, a group of women have taken on an unlikely role: protecting one of Asia’s most elusive predators, the snow leopard.
Snow leopards are found in just 12 countries across Central and South Asia. India is home to one of the world’s largest populations, with a nationwide survey in 2023 – the first comprehensive count ever carried out in the country – estimating more than 700 animals, .
One of the places they roam is around Kibber village in Himachal Pradesh state’s Spiti Valley, a stark, high-altitude cold desert along the Himalayan belt. Here, snow leopards are often called the “ghosts of the mountains”, slipping silently across rocky slopes and rarely revealing themselves.
For generations, the animals were seen largely as a threat, for attacking livestock. But attitudes in Kibber and neighbouring villages are beginning to shift, as people increasingly recognise the snow leopard’s role as a top predator in the food chain and its importance in maintaining the region’s fragile mountain ecosystem.
Nearly a dozen local women are now working alongside the Himachal Pradesh forest department and conservationists to track and protect the species, playing a growing role in conservation efforts.
Locally, the snow leopard is known as Shen and the women call their group “Shenmo”. Trained to install and monitor camera traps, they handle devices fitted with unique IDs and memory cards that automatically photograph snow leopards as they pass.
“Earlier, men used to go and install the cameras and we kept wondering why couldn’t we do it too,” says Lobzang Yangchen, a local coordinator working with a small group supported by the non-profit Nature Conservation Foundation (NCF) in collaboration with the forest department.
Yangchen was among the women who helped collect data for Himachal Pradesh’s snow leopard survey in 2024, which found that the state was home to 83 snow leopards – up from 51 in 2021.

The survey documented snow leopards and 43 other species using camera traps spread across an area of nearly 26,000sq km (10,000sq miles). Individual leopards were identified by the unique rosette patterns on their fur, a standard technique used for spotted big cats. The findings are now feeding into wider conservation and habitat-management plans.
“Their contribution was critical to identifying individual animals,” says Goldy Chhabra, deputy conservator of forests with the Spiti Wildlife Division.
Collecting the data is demanding work. Most of it takes place in winter, when heavy snowfall pushes snow leopards and their prey to lower altitudes, making their routes easier to track.
On survey days, the women wake up early, finish household chores and gather at a base camp before travelling by vehicle as far as the terrain allows. From there, they trek several kilometres to reach camera sites, often at altitudes above 14,000ft (4,300m), where the thin air makes even simple movement exhausting.
The BBC accompanied the group on one such trek in December. After hours of walking in biting cold, the women suddenly stopped on a narrow trail.
Yangchen points to pugmarks in the dust: “This shows the snow leopard has been here recently. These pugmarks are fresh.”

Along with pugmarks, the team looks for other signs, including scrapes and scent‑marking spots, before carefully fixing a camera to a rock along the trail.
One woman then carries out a “walk test”, crawling along the path to check whether the camera’s height and angle will capture a clear image.
The group then moves on to older sites, retrieving memory cards and replacing batteries installed weeks earlier.
By mid-afternoon, they return to camp to log and analyse the images using specialised software – tools many had never encountered before.
“I studied only until grade five,” says Chhering Lanzom. “At first, I was scared to use the computer. But slowly, we learned how to use the keyboard and mouse.”
The women joined the camera-trapping programme in 2023. Initially, conservation was not their motivation. But winters in the Spiti Valley are long and quiet, with little agricultural work to fall back on.
“At first, this work on snow leopards didn’t interest us,” Lobzang says. “We joined because we were curious and we could earn a small income.”
The women earn between 500 ($5.46; £4) and 700 rupees a day.
But beyond the money, the work has helped transform how the community views the animal.
“Earlier, we thought the snow leopard was our enemy,” says Dolma Zangmo, a local resident. “Now we think their conservation is important.”
Alongside survey work, the women help villagers access government insurance schemes for their livestock and promote the use of predator‑proof corrals – stone or mesh enclosures that protect animals at night.
Their efforts come at a time of growing recognition for the region. Spiti Valley has recently been included in the Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve, a Unesco-recognised network aimed at conserving fragile ecosystems while supporting local livelihoods.
As climate change reshapes the fragile trans-Himalayan landscape, conservationists say such community participation will be crucial to safeguarding species like the snow leopard.
“Once communities are involved, conservation becomes more sustainable,” says Deepshikha Sharma, programme manager with NCF’s High Altitudes initiative.
“These women are not just assisting, they are becoming practitioners of wildlife conservation and monitoring,” she adds.
As for the women, their work makes them feel closer to their home, the village and the mountains that raised them, they say.
“We were born here, this is all we know,” Lobzang says. “Sometimes we feel afraid because these snow leopards are after all predatory animals, but this is where we belong.”
[BBC]
Features
Freedom for giants: What Udawalawe really tells about human–elephant conflict

If elephants are truly to be given “freedom” in Udawalawe, the solution is not simply to open gates or redraw park boundaries. The map itself tells the real story — a story of shrinking habitats, broken corridors, and more than a decade of silent but relentless ecological destruction.
“Look at Udawalawe today and compare it with satellite maps from ten years ago,” says Sameera Weerathunga, one of Sri Lanka’s most consistent and vocal elephant conservation activists. “You don’t need complicated science. You can literally see what we have done to them.”
What we commonly describe as the human–elephant conflict (HEC) is, in reality, a land-use conflict driven by development policies that ignore ecological realities. Elephants are not invading villages; villages, farms, highways and megaprojects have steadily invaded elephant landscapes.
Udawalawe: From Landscape to Island
Udawalawe National Park was once part of a vast ecological network connecting the southern dry zone to the central highlands and eastern forests. Elephants moved freely between Udawalawe, Lunugamvehera, Bundala, Gal Oya and even parts of the Walawe river basin, following seasonal water and food availability.
Today, Udawalawe appears on the map as a shrinking green island surrounded by human settlements, monoculture plantations, reservoirs, electric fences and asphalt.
“For elephants, Udawalawe is like a prison surrounded by invisible walls,” Sameera explains. “We expect animals that evolved to roam hundreds of square nationakilometres to survive inside a box created by humans.”
Elephants are ecosystem engineers. They shape forests by dispersing seeds, opening pathways, and regulating vegetation. Their survival depends on movement — not containment. But in Udawalawa, movement is precisely what has been taken away.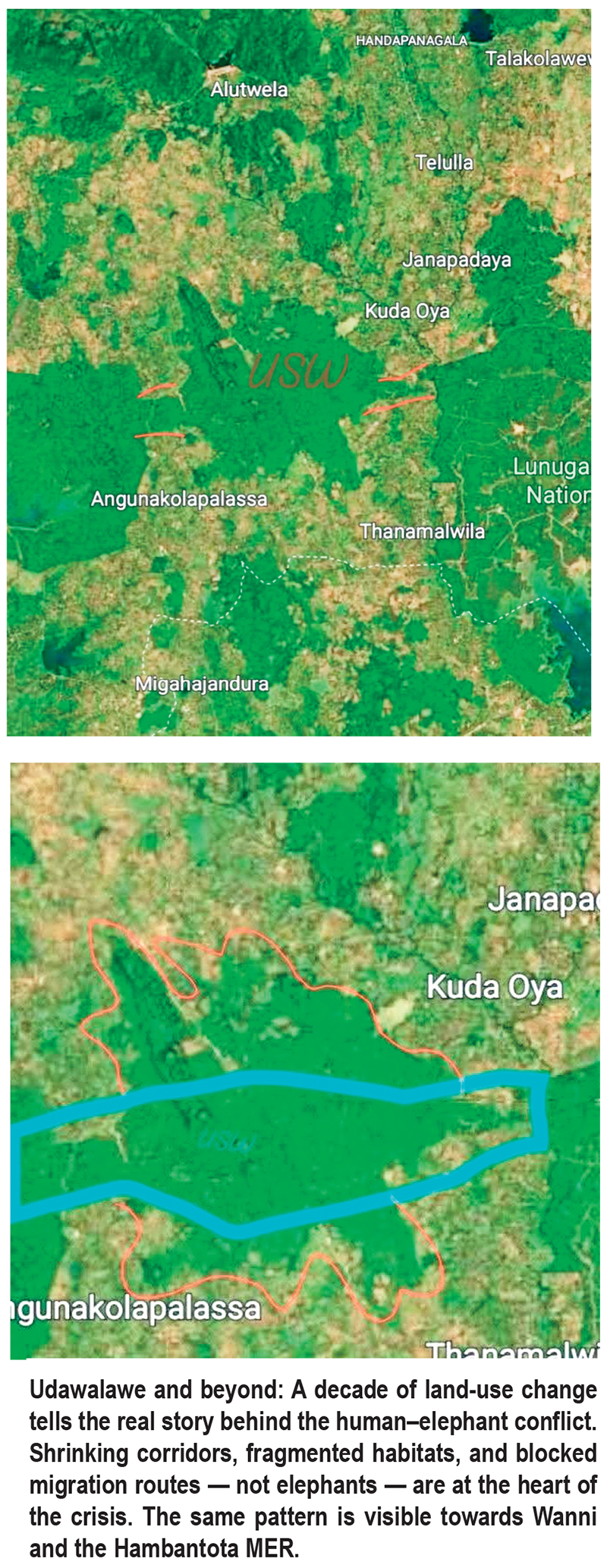
Over the past decade, ancient elephant corridors have been blocked or erased by:
Irrigation and agricultural expansion
Tourism resorts and safari infrastructure
New roads, highways and power lines
Human settlements inside former forest reserves
“The destruction didn’t happen overnight,” Sameera says. “It happened project by project, fence by fence, without anyone looking at the cumulative impact.”
The Illusion of Protection
Sri Lanka prides itself on its protected area network. Yet most national parks function as ecological islands rather than connected systems.
“We think declaring land as a ‘national park’ is enough,” Sameera argues. “But protection without connectivity is just slow extinction.”
Udawalawe currently holds far more elephants than it can sustainably support. The result is habitat degradation inside the park, increased competition for resources, and escalating conflict along the boundaries.
“When elephants cannot move naturally, they turn to crops, tanks and villages,” Sameera says. “And then we blame the elephant for being a problem.”
The Other Side of the Map: Wanni and Hambantota
Sameera often points to the irony visible on the very same map. While elephants are squeezed into overcrowded parks in the south, large landscapes remain in the Wanni, parts of Hambantota and the eastern dry zone where elephant density is naturally lower and ecological space still exists.
“We keep talking about Udawalawe as if it’s the only place elephants exist,” he says. “But the real question is why we are not restoring and reconnecting landscapes elsewhere.”
The Hambantota MER (Managed Elephant Reserve), for instance, was originally designed as a landscape-level solution. The idea was not to trap elephants inside fences, but to manage land use so that people and elephants could coexist through zoning, seasonal access, and corridor protection.
“But what happened?” Sameera asks. “Instead of managing land, we managed elephants. We translocated them, fenced them, chased them, tranquilised them. And the conflict only got worse.”
The Failure of Translocation
For decades, Sri Lanka relied heavily on elephant translocation as a conflict management tool. Hundreds of elephants were captured from conflict zones and released into national parks like Udawalawa, Yala and Wilpattu.
The logic was simple: remove the elephant, remove the problem.
The reality was tragic.
“Most translocated elephants try to return home,” Sameera explains. “They walk hundreds of kilometres, crossing highways, railway lines and villages. Many die from exhaustion, accidents or gunshots. Others become even more aggressive.”
Scientific studies now confirm what conservationists warned from the beginning: translocation increases stress, mortality, and conflict. Displaced elephants often lose social structures, familiar landscapes, and access to traditional water sources.
“You cannot solve a spatial problem with a transport solution,” Sameera says bluntly.
In many cases, the same elephant is captured and moved multiple times — a process that only deepens trauma and behavioural change.
Freedom Is Not About Removing Fences
The popular slogan “give elephants freedom” has become emotionally powerful but scientifically misleading. Elephants do not need symbolic freedom; they need functional landscapes.
Real solutions lie in:
Restoring elephant corridors
Preventing development in key migratory routes
Creating buffer zones with elephant-friendly crops
Community-based land-use planning
Landscape-level conservation instead of park-based thinking
“We must stop treating national parks like wildlife prisons and villages like war zones,” Sameera insists. “The real battlefield is land policy.”
Electric fences, for instance, are often promoted as a solution. But fences merely shift conflict from one village to another.
“A fence does not create peace,” Sameera says. “It just moves the problem down the line.”
A Crisis Created by Humans
Sri Lanka loses more than 400 elephants and nearly 100 humans every year due to HEC — one of the highest rates globally.
Yet Sameera refuses to call it a wildlife problem.
“This is a human-created crisis,” he says. “Elephants are only responding to what we’ve done to their world.”
From expressways cutting through forests to solar farms replacing scrublands, development continues without ecological memory or long-term planning.
“We plan five-year political cycles,” Sameera notes. “Elephants plan in centuries.”
The tragedy is not just ecological. It is moral.
“We are destroying a species that is central to our culture, religion, tourism and identity,” Sameera says. “And then we act surprised when they fight back.”
The Question We Avoid Asking
If Udawalawe is overcrowded, if Yala is saturated, if Wilpattu is bursting — then the real question is not where to put elephants.
The real question is: Where have we left space for wildness in Sri Lanka?
Sameera believes the future lies not in more fences or more parks, but in reimagining land itself.
“Conservation cannot survive as an island inside a development ocean,” he says. “Either we redesign Sri Lanka to include elephants, or one day we’ll only see them in logos, statues and children’s books.”
And the map will show nothing but empty green patches — places where giants once walked, and humans chose. roads instead.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
Challenges faced by the media in South Asia in fostering regionalism

 SAARC or the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation has been declared ‘dead’ by some sections in South Asia and the idea seems to be catching on. Over the years the evidence seems to have been building that this is so, but a matter that requires thorough probing is whether the media in South Asia, given the vital part it could play in fostering regional amity, has had a role too in bringing about SAARC’s apparent demise.
SAARC or the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation has been declared ‘dead’ by some sections in South Asia and the idea seems to be catching on. Over the years the evidence seems to have been building that this is so, but a matter that requires thorough probing is whether the media in South Asia, given the vital part it could play in fostering regional amity, has had a role too in bringing about SAARC’s apparent demise.
That South Asian governments have had a hand in the ‘SAARC debacle’ is plain to see. For example, it is beyond doubt that the India-Pakistan rivalry has invariably got in the way, particularly over the past 15 years or thereabouts, of the Indian and Pakistani governments sitting at the negotiating table and in a spirit of reconciliation resolving the vexatious issues growing out of the SAARC exercise. The inaction had a paralyzing effect on the organization.
Unfortunately the rest of South Asian governments too have not seen it to be in the collective interest of the region to explore ways of jump-starting the SAARC process and sustaining it. That is, a lack of statesmanship on the part of the SAARC Eight is clearly in evidence. Narrow national interests have been allowed to hijack and derail the cooperative process that ought to be at the heart of the SAARC initiative.
However, a dimension that has hitherto gone comparatively unaddressed is the largely negative role sections of the media in the SAARC region could play in debilitating regional cooperation and amity. We had some thought-provoking ‘takes’ on this question recently from Roman Gautam, the editor of ‘Himal Southasian’.
Gautam was delivering the third of talks on February 2nd in the RCSS Strategic Dialogue Series under the aegis of the Regional Centre for Strategic Studies, Colombo, at the latter’s conference hall. The forum was ably presided over by RCSS Executive Director and Ambassador (Retd.) Ravinatha Aryasinha who, among other things, ensured lively participation on the part of the attendees at the Q&A which followed the main presentation. The talk was titled, ‘Where does the media stand in connecting (or dividing) Southasia?’.
Gautam singled out those sections of the Indian media that are tamely subservient to Indian governments, including those that are professedly independent, for the glaring lack of, among other things, regionalism or collective amity within South Asia. These sections of the media, it was pointed out, pander easily to the narratives framed by the Indian centre on developments in the region and fall easy prey, as it were, to the nationalist forces that are supportive of the latter. Consequently, divisive forces within the region receive a boost which is hugely detrimental to regional cooperation.
Two cases in point, Gautam pointed out, were the recent political upheavals in Nepal and Bangladesh. In each of these cases stray opinions favorable to India voiced by a few participants in the relevant protests were clung on to by sections of the Indian media covering these trouble spots. In the case of Nepal, to consider one example, a young protester’s single comment to the effect that Nepal too needed a firm leader like Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi was seized upon by the Indian media and fed to audiences at home in a sensational, exaggerated fashion. No effort was made by the Indian media to canvass more opinions on this matter or to extensively research the issue.
In the case of Bangladesh, widely held rumours that the Hindus in the country were being hunted and killed, pogrom fashion, and that the crisis was all about this was propagated by the relevant sections of the Indian media. This was a clear pandering to religious extremist sentiment in India. Once again, essentially hearsay stories were given prominence with hardly any effort at understanding what the crisis was really all about. There is no doubt that anti-Muslim sentiment in India would have been further fueled.
Gautam was of the view that, in the main, it is fear of victimization of the relevant sections of the media by the Indian centre and anxiety over financial reprisals and like punitive measures by the latter that prompted the media to frame their narratives in these terms. It is important to keep in mind these ‘structures’ within which the Indian media works, we were told. The issue in other words, is a question of the media completely subjugating themselves to the ruling powers.
Basically, the need for financial survival on the part of the Indian media, it was pointed out, prompted it to subscribe to the prejudices and partialities of the Indian centre. A failure to abide by the official line could spell financial ruin for the media.
A principal question that occurred to this columnist was whether the ‘Indian media’ referred to by Gautam referred to the totality of the Indian media or whether he had in mind some divisive, chauvinistic and narrow-based elements within it. If the latter is the case it would not be fair to generalize one’s comments to cover the entirety of the Indian media. Nevertheless, it is a matter for further research.
However, an overall point made by the speaker that as a result of the above referred to negative media practices South Asian regionalism has suffered badly needs to be taken. Certainly, as matters stand currently, there is a very real information gap about South Asian realities among South Asian publics and harmful media practices account considerably for such ignorance which gets in the way of South Asian cooperation and amity.
Moreover, divisive, chauvinistic media are widespread and active in South Asia. Sri Lanka has a fair share of this species of media and the latter are not doing the country any good, leave alone the region. All in all, the democratic spirit has gone well into decline all over the region.
The above is a huge problem that needs to be managed reflectively by democratic rulers and their allied publics in South Asia and the region’s more enlightened media could play a constructive role in taking up this challenge. The latter need to take the initiative to come together and deliberate on the questions at hand. To succeed in such efforts they do not need the backing of governments. What is of paramount importance is the vision and grit to go the extra mile.
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoHayleys Mobility ushering in a new era of premium sustainable mobility
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoSLIM-Kantar People’s Awards 2026 to recognise Sri Lanka’s most trusted brands and personalities
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoAdvice Lab unveils new 13,000+ sqft office, marking major expansion in financial services BPO to Australia
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoArpico NextGen Mattress gains recognition for innovation
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoAltair issues over 100+ title deeds post ownership change
-

 Editorial7 days ago
Editorial7 days agoGovt. provoking TUs
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoSri Lanka opens first country pavilion at London exhibition
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoAll set for Global Synergy Awards 2026 at Waters Edge















