Features
Living with Covid 19
Remembered Yesterdays
by J. Godwin Perera
This Covid thing has put me in a mess
The more I read of it, up goes my stress
Should I pour some charmed water to the river
And chant ‘the Nation’ ‘the Nation ‘ is the giver
So bless the nation may the virus now recede
Docs and all the bosses please take heed
It’s not about the mask you wanted us to wear
The secret’s in that water and by it we will swear.
A Sunday paper had this headline ‘Has Govt’s strategy to dam the Covid spread gone to pot ?’ Under this there is a photograph of The Minister of Health, Honorable Pavithra Wanniarachchi embracing a pot of what the Honorable Minister claims to be, charmed water. The said news item explains that the Honorable Minister had gently thrown this pot into the Kalu Ganga. Not to be outdone at the same auspicious moment the Minister of Energy the Honorable Udaya Gamanpilla had reverently thrown a similar pot into the Kelani Ganga. There is a photo of him performing this ritual. Also at the simultaneous moment the Minister of Tourism the Honorable Prasanna Ranatunge had thrown another similar pot but this one, rather casually, into the Kelani Ganga. And of course there is a photo of him. Keep in mind that no Minister does anything in public without being videoed and photographed. And these videos and photographs are circulated through the length and breadth of Sri Lanka. All this is to show the people how our Parliamentarians are working hard. Did someone say ‘Hardly working’- No. Maybe it was just the ‘keech, keech’ of a gecko.
Anyway let’s continue. At a debate in Parliament which had nothing to do with pots or charmed water, the Honorable Pavithra Wanniarachchi had lamented that a Facebook comment has been made criticizing her for throwing the pot of charmed water into the river and had suggested that she should jump into the sea to end this pandemic. In a Siri Sangaboesque reply the Honorable Minister had stated that she will do that if it could solve the Covid 19 problem. Surely such fervent patriotism must be admired and emulated by others especially by those who adorn the comfortable seats in Parliament at the tax-payers expense. However later in Parliament she assured her people in her electorate who may have been in impending mourning at losing her to the lashing waves of the sea, and to the people at large, that ‘ the Government always followed the advice of medical experts when dealing with the pandemic.’ On hearing this statement there was a very loud, collective sigh of relief, so loud and clear that it even blew the rain clouds away.
And now we come to the Venerable Muruththettuwe Ananda Thero. In a front page press statement on the Covid 19 crisis the Venerable Thera states ‘ I have been closely associated with Health Ministers, Secretaries and Directors –General, since 1966 but never come across a pathetic situation where the whole sector has lost its sense of direction with the administrative process in a knotty mess.’ The Venerable Thero must surely know all about the health sector, because he is the President of the Public Service United Nurses Union. But hark! Here is something which also appeared in the same newspaper. This is repeated for your enlightenment but as the lawyers would say ‘Without Prejudice. ’ It is by Dr Upul Wijayawardhana and we quote ‘ It is a great shame that nurses in Sri Lanka who are second to none are not able to find a member of their own profession to lead their union. In the country that produced the first female Prime Minister in the world, is there no lady with leadership qualities to lead the union of a profession still largely dominated by women? It is indeed an outrage for a Buddhist priest to lead a trade union , nursing or otherwise.’ Unquote. What had provoked the good doctor to make these comments was a threat of trade union action within 48 hours if the demands of this union are not met. And this union was the above mentioned Public Service United Nurses Union.
We report . You decide.
Next there is the Brandix Covid 19 cluster. This it seems has been relegated to the back burner. According to reports the Attorney – General’s order to the Police to conduct a probe is being delayed for various reasons. A spokesperson from the Attorney- General’s office has stated that despite three reminders no response has been received as of Friday. That particular Friday has passed and it is hoped that by the time this article is being read the necessary response would have been received. If not, may we ask, why not?
And now to a group of professionals who should know more about Covid 19 than any ordinary lay person. The Government Medical Officers Forum (GMOF). They are different from the Government Medical Officers Association (GMOA). Though ordinary lay persons will not know how, when and why this difference came about. But both groups are government officials. The GMOF has been very critical of the Government for the two month delay in appointing a Director – General of Health Services after the previous incumbent left. Further and here let it come straight off the bat, ‘ By appointing a retired military senior army official as the Health Secretary we thought we will be able to watch ‘Sinhabahu’ but for the last six months what we have being seeing is a ‘Sergeant Nallathamby’ drama. Pretty strong stuff !
Would the GMOF have anything to say about another retired senior army officer who is now the President of this country? But let that pass. The point is why cannot the GMOF and GMOA get together and submit a joint set of proposals as to how this country –it’s their country and our country, can overcome the challenge of Covid 19. And if they have already done this then what is the present Director–General of Health Services doing about it ? Another matter of importance to the general public is that there seems to be too many spokespersons talking too frequently on the subject of Covid 19. For instance there is the Minister of Health, the Director –General of Health Services, the Chief Epidemiologist, the Deputy Director of the Medical Research Institute, the DIG of Police, the Government Information Department.
Let’s face it. Covid 19 is the most serious crisis this country has faced in several decades. It is alarming. When there are too many spokespersons it leads to confusion which is not in the best interest of everyone. Or it leads to total indifference because no one knows whose instructions should be followed, which is certainly a far worse situation. The Army Commander, Lt. General Shavendra Silva is the Head of the National Operation Centre for Prevention of Covid 19 Outbreak. That is very clear. Since the very onset of Covid 19 in this country it is Lt. General Shavendra Silva who has been addressing us. On TV, in the press on radio. Therefore is it not logical and indeed practical for Lt. General Shavendra Silva to be the sole spokesperson on behalf of the Government, on Covid 19. Other than of course the President himself, who has every right and responsibility to address the nation. Furthermore the people have the highest respect for him. No one else could have undertaken this task in the confident manner that he is performing it.
But we the people have our responsibilities too. Yes we do wear the face mask. But social distancing? Hand washing before and after leaving any premises? Why worry! Yes, we Sri Lankans are such an over complacent lot. We remember to forget. Forget the appeals, regulations, warnings, instructions. There is this senile mentality that the worst will always happen to someone else. Never to one’s own self. Like keeping one’s premises garbage free by simply dumping that garbage on a road where someone else lives. The Covid 19 pandemic! That’s the Government’s problem. Not ours. No, it is very much our problem. It is very much our responsibility. If we do not take this seriously and take every precaution to get this pandemic well under control, no amount of charmed water, whether poured into rivers or sprinkled from the skies can ever save us.
Features
Building on Sand: The Indian market trap

(Part III in a series on Sri Lanka’s tourism stagnation.)
 Every SLTDA (Sri Lanka Tourism Development Authority) press release now leads with the same headline: India is Sri Lanka’s “star market.” The numbers seem to prove it, 531,511 Indian arrivals in 2025, representing 22.5% of all tourists. Officials celebrate the “half-million milestone” and set targets for 600,000, 700,000, more.
Every SLTDA (Sri Lanka Tourism Development Authority) press release now leads with the same headline: India is Sri Lanka’s “star market.” The numbers seem to prove it, 531,511 Indian arrivals in 2025, representing 22.5% of all tourists. Officials celebrate the “half-million milestone” and set targets for 600,000, 700,000, more.
But follow the money instead of the headcount, and a different picture emerges. We are building our tourism recovery on a low-spending, short-stay, operationally challenging segment, without any serious strategy to transform it into a high-value market. We have confused market size with market quality, and the confusion is costing us billions.
Per-day spending: While SLTDA does not publish market-specific daily expenditure data, industry operators and informal analyses consistently report Indian tourists in the $100-140 per day range, compared to $180-250 for Western European and North American markets.
The math is brutal and unavoidable: one Western European tourist generates the revenue of 3-4 Indian tourists. Building tourism recovery primarily on the low-yield segment is strategically incoherent, unless the goal is arrivals theater rather than economic contribution.
Comparative Analysis: How Competitors Handle Indian Outbound Tourism
India is not unique to Sri Lanka. Indian outbound tourism reached 30.23 million departures in 2024, an 8.4% year-on-year increase, driven by a growing middle class with disposable income. Every competitor destination is courting this market.
This is not diversification. It is concentration risk dressed up as growth.
How did we end up here? Through a combination of policy laziness, proximity bias, and refusal to confront yield trade-offs.
1. Proximity as Strategy Substitute
India is next door. Flights are short (1.5-3 hours), frequent, and cheap. This makes India the easiest market to attract, low promotional cost, high visibility, strong cultural and linguistic overlap. But easiest is not the same as best.
Tourism strategy should optimize for yield-adjusted effort. Yes, attracting Europeans requires longer promotional cycles, higher marketing spend, and sustained brand-building. But if each European generates 3x the revenue of an Indian tourist, the return on investment is self-evident.
We have chosen ease over effectiveness, proximity over profitability.
2. Visa Policy as Blunt Instrument
3. Failure to Develop High-Value Products for Indian Market

There are segments of Indian outbound tourism that spend heavily:
* Wedding tourism: Indian destination weddings can generate $50,000-200,000+ per event
* Wellness/Ayurveda tourism: High-net-worth Indians seek authentic wellness experiences and will pay premium rates
* MICE tourism: Corporate events, conferences, incentive travel
Sri Lanka has these assets—coastal venues for weddings, Ayurvedic heritage, colonial hotels suitable for corporate events. But we have not systematically developed and marketed these products to high-yield Indian segments.
For the first time in 2025, Sri Lanka conducted multi-city roadshows across India to promote wedding tourism. This is welcome—but it is 25 years late. The Maldives and Mauritius have been curating Indian wedding and MICE tourism for decades, building specialised infrastructure, training staff, and integrating these products into marketing.
We are entering a mature market with no track record, no specialised infrastructure, and no price positioning that signals premium quality.
4. Operational Challenges and Quality Perceptions
Indian tourists, particularly budget segments, present operational challenges:
* Shorter stays mean higher turnover, more check-ins, more logistical overhead per dollar of revenue
* Price sensitivity leads to aggressive bargaining, complaints over perceived overcharging
* Large groups (families, wedding parties) require specialised handling
None of these are insurmountable, but they require investment in training, systems, and service design. Sri Lanka has not made these investments systematically. The result: operators report higher operational costs per Indian guest while generating lower revenue, a toxic margin squeeze.
Additionally, Sri Lanka’s positioning as a “budget-friendly” destination reinforces price expectations. Indians comparing Sri Lanka to Thailand or Malaysia see Sri Lanka as cheaper, not better. We compete on price, not value, a race to the bottom.
The Strategic Error: Mistaking Market Size for Market Fit
India’s outbound tourism market is massive, 30 million+ and growing. But scale is not the same as fit.
Market size ≠ market value: The UAE attracts 7.5 million Indians, but as a high-yield segment (business, luxury shopping, upscale hospitality). Saudi Arabia attracts 3.3 million—but for religious pilgrimage with high per-capita spending and long stays.
Thailand attracts 1.8 million Indians as part of a diversified 35-million-tourist base. Indians represent 5% of Thailand’s mix. Sri Lanka has made Indians 22.5% of our mix, 4.5 times Thailand’s concentration, while generating a fraction of Thailand’s revenue.
This reveals the error. We have prioritised volume from a market segment without ensuring the segment aligns with our value proposition.
These needs are misaligned. Indians seek budget value; Sri Lanka needs yield. Indians want short trips; Sri Lanka needs extended stays. Indians are price-sensitive; Sri Lanka needs premium segments to fund infrastructure.
We have attracted a market that does not match our strategic needs—and then celebrated the mismatch as success.
The Way Forward: From Dependency to Diversification
Fixing the Indian market trap requires three shifts: curation, diversification, and premium positioning.
First
 , segment the Indian market and target high-value niches explicitly:
, segment the Indian market and target high-value niches explicitly:
* Wedding tourism: Develop specialised wedding venues, train planners, create integrated packages ($50k+ per event)
* Wellness tourism: Position Sri Lanka as authentic Ayurveda destination for high-net-worth health seekers
* MICE tourism: Target Indian corporate incentive travel and conferences
* Spiritual/religious tourism: Leverage Buddhist and Hindu heritage sites with premium positioning
Market these high-value niches aggressively. Let budget segments self-select out through pricing signals.
Second
, rebalance market mix toward high-yield segments:
* Increase marketing spend on Western Europe, North America, and East Asian premium segments
* Develop products (luxury eco-lodges, boutique heritage hotels, adventure tourism) that appeal to high-yield travelers
* Use visa policy strategically, maintain visa-free for premium markets, consider tiered visa fees or curated visa schemes for volume markets
Third
, stop benchmarking success by Indian arrival volumes. Track:
* Revenue per Indian visitor
* Indian market share of total revenue (not arrivals)
* Yield gap: Indian revenue vs. other major markets
If Indians are 22.5% of arrivals but only 15% of revenue, we have a problem. If the gap widens, we are deepening dependency on a low-yield segment.
Fourth
, invest in Indian market quality rather than quantity:
* Train staff on Indian high-end expectations (luxury service standards, dietary needs)
* Develop bilingual guides and materials (Hindi, Tamil)
* Build partnerships with premium Indian travel agents, not budget consolidators
We should aim to attract 300,000 Indians generating $1,500 per trip (through wedding, wellness, MICE targeting), not 700,000 generating $600 per trip. The former produces $450 million; the latter produces $420 million, while requiring more than twice the operational overhead and infrastructure load.
Fifth
, accept the hard truth: India cannot and should not be 30-40% of our market mix. The structural yield constraints make that model non-viable. Cap Indian arrivals at 15-20% of total mix and aggressively diversify into higher-yield markets.
This will require political courage, saying “no” to easy volume in favour of harder-won value. But that is what strategy means: choosing what not to do.
The Dependency Trap

Every market concentration creates path dependency. The more we optimize for Indian tourists, visa schemes, marketing, infrastructure, pricing, the harder it becomes to attract high-yield markets that expect different value propositions.
Hotels that compete on price for Indian segments cannot simultaneously position as luxury for European segments. Destinations known for “affordability” struggle to pivot to premium. Guides trained for high-turnover, short-stay groups do not develop the deep knowledge required for extended cultural tours.
We are locking in a low-yield equilibrium. Each incremental Indian arrival strengthens the positioning as a “budget-friendly” destination, which repels high-yield segments, which forces further volume-chasing in price-sensitive markets. The cycle reinforces itself.
Breaking the cycle requires accepting short-term pain—lower arrival numbers—for long-term gain—higher revenue, stronger positioning, sustainable margins.
The Hard Question
Is Sri Lanka willing to attract two million tourists generating $5 billion, or three million tourists generating $4 billion?
The current trajectory is toward the latter, more arrivals, less revenue, thinner margins, greater fragility. We are optimizing for metrics that impress press releases but erode economic contribution.
The Indian market is not the problem. The problem is building tourism recovery primarily on a low-yield segment without strategies to either transform that segment to high-yield or balance it with high-yield markets.
We are building on sand. The foundation will not hold.
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT, Malabe. The views and opinions expressed in this article are personal.)
Features
Digital transformation in the Global South

Understanding Sri Lanka through the India AI Impact Summit 2026
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly moved from being a specialised technological field into a major social force that shapes economies, cultures, governance, and everyday human life. The India AI Impact Summit 2026, held in New Delhi, symbolised a significant moment for the Global South, especially South Asia, because it demonstrated that artificial intelligence is no longer limited to advanced Western economies but can also become a development tool for emerging societies. The summit gathered governments, researchers, technology companies, and international organisations to discuss how AI can support social welfare, public services, and economic growth. Its central message was that artificial intelligence should be human centred and socially useful. Instead of focusing only on powerful computing systems, the summit emphasised affordable technologies, open collaboration, and ethical responsibility so that ordinary citizens can benefit from digital transformation. For South Asia, where large populations live in rural areas and resources are unevenly distributed, this idea is particularly important.
People friendly AI
One of the most important concepts promoted at the summit was the idea of “people friendly AI.” This means that artificial intelligence should be accessible, understandable, and helpful in daily activities. In South Asia, language diversity and economic inequality often prevent people from using advanced technology. Therefore, systems designed for local languages, and smartphones, play a crucial role. When a farmer can speak to a digital assistant in Sinhala, Tamil, or Hindi and receive advice about weather patterns or crop diseases, technology becomes practical rather than distant. Similarly, voice based interfaces allow elderly people and individuals with limited literacy to use digital services. Affordable mobile based AI tools reduce the digital divide between urban and rural populations. As a result, artificial intelligence stops being an elite instrument and becomes a social assistant that supports ordinary life.
Transformation in education sector
The influence of this transformation is visible in education. AI based learning platforms can analyse student performance and provide personalised lessons. Instead of all students following the same pace, weaker learners receive additional practice while advanced learners explore deeper material. Teachers are able to focus on mentoring and explanation rather than repetitive instruction. In many South Asian societies, including Sri Lanka, education has long depended on memorisation and private tuition classes. AI tutoring systems could reduce educational inequality by giving rural students access to learning resources, similar to those available in cities. A student who struggles with mathematics, for example, can practice step by step exercises automatically generated according to individual mistakes. This reduces pressure, improves confidence, and gradually changes the educational culture from rote learning toward understanding and problem solving.
Healthcare is another area where AI is becoming people friendly. Many rural communities face shortages of doctors and medical facilities. AI-assisted diagnostic tools can analyse symptoms, or medical images, and provide early warnings about diseases. Patients can receive preliminary advice through mobile applications, which helps them decide whether hospital visits are necessary. This reduces overcrowding in hospitals and saves travel costs. Public health authorities can also analyse large datasets to monitor disease outbreaks and allocate resources efficiently. In this way, artificial intelligence supports not only individual patients but also the entire health system.
Agriculture, which remains a primary livelihood for millions in South Asia, is also undergoing transformation. Farmers traditionally rely on seasonal experience, but climate change has made weather patterns unpredictable. AI systems that analyse rainfall data, soil conditions, and satellite images can predict crop performance and recommend irrigation schedules. Early detection of plant diseases prevents large-scale crop losses. For a small farmer, accurate information can mean the difference between profit and debt. Thus, AI directly influences economic stability at the household level.
Employment and communication reshaped
Artificial intelligence is also reshaping employment and communication. Routine clerical and repetitive tasks are increasingly automated, while demand grows for digital skills, such as data management, programming, and online services. Many young people in South Asia are beginning to participate in remote work, freelancing, and digital entrepreneurship. AI translation tools allow communication across languages, enabling businesses to reach international customers. Knowledge becomes more accessible because information can be summarised, translated, and explained instantly. This leads to a broader sociological shift: authority moves from tradition and hierarchy toward information and analytical reasoning. Individuals rely more on data when making decisions about education, finance, and career planning.
Impact on Sri Lanka
The impact on Sri Lanka is especially significant because the country shares many social and economic conditions with India and often adopts regional technological innovations. Sri Lanka has already begun integrating artificial intelligence into education, agriculture, and public administration. In schools and universities, AI learning tools may reduce the heavy dependence on private tuition and help students in rural districts receive equal academic support. In agriculture, predictive analytics can help farmers manage climate variability, improving productivity and food security. In public administration, digital systems can speed up document processing, licensing, and public service delivery. Smart transportation systems may reduce congestion in urban areas, saving time and fuel.
Economic opportunities are also expanding. Sri Lanka’s service based economy and IT outsourcing sector can benefit from increased global demand for digital skills. AI-assisted software development, data annotation, and online service platforms can create new employment pathways, especially for educated youth. Small and medium entrepreneurs can use AI tools to design products, manage finances, and market services internationally at low cost. In tourism, personalised digital assistants and recommendation systems can improve visitor experiences and help small businesses connect with travellers directly.
Digital inequality
However, the integration of artificial intelligence also raises serious concerns. Digital inequality may widen if only educated urban populations gain access to technological skills. Some routine jobs may disappear, requiring workers to retrain. There are also risks of misinformation, surveillance, and misuse of personal data. Ethical regulation and transparency are, therefore, essential. Governments must develop policies that protect privacy, ensure accountability, and encourage responsible innovation. Public awareness and digital literacy programmes are necessary so that citizens understand both the benefits and limitations of AI systems.
Beyond economics and services, AI is gradually influencing social relationships and cultural patterns. South Asian societies have traditionally relied on hierarchy and personal authority, but data-driven decision making changes this structure. Agricultural planning may depend on predictive models rather than ancestral practice, and educational evaluation may rely on learning analytics instead of examination rankings alone. This does not eliminate human judgment, but it alters its basis. Societies increasingly value analytical thinking, creativity, and adaptability. Educational systems must, therefore, move beyond memorisation toward critical thinking and interdisciplinary learning.
AI contribution to national development
In Sri Lanka, these changes may contribute to national development if implemented carefully. AI-supported financial monitoring can improve transparency and reduce corruption. Smart infrastructure systems can help manage transportation and urban planning. Communication technologies can support interaction among Sinhala, Tamil, and English speakers, promoting social inclusion in a multilingual society. Assistive technologies can improve accessibility for persons with disabilities, enabling broader participation in education and employment. These developments show that artificial intelligence is not merely a technological innovation but a social instrument capable of strengthening equality when guided by ethical policy.
Symbolic shift
Ultimately, the India AI Impact Summit 2026 represents a symbolic shift in the global technological landscape. It indicates that developing nations are beginning to shape the future of artificial intelligence according to their own social needs rather than passively importing technology. For South Asia and Sri Lanka, the challenge is not whether AI will arrive but how it will be used. If education systems prepare citizens, if governments establish responsible regulations, and if access remains inclusive, AI can become a partner in development rather than a source of inequality. The future will likely involve close collaboration between humans and intelligent systems, where machines assist decision making while human values guide outcomes. In this sense, artificial intelligence does not replace human society, but transforms it, offering Sri Lanka an opportunity to build a more knowledge based, efficient, and equitable social order in the decades ahead.
by Milinda Mayadunna
Features
Governance cannot be a postscript to economics
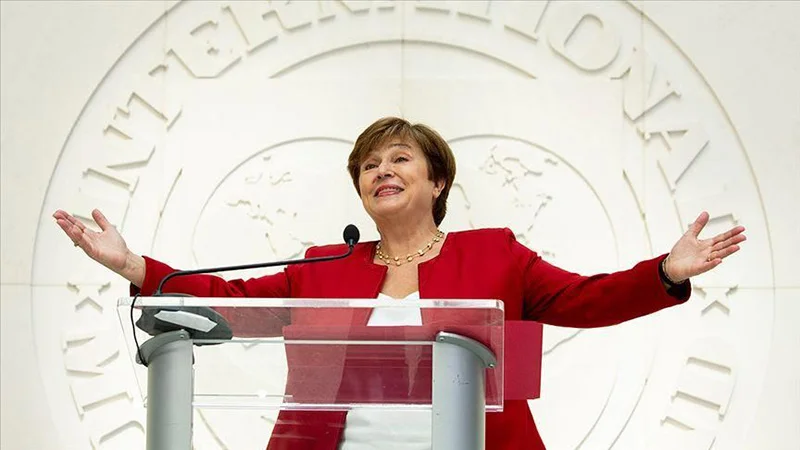

The visit by IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva to Sri Lanka was widely described as a success for the government. She was fulsome in her praise of the country and its developmental potential. The grounds for this success and collaborative spirit go back to the inception of the agreement signed in March 2023 in the aftermath of Sri Lanka’s declaration of international bankruptcy. The IMF came in to fulfil its role as lender of last resort. The government of the day bit the bullet. It imposed unpopular policies on the people, most notably significant tax increases. At a moment when the country had run out of foreign exchange, defaulted on its debt, and faced shortages of fuel, medicine and food, the IMF programme restored a measure of confidence both within the country and internationally.
Since 1965 Sri Lanka has entered into agreements with the IMF on 16 occasions none of which were taken to their full term. The present agreement is the 17th agreement . IMF agreements have traditionally been focused on economic restructuring. Invariably the terms of agreement have been harsh on the people, with priority being given to ensure the debtor country pays its loans back to the IMF. Fiscal consolidation, tax increases, subsidy reductions and structural reforms have been the recurring features. The social and political costs have often been high. Governments have lost popularity and sometimes fallen before programmes were completed. The IMF has learned from experience across the world that macroeconomic reform without social protection can generate backlash, instability and policy reversals.
The experience of countries such as Greece, Ireland and Portugal in dealing with the IMF during the eurozone crisis demonstrated the political and social costs of austerity, even though those economies later stabilised and returned to growth. The evolution of IMF policies has ensured that there are two special features in the present agreement. The first is that the IMF has included a safety net of social welfare spending to mitigate the impact of the austerity measures on the poorest sections of the population. No country can hope to grow at 7 or 8 percent per annum when a third of its people are struggling to survive. Poverty alleviation measures in the Aswesuma programme, developed with the agreement of the IMF, are key to mitigating the worst impacts of the rising cost of living and limited opportunities for employment.
Governance Included
The second important feature of the IMF agreement is the inclusion of governance criteria to be implemented alongside the economic reforms. It goes to the heart of why Sri Lanka has had to return to the IMF repeatedly. Economic mismanagement did not take place in a vacuum. It was enabled by weak institutions, politicised decision making, non-transparent procurement, and the erosion of checks and balances. In its economic reform process, the IMF has included an assessment of governance related issues to accompany the economic restructuring process. At the top of this list is tackling the problem of corruption by means of publicising contracts, ensuring open solicitation of tenders, and strengthening financial accountability mechanisms.
The IMF also encouraged a civil society diagnostic study and engaged with civil society organisations regularly. The civil society analysis of governance issues which was promoted by Verite Research and facilitated by Transparency International was wider in scope than those identified in the IMF’s own diagnostic. It pointed to systemic weaknesses that go beyond narrow fiscal concerns. The civil society diagnostic study included issues of social justice such as the inequitable impact of targeting EPF and ETF funds of workers for restructuring and the need to repeal abuse prone laws such as the Prevention of Terrorism Act and the Online Safety Act. When workers see their retirement savings restructured without adequate consultation, confidence in policy making erodes. When laws are perceived to be instruments of arbitrary power, social cohesion weakens.
During a meeting between the IMF Managing Director Georgeiva and civil society members last week, there was discussion on the implementation of those governance measures in which she spoke in a manner that was not alien to the civil society representatives. Significantly, the civil society diagnostic report also referred to the ethnic conflict and the breakdown of interethnic relations that led to three decades of deadly war, causing severe economic losses to the country. This was also discussed at the meeting. Governance is not only about accounting standards and procurement rules. It is about social justice, equality before the law, and political representation. On this issue the government has more to do. Ethnic and religious minorities find themselves inadequately represented in high level government committees. The provincial council system that ensured ethnic and minority representation at the provincial level continues to be in abeyance.
Beyond IMF
The significance of addressing governance issues is not only relevant to the IMF agreement. It is also important in accessing tariff concessions from the European Union. The GSP Plus tariff concession given by the EU enables Sri Lankan exports to be sold at lower prices and win markets in Europe. For an export dependent economy, this is critical. Loss of such concessions would directly affect employment in key sectors such as apparel. The government needs to address longstanding EU concerns about the protection of human rights and labour rights in the country. The EU has, for several years, linked the continuation of GSP Plus to compliance with international conventions. This includes the condition that the Prevention of Terrorism Act (PTA) be brought into line with international standards. The government’s alternative in the form of the draft Protection of the State from Terrorism Act (PTSA) is less abusive on paper but is wider in scope and retains the core features of the PTA.
Governance and social justice factors cannot be ignored or downplayed in the pursuit of economic development. If Sri Lanka is to break out of its cycle of crisis and bailout, it must internalise the fact that good governance which promotes social justice and more fairly distributes the costs and fruits of development is the foundation on which durable economic growth is built. Without it, stabilisation will remain fragile, poverty will remain high, and the promise of 7 to 8 percent growth will remain elusive. The implementation of governance reforms will also have a positive effect through the creative mechanism of governance linked bonds, an innovation of the present IMF agreement.
The Sri Lankan think tank Verité Research played an important role in the development of governance linked bonds. They reduce the rate of interest payable by the government on outstanding debt on the basis that better governance leads to a reduction in risk for those who have lent their money to Sri Lanka. This is a direct financial reward for governance reform. The present IMF programme offers an opportunity not only to stabilise the economy but to strengthen the institutions that underpin it. That opportunity needs to be taken. Without it, the country cannot attract investment, expand exports and move towards shared prosperity and to a 7-8 percent growth rate that can lift the country out of its debt trap.
by Jehan Perera
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoWhy does the state threaten Its people with yet another anti-terror law?
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoReconciliation, Mood of the Nation and the NPP Government
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoVictor Melder turns 90: Railwayman and bibliophile extraordinary
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoLOVEABLE BUT LETHAL: When four-legged stars remind us of a silent killer
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoVictor, the Friend of the Foreign Press
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoNew Zealand meet familiar opponents Pakistan at spin-friendly Premadasa
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoTariffs ruling is major blow to Trump’s second-term agenda
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoECB push back at Pakistan ‘shadow-ban’ reports ahead of Hundred auction













