Features
KUSHTARAJAGALA – Wrapped in mystery, King or Bodhisatta?

by Dr.P.G.Punchihewa
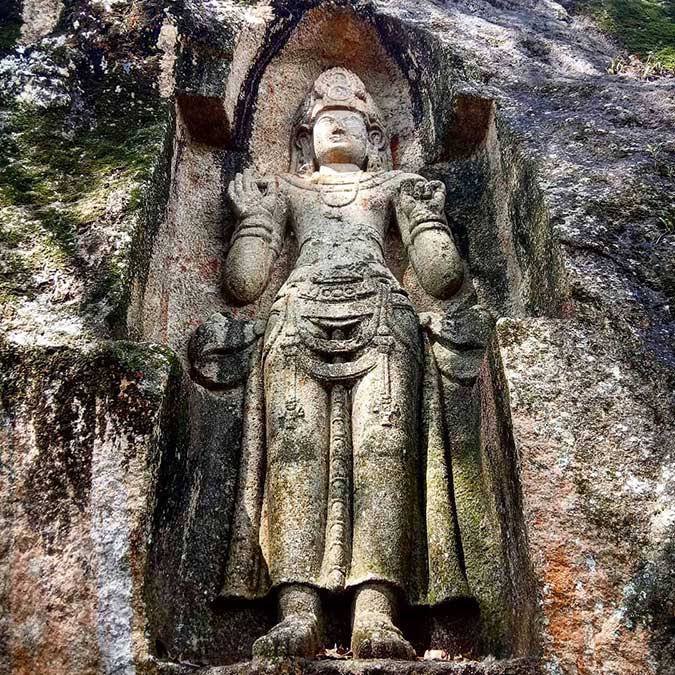
The rock sculpture at Valigama, known as Kushtarajagala could be seen as one travels along the old road for about one kilometer from the town, towards Galle and past the rail level crossing, to one’ s left. Across the road a few meters away is Aggrabodhi Viharaya which traces its history to the time of King Devanampiyatissa.
The image is carved in high relief inside an arched niche in a rock boulder of gneiss and is about twelve feet high. The head dress has four Buddha images. The image is draped in kingly attire, giving the belief that the image is that of a king. For a folk poet this image was the subject, as he put it in verse form.

(There is neither good nor bad, no movements, no sleep or not awake, no words spoken, no fixed meals; there is an immortal king on the shores of Valigama.)
That gives some credence to the local belief that the figure represents a king who left his native country, because he suffered from an attack of eczema, landed at Valigama and was cured by a local physician.
According to Dr.L. Prematilake of the University of Ceylon “stylistically the sculpture could be dated to the eighth or the ninth century,” and he adds that some would attempt to identify the king under reference with Aggabodhi iv (667-683 AD) who according to Culavamsa “was attacked by an incurable disease and when he saw that the time had come for his death he called his subjects and exhorted them to piety. When dead his subjects performed for him on his pyre all ceremonies without fail, made for themselves medicine from the ashes of the pyre.”Culavamsa Chap 46.35
Aggabodhi IV ruled for 16 years. Culavamsa says he was a just monarch, gifted with right views. During his reign he and his subordinates, some of whom were even Damilas, built viharas and parivenas and had been a very popular ruler. Culavamsa says ‘when he was dead his subjects mourned all in deep grief’. (However, there is no record to say that he was deified like one of his predecessors, King Mahasen who was responsible for the construction of Minneriya Tank and Jetavana Chaitya.)
The four Dhyana Buddhas in the head dress of the image preclude that it is that of a human being. However Ven. Dr.Kamburupitiye Vanaratana Thera is of opinion that the King would have made a vow to put up the image to cure himself from the eczema he suffered from. But he does not mention whether the figure represents the King or God/Bodhisattawho affected the cure. Dr.Prematilake states that the popularity of Avalokitesvara in Sri Lanka in his capacity as a healer of diseases is evident. Literary and archaeological evidence amply show the prevalence of the cult of the Bodhisatva Avalokesvara was worshipped under the name “Natha.”
That leaves the scholars with the conclusion that the statue could be that of one of the deities or Boddhisatvas.
Sri Lanka is the home of Theravada, the orthodox and the earliest form of Buddhism. It had no rivals up to about the third century A.D, during King Voharikatissa’s time when Vaitulya doctrine, a form of Mahayana had first appeared but had been suppressed. With the victory of Mahayana over Theravada in India, in about the sixth century Sri Lanka too was subjected to Mahayana influence on and off. Abhayagiri and Jetavana became their centers. The heretical teachings however though officially not recognized were said to have had a following among the people. Sanskrit language and literature gradually came into vogue. Prof. Paranavitane reports of a fragmentary record engraved on a rock in Mihintale which consists of a Sanskrit poem praising Buddha belonging to about the eighth century.
Kushtarajagala is one of the most visible Mahayana influences in the Island. There is one other Mahayana site, that at Buduruvagala near Vellavaya, in Moneragala District, where a group of colossal figures have been carved on the rock. The key figure of the group is Buddha. On the right hand is Avalokitesvara and the figure on the left is identified as that of Maitriya. The female figure to the right is identified as that of Goddess Tara.
Prof.Paranavitana, on grounds of style ascribed the figures to a period anterior to the Polonnaruava period. Both Kushtarajagala and the figures of Buduruvagala seem to have been constructed at a time close to each other and a time when there would have been much Mahayana activity. Unlike during the earlier period, there were no powerful rulers to back Theravada against the onslaughts of Mahayana and its beliefs came to infiltrate the social fabric.
The fact that both the Kushtarajagala figure and the figure at Buduruvagala to the right of Buddha have dhyani Buddhas on the head dress make believe that they could be identified as that of Avalokititeswara , as had been suggested by Dr A. Nell earlier.
There are several other scholars who tried to identify Kushtaraja with some other gods or bodhisattvas. Dr .Prematilake who questioned ,as to how we are to settle the problem of the four Dhyani Buddhas in the head dress, after some careful study concludes “Kushtaraja image may therefore well be a representation of the Dhyani Bodhisatva in his Sambogakaya aspect.”
Earlier van Lohuizen -de Leeuw stated that Mahayana sects introduced Samantabadra in Ceylon as Adi Buddha and he was worshipped actively in the eighth-ninth centuries and drew a parallel between the Veligama image and Samantabadra in his Adi buddha aspect.
According to Dr. Mudiyanse of the University Kelaniya ‘there is sufficient evidence to identify the figure as a representation of Avalokitesvara.’ Ven,Dr .Kamburupitiye Vanaratana Thera, thinks that the statue was built by Agbo IV. With the spread of Mahayana in Sri Lanka Avalokitesvara Natha came to be respected by the Buddhists. Sri Lankan Buddhists came to address him as Natha.
As a matter of fact the Bodhisatva Avalokita is still worshipped by the Sri Lankan Buddhists but under the name of Natha which has obscured his identity. (Paranavitana).
The question is being asked as to why the image was put up at Veligama. Going by the Mayura Sandesaya which belongs to about the 1400 AD, Veligama had been a prosperous town described as a beautiful one filled with riches and pretty women. Also one of the predecessors of Aggabodhi IV, Aggabodhi I according to Culavamsa had grown a huge coconut plantation, the first recorded one in the island. The harbor would have helped to develop relations with outside world. The foreign ruler who came in search of a cure would have landed at Veligama.
As we saw, the image of Kushtarajagala has remained a controversial one. It may be possible that Aggabodhi IV built the image seeking succor from Bodhisatva Avalokitesvara who was considered as a healer of diseases. Even today people visit Kataragama and, Dondra seeking intervention of gods, in time of sicknesses and what they promise in return is a figure for figure.(roopeta roopayak) to god. Until further evidence is found, the image will remain an enigma and the public will have to be satisfied with the findings of the few studies done so far.
Features
Democracy faces tougher challenges as political Right beefs-up presence

 It is becoming increasingly evident that the democracy-authoritarianism division would be a major polarity in international politics going forward. It shouldn’t come as a surprise if quite a few major states of both East and West gain increasing inspiration from the ‘world’s mightiest democracy’ under President Donald Trump from now on and flout the core principles of democratic governance with impunity.
It is becoming increasingly evident that the democracy-authoritarianism division would be a major polarity in international politics going forward. It shouldn’t come as a surprise if quite a few major states of both East and West gain increasing inspiration from the ‘world’s mightiest democracy’ under President Donald Trump from now on and flout the core principles of democratic governance with impunity.
It is the political Right that would gain most might in this evolving new scheme of things. Whether it be the US itself, France, Israel or Turkey, to name just a few countries in the news, it is plain to see that the Right is unleashing its power with hardly a thought for the harm being done to key democratic institutions and norms.
In fact, Donald Trump and his Republican hard liners led from the front, so to speak, in this process of unleashing the power of the Right in contemporary times. It remains a very vital piece of history that the Right in the US savaged democracy’s most valued institutions on January 6, 2021, when it ran amok with the tacit backing of Trump in the US Capitol.
What was being challenged by the mob most was the ‘will of the people’ which was manifest in the latter’s choice of Joe Biden as US President at the time. To date Trump does not accept that popular verdict and insists that the election in question was a flawed one. He does so in the face of enlightened pronouncements to the contrary.
The US Right’s protégé state, Israel, is well on course to doing grave harm to its democratic institutions, with the country’s judiciary being undermined most. To cite two recent examples to support this viewpoint, the Israeli parliament passed a law to empower the country’s election officials to appoint judges, while Prime Minister Netanyahu has installed the new head of the country’s prime security agency, disregarding in the process a Supreme Court decision to retain the former head.
Such decisions were made by the Netanyahu regime in the face of mounting protests by the people. While nothing new may be said if one takes the view that Israel’s democratic credentials have always left much to be desired, the downgrading of a democratic country’s judiciary is something to be sorely regretted by democratic opinion worldwide. After all, in most states, it is the judiciary that ends up serving the best interests of the people.
Meanwhile in France, the indications are that far Right leader Marine Le Pen would not be backing down in the face of a judicial verdict that pronounces her guilty of corruption that may prevent her from running for President in 2027. She is the most popular politician in France currently and it should not come as a surprise if she rallies further popular support for herself in street protests. Among other things, this will be proof of the growing popular appeal of the political Right. Considering that France has been a foremost democracy, this is not good news for democratic opinion.
However, some heart could be taken from current developments in the Gaza and Turkey where the people are challenging their respective dominant governing forces in street protests largely peacefully. In the Gaza anti-Hamas protests have broken out demanding of the group to step down from power, while in Turkey, President Erdogan’s decades-long iron-fist rule is being challenged by pro-democracy popular forces over the incarceration of his foremost political rival.
Right now, the Turkish state is in the process of quashing this revolt through a show of brute force. Essentially, in both situations the popular demand is for democracy and accountable governance and such aims are generally anathema in the ears of the political Right whose forte is repressive, dictatorial rule.
The onus is on the thriving democracies of the world to ensure that the Right anywhere is prevented from coming to power in the name of the core principles and values of democracy. Right now, it is the European Union that could fit into this role best and democratic opinion is obliged to rally behind the organization. Needless to say, peaceful and democratic methods should be deployed in this historic undertaking.
Although the UN is yet to play an effective role in the current international situation, stepped up efforts by it to speed up democratic development everywhere could yield some dividends. Empowerment of people is the goal to be basically achieved.
Interestingly, the Trump administration could be seen as being in league with the Putin regime in Russia at present. This is on account of the glaringly Right wing direction that the US is taking under Trump. In fact, the global balance of political forces has taken an ironic shift with the hitherto number one democracy collaborating with the Putin regime in the latter’s foreign policy pursuits that possess the potential of plunging Europe into another regional war.
President Trump promised to bring peace to the Ukraine within a day of returning to power but he currently is at risk of cutting a sorry figure on the world stage because Putin is far from collaborating with his plans regarding Ukraine. Putin is promising the US nothing and Ukraine is unlikely to step down from the position it has always held that its sovereignty, which has been harmed by the Putin regime, is not negotiable.
In fact, the China-Russia alliance could witness a firming-up in the days ahead. Speculation is intense that the US is contemplating a military strike on Iran, but it would face strong opposition from China and Russia in the event of such an adventurist course of action. This is on account of the possibility of China and Russia continuing to be firm in their position that Western designs in the Gulf region should be defeated. On the other hand, Iran could be expected to hit back strongly in a military confrontation with the US.
Considering that organizations such as the EU could be expected to be at cross-purposes with the US on the Ukraine and connected questions, the current world situation could not be seen as a replication of the conventional East-West polarity. The East, that is mainly China and Russia, is remaining united but not so the West. The latter has broadly fragmented into a democratic states versus authoritarian states bipolarity which could render the international situation increasingly unstable and volatile.
Features
Chikungunya Fever in Children
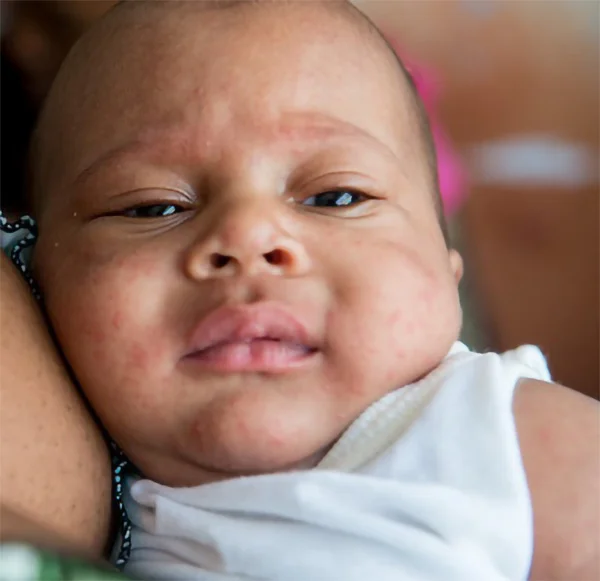
Chikungunya fever, a viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes, poses a significant health concern, particularly for children. It has been around in Sri Lanka sporadically, but there are reports of an increasing occurrence of it in more recent times. While often associated with debilitating joint pain in adults, its manifestations in children can present unique challenges. Understanding the nuances of this disease is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Chikungunya fever is caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV), an alphavirus transmitted to humans through the bites of infected Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. These are the same mosquitoes that transmit dengue and Zika viruses, highlighting the overlapping risks in many areas of the world. It is entirely possible for chikungunya and dengue to co-circulate in the same area, leading to co-infections in individuals.
When a mosquito bites a person infected with CHIKV, it ingests the virus. After a period of growth and multiplication of the virus within the mosquito, the virus can be transmitted to another person through subsequent bites. Therefore, the mosquito acts as a vector or an intermediate transmitting agent that spreads the disease, but not as a reservoir of the disease. The spread of chikungunya is influenced by environmental factors that support mosquito breeding, such as stagnant water and warm climates. Urbanization and poor sanitation can exacerbate the problem by creating breeding grounds for these mosquitoes.
The clinical presentation of chikungunya in children can vary, ranging from mild to severe. While some infected children may even be asymptomatic and be normal for all intents and purposes, others can experience a range of symptoms, including a sudden onset of high fever, a common initial symptom. Pain in the joints of the body, while being a hallmark of chikungunya in adults, may be less pronounced in children. However, they can still experience significant discomfort and this must be kept in mind during processes of diagnosis and treatment. It is also important to remember that joint pains can present in various forms, as well as in different locations of the body. There is no characteristic pattern or sites of involvement of joints. Muscle aches and pains can accompany the fever and joint pain as well. A headache, too, could occur at any stage of the disease. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and fatigue as well.
A reddish elevated rash, referred to in medical jargon as a maculopapular rash, is frequently observed in children, sometimes more so than in adults. While chikungunya is known to cause such a rash, there is a specific characteristic related to nasal discoloration that is worth noting. It is called the “Chik sign” or “Brownie nose” and refers to an increased darkening of the skin, particularly on the nose. This discolouration just appears and is not associated with pain or itching. It can occur during or after the fever, and it can be a helpful clinical sign, especially in areas with limited diagnostic resources. While a generalised rash is a common symptom of chikungunya, a distinctive darkening of the skin on the nose is a particular characteristic that has been observed.
In some rare instances, particularly in infants and very young children, chikungunya can lead to neurological complications, such as involvement of the brain, known as encephalitis. This is associated with a change in the level of alertness, drowsiness, convulsions and weakness of limbs. Equally rarely, some studies indicate that children can experience bleeding tendencies and haemorrhagic manifestations more often than adults.
Diagnosis is typically made through evaluating the patient’s symptoms and medical history, as well as by special blood tests that can detect the presence of CHIKV antibodies (IgM and IgG) or the virus itself through PCR testing.
There is no specific antiviral treatment for chikungunya. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and allowing the body to recover on its own. Adequate rest is essential for recovery, and maintaining hydration is crucial, especially in children with fever. Paracetamol in the correct dosage can be used to reduce fever and pain. It is important to avoid aspirin, as it can increase the risk of a further complication known as Reye’s syndrome in children. In severe cases, hospitalisation and supportive care may be necessary.
While most children recover from chikungunya without any major issues, some may experience long-term sequelae. Joint pain can persist for months or even years in some individuals, impacting their quality of life. In rare cases, chikungunya can lead to chronic arthritis. Children that have suffered from neurological complications can have long term effects.
The ultimate outcome or prognosis for chikungunya in children is generally favourable. Most children recover fully within a few days or a couple of weeks. However, the duration and severity of symptoms can vary quite significantly.
Prevention is key to controlling the spread of chikungunya. Mosquito control is of paramount importance. These include eliminating stagnant water sources where mosquitoes breed, using mosquito repellents, wearing long-sleeved clothing and pants, using mosquito nets, especially for young children and installing protective screens on windows and doors. While a chikungunya vaccine is available, its current use is mainly for adults, especially those traveling to at risk areas. More research is being conducted for child vaccinations.
Chikungunya outbreaks can strain healthcare systems and have significant economic consequences. Public health initiatives aimed at mosquito control and disease surveillance are crucial for preventing and managing outbreaks.
Key considerations for children are that some of them, especially infants and young children, are more vulnerable to severe chikungunya complications and early diagnosis and supportive care are essential for minimising the risk of long-term sequelae. Preventing mosquito bites is the most effective way to protect children from chikungunya. By understanding the causation, clinical features, treatment, and prevention of chikungunya, parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals can work together to protect children from this illness that could sometimes be quite debilitating.
 Dr B. J. C. Perera
Dr B. J. C. Perera
MBBS(Cey), DCH(Cey), DCH(Eng), MD(Paed), MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin), FRCP(Lond), FRCPCH(UK), FSLCPaed, FCCP, Hony. FRCPCH(UK), Hony. FCGP(SL)
Specialist Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Fellow, Postgraduate Institute of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka.
Joint Editor, Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health and Section Editor, Ceylon Medical Journal
Founder President, Sri Lanka College of Paediatricians – 1996-97)
Features
The Great and Little Traditions and Sri Lankan Historiography

Power, Culture, and Historical Memory:
(Continued from yesterday)
Newton Gunasinghe, a pioneering Sri Lankan sociologist and Marxist scholar, made significant contributions to the study of culture and class in Sri Lanka by incorporating the concepts of great and little traditions within an innovative Marxist framework. His theoretical synthesis offered historians a fresh perspective for evaluating the diversity of past narratives.
At the same time, Michel Foucault’s philosophical intervention significantly influenced the study of historical knowledge. In particular, two of his key concepts have had a profound impact on the discipline of history:
1. The relationship between knowledge and power – Knowledge is not merely an objective truth but a manifestation of the power structures of its time.
2. The necessity of considering the ‘other’ in any conceptual construction – Every idea or framework takes shape in relation to its opposite, highlighting the duality inherent in all intellectual constructs.
These concepts challenged historians to rethink their approaches, prompting them to explore the dynamic interplay between knowledge, power, and culture. The existence of Little Tradition prompted historians to pay attention to ‘other’ histories.
The resurgence of ethnic identities and conflicts has brought renewed attention to the dichotomy of culture, steering the discourse in a new direction. The ethnic resurgence raises three key issues. First, the way non-dominant cultures interpret the past often differs from the narratives produced by dominant cultures, prompting the question: What is historical truth? Second, it underscores the importance of studying the histories of cultural identities through their own perspectives. Finally, and most importantly, it invites reflection on the relationship between ‘Little Traditions’ and the ‘Great Tradition’—how do these ‘other’ histories connect to broader historical narratives?
When the heuristic construct of the cultural dichotomy is applied to historical inquiry, its analytical scope expands far beyond the boundaries of social anthropology. In turn, it broadens the horizons of historical research, producing three main effects:
1. It introduces a new dimension to historical inquiry by bringing marginalised histories to the forefront. In doing so, it directs the attention of professional historians to areas that have traditionally remained outside their scope.
2. It encourages historians to seek new categories of historical sources and adopt more innovative approaches to classifying historical evidence.
3. It compels historians to examine the margins in order to gain a deeper understanding of the center.
The rise of a new theoretical school known as Subaltern Studies in the 1980s provided a significant impetus to the study of history from the perspective of marginalised and oppressed groups—those who have traditionally been excluded from dominant historical narratives and are not linked to power and authority. This movement sought to challenge the Eurocentric and elitist frameworks that had long shaped the study of history, particularly in the context of colonial and postcolonial societies. The writings of historians such as Ranajit Guha and Eric Stokes played a pioneering role in opening up this intellectual path. Guha, in particular, critiqued the way history had been written from the perspective of elites—whether colonial rulers or indigenous upper classes—arguing that such narratives ignored the agency and voices of subaltern groups, such as peasants, laborers, and tribal communities.
Building upon this foundation, several postcolonial scholars further developed the critical examination of power, knowledge, and representation. In her seminal essay Can the Subaltern Speak?, Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak questioned whether marginalized voices—especially those of subaltern women—could truly be represented within dominant intellectual and cultural frameworks, or whether they were inevitably silenced by hegemonic. Another major theorist in this field, Homi Bhabha, also focused on the relationship between knowledge and social power relations. His analysis of identity formation under colonialism revealed the complexities of power dynamics and how they persist in postcolonial societies.
Together, these scholars significantly reshaped historical and cultural studies by emphasising the voices and experiences of those previously ignored in dominant narratives. Their work continues to influence contemporary debates on history, identity, and the politics of knowledge production.
The Sri Lankan historiography from very beginning consists of two distinct yet interrelated traditions: the Great Tradition and the Little Traditions. These traditions reflect different perspectives, sources, and modes of historical transmission that have influenced the way Sri Lanka’s past has been recorded and understood. The Great Tradition refers to the formal, written historiography primarily associated with elite, religious, and state-sponsored chronicles. The origins of the Great Tradition of historiography directly linked to the introduction of Buddhism to the island by a mission sent by Emperor Asoka of the Maurya dynasty of India in the third century B.C. The most significant sources in this tradition include the Mahāvaṃsa, Dīpavaṃsa, Cūḷavaṃsa, and other Buddhist chronicles that were written in Pali and Sanskrit. These works, often compiled by Buddhist monks, emphasise the island’s connection to Buddhism, the role of kingship, and the concept of Sri Lanka as a sacred land linked to the Buddha’s teachings. The Great Tradition was influenced by royal patronage and aimed to legitimise rulers by presenting them as protectors of Buddhism and the Sinhala people.
In contrast, the Little Tradition represents oral histories, folk narratives, and local accounts that were passed down through generations in vernacular languages such as Sinhala and Tamil. These traditions include village folklore, ballads, temple stories, and regional histories that were not necessarily written down but played a crucial role in shaping collective memory. While the Great Tradition often portrays a centralised, Sinhala-Buddhist perspective, the Little Tradition captures the diverse experiences of various communities, including Tamils, Muslims.
What about the history of those who are either unrepresented or only marginally represented in the Great Tradition? They, too, have their own interpretations of the past, independent of dominant narratives. Migration from the four corners of the world did not cease after the 3rd century BC—so what about the cultural traditions that emerged from these movements? Can we reduce these collective memories solely to the Sokari Nadagams?
The Great Traditions often celebrate the history of the ruling or majority ethnic group. However, Little Traditions play a crucial role in preserving the historical memory and distinct identities of marginalised communities, such as the Vedda and Rodiya peoples. Beyond caste history, Little Traditions also reflect the provincial histories and historical memories of peripheral communities. Examples include the Wanni Rajawaliya and the Kurunegala Visthraya. The historical narratives presented in these sources do not always align with those of the Great Tradition.
The growth of caste histories is a key example of Little Historical Traditions. Jana Wansaya remains an important source in this context. After the 12th century, many non-Goigama castes in Sri Lanka preserved their own oral historical traditions, which were later documented in written form. These caste-based histories are significant because they provide a localised, community-centered perspective on historical developments. Unlike the dominant narratives found in the Great Tradition, they capture the social, economic, and cultural transformations experienced by different caste groups. For instance, the Karava, Salagama, and Durava castes have distinct historical narratives that have been passed down through generations.
Ananda S. Kulasuriya traced this historical tradition back to the formal establishment of Buddhism, noting that it continued even after the decline of the Polonnaruwa Kingdom. He identified these records as “minor chronicles” and classified them into three categories: histories of the Sangha and Sasana, religious writings of historical interest, and secular historical works. According to him, the first category includes the Pujavaliya, the Katikavatas, the Nikaya Sangrahaya, and the Sangha Sarana. The second category comprises the Thupavamsa, Bodhi Vamsa, Anagatha Vamsa, Dalada Sirita, and Dhatu Vamsa, along with the two Sinhalese versions of the Pali Hatthavanagalla Vihara Vamsa, namely the Ehu Attanagalu Vamsa and the Saddharma Ratnakaraya. The third category consists of works that focus more on secular events than religious developments, primarily the Rajavaliya. Additionally, this category includes the Raja Ratnakaraya and several minor works such as the Sulu Rajavaliya, Vanni Rajavaliya, Alakesvara Yuddhaya, Sri Lanka Kadaim Pota, Kurunegala Vistaraya, Buddharajavaliya, Bamba Uppattiya, Sulu Pujavaliya, Matale Kadaim Pota, Kula Nitiya, and Janavamsaya (Kulasuriya, 1978:5). Except for a few mentioned in the third category, all other works are products of the Great Historical tradition.
Over the last few decades, Gananath Obeyesekera has traversed the four corners of Sri Lanka, recovering works of the Little Historical Traditions and making them accessible for historical inquiry, offering a new lens through which to reread Sri Lankan history. Obeyesekera’s efforts to recover the Little Historical Traditions remind us that history is never monolithic; rather, it is a contested space where power, culture, and memory continuously shape our understanding of the past. By bringing the Little Historical Traditions into the fold of Sri Lankan historiography, Obeyesekera challenges us to move beyond dominant narratives and embrace a more pluralistic understanding of the past. The recovery of these traditions is not just an act of historical inquiry but a reminder that power shapes what we remember—and what we forget. Sri Lankan history, like all histories, is a dialogue between great and little traditions and it is to engage both of them. His latest work, The Doomed King: A Requiem for Sri Vikrama Rajasinghe, is a true testament to his re-reading of Sri Lankan history.
BY GAMINI KEERAWELLA
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoSri Lanka’s eternal search for the elusive all-rounder
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoBid to include genocide allegation against Sri Lanka in Canada’s school curriculum thwarted
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoGnanasara Thera urged to reveal masterminds behind Easter Sunday terror attacks
-

 Sports16 hours ago
Sports16 hours agoTo play or not to play is Richmond’s decision
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoAIA Higher Education Scholarships Programme celebrating 30-year journey
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoComBank crowned Global Finance Best SME Bank in Sri Lanka for 3rd successive year
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoSanctions by The Unpunished
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoMore parliamentary giants I was privileged to know











