Features
How rare minerals are reshaping geopolitics

Who truly commands the foundations of the 21st-century economy? Which states possess the leverage to dictate the supply of critical minerals that underpin modern defence systems, renewable energy technologies, and digital infrastructure? How did a single nation come to dominate a market indispensable to the West’s industrial and military ambitions?
The story begins in Burma, a region historically endowed with rich deposits of tin, tungsten, and rare earths. During the colonial era, British, and later Japanese, interests exploited these resources, extracting wealth with scant regard for local populations or ecological degradation. Historical accounts indicate that tungsten extraction during the Second World War directly financed Japan’s war machine, illustrating how control over strategic minerals could translate into military advantage. Even in those early decades, however, the extraction and transport of such metals were fraught with geopolitical complexities: jungle warfare, fragile rail networks, and local resistance ensured that mineral wealth was rarely fully harnessed, leaving a template of exploitation and global competition that would resonate across subsequent decades.
Rare earth elements (REEs)—a group of 17 metals including neodymium, dysprosium, and praseodymium—are deceptively named, yet indispensable in the manufacture of permanent magnets, smartphones, electric vehicles, and fighter jets. Despite over a decade of Western efforts to loosen China’s grip, Beijing remains preeminent. Chinese President Xi Jinping’s 2019 visit to a rare earth magnet factory in Jiangxi Province was widely interpreted by the Washington Post as “muscle flexing,” a deliberate reminder to Washington of its dependency on Beijing for these critical materials.
China’s strategic foresight traces back to Deng Xiaoping’s 1992 observation in Baotou, Inner Mongolia: “The Middle East has oil, China has rare earths.” Deng’s statement proved prescient, foreshadowing the creation of a meticulously orchestrated industrial ecosystem encompassing mining, separation, refining, and magnet production.
By consolidating thousands of small-scale mines and vertically integrating the value chain, China transformed raw mineral wealth into a geopolitical lever. As Xigang Zhang, chief of Rising Nonferrous Metals Share Co, affirmed to the Financial Times, “International markets will remain dependent on China’s rare earth supply chain for the foreseeable future.”
This concentration of power has forced the West into a reactive scramble. The United States, for instance, possesses only one active rare earth mine, Mountain Pass in California, which extracts neodymium and praseodymium but remains heavily reliant on China for processing. As the Financial Times observed, the Pentagon’s $400 million direct investment in MP Materials to build a domestic magnet manufacturing facility represents a rare and decisive intervention, intended to “accelerate American supply chain independence.” Yet even such measures confront formidable technological and economic barriers, as China dominates not merely extraction but also downstream processing and magnet production, controlling 70 per cent of mining, 90 per cent of separation and processing, and 93 per cent of global magnet manufacturing.
Western powers have pursued alternative sources in unconventional geographies. Greenland, home to some of the largest untapped rare earth deposits, has attracted U.S. interest under the Trump administration. According to the Washington Post, the proposed Tanbreez mine in southwestern Greenland would extract tantalum, niobium, zirconium, and REEs from a remote fjord, necessitating a floating deepwater port, worker housing, and substantial energy infrastructure. Tony Sage, CEO of Critical Metals Corp, told the Washington Post that President Trump’s aim was not the acquisition of Greenland itself, but “favoured access to mining deals that benefit U.S. manufacturers and defence contractors.”
The United States has also sought to exploit domestic waste streams as a source of critical minerals. A 2025 study from the Colorado School of Mines, concluded that “recovering even small quantities of the byproducts from existing mining operations would substantially reduce net import reliance for most critical minerals.” For 15 elements—including rare earths, gallium, and germanium—recovering less than one per cent of potential byproducts could supplant imports, highlighting a largely untapped domestic reservoir. Translating these findings into economically viable operations, however, remains a formidable challenge, requiring “a lot more research, development and policy.”
China has leveraged its rare earth dominance as a potent geopolitical instrument. In April 2023, Beijing temporarily restricted exports of seven rare earth elements, disrupting U.S. and Japanese supply chains, widely interpreted as a response to American tariffs. Gracelin Baskaran, a critical minerals expert at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, explained that China “doesn’t turn around and curb production to raise prices—rather, it uses market dominance to retain leverage and weaponise these resources.” Such measures confirm that rare earths are neither mere commodities nor traditional resources, but instruments capable of reshaping alliances, supply networks, and international trade norms.
Western responses have been uneven. The U.S. has invested in Pentagon-backed projects, imposed tariffs, and explored international partnerships, while the EU and Japan pursue recycling, stockpiling, and domestic development. The G7, in its 2025 Critical Minerals Action Plan, emphasized diversification, traceability, sustainable mining, and innovation, explicitly recognizing the threat posed by “non-market policies and practices in the critical minerals sector,” according to the official communiqué.
Yet, as Gareth Hatch, founder of Technology Materials Research, observed, “The mantra of most western companies has always been ‘lowest cost at any cost.’ Why would you buy from a higher-cost producer if lower-cost alternatives are available?”
Attempts to replicate China’s industrial mastery confront both technological and historical inertia. Bloomberg reported that the solvent extraction process crucial to rare earth separation, though originally developed in the United States, was abandoned domestically due to environmental and regulatory constraints, permitting Chinese engineers to perfect the technique over decades. Between 1950 and 2018, China filed over 25,000 rare earth patents, surpassing U.S. filings by more than 150 per cent. Biological and green-tech alternatives, such as the DARPA-funded EMBER project using microbes to process REEs, remain years from industrial scalability, according to the Washington Post.
Even as the U.S. pursues Greenland and domestic mining initiatives, China has consolidated its control over rare earths through new licensing and reporting regulations, centralizing oversight under the ostensible guise of environmental protection, the Washington Post reported in 2025. This underscores a stark paradox: abundance alone does not confer strategic autonomy. True leverage resides in control over processing, technology, and supply chain governance, areas where China has invested systematically and consolidated expertise.
Rare earths have become instruments of influence at the intersection of technology, commerce, and military power. As the Financial Times observed, “breaking China’s grip will be challenging,” given decades of state planning, technological mastery, and market manipulation. Even U.S. interventions—from price floors to G7 initiatives—confront the scale and sophistication of China’s advantage. From Greenland to Mountain Pass, and from Pentagon investments in MP Materials to U.S.-Japan stockpiling, the global race illustrates a critical lesson: in the era of rare earths, mineral supply chains are inseparable from statecraft, and technological command is synonymous with geopolitical power. It is in this context that Trump wages his tariff war, while Xi Jinping and Narendra Modi are set to meet on Monday, September 1, after seven years, a meeting that could reshape strategic alignments in the rare minerals race.
by Nilantha Ilangamuwa ✍️
Features
Cyclones, greed and philosophy for a new world order

Further to my earlier letter titled, “Psychology of Greed and Philosophy for a New World Order” (The Island 26.11.2025) it may not be far-fetched to say that the cause of the devastating cyclones that hit Sri Lanka and Indonesia last week could be traced back to human greed. Cyclones of this magnitude are said to be unusual in the equatorial region but, according to experts, the raised sea surface temperatures created the conditions for their occurrence. This is directly due to global warming which is caused by excessive emission of Greenhouse gases due to burning of fossil fuels and other activities. These activities cannot be brought under control as the rich, greedy Western powers do not want to abide by the terms and conditions agreed upon at the Paris Agreement of 2015, as was seen at the COP30 meeting in Brazil recently. Is there hope for third world countries? This is why the Global South must develop a New World Order. For this purpose, the proposed contentment/sufficiency philosophy based on morals like dhana, seela, bhavana, may provide the necessary foundation.
Further, such a philosophy need not be parochial and isolationist. It may not be necessary to adopt systems that existed in the past that suited the times but develop a system that would be practical and also pragmatic in the context of the modern world.
It must be reiterated that without controlling the force of collective greed the present destructive socioeconomic system cannot be changed. Hence the need for a philosophy that incorporates the means of controlling greed. Dhana, seela, bhavana may suit Sri Lanka and most of the East which, as mentioned in my earlier letter, share a similar philosophical heritage. The rest of the world also may have to adopt a contentment / sufficiency philosophy with strong and effective tenets that suit their culture, to bring under control the evil of greed. If not, there is no hope for the existence of the world. Global warming will destroy it with cyclones, forest fires, droughts, floods, crop failure and famine.
Leading economists had commented on the damaging effect of greed on the economy while philosophers, ancient as well as modern, had spoken about its degenerating influence on the inborn human morals. Ancient philosophers like Plato, Aristotle, and Epicurus all spoke about greed, viewing it as a destructive force that hindered a good life. They believed greed was rooted in personal immorality and prevented individuals from achieving true happiness by focusing on endless material accumulation rather than the limited wealth needed for natural needs.
Jeffry Sachs argues that greed is a destructive force that undermines social and environmental well-being, citing it as a major driver of climate change and economic inequality, referencing the ideas of Adam Smith, John Maynard Keynes, etc. Joseph Stiglitz, a Nobel Laureate economist, has criticised neoliberal ideology in similar terms.
In my earlier letter, I have discussed how contentment / sufficiency philosophy could effectively transform the socioeconomic system to one that prioritises collective well-being and sufficiency over rampant consumerism and greed, potentially leading to more sustainable economic models.
Obviously, these changes cannot be brought about without a change of attitude, morals and commitment of the rulers and the government. This cannot be achieved without a mass movement; people must realise the need for change. Such a movement would need leadership. In this regard a critical responsibility lies with the educated middle class. It is they who must give leadership to the movement that would have the goal of getting rid of the evil of excessive greed. It is they who must educate the entire nation about the need for these changes.
The middle class would be the vanguard of change. It is the middle class that has the capacity to bring about change. It is the middle class that perform as a vibrant component of the society for political stability. It is the group which supplies political philosophy, ideology, movements, guidance and leaders for the rest of the society. The poor, who are the majority, need the political wisdom and leadership of the middle class.
Further, the middle class is the font of culture, creativity, literature, art and music. Thinkers, writers, artistes, musicians are fostered by the middle class. Cultural activity of the middle class could pervade down to the poor groups and have an effect on their cultural development as well. Similarly, education of a country depends on how educated the middle class is. It is the responsibility of the middle class to provide education to the poor people.
Most importantly, the morals of a society are imbued in the middle class and it is they who foster them. As morals are crucial in the battle against greed, the middle class assume greater credentials to spearhead the movement against greed and bring in sustainable development and growth. Contentment sufficiency philosophy, based on morals, would form the strong foundation necessary for achieving the goal of a new world order. Thus, it is seen that the middle class is eminently suitable to be the vehicle that could adopt and disseminate a contentment/ sufficiency philosophy and lead the movement against the evil neo-liberal system that is destroying the world.
The Global South, which comprises the majority of the world’s poor, may have to realise, before it is too late, that it is they who are the most vulnerable to climate change though they may not be the greatest offenders who cause it. Yet, if they are to survive, they must get together and help each other to achieve self-sufficiency in the essential needs, like food, energy and medicine. Trade must not be via exploitative and weaponised currency but by means of a barter system, based on purchase power parity (PPP). The union of these countries could be an expansion of organisations,like BRICS, ASEAN, SCO, AU, etc., which already have the trade and financial arrangements though in a rudimentary state but with great potential, if only they could sort out their bilateral issues and work towards a Global South which is neither rich nor poor but sufficient, contented and safe, a lesson to the Global North. China, India and South Africa must play the lead role in this venture. They would need the support of a strong philosophy that has the capacity to fight the evil of greed, for they cannot achieve these goals if fettered by greed. The proposed contentment / sufficient philosophy would form a strong philosophical foundation for the Global South, to unite, fight greed and develop a new world order which, above all, will make it safe for life.
by Prof. N. A. de S. Amaratunga
PHD, DSc, DLITT
Features
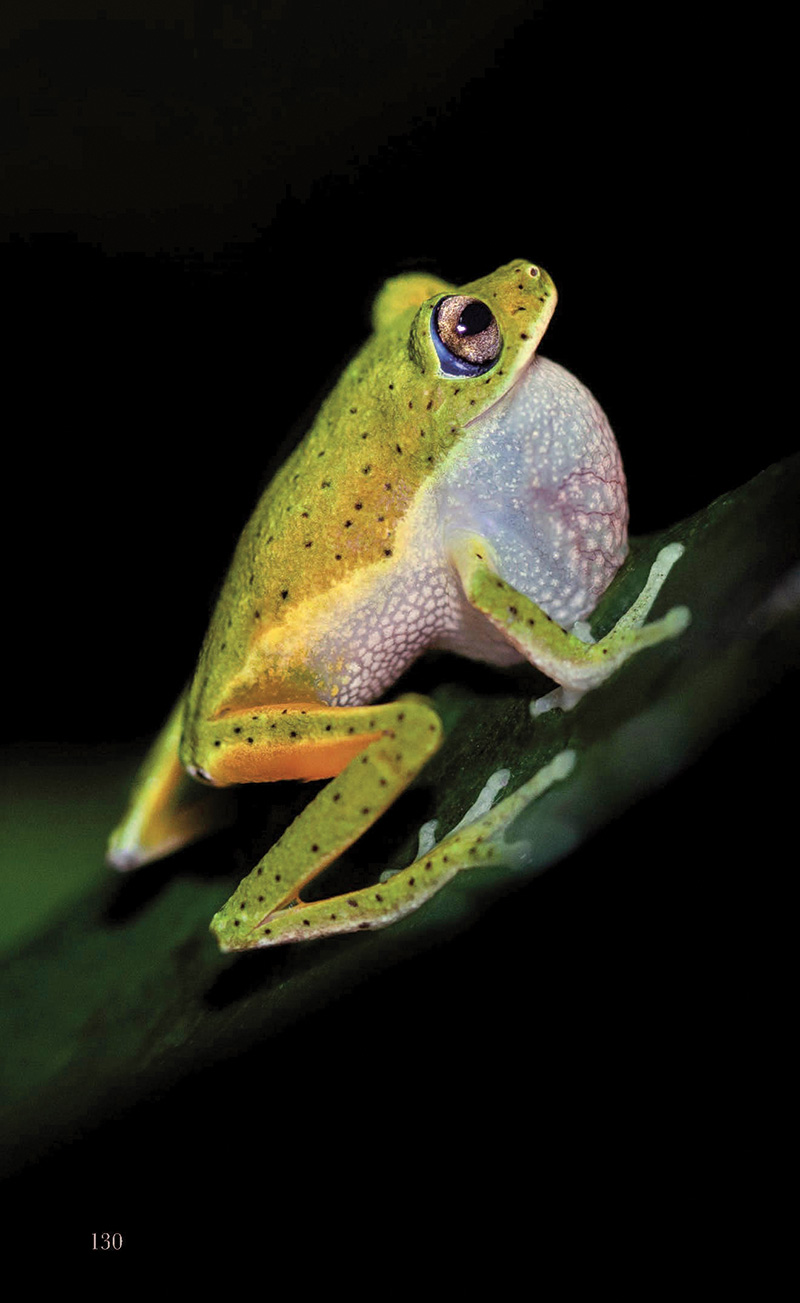
SINHARAJA: The Living Cathedral of Sri Lanka’s Rainforest Heritage

When Senior biodiversity scientist Vimukthi Weeratunga speaks of Sinharaja, his voice carries the weight of four decades spent beneath its dripping emerald canopy. To him, Sri Lanka’s last great rainforest is not merely a protected area—it is “a cathedral of life,” a sanctuary where evolution whispers through every leaf, stream and shadow.
“Sinharaja is the largest and most precious tropical rainforest we have,” Weeratunga said.
“Sixty to seventy percent of the plants and animals found here exist nowhere else on Earth. This forest is the heart of endemic biodiversity in Sri Lanka.”
A Magnet for the World’s Naturalists
Sinharaja’s allure lies not in charismatic megafauna but in the world of the small and extraordinary—tiny, jewel-toned frogs; iridescent butterflies; shy serpents; and canopy birds whose songs drift like threads of silver through the mist.
“You must walk slowly in Sinharaja,” Weeratunga smiled.
“Its beauty reveals itself only to those who are patient and observant.”
For global travellers fascinated by natural history, Sinharaja remains a top draw. Nearly 90% of nature-focused visitors to Sri Lanka place Sinharaja at the top of their itinerary, generating a deep economic pulse for surrounding communities.
A Forest Etched in History
Centuries before conservationists championed its cause, Sinharaja captured the imagination of explorers and scholars. British and Dutch botanists, venturing into the island’s interior from the 17th century onward, mapped streams, documented rare orchids, and penned some of the earliest scientific records of Sri Lanka’s natural heritage.
These chronicles now form the backbone of our understanding of the island’s unique ecology.
The Great Forest War: Saving Sinharaja
But Sinharaja nearly vanished.
In the 1970s, the government—guided by a timber-driven development mindset—greenlit a Canadian-assisted logging project. Forests around Sinharaja fell first; then, the chainsaws approached the ancient core.
“There was very little scientific data to counter the felling,” Weeratunga recalled.
- Poppie’s shrub frog
- Endemic Scimitar babblers
- Blue Magpie
“But people knew instinctively this was a national treasure.”
The public responded with one of the greatest environmental uprisings in Sri Lankan history. Conservation icons Thilo Hoffmann and Neluwe Gunananda Thera led a national movement. After seven tense years, the new government of 1977 halted the project.
What followed was a scientific renaissance. Leading researchers—including Prof. Savithri Gunathilake and Prof. Nimal Gunathilaka, Prof. Sarath Kottagama, and others—descended into the depths of Sinharaja, documenting every possible facet of its biodiversity.
“Those studies paved the way for Sinharaja to become Sri Lanka’s very first natural World Heritage Site,” Weeratunga noted proudly.
- Vimukthi
- Nadika
- Janaka
A Book Woven From 30 Years of Field Wisdom
For Weeratunga, Sinharaja is more than academic terrain—it is home. Since joining the Forest Department in 1985 as a young researcher, he has trekked, photographed, documented and celebrated its secrets.
Now, decades later, he joins Dr. Thilak Jayaratne, the late Dr. Janaka Gallangoda, and Nadika Hapuarachchi in producing, what he calls, the most comprehensive book ever written on Sinharaja.
“This will be the first major publication on Sinharaja since the early 1980s,” he said.
“It covers ecology, history, flora, fauna—and includes rare photographs taken over nearly 30 years.”
Some images were captured after weeks of waiting. Others after years—like the mysterious mass-flowering episodes where clusters of forest giants bloom in synchrony, or the delicate jewels of the understory: tiny jumping spiders, elusive amphibians, and canopy dwellers glimpsed only once in a lifetime.
The book even includes underwater photography from Sinharaja’s crystal-clear streams—worlds unseen by most visitors.
A Tribute to a Departed Friend
Halfway through the project, tragedy struck: co-author Dr. Janaka Gallangoda passed away.
“We stopped the project for a while,” Weeratunga said quietly.
“But Dr. Thilak Jayaratne reminded us that Janaka lived for this forest. So we completed the book in his memory. One of our authors now watches over Sinharaja from above.”
An Invitation to the Public
A special exhibition, showcasing highlights from the book, will be held on 13–14 December, 2025, in Colombo.
“We cannot show Sinharaja in one gallery,” he laughed.
“But we can show a single drop of its beauty—enough to spark curiosity.”
A Forest That Must Endure
What makes the book special, he emphasises, is its accessibility.
“We wrote it in simple, clear language—no heavy jargon—so that everyone can understand why Sinharaja is irreplaceable,” Weeratunga said.
“If people know its value, they will protect it.”
To him, Sinharaja is more than a rainforest.
It is Sri Lanka’s living heritage.
A sanctuary of evolution.
A sacred, breathing cathedral that must endure for generations to come.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
How Knuckles was sold out

Leaked RTI Files Reveal Conflicting Approvals, Missing Assessments, and Silent Officials
“This Was Not Mismanagement — It Was a Structured Failure”— CEJ’s Dilena Pathragoda
An investigation, backed by newly released Right to Information (RTI) files, exposes a troubling sequence of events in which multiple state agencies appear to have enabled — or quietly tolerated — unauthorised road construction inside the Knuckles Conservation Forest, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
At the centre of the unfolding scandal is a trail of contradictory letters, unexplained delays, unsigned inspection reports, and sudden reversals by key government offices.
“What these documents show is not confusion or oversight. It is a structured failure,” said Dilena Pathragoda, Executive Director of the Centre for Environmental Justice (CEJ), who has been analysing the leaked records.
“Officials knew the legal requirements. They ignored them. They knew the ecological risks. They dismissed them. The evidence points to a deliberate weakening of safeguards meant to protect one of Sri Lanka’s most fragile ecosystems.”
A Paper Trail of Contradictions
RTI disclosures obtained by activists reveal:
Approvals issued before mandatory field inspections were carried out
Three departments claiming they “did not authorise” the same section of the road
A suspiciously backdated letter clearing a segment already under construction
Internal memos flagging “missing evaluation data” that were never addressed
“No-objection” notes do not hold any legal weight for work inside protected areas, experts say.
One senior officer’s signature appears on two letters with opposing conclusions, sent just three weeks apart — a discrepancy that has raised serious questions within the conservation community.
“This is the kind of documentation that usually surfaces only after damage is done,” Pathragoda said. “It shows a chain of administrative behaviour designed to delay scrutiny until the bulldozers moved in.”
The Silence of the Agencies
Perhaps, more alarming is the behaviour of the regulatory bodies.
Multiple departments — including those legally mandated to halt unauthorised work — acknowledged concerns in internal exchanges but issued no public warnings, took no enforcement action, and allowed machinery to continue operating.
“That silence is the real red flag,” Pathragoda noted.
“Silence is rarely accidental in cases like this. Silence protects someone.”
On the Ground: Damage Already Visible
Independent field teams report:
Fresh erosion scars on steep slopes
Sediment-laden water in downstream streams
Disturbed buffer zones
Workers claiming that they were instructed to “complete the section quickly”
Satellite images from the past two months show accelerated clearing around the contested route.
Environmental experts warn that once the hydrology of the Knuckles slopes is altered, the consequences could be irreversible.
CEJ: “Name Every Official Involved”
CEJ is preparing a formal complaint demanding a multi-agency investigation.
Pathragoda insists that responsibility must be traced along the entire chain — from field officers to approving authorities.
“Every signature, every omission, every backdated approval must be examined,” she said.
“If laws were violated, then prosecutions must follow. Not warnings. Not transfers. Prosecutions.”
A Scandal Still Unfolding
More RTI documents are expected to come out next week, including internal audits and communication logs that could deepen the crisis for several agencies.
As the paper trail widens, one thing is increasingly clear: what happened in Knuckles is not an isolated act — it is an institutional failure, executed quietly, and revealed only because citizens insisted on answers.
by Ifham Nizam
-
News6 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 News19 hours ago
News19 hours agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
 News5 days ago
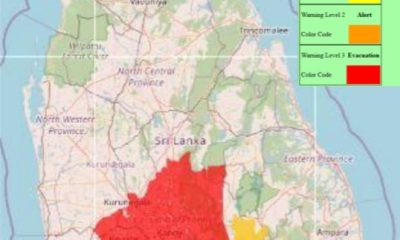
News5 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoDitwah: An unusual cyclone
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News19 hours ago
News19 hours agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale