Foreign News
Huge ancient city found in the Amazon
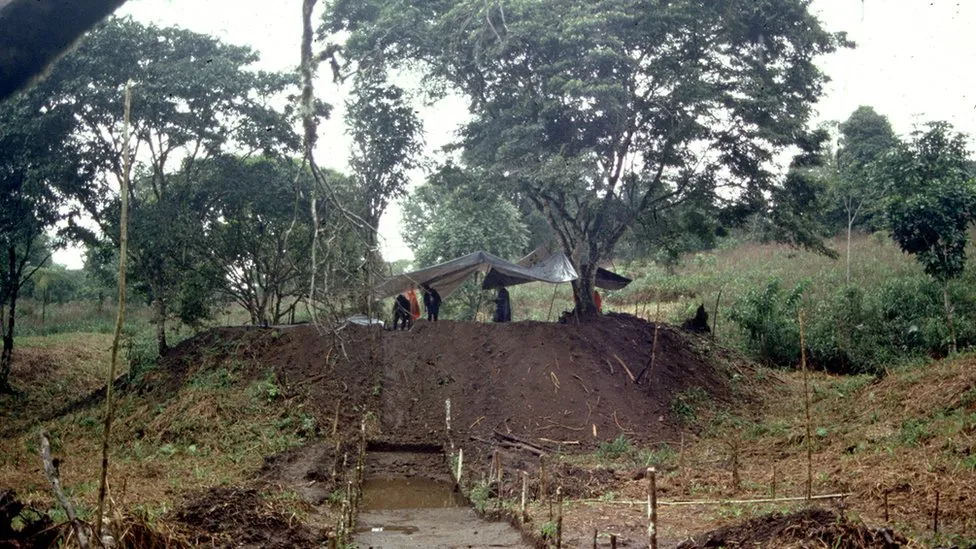

A huge ancient city has been found in the Amazon, hidden for thousands of years by lush vegetation.
The discovery changes what we know about the history of people living in the Amazon. The houses and plazas in the Upano area in eastern Ecuador were connected by an astounding network of roads and canals.
The area lies in the shadow of a volcano that created rich local soils but also may have led to the destruction of the society.
While we knew about cities in the highlands of South America, like Machu Picchu in Peru, it was believed that people only lived nomadically or in tiny settlements in the Amazon. “This is older than any other site we know in the Amazon. We have a Eurocentric view of civilisation, but this shows we have to change our idea about what is culture and civilisation,” says Prof Stephen Rostain, director of investigation at the National Centre for Scientific Research in France, who led the research.
“It changes the way we see Amazonian cultures. Most people picture small groups, probably naked, living in huts and clearing land – this shows ancient people lived in complicated urban societies,” says co-author Antoine Dorison. The city was built around 2,500 years ago, and people lived there for up to 1,000 years, according to archaeologists.
It is difficult to accurately estimate how many people lived there at any one time, but scientists say it is certainly in the 10,000s if not 100,000s.
The archaeologists combined ground excavations with a survey of a 300 sq km (116 sq mile) area using laser sensors flown on a plane that could identify remains of the city beneath the dense plants and trees.
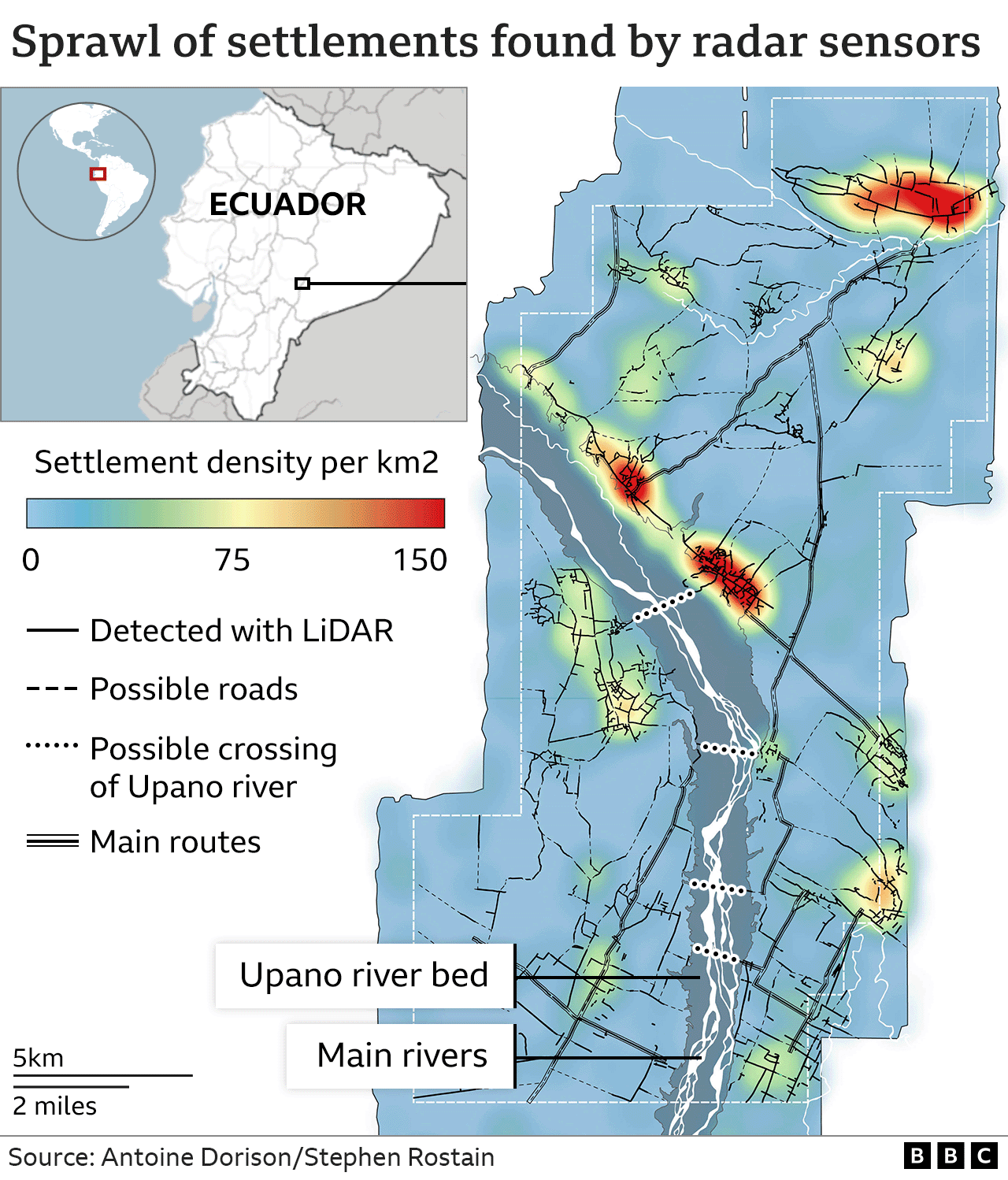
This LiDAR technology found 6,000 rectangular platforms measuring about 20m (66 ft) by 10m (33 ft) and 2-3m high. They were arranged in groups of three to six units around a plaza with a central platform.
The scientists believe many were homes, but some were for ceremonial purposes. One complex, at Kilamope, included a 140m (459 ft) by 40m (131 ft) platform.
They were built by cutting into hills and creating a platform of earth on top.
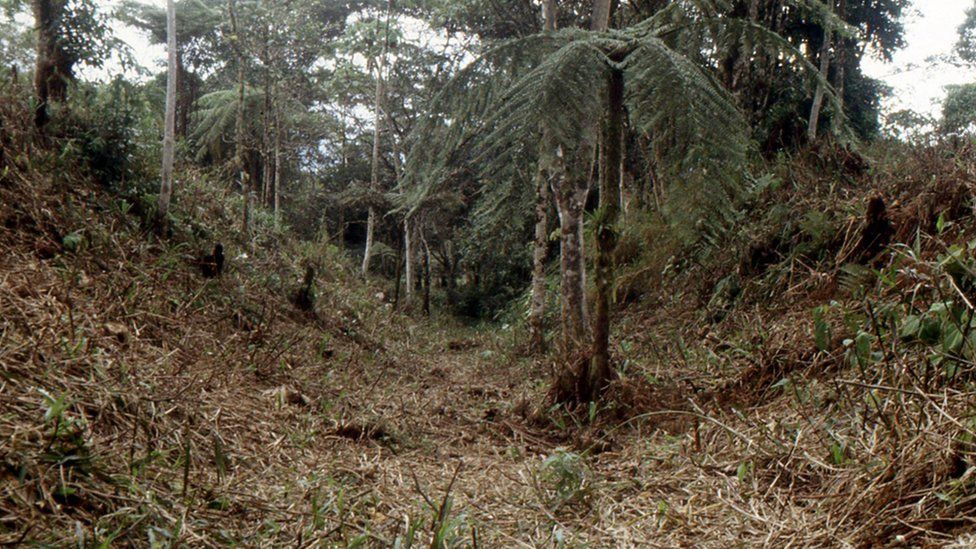

A network of straight roads and paths connected many of the platforms, including one that extended 25km (16 miles).
Dr Dorison said these roads were the most striking part of the research. “The road network is very sophisticated. It extends over a vast distance, everything is connected. And there are right angles, which is very impressive,” he says, explaining that it is much harder to build a straight road than one that fits in with the landscape.
He believes some had a “very powerful meaning”, perhaps linked to a ceremony or belief.
The scientists also identified causeways with ditches on either side which they believe were canals that helped manage the abundant water in the region.
There were signs of threats to the cities – some ditches blocked entrances to the settlements, and may be evidence of threats from nearby people.
Researchers first found evidence of a city in the 1970s, but this is the first time a comprehensive survey has been completed, after 25 years of research.
It reveals a large, complex society that appears to be even bigger than the well-known Mayan societies in Mexico and Central America. “Imagine that you discovered another civilisation like the Maya, but with completely different architecture, land use, ceramics,” says José Iriarte, a professor of archaeology at University of Exeter, who was not involved in this research.
Some of the findings are “unique” for South America, he explains, pointing to the octagonal and rectangular platforms arranged together. The societies were clearly well-organised and interconnected, he says, highlighting the long sunken roads between settlements.
Not a huge amount is known about the people who lived there and what their societies were like. Pits and hearths were found in the platforms, as well as jars, stones to grind plants and burnt seeds.
The Kilamope and Upano people living there probably mostly focussed on agriculture. People ate maize and sweet potato, and probably drank “chicha”, a type of sweet beer.
Prof Rostain says he was warned against this research at the start of his career because scientists believed no ancient groups had lived in the Amazon. “But I’m very stubborn, so I did it anyway. Now I must admit I am quite happy to have made such a big discovery,” he says.
The next step for the researchers is understanding what lies in an adjoining 300 sq km (116 sq mile) area not yet surveyed.
(BBC)
Foreign News
Qatar partially reopens airspace as Iranian strikes continue to hit Gulf

Qatar has partially reopened its airspace days after Iranian missile and drone strikes forced the country to ground all flights as a United States-Israeli military campaign against Iran continues into its seventh day.
The Qatar Civil Aviation Authority announced the limited opening on Friday evening, saying flights would operate through “designated navigational contingency routes with limited operational capacity” in coordination with the Qatari armed forces.
The move marks a cautious first step towards restoring air links to one of the Gulf’s most important aviation hubs but falls well short of a return to normality, with scheduled commercial flights to and from Doha remaining suspended until a further official announcement is made.
The Qatar Civil Aviation Authority said the partial reopening covers only a narrow category of flights “designated for passenger evacuation” and air cargo services.
Passengers with confirmed bookings were urged to follow updates from their airlines directly before travelling to the airport.
Early on Saturday, Qatar Airways said it “intends to operate repatriation flights on 07 March, departing Hamad International Airport to the following airports: London (LHR), Paris (CDG), Madrid (MAD), Rome (FCO), Frankfurt (FRA)”.
It added that priority would be given to “stranded passengers with families, elderly passengers, and those with urgent medical and compassionate travel needs”.
The Gulf country has been repeatedly struck by Iranian missiles and drones throughout the now seven-day conflict, forcing the country to activate its air force and use interceptors to defend its territory. Qatar’s Ministry of Defence confirmed the country had been struck by 14 ballistic missiles and four drones fired from Iran on Thursday.
More than 2,000 flights have been cancelled at Doha’s Hamad international airport since the conflict began.
Aviation across the Gulf
Across the Gulf, airports and airlines have been scrambling to manage the fallout from nearly a week of Iranian missile and drone barrages, launched in retaliation for the ongoing US-Israeli military campaign – codenamed Operation Epic Fury – which has killed at least 1,332 people in Iran since strikes began last Saturday, according to Iranian officials.
Emirates airline announced it is operating a reduced schedule while working to restore full network operations, carrying approximately 30,000 passengers out of Dubai on Friday alone.
By Saturday, the airline said it would have 106 daily return flights operating to 83 destinations, close to 60 percent of its full network, with a return to 100 percent expected “within the coming days, subject to airspace availability”.
Dubai international airport, the world’s busiest airport for international passengers, was evacuated on Sunday following Iranian strikes and has recorded close to 4,000 flight cancellations since Monday.
Abu Dhabi’s Zayed international airport has seen more than 1,000 cancellations and continues to operate at limited capacity.
Kuwait, also impacted by Iranian strikes, saw its airport undergo sustained physical damage in drone strikes, leaving some workers with minor injuries, and its airspace remains fully closed to commercial traffic.
Kuwait Airways has begun rerouting citizens with prior bookings through Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
An estimated 23,000 flights have been cancelled since late February, according to analytics firm Cirium.
[Aljazeera]
Foreign News
Human rights court orders reparations for forced sterilization case in Peru

The Inter-American Court of Human Rights (IACHR) has ordered Peru to pay reparations to the family of Celia Ramos, a mother of three whose death resulted from a campaign of forced sterilizations during the 1990s.
Thursday’s landmark ruling stated that the 34-year-old Ramos was coerced into sterilization against her will, causing an allergic reaction that led to her death.
The court ordered Peru to pay her family $340,000 as part of the ruling.
It noted that the Peruvian government had “failed to fulfill its obligation to initiate and conduct a thorough investigation” into Ramos’s case, heightening the strain on her family.
“Ms Ramos Durand’s family members — especially her three daughters, who were children at the time of the events — suffered profound harm as a consequence of the sterilization and death of Celia Edith Ramos Durand and the impunity surrounding the case,” the IACHR wrote in its decision.
Peru’s campaign of forced sterilization took place under the late President Alberto Fujimori, whose tenure included widespread human rights abuses that continue to cast a shadow over the country.
The scheme largely targeted poor and Indigenous women who were often tricked or coerced into sterilisation procedures.
This week’s ruling is the first time the human rights court has weighed in on the issue, which has been the subject of years of legal contestation in Peru.
“After almost 30 years of searching for justice, the Inter-American Court of Human Rights recognised the responsibility of the Peruvian state in the forced sterilization and death of Celia Ramos,” the Peruvian feminist organisation DEMUS said in a social media post, celebrating the ruling.
“This ruling marks a fundamental step in reparations for Celia, her family and the thousands of victims of forced sterilizations in Peru.”
As many as 314,000 women and 24,000 men were sterilized against their will in Peru under Fujimori’s government, which sought to forcibly lower the birth rate as a means of addressing poverty.
The procedures were particularly invasive for the women involved, and some suffered long-term complications, including death.
Family members often received little information about the circumstances that led to loved ones dying after the unnecessary operations. Some survivors did not realise what had happened to them until years later, when they discovered they were unable to have children.
In Ramos’s case, the 34-year-old mother had gone to a state health clinic for medical assistance on July 3, 1997, but was instead forced to undergo tubal ligation.
Ramos, however, suffered a severe allergic reaction during the procedure. She was placed in a recovery room, but the clinic was not able to treat her adequately.
In its decision, the IACHR explained that the clinic “lacked the necessary equipment and medications for adequate risk assessment or to handle emergencies”.
Ramos was ultimately transferred to an intensive care unit in the city of Piura, where she died 19 days later, on July 22, 1997.
The state did not carry out an autopsy and declined to share details with her family.
The compensation outlined in this week’s ruling includes reimbursement for the costs of medical procedures conducted to save Ramos’s life and the estimated loss of income from her death.
In October 2024, the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women at the United Nations ruled that Peru’s sterilization programme amounted to sex-based violence and discrimination against poor, rural and Indigenous women.
The committee’s statement cited a lack of adequate medical facilities and a lack of informed consent, just as the IACHR did in its decision this week.
“The victims described a consistent pattern of being coerced, pressured, or deceived into undergoing sterilizations at clinics lacking proper infrastructure or trained personnel,” committee member Leticia Bonifaz said.
“The procedures were carried out without informed consent from these victims, with some of them, especially those from remote areas, unable to read and speak Spanish, or fully understand the nature of the procedure.”
Scholars have concluded that Fujimori’s sterilization campaign was driven, in part, by racist views among government officials who saw rural, Indigenous communities as an obstacle to economic modernisation.
[Aljazeera]
Foreign News
Cost to US for war on Iran is $3.7bn in first 100 hours, says think tank

The United States-Israeli war on Iran is estimated to have cost Washington $3.7bn so far in its first 100 hours alone, or nearly $900m a day, driven largely by the huge expenditure of munitions, according to new research.
An analysis by Washington-based think tank the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) underlined the colossal cost of the war, which entered its seventh day on Friday, as the US attacks Iran with stealth bombers and advanced weapons systems.
Researchers Mark Cancian and Chris Park said only a small amount of the estimated $3.7bn cost of the war in the first 100 hours – or $891.4m each day – was already budgeted for, while most of the costs – $3.5bn – were not.
That meant the Pentagon would likely need to request more funding soon to cover the unbudgeted costs, they said, which was likely to prove a political challenge for the Trump administration and provide “a focal point for opposition to the war,” they said.
Domestic cost-of-living concerns, inflation, and now a knock-on effect of rising gas prices due to the conflict are likely to further diminish support among US citizens for the war. It is also dividing Trump’s “America First” base, which he had promised in his presidential campaigns to not enter “foreign wars”.
Noting that the US Department of Defense had released limited specifics on its operations, the researchers said their analysis drew on Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates of the operations and support costs for each unit, adjusting for inflation and unit size, and adding 10 percent for costs of “a higher operational tempo”.
Their analysis said the US had expended more than 2,000 munitions of various types in the first 100 hours of the war, and estimated it would cost $3.1bn to replenish the munitions inventory on a like-for-like basis, with the costs increasing by $758.1m a day.
(Aljazeera)
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoLegal experts decry move to demolish STC dining hall
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoA life in colour and song: Rajika Gamage’s new bird guide captures Sri Lanka’s avian soul
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoCabinet nod for the removal of Cess tax imposed on imported good
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoOverseas visits to drum up foreign assistance for Sri Lanka
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoFemale lawyer given 12 years RI for preparing forged deeds for Borella land

















