Opinion
Maha Jana Handa at Nugegoda, cyclone destruction, and contenders positioning for power in post-NPP Sri Lanka – I
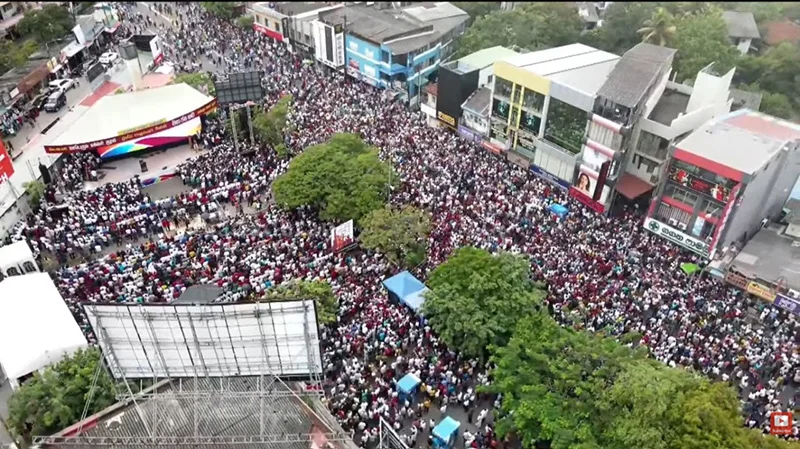

The Joint Opposition rally dubbed the ‘Maha Jana Handa’ (Vox Populi/ Voice of the People) held at the Ananda Samarakoon Open Air Theatre, Nugegoda on 21 November, 2025 has suddenly acquired a growing potential to be remembered as a significant turning point in post-civil conflict Sri Lankan politics, in the wake of the meteorological catastrophe caused by the calamitous Ditwah cyclonic storm that devastated the whole country from north to south and east to west on an unprecedented scale. But the strength of this prospect depends on the collective coordinated success of the future public awareness raising rallies, promised by the participating opposition parties, against the incumbent JVP-led NPP government. They are set to expose what they perceive as the government’s utterly inexperienced and unexpectedly authoritarian stand on certain vitally important issues including the country’s national security and independence, political and economic stability, and the Lankan state’s unitary status. The government is also alleged to be moving towards establishing a form of old-fashioned single party Marxist dictatorship in place of the firmly established system of governance based on parliamentary democracy, which was almost toppled by the adventitious Aragalaya protest of 2022 but saved by the timely intervention of some patriotic elements.
The minefield of policy making that the government must negotiate is strewn with issues including, among others: the seven or so recent agreements or MOUs (?) secretly signed with India; the unresolved controversy over the allegedly illegal clearance of some 323 containers (with unknown goods) without mandatory Customs inspection, from the Colombo Port; the Prime Minister’s arbitrary, apparently ill-considered and hasty education reforms without proper parliamentary discussion; the proposed culturally sensitive lgbtqia+ legislation non-issue (it is a non-issue for Sri Lanka, given its dominant culture); the so-called IMF debt trap; dealing with the unfair, virtually unilateral UNHRC resolutions against Sri Lanka; the inexplicably submissive surrender of the control of the profit-making Colombo Dockyard PLC to India; some government personal assets declarations that have raised many eyebrows, and the government’s handling of anti-narcotic and anti-corruption operations. The opposition politicians relentlessly criticise the ruling JVP/NPP’s failure to come out clean on these matters. But they themselves are not likely to be on an easy wicket if challenged to reveal their own positions regarding the above-mentioned issues.
In addition to those problems, the much more formidable challenge of unsolicited foreign-power interference in Sri Lanka’s internal affairs, in the guise of friendly intervention, remains an unavoidable circumstance that we are required to survive in the geostrategically sensitive region where Sri Lanka is located. Having been active right from the departure of the British colonialists in 1948, the foreign interference menace intensified after the successful ending of armed separatist terrorism in 2009. Such external interferences are locally assisted by latent domestic communal disharmony as well as real political factionalism, both of which are normal in any democratic country.
The war-winning President Mahinda Rajapaksa, as the leader of the SLFP-led United People’s Freedom Alliance (UPFA), was made to suffer a largely unexpected electoral defeat in 2015 through a foreign-engineered regime change operation that tacitly favoured his key rival, UNP leader Ranil Wickremesinghe. Mahinda was betrayed by his most trusted lieutenant Maithripala Sirisena.
The SLFP, a more middle of the way socialist-leaning rival political party, was formed in September 1951—five years after the birth of the UNP—and was elected to power in 1956, ending a near decade under the rather West-friendly latter party. It was deemed to be a ‘revolution’ that started an era of ‘transition’ (from elitist to common citizen rule). From nominal independence in 1948, governing power has to date alternated between these two parties or alliances led by them, except for the last electoral year, 2024. Though incumbent Executive President Anura Kumara Dissanayake may be said to have made history in this sense, the fact remains that he was barely able to scrape just 43% of the popular vote as the head of a newly formed, JVP-led NPP. Dissanayake was sworn in as President in September 2024. But his less than convincing electoral approval triggered a massive victory for the NPP at the parliamentary election that followed in November, giving him a parliament with 159 members, which is unprecedented in Sri Lanka’s electoral history.
In my opinion, there are two main reasons for this outcome. One is that the average Sri Lankan voters trust democracy. Since the president elect is accepted as having won the favour of the majority of the pan-Sri Lankan electorate, the general public choose to forget about their personal party affiliations and tend to vote for the parliamentary candidates from the party of the elected president. This is particularly true of the majority Sinhalese Buddhist community represented by the two mainstream, non-communal national parties, the UNP and the SLFP. The brittle foundation of that victory is not likely to sustain a strong enough administration that is capable of introducing the nebulous ‘system change’ that they have promised in their manifesto, while it is becoming clear that the general performance of the government seems to be falling far short of the real public expectations, which are not identical with the unconscionable demands made by the few separatist elements among the peaceful Tamil diaspora in the West, to whom the JVP/NPP alliance seems to owe its significantly qualified electoral success in 2024.
The Maha Jana Handa reminded me of the long Janabalaya Protest March from Kandy to Colombo where it ended in a mass rally on September 5, 2018. That hugely successful event was organised by the youth wing of the SLPP led by Namal Rajapaksa, who was an Opposition MP during the Yahapalanaya. He has played the same role just as efficiently on the most recent occasion, too. At the end of his address during the Maha Jana Handa, he declared his determination to bring down the malfunctioning JVP/NPP government at the earliest instance possible. Probably, he missed Ranil’s protege Harin Fernando’s speech that came earlier. This was because Namal Rajapaksa joined the rally midway. Harin had brought a message from his mentor Ranil to be read out to the rally audience. But he said he didn’t want to do so after all, saying that it was not suitable for that moment. Anyway, during his speech, Harin said emphatically that the era of heirs apparent or crown princes was gone for good. People knew that he was alluding to Sajith Premadasa and Namal Rajapaksa (sons of former Presidents hopeful of succeeding Anura Kumara Dissanayake). Harin was seen biting his tongue or sticking it out a little as he was preparing to leave the stage at the end of his address. Was he regretting what he had just said or was he cocking a snook at what, he was sure, was Namal’s ambition that would be revealed in his speech, the rally having been organised by the Pohottuwa or the SLPP? (To be continued)
by Rohana R. Wasala
Opinion
Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Act 2026 fails all affacted communities
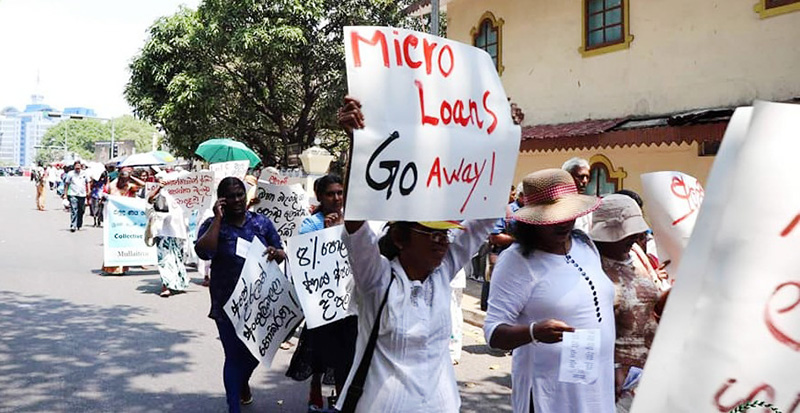
The Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill was passed into law by the Parliament of Sri Lanka on 4 March. According to Deputy Minister of Finance and Planning Dr. Anil Jayantha, the main object of the Act is to establish an Authority to “license and supervise the under-regulated microfinance and moneylending sector, aiming to protect borrowers from exploitation and ensure financial stability”.
However, the Yukthi Collective is saddened and disappointed that a government which pledged to take “measures to alleviate the burden of predatory microfinance loans with high interest rates on women” (NPP Manifesto, 2024: Page no. 44), will now add to their unbearable weight.
The new Act, as virtually all legislation enacted by Anura Kumara Dissanayake’s government, is a legacy of the anti-working class Ranil Wickremesinghe regime. It evades the root causes of the microfinance trap, and ignores debt justice for women borrowers.
It fails in understanding the connections between household debt and public debt. The vicious cycle of national debt is sustained by lack of growth in economic activity because of poor access to affordable credit.
It fails to make equal representation of women mandatory in the new Authority. If representatives of women borrowers and their self-run organisations are not present in the regulatory body, how will its members know of their lived experiences and make decisions that value women’s unpaid and paid contributions to sustaining life?
System Change
Millions of indebted households voted for the NPP with hope and expectation of ‘system change’. But instead of honouring its manifesto promise to them, the government has let them down in the law-making process; as well as the focus and substance of the new Act.
It is appalling that NPP parliamentarians, including some of its women members, appear not to have read and understood the bill they enacted into law, nor spoke to the rural credit community providers in their electorates for their views.
Predatory lending exists in the formal and informal sectors. Within this ecosystem, the Act fails to understand, identify, and prohibit predatory lending and recovery practices. It is a cover for the Central Bank’s failure to properly regulate ‘Licensed Finance Companies’ in the interests of citizens.
The biggest offenders are the big finance companies, in which some parliamentarians are deposit-holders. Therefore, some lawmakers benefit from excess profitmaking through exploitative practices, at the expense of poor mostly rural women.
Where law reform should discipline the bullies and thugs in credit delivery, it will instead wipe out, through over-regulation, community-based and managed lenders such as death donation societies, farmer associations, and urban and rural women’s collectives, which have been a lifeline for vulnerable working-class women and a defence from harmful recovery practices.
Structural Adjustment Programmes
The motivation for this new law are the market- and capital- friendly structural reforms insisted by International Financial Institutions; not the concerns and needs of those at the mercy of predatory lenders.
From the Microfinance Act 2016, to the 2023 version of the Ranil Wickremesinghe regime, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) through its loans has been a promoter of these regressive reforms.
The 2026 Act, with some changes suggested by the Supreme Court in 2024 and hardly any of the changes demanded by affected communities, has been moved forward by the NPP government in line with ADB loan conditionalities.
The path of de-regulation for banking, finance, trade, and investment; and over-regulation of poor people’s savings and credit institutions, smacks of the bias to big capital, which the NPP in opposition once criticised.
Reforms needed
The financial and banking reforms we want to see are to make credit from state banks and public funds accessible and affordable to women producers in agriculture and micro and small business operators; with decent wages and social protection for workers; that improve household opportunity for a dignified livelihood and decent lives.
Yukthi is a forum supporting working people’s movements and people’s struggles for democracy and justice in Sri Lanka.
by Yukthi Collective
Opinion
Illegal Bus Halt at Gate Number 11 of NHSL
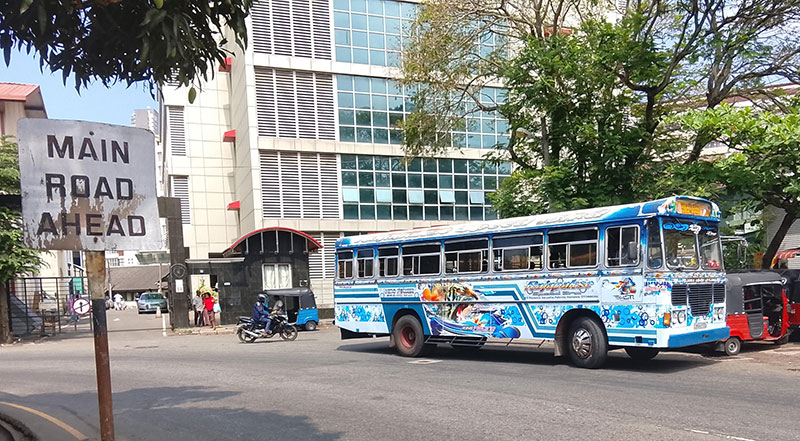

There is an unofficial bus halt at Gate Number 11 of the National Hospital at the 90-degree bend at the Prof. Nandadasa Kodagoda Mawatha (Old Norris Canal Road) which creates traffic jams at peak hours. Especially at the school opening and closing times at Carey College and hospital visiting hours.
Prospective passengers stand by the bend and then the busses stop suddenly on the middle of the road. The motorcycle in the picture is put into danger. The next bus halt is a few yards further near Carey College and Medical College Junction.
The problem is that illegal practices such as these, end up as approved procedure in our neck of the woods!
It must be nipped in the bud.
G. Fernando
Opinion
Naval hostilities close to a neutral coastal state: Legal assessment of a submarine attack on an Iranian warship near Sri Lanka

A submarine attack on an Iranian destroyer proximate to Sri Lanka represents more than a discrete naval engagement; it signals a potential horizontal escalation of conflict into the wider Indian Ocean Region (IOR). Historically, confrontations between Iran and Western powers have been largely confined to the Persian Gulf and adjacent regional waters. A strike near Sri Lanka, however, shifts the operational theatre from a semi-enclosed regional sea into the open Indian Ocean. This globally vital maritime space encompasses critical trade routes, energy supply corridors, and strategically sensitive naval zones.
This geographic expansion carries multiple strategic implications. First, it demonstrates the long-range maritime strike capabilities and blue-water operational reach of the belligerent forces. Second, it functions as a form of deterrence signalling, conveying a willingness to project force beyond traditional conflict zones. Third, it widens the theatre of operations, increasing the probability of third-party entanglement and amplifying regional instability.
Beyond its immediate military and strategic dimensions, the incident raises complex legal questions under both jus ad bellum—the body of law governing the use of force between states—and jus in bello, encompassing international humanitarian law applicable to armed conflict at sea. The central questions addressed in this paper are:
a. Lawfulness of Force:
Whether the use of force against the Iranian warship was lawful under the United Nations Charter, including considerations of self-defence and Security Council authorisation.
b. Compliance with International Humanitarian Law:
Whether the attack adhered to the principles and norms of international humanitarian law governing naval warfare, including the lawfulness of the target, proportionality, distinction, and obligations toward shipwrecked personnel.
c. Neutrality and Coastal State Rights:
Whether Sri Lanka’s rights and obligations as a neutral coastal state were violated, particularly within its territorial sea and Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
d. Operational and Geostrategic Implications:
The broader implications of conducting military operations within or near neutral maritime zones, and the interplay between legal permissibility, maritime security, environmental obligations, and regional stability.
These questions form the analytical framework that will guide the discussion throughout this paper, providing a structured lens for examining the legal, humanitarian, and strategic dimensions of the incident.
Jus ad Bellum and Jus in Bello:
Legality of the Use of Force
The legality of a submarine attack against a commissioned warship during an armed conflict must be assessed within a structured framework of international law comprising the jus ad bellum regime under the United Nations Charter, the corpus of international humanitarian law (IHL), and customary principles of naval warfare as reflected in the San Remo Manual on International Law Applicable to Armed Conflicts at Sea.
At the threshold level, the UN Charter governs the lawfulness of the use of force between states. Article 2(4) establishes a general prohibition on the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state, subject only to narrow exceptions. These exceptions include the inherent right of self-defence under Article 51 and actions authorised by the United Nations Security Council under Chapter VII.
Accordingly, if an Iranian warship were torpedoed by a submarine, the attacking state would be required to demonstrate that the action was undertaken either pursuant to a valid claim of self-defence, necessitated by an armed attack or imminent threat, or as part of an already existing international armed conflict. Absent such justification, the attack could constitute an unlawful use of force in violation of the Charter’s collective security framework.
Where an international armed conflict is already in existence, the analysis shifts from jus ad bellum to Jus in bello, namely the rules governing the conduct of hostilities.
Jus in bello
: Naval Warfare and Attack Against an Iranian Naval Ship
Where an international armed conflict exists between the United States and Iran, the analysis shifts to jus in Bello. Commissioned warships form part of a state’s armed forces and constitute lawful military objectives. Under customary naval warfare law, as reflected in the San Remo Manual on International Law Applicable to Armed Conflicts at Sea, enemy warships may be attacked, including by submarine-launched torpedoes, without prior warning. An Iranian destroyer operating as part of Iran’s navy would therefore constitute a legitimate military objective in principle.
However, the legality of a torpedo attack by a United States submarine remains subject to the foundational principles of international humanitarian law, including distinction, proportionality, military necessity, and precautions in attack. The principle of distinction requires that the target be military in nature; proportionality prohibits attacks expected to cause incidental harm excessive in relation to the anticipated military advantage; and military necessity demands that the force employed be directed toward achieving a legitimate military objective.
These obligations are particularly significant in maritime theatres characterised by dense commercial traffic, such as the sea lanes south of Sri Lanka. Incidental harm to neutral merchant vessels, offshore installations, or third-state interests must therefore be carefully assessed in relation to the anticipated concrete and direct military advantage.Submarine warfare, though technologically sophisticated and strategically consequential, remains subject to these enduring normative constraints, which seek to balance operational effectiveness with humanitarian considerations in the maritime domain.
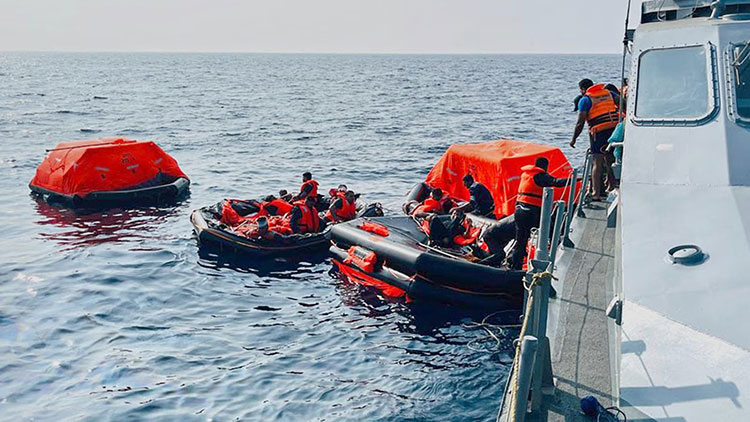
Customary humanitarian law further requires that feasible measures be taken to search for and rescue the shipwrecked, wounded, and dead following an engagement. In this respect, any action by the Sri Lanka Navy to rescue surviving sailors and recover bodies from the destroyed vessel represents a prudent and legally consonant exercise of humanitarian responsibility. Such conduct reflects long-standing maritime tradition and aligns with the duties recognised under the law of armed conflict and the broader law of the sea, without compromising Sri Lanka’s neutral status.
Sri Lanka’s Legal Position Concerning the Torpedoed Iranian Vessel
Sri Lanka’s legal position is largely determined by the maritime location in which the submarine attack occurred. Should the hostilities have taken place within Sri Lanka’s territorial sea, defined as extending up to 12 nautical miles from the baseline, such conduct would constitute a breach of Sri Lanka’s sovereignty and a violation of the law of neutrality, which forbids belligerent states from engaging in hostilities within neutral waters and imposes a duty on the coastal state to prevent such actions within its jurisdiction. In that circumstance, Sri Lanka would be entitled to issue a diplomatic protest and potentially pursue reparative claims.
By contrast, as the engagement took place within Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), the analysis is more nuanced under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. The EEZ confers sovereign rights for resource exploitation rather than full sovereignty, and prevailing state practice accepts that military operations, including naval manoeuvres, are not per se unlawful in another state’s EEZ. While such an engagement would not automatically breach international law, it would nonetheless generate significant security concerns, including risks to navigational safety, potential environmental damage, and heightened regional instability. Should the sinking result in oil discharge, hazardous material release, or debris affecting shipping lanes, obligations under UNCLOS to protect and preserve the marine environment would be engaged.
Although the Rio Declaration on Environment and Development does not explicitly regulate armed conflict, its principles highlight an increasing expectation for states to protect the environment during hostilities. Similarly, UNCLOS mandates that states protect and preserve the marine environment. Consequently, should the sinking of the Iranian destroyer cause an oil spill, the release of hazardous materials, or navigational hazards, specific environmental liabilities would be triggered. Strategically, a submarine strike near Sri Lanka signals more than a discrete tactical engagement. It reflects the projection of great-power naval capabilities into a strategically sensitive maritime space through which a substantial proportion of global trade transits.
Sri Lanka occupies a pivotal geostrategic position astride the principal East–West Sea Lines of Communication linking Gulf energy supplies, East Asian manufacturing centres, and European markets via the Suez Canal. A substantial proportion of global container traffic transits south of the island, rendering these waters acutely sensitive to instability. Even a limited naval engagement can elevate war-risk insurance premiums, disrupt commercial routing, and indirectly affect port operations in Colombo and Hambantota.
From a jus ad bellum perspective, geographic expansion does not in itself render hostilities unlawful; yet it complicates assessments of necessity and proportionality and increases the risk of escalation affecting neutral states.
The torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in maritime zones proximate to Sri Lanka necessitates a carefully layered legal assessment situated at the confluence of jus ad bellum, jus in bello, and the law of the sea. As this paper has demonstrated, the legality of the incident ultimately turns on four interrelated determinations:
(a) whether a lawful basis for the use of force existed under Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations, grounded in self-defence;
(b) whether the attack complied with the principles of distinction, proportionality, and military necessity under international humanitarian law;
(c) whether the engagement occurred within Sri Lanka’s territorial sea, thereby infringing its sovereignty and violating the law of neutrality; and
(d) whether the obligations owed to survivors, shipwrecked personnel, and the marine environment were respected in accordance with the law of armed conflict at sea and relevant maritime conventions.
If the attack did not occur within Sri Lanka’s territorial sea, it would not amount to a violation of sovereignty or a breach of the law of neutrality capable of engaging state responsibility on that ground.
By contrast, where the engagement occurred beyond the territorial sea whether within the Exclusive Economic Zone or on the high seas prevailing interpretations of the law of naval warfare, reinforced by consistent state practice, suggest that the operation may be regarded as legally defensible, provided that the cumulative requirements of necessity, proportionality, distinction, and humanitarian obligation were satisfied.
Nevertheless, legal permissibility does not equate to strategic prudence. The deployment of a United States submarine to conduct kinetic operations in proximity to a neutral coastal state within the Indian Ocean underscores the increasingly complex convergence of naval power projection, humanitarian norms, environmental obligations, and coastal state rights within the contemporary maritime domain.
Even where consistent with international law, the extension of submarine warfare into the wider Indian Ocean carries destabilising implications for regional security, commercial shipping, and the safety of neutral coastal states situated along critical sea lines of communication. The geographic expansion of hostilities into this maritime space heightens the risks of miscalculation, escalation, and unintended third-party involvement.
For Sri Lanka, the incident underscores the delicate equilibrium between maintaining neutrality, safeguarding maritime security, and upholding the international legal order. The actions undertaken by the Sri Lanka Navy in conducting rescue and recovery operations for surviving sailors and deceased personnel reflect the discharge of well-established humanitarian duties under international law and exemplify responsible conduct at sea.
Ultimately, this episode illustrates the increasingly complex convergence of naval power projection, international humanitarian norms, and coastal state rights within the contemporary maritime domain. In an era marked by intensifying great-power competition and expanding operational reach in the Indian Ocean, the preservation of legal clarity, strategic restraint, and respect for neutral maritime spaces remains essential to sustaining regional stability and safeguarding the integrity of the international maritime order.
by REAR ADMIRAL (RTD.) JAGATH RANASINGHE
VSV, USP, psc, MSc (DS) Mgt, MMaritimePol (Aus),
PG Dip in CPS, DIP in CR, FNI (Lond), Former Govt Fellow GCSP
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoLegal experts decry move to demolish STC dining hall
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoFemale lawyer given 12 years RI for preparing forged deeds for Borella land
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoPeradeniya Uni issues alert over leopards in its premises
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoCabinet nod for the removal of Cess tax imposed on imported good
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoLibrary crisis hits Pera university
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoWar in Middle East sends shockwaves through Sri Lanka’s export sector













