Features
How Janasaviya was born and food distribution amid JVP terror

In 1988, a Cabinet decision landed on my table indicating that I was appointed as a member of a very senior group to be chaired by the Governor of the Central Bank, Dr. Warnasena Rasaputram to study and produce a report within one month on issues relating to poverty alleviation, with recommendations for ameliorating these conditions. We had about 15 meetings of intensive discussions held in the Central Bank. Practically all these discussions, took place after normal office hours often going into the night, and ending up with a quick dinner there.
These discussions were supplemented by special meetings over some week-ends. Since the deadline given to us was very tight, we had to read and assimilate a large amount of material, which we had to do at home, before coming for the next meeting. It was an intense and extremely busy period. The report was finalized just before the deadline expired.
Susil Sirivardana of the Sri Lanka Administrative Service who acted both as a member and as Secretary to the Committee, displayed extraordinary skills, knowledge, energy and commitment. It was largely due to him that the Committee finished its work in time. The report was discussed at a special Cabinet meeting convened to discuss it at which we were present, adopted, and published as a sessional paper. Later, this report formed the basis of Prime Minister Premadasa’s Janasaviya proposals.
He added the ingredients of a political programme to the recommendations of the Rasaputram Committee. After Mr. Premadasa’s victory in the Presidential elections of December 1988, his government was able to attract World Bank and German KFW. and UNDP. assistance for his poverty alleviation programme. I was once again put into a senior group to work with the World Bank teams in discussing and finalizing the programme. Here too, as is not uncommon in such circumstances, President Premadasa added his own strong political input into the final result by suitably modifying our recommendations.
The Janasaviya Programme was his programme and he gave his personal attention to all aspects of it. In due course when the Janasaviya Trust Fund was set up I found myself appointed as one of the Trustees, and when the Government changed in 1994, the President Mrs. Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga appointed me as Chairman of the Trust, which position I still hold at the date of this writing in the year 2000.
The programme was an innovative attempt to use the expertise of NGOS with a proven track record of working with the poor at grassroots level, in order to alleviate poverty through a multi-pronged programme of training and skills development; community works; credit and nutrition interventions. The government through the Trust channeled funds to these NGOs giving them a sufficient interest spread to finance their activities.
The programme itself has had mixed results. It had undoubtedly achieved much. But more could have been achieved if not for numerous impediments and weaknesses ranging over many aspects of it, including human short comings.
The JVP insurrection and food supplies
1988 was a bad year. In fact it was the beginning of a couple of bad years. The main reason for this was the second JVP insurrection which manifested itself during this period. This compounded the normal unstable conditions which occur during the tail end of a government. Even normally, such a period is one of trade union demands, political maneuvering, and vigorous opposition moves which puts a government on the defensive, which in turn leads it to panicky compromises and attempts to spread largesse. These are usually periods where fiscal responsibility goes out through the window and every strategy used to please the electorate. The JVP militancy which progressively became a serious attempt to take over the State through the use of violent means added seriously to government’s problems. At a certain point there was even doubt as to whether a Presidential election could be held in the prevailing climate of violence.
The general populace became so intimidated that practically the whole country shut down in obedience to the JVP demand to observe a hartal, or desist from work. These demands accompanied by threats were circulated through a system of chits that went from hand to hand. Word of mouth of a panicked population did the rest. Alarming rumours were rife. In addition several public servants, members of elected bodies, and others were being killed. There developed a general fear psychosis which paralyzed work and effort. Nobody knew whether they were on somebody’s hit list or not, and a period of time came when people were living for the day and hoping that the next day would not bring any serious problems.
The overall situation had a major impact on the food operation. The working of the ports, the stores and transport became affected. I have already recorded previously why the food operation had to go on smoothly and without impediment day in and day out, and the consequences of a break down in this flow. Now this problem was upon us in unexpected and random ways. On some days Storekeepers were threatened and told not to come to work. On other days lorry drivers were threatened. The railway had its own problems. So did the port. The multifarious activities connected with food supplies became therefore a major problem.
To compound this situation, political leaders were under serious threat. Mr. Sarathchandra Rajakaruna, who had been for long Deputy Minister of Food, was appointed Minister of Food in May 1988. He was also under threat. Elections were now looming and even with difficulty, legitimate political activity had to be carried out. Ministers and others therefore faced the hardship and danger of political campaigning whilst under severe personal threat. For these reasons, they did not often come to their Ministries.
A heavy load came on the shoulders of the Secretary and other officials. In addition to dealing with the normal problems of food supplies they had to constantly cope with disruptions and breakdowns, in a situation where they did not know whether carrying out their normal duties meant death. It would be idle to deny that we were not afraid. As things worsened, we were in very real fear. There was no question however of abandoning one’s post or neglecting one’s responsibilities. We steeled ourselves to do our duty, with the prospect of death ever present in our minds.
No one must think that this is an exaggeration. This was the reality we faced. The killing in broad daylight in the heart of Colombo of the lady Chairman of the State Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Engineers in the Port and others, constantly reminded us of what might lie in store for us. The climate of fear was so pervasive that it affected all of us. When I went home generally between 7.30 and 8 p.m. I used to close the sitting room windows, some times over the protests of my wife who complained that she had opened all the windows because it was so warm.
I did not wish to upset her by communicating my fears, and got away by giving some vague reply. This act of mine was perhaps not rational. What could closed windows do if some one came for you? It however created a degree of security psychologically. One clung to surface satisfactions such as closing windows. The worst thing was that one could not discuss one’s fears with anyone. You couldn’t do it at home, because you would have panicked the family. You couldn’t do it in office, because of the responsibility you had in a vital area of activity. If you appeared to have panicked, you would have communicated it to your officials, who were themselves in fear. In such circumstances, operations would have collapsed, for there were days when due to fear and intimidation the Treasury couldn’t open, or for that matter the Ministry of Public Administration.
We couldn’t afford to close under any circumstances. If food did not move that would have been the end. This psychological isolation was extremely stressful. It affected sleep. The mind was often over-active and could not easily be quieted. You became startled at sounds. To this day I think that I would have lost a couple of years of my life span, due to the tension and stress during this period.
In early 1989, after Mr. Premadasa’s victory in the Presidential elections, I had to work with Mr. Lalith Athulathmudali in a new expanded Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Cooperatives. Even then, we were still engaged in a continuing battle to keep the food lines open. During this period too, on two different occasions, Mr. Athulathmudali told me “Dharmasiri, I am worried about your security.” Having previously been Minister of National Security, he had wide access to officers of the police and the armed services and through this access picked up a great deal of information.
On one of the occasions, he was so concerned that he asked me whether I had any kind of weapon at home. “Three broomsticks and a couple of kitchen knives where a person is more likely to die of tetanus than stab wounds, if any cut was inflicted with them,” I replied lightly, although my blood ran cold. I had long decided to be philosophic and take what comes. Mr. Athulathmudali said “Never mind all that, can I come and see your place?”
This question certainly didn’t improve the temperature of my blood. It became still colder. I thanked him and said that I appreciated his concern and that he was welcome to come. He said “I will drop in some time.” This however posed another problem. If the Minister came home, he would have come with a procession of security vehicles and a significant number of personnel carrying automatic weapons. The whole neighbourhood would have been attracted to this spectacle and any JVP supporters around would have drawn all kinds of erroneous conclusions.
I did not mention any of this to Mr. Athulathmudali, but spoke to his Chief Security Officer, Superintendent of Police Mr. Muthu Banda. I told him of the Minister’s intentions and my reservations.
Mr. Muthu Banda agreed with me. I finally told him to bring the Minister along privately, if possible, in case he insisted on coming and to avoid at all costs, his coming in a motorcade. He promised to do what he could. In the end this event did not come to pass. A couple of days later, the Minister, to my great relief told me, “I have been checking on your matter further. There’s nothing to worry at the moment.”
This episode occurred in early 1989. But, as mentioned we were having serious problems in managing the food supply during the last quarter of 1988. Things were gradually building up, and by the last quarter, the JVP was seriously attempting to disrupt the Presidential election which was now falling due. Threats to officers in the Ports, the Railways, the Food Department, particularly to Store-keepers, and to private transport contractors increased both in frequency and intensity. We had to close down some stores temporarily, because the officers were so frightened. This threw a bigger load on other stores, and disrupted their smooth functioning.
By the time we opened the closed stores, threats had reached a peak to officers working in the other stores. Matters came to such a pass eventually, that the Army had to take Store-keepers and other store officials into their protective custody and force them to work, under the Emergency Regulations. But the security forces were also stretched. They were already fighting a battle in the North and East of the country against the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE.) Now they were confronted with a serious insurgency in the rest of the country.
Therefore, although they helped us to minimize some of our problems, they could not be everywhere. Disruption continued, with threats to lorry drivers and other categories. We had to improvise solutions as we went along, fight fires as and when they were lit, and also find the time in between to anticipate and head off possible problems yet to come. But the closer we got to the Presidential elections of
December 1988, greater was the intensity of disruption. By this time, most of my officers were getting increasingly ineffective due to overwork, strain and fear.
The numbers I could depend on, whatever the circumstances, dwindled. Fortunately, my Deputy Food Commissioner (Supplies), Mr. Rodrigo, was amongst these dwindling numbers. This was a key position in the whole chain of food supplies and a post I myself held in the mid 1960’s. Mr. Rodrigo acted with a high regard for public duty at great personal risk. His co-operation was both essential and invaluable.
(Excerpted from In Pursuit of Governance, autobigraphy of MDD Pieris) ✍️
Features
The middle-class money trap: Why looking rich keeps Sri Lankans poor

 Every January, we make grand resolutions about our finances. We promise ourselves we’ll save more, spend less, and finally get serious about investments. By March, most of these promises were abandoned, alongside our unused gym memberships.
Every January, we make grand resolutions about our finances. We promise ourselves we’ll save more, spend less, and finally get serious about investments. By March, most of these promises were abandoned, alongside our unused gym memberships.
The problem isn’t our intentions, it’s our approach. We treat financial management as a personality flaw that needs fixing, rather than a skill that needs the right strategy. This year let’s try something different. Let’s put actual behavioural science behind how we handle our rupees.
Based on the article ‘Seven proven, realistic ways to improve your finances in 2026’ published on 1news.co.nz, I aim to adapt these recommended financial strategies to the Sri Lankan context.” Here are seven money habits that work because they’re grounded in how humans actually behave, not how we wish we would.
While these strategies offer useful direction for strengthening personal financial management, it is important to acknowledge that they may not be suitable for everyone. Many households face severe financial pressure and cannot realistically follow traditional income allocation frameworks, such as the well-known but outdated Singalovada Sutta guidelines, when even meeting daily food expenses has become a struggle. For individuals and families who are burdened by escalating costs of essentials, including electricity, water, mobile connectivity, transport, and other non-negotiable commitments, strict adherence to prescriptive models is neither practical nor fair to expect. Therefore, readers should remain mindful of their own financial realities and adapt these strategies in ways that align with their income levels, essential obligations, and broader personal circumstances.
1. Your Money Problems Aren’t Moral Failures, They’re Data Points
When every rupee misspent becomes evidence of personal failure, we stop looking for solutions. Shame is a terrible problem-solver. It makes us hide from our bank statements, avoid difficult conversations, and repeat the same mistakes because we’re too embarrassed to examine them.
Instead, try replacing judgment with curiosity. Transform “I’m terrible with money” into “That’s interesting, why did I make that choice?” Suddenly, mistakes become information rather than indictments. You might notice you overspend at Odel or high-end restaurant when stressed about work. Or that you commit to expensive plans when feeling socially pressured. Perhaps your online shopping peaks during power cuts when you’re bored and frustrated.
2. Forget the Year-Long Marathon, Focus on 90-Day Sprints
A Sri Lankan year is densely packed with financial obligations: Sinhala/Tamil Avurudu, Christmas, Vesak, and Poson celebrations; recurring school fees; seasonal festival shopping; wedding and almsgiving periods; yearend festivities; and an evergrowing list of marketing-driven occasions such as Valentine’s Day, Father’s Day, Mother’s Day, and many others. Each of these events carries its own financial weight, often placing additional pressure on already-stretched household budgets.
Research consistently shows that shorter time frames work better. Ninety days is long enough to create a meaningful change, but short enough to maintain focus and momentum. So instead of one overwhelming annual goal, give yourself four quarterly upgrades.
In the first quarter, the focus may be on organising your contributions toward key duties and responsibilities, while also ensuring that you are maximising the available benefits for your designated beneficiaries. Quarter two could be about building a small emergency fund, even Rs. 10,000 provides breathing room. Quarter three might involve auditing your bills and subscriptions to eliminate unnecessary expenses. Quarter four could be when you finally start that investment you’ve been postponing. You don’t need superhuman discipline or complicated spreadsheets, just focused attention, one quarter at a time.
3. Make One Decision That Eliminates Weekly Worry
The best money decisions are the ones you make once but benefit from repeatedly. These are decisions that permanently reduce what behavioural economists call “decision fatigue”, the mental exhaustion that comes from constantly managing money in your head. What’s one choice you could make today that would remove a recurring financial worry?
It might be setting up an automatic standing order to transfer Rs. 10,000 to savings the day your salary arrives, before you can spend it. Maybe it’s consolidating your scattered savings accounts into one that actually pays decent return.
These aren’t dramatic moves that require personality transplants. They’re structural decisions that work with your human tendency toward inertia rather than against it. Most banks now offer seamless digital automation. You can set it up once and benefit from that decision every single month without additional effort or willpower. You make the decision once. You benefit all year. That’s leveraging your energy intelligently.
4. Stop Spending on Who You Think You Should Be
Sri Lankan society comes with heavy expectations. The car you drive, the school your children attend, the hotels you patronise, the brands you wear, all communicate your worth, or so we’re told. Much of our spending isn’t about actual enjoyment. It’s about meeting unspoken expectations, keeping up appearances, or aspiring to a version of us that doesn’t actually exist.
We buy expensive saris we’ll wear once because everyone does. We maintain memberships to clubs we rarely visit because it looks good. We say yes to weekend plans at overpriced restaurants because declining feels like admitting we can’t afford it. We upgrade phones not because ours stopped working, but because others have.
Before your next purchase, ask yourself: do I actually want this, or do I want to want it? If it’s the second one, walk away. You won’t miss it. This isn’t about deprivation, it’s about precision. When you stop spending to perform and start spending to support the life you genuinely enjoy, money pressure eases dramatically. Your resources align with your actual values rather than imagined expectations.
Maybe you don’t care about fancy restaurants, but you love long drives along the southern coast. Maybe branded clothing leaves you cold, but you’d spend any amount on art supplies or books. That’s fine. Spend accordingly.
5. Break One Habit, See If You Actually Miss It
We’re creatures of routine, which serves us well until those routines outlive their usefulness. Sometimes we spend money on habits that started for good reasons but no longer serve us. Alpechchathava, in Buddha’s teaching, means living contentedly with few desires. It guides a person to manage money wisely by avoiding excess spending, unnecessary debt, and craving, and by focusing on essential needs and wholesome priorities. In this way, wealth supports mental cultivation, generosity, and spiritual progress.
The daily kottu roti that once felt like a convenient solution after working late may now have turned into an unnecessary routine. Similarly, frequent P&S or Caravan snack runs, and the habit of picking up sugary treats like cakes and sweets, are not only costly but also wellknown to be unhealthy, as nutritionists consistently point out. Beyond food, other expenses such as magazine subscriptions, the monthly coffee meetup, or weekend mall browsing often continue on autopilot without us realising how much they add up. These seemingly small, habitual expenses can quietly drain your budget while offering very little longterm value.
Try this experiment: keep a money diary for one week. Note every expense, no matter how small. Then identify one regular spend and eliminate it for the following week. If you don’t miss it? Excellent, keep it gone. If you genuinely miss it? Add it back without guilt. This isn’t about permanent sacrifice.
It’s about snapping yourself out of autopilot and checking whether your spending still reflects your current reality, priorities and purchasing power. You might discover you’re spending Rs. 15,000 monthly on things you barely notice.
6. Create Your Crisis Playbook on a Good Day
Many financial disasters don’t happen because we’re careless, they happen because we’re panicked. When crisis strikes, job loss, medical emergency, unexpected business downturn, fear hijacks our decision-making. Our rational brain exists while panic makes expensive choices: high-interest personal loans, selling investments at losses, making commitments we can’t sustain.
The solution? Make your crisis plan before the crisis arrives. On a calm day, sit down and document: If I lost my income tomorrow, what would I do first? Which expenses are truly essential? What’s the absolute minimum I need to function? Who could I call for advice? Which savings are untouchable, which could be accessed if necessary? What government support or loan restructuring options exist (Not in Sri Lanka)? This is a sort of preparation for sudden shocks.
7. Question the Money Stories You Inherited
Sometimes our biggest financial obstacles aren’t failed attempts, they’re the attempts we never make because we’ve internalised limiting stories. “Our family was never good with money.” “Investing is for rich people.” “I’m just not the type who earns more.” “Women don’t understand finance.” These narratives, absorbed from family, culture, or past experiences, become invisible fences.
Question them. Where did this belief originate? Is it actually true, or is it a story you’ve been telling yourself for so long, it feels like fact? What would happen if you tested it? Often, these stories protect us from the discomfort of trying and potentially failing. But they also protect us from the possibility of succeeding. And that’s a far costlier protection than most of us realise.
The Bottom Line
Improving your finances in 2026 doesn’t require becoming a different person. It requires understanding the person you already are, your patterns, triggers, and tendencies, and working with them rather than against them.
These aren’t magic solutions. They’re evidence-based approaches that acknowledge a simple truth: you’re not broken, and your money management doesn’t need fixing through willpower alone. It needs better systems, clearer thinking, and a lot less shame.
Features
Public scepticism regarding paediatric preventive interventions
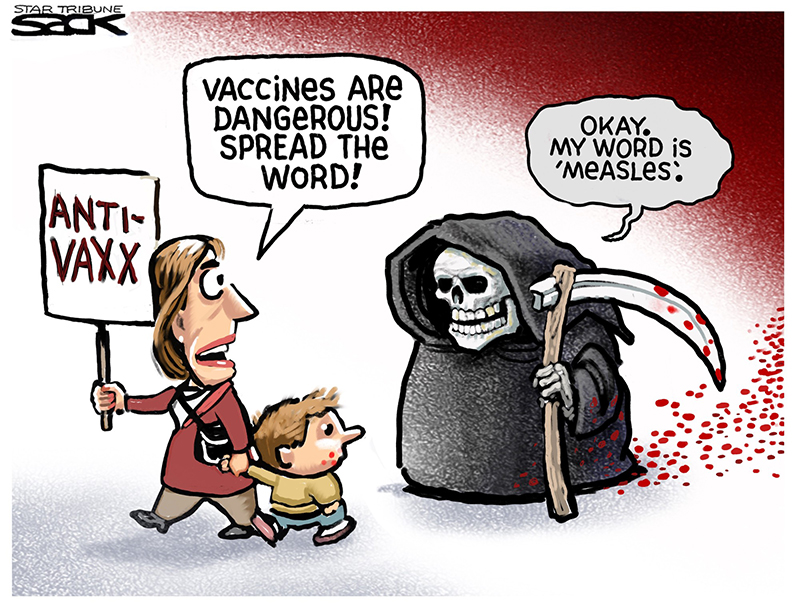
A significant portion of the history of paediatrics is a triumph of prevention. From the simple act of washing hands to the miracle of vaccines, preventive strategies have been the unsung heroes, drastically lowering child mortality rates and setting the stage for healthier, longer lives across the globe. Simple measures like promoting personal hygiene, ensuring the proper use of toilets, and providing Vitamin K immediately after birth to prevent dangerous bleeding, have profound impacts. Advanced interventions like inhalers for asthma, robust trauma care systems, and even cutting-edge genetic manipulations are testament to the relentless and wonderful progress of paediatric science.
A shining beacon that has signified increased survival and marked reductions in mortality across the board in all paediatric age groups has been the development of various preventive strategies in the science of children’s health, from newborns to adolescents. The institution of such proven measures across the globe, has resulted in gains that are almost too good to be true. From a Sri Lankan perspective, these measures have contributed towards the unbelievable reduction of the under-5-year mortality rate from over 100 per 1000 live births in the 1960s to the seminal single-digit figure of 07 per 1000 live births in the 2020s.
Yet for all this, despite the overwhelming evidence of success, a most worrying trend is emerging. That is public scepticism and pessimism regarding these vital interventions. This doubt is not a benign phenomenon; it poses a real danger to the health of our children. At the heart of this challenge lies the potent, often insidious, spread of misinformation and disinformation.
The success of any preventive health strategy in paediatrics rests not just on its scientific efficacy, but on parental cooperation and commitment. When parents hesitate or refuse to follow recommended guidelines, the shield of prevention is compromised. Today, the most potent threat to this partnership is the flood of false information.
Misinformation is false information spread unintentionally. A well-meaning friend sharing a rumour about a vaccine side-effect they heard online is spreading misinformation.
Disinformation is false information deliberately created and disseminated to cause harm or sow doubt. This often comes from organised groups or individuals with vested interests; sometimes financial, sometimes ideological, who seek to undermine public trust in medical institutions and scientific consensus.
The digital age, particularly social media, has become the prime breeding ground for these falsehoods. Complex scientific data is reduced to emotionally charged, simplistic, and often sensationalist soundbites that travel faster and farther than the truth.
The most visible battleground is childhood vaccination. Decades of robust, high-quality research have confirmed vaccines as one of the most cost-effective and successful public health interventions ever conceived. Global vaccination efforts have saved an estimated 150 million lives in the past 50 years, eradicating or drastically controlling diseases like polio, measles, diphtheria, and tetanus.
However, a single, long-retracted, and scientifically debunked paper claiming a link between the Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR) vaccine and autism continues to be weaponised by disinformation campaigns. This persistent myth, despite being soundly disproven, taps into deep-seated fears about children’s development. Other common vaccine myths target ingredients such as trace amounts of aluminium or mercury, which are harmless in the quantities used and often less than what is naturally found in food or the idea that “natural immunity” from infection is superior, totally ignoring the fact that natural infection carries the devastating risk of severe complications, long-term disability, and even death. The tangible consequence of this doubt is the dropping of childhood vaccination rates in various communities, leading to the wholly unnecessary re-emergence of vaccine-preventable diseases like measles.
Scepticism is not limited to vaccines. It can touch any area of paediatric preventive care where an intervention might seem unnecessary, invasive, or have perceived risks. Routine screenings for speech disorders, motor skills, or mental health issues can sometimes be perceived as medicalising normal childhood variations or putting a “label” on a child. Parents may resist or delay screening, missing the critical window for early intervention of proven measures that are likely to help. Advice on managing childhood obesity, reducing screen time, or adopting a balanced diet can be viewed by some parents as intrusive or judgmental, leading to poor adherence to essential health-promoting behaviours.
The regular use of inhalers for asthma or other chronic conditions might be looked down upon due to the fear of “dependency”, “addiction”, or long-term side effects, despite medical consensus that these preventive measures keep conditions controlled and prevent life-threatening exacerbations.
The common thread is a lack of understanding of the risk-benefit ratio. Parents, bombarded by fear-mongering narratives, often overestimate the rare, mild risks of an intervention while catastrophically underestimating the severe and permanent risks of the disease or condition itself.
The power of paediatric preventive medicine is not in a single shot or pill, but in the consistent, committed partnership between healthcare providers and parents. Paediatric science, driven by rigorous evidence-based medicine, do continue to refine guidelines, conduct transparent research, and communicate its findings clearly. When guidelines are confusing or lack robust evidence, it naturally creates openings for doubt. The scientific community’s commitment to continuous quality improvement and accessibility is paramount.
Ultimately, the success of prevention rests with the parents. Parenting, as a vital form of preventive care, includes all activities that raise happy, healthy, and capable children. The simple, non-medical steps mentioned in the introduction, proper handwashing, good sanitation, and encouraging exercise, are all forms of parental preventive intervention.
For more complex interventions, parental commitment requires several actions. They need to seek and trust the guidance provided by qualified healthcare professionals over anonymous, unsubstantiated online claims. They need to engage in an open dialogue by asking relevant questions and expressing concerns to doctors in an open, non-confrontational manner. A good healthcare provider will use this as an opportunity to educate and build trust, and not a portal to simply dismiss concerns. Then, of course, there is the spectre of adherence to various protocols and actions by the parents. These include consistently following recommended schedules, whether for well-child checkups, vaccinations, or daily medication protocols.
Addressing public scepticism requires a multi-pronged, collaborative strategy. It is not just about correcting false facts (debunking), but about building resilience against future falsehoods (prebunking). The single most influential voice in a parent’s decision-making process is their paediatrician or primary care provider. Clinicians must move beyond simply reciting facts. They need to use empathetic communication techniques, like Motivational Interviewing (MI), which focuses on active listening, validating parental concerns, and then collaboratively guiding them toward evidence-based decisions. For example, responding with, “I hear you’re worried about the side-effects you read about. Can I share what we know from decades of safety monitoring?” Being open about common, minor side effects such as a short-lasting fever after a vaccine pre-empts the shock and distrust that occurs when an expected, yet unmentioned, reaction happens.
Public health campaigns must go on the offensive, not just a defensive fact-checking spree. Teaching the general public how disinformation works, the use of “fake experts”, selective cherry-picked data, and conspiracy theories all add up to a most powerful form of inoculation (prebunking) against future exposure. Health institutions must simplify their communications and make verified, high-quality information easily accessible on platforms where parents are already looking.
Parents often trust their peers as much as their doctors. Engaging local community leaders, faith leaders, and even trusted social media influencers to share accurate, positive messages about paediatric health can shift the public narrative at a grassroots level. While protecting privacy, sharing aggregate data and stories about the dramatic decline in childhood diseases thanks to prevention can re-emphasise the collective good.
The battle against child mortality and morbidity has been one of the great human achievements, a testament to scientific ingenuity and collective effort. Today, the greatest threat to maintaining these gains is not a new virus, but a breakdown of trust fuelled by unchecked falsehoods.
Paediatric preventive interventions, from a cake of soap and a proper toilet to the most sophisticated genetic therapies, are the foundation of a healthy future for every child. To secure this future, the scientific community must remain transparent, the healthcare system must lead with empathy, and the public must commit to informed, critical thinking. By rejecting the noise of disinformation and embracing the clear, evidence-based consensus of science, we can ensure that every child continues to benefit from the life-saving progress that defines modern paediatrics. The well-being of the next generation demands nothing less than this renewed commitment.
Little children are not in a position to make abiding decisions regarding their health, especially regarding preventive strategies in health. It is ultimately the crucial decisions made by responsible parents regarding the health of their children that really matter. As doctors, our commitment is never to leave any child behind.
by Dr B. J. C. Perera ✍️
MBBS(Cey), DCH(Cey), DCH(Eng), MD(Paediatrics), MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin), FRCP(Lond), FRCPCH(UK), FSLCPaed, FCCP, Hony. FRCPCH(UK), Hony. FCGP(SL)
Specialist Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Fellow, Postgraduate Institute of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka.
Joint Editor, Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health
Section Editor, Ceylon Medical Journal
Features
Attacks on PM vulgar, misogynistic; education reforms welcome

We express our profound concern and deep outrage at the vulgar, misogynistic, and defamatory attacks being directed at the Prime Minister and Minister of Education, Dr. Harini Amarasuriya.
Dr. Harini Amarasuriya is not merely a political leader; she is a scholar, public intellectual, and lifelong advocate of social justice, equality, and education. Attempts to discredit her through personal abuse rather than reasoned policy debate are not only an insult to her, but an assault on democratic values, women’s leadership, and intellectual integrity in public life.
Such attacks are unjust and unethical, and they corrode democratic discourse. We are deeply disappointed that certain political actors and their supporters continue to rely on misinformation, prejudice, and emotional manipulation, instead of engaging in rational, evidence-based, and constructive debate.
Sri Lanka has already paid a heavy price for decades of politics rooted in fear, communal division, and sentiment-driven populism. The country’s economic collapse and social breakdown are the direct consequences of these failed approaches. The people decisively rejected this style of politics through the Aragalaya, signaling a clear demand for change. Sri Lanka now stands at a historic turning point. After decades of corruption, ethnic manipulation, and policy paralysis, the people have given a clear mandate for systemic reform.
At this critical moment, Sri Lanka urgently needs structural reforms, particularly in education, which is the foundation of long-term national development, social mobility, and global competitiveness. Yet we observe that the very forces responsible for the country’s decline are once again attempting to block or derail reforms by exploiting religious, cultural, and emotional narratives.
We strongly affirm that no nation can be rebuilt through hatred, fear, or division. Education reform is not a political threat; it is a national necessity. Efforts to undermine reform through personal attacks and manufactured controversies serve only those who seek to return to power by keeping the country weak, divided, and intellectually impoverished.
Those who now attack Dr. Harini Amarasuriya are not defending culture or morality. They are defending privilege and political survival. Having failed the country for over seventy-five years through communalism, patronage, and anti-intellectualism, they now fear that an educated, critical, and empowered generation will render their outdated politics irrelevant.
This is why they target:
=a woman,
=an academic,
=and a reformer.
We therefore state clearly that we:
1. Condemn all forms of character assassination, gender-based attacks, and hate propaganda against the Prime Minister and Minister of Education.
2. Affirm our full support for Dr. Harini Amarasuriya’s leadership in advancing Sri Lanka’s education reforms.
3. Urge the government to proceed firmly and without retreat in implementing the proposed education reforms, in line with national policy and the public mandate.
4. Call upon academics, professionals, teachers, parents, and citizens to stand together against reactionary forces that seek to sabotage reform through fear mongering and disinformation.
A country cannot be rebuilt by those who destroyed it. A future cannot be created by those who fear education reforms.
Sri Lanka’s future must not be sacrificed for the ambitions of a few.Sri Lanka must move forward — with knowledge, dignity, and courage.
Signatories:
1. Markandu Thiruvathavooran, Attorney at law
2. S. Arivalzahan, University of Jaffna
3. Dr S.Ramesh, University of Jaffna
4. Dr. Mariadas Alfred, Former Dean, University of Peradeniya
5. Prof B.Nimalathasan, Senior Professor, University of Jaffna
6. S. Srivakeesan, Station Master, SriLankan Railways
7. A. T. Aravinthan, Branch Manager, Commercial Bank
8. Dr. S. Niththiyaruban, Paediatrician, Teaching Hospital, Jaffna
9. Dr. S. Selvaganesh, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeon, Teaching Hospital, Jaffna
10. Dr. S. Mathievaanan, Consultant Surgeon, Teaching Hospital, Jaffna
11. Prof. P. Iyngaran, University of Jaffna
12. Eng. M. Sooriasegaram, President, Education Development Consortium
13. Dr. S. Raviraj, Senior Consultant Surgeon, Former Dean, Faculty of Medicine, University, Jaffna.
14. Mr. Saminadan Wimal, University of Jaffna
15. Dr. A. Antonyrajan, University of Jaffna
16. P. Regno, Attorney at Law
17. Prof. J. Prince Jeyadevan, University of Jaffna
18. Prof. S. Muhunthan, University of Jaffna
19. Prof. R. Kapilan, University of Jaffna
20. Dr. S. Jeevasuthan, University of Jaffna
21. J.S. Thevaruban, University of Jaffna
22. S. Balaputhiran, University of Jaffna
23. Dr. N. Sivapalan, Retired Senior lecturer, University of Jaffna
24. I. P. Dhanushiyan, University of Jaffna
25. Dr. K. Thabotharan, University of Jaffna
26. Dr. Bahirathy J. Rasanen, University of Jaffna
27. Perinpanayagam Ronibus, Vice Secretary, Change Charitable Trust, Jaffna
28. Dr. S. Maheswaran, University of Peradeniya
29. Mr. S. Laleesan, Principal, Kopay Teachers’ College
30. Victor Antany, Teacher, Kilinochchi
31. K. Shanthakumar, Principal, Technical College, Vavuniya
32. S. Thirikaran, Principal, J/ Puttur Srisomaskanda College
33. Dr. T. Vannarajan, Advanced Technical Institute, Jaffna.
34. X. Don Bosco, Resource person, Piliyandala Educational Zone
35. K. Ravikumar, Regional Manager, Powerhands Pvt Ltd
36. Sathiyapriya Jeyaseelan, DO, Economist
37. A. Kalaichelvan, Chief Accountant, Animal Productive & Health
38. C. Vathanakumar, Retired Project Director
39. P. Kirupakaran, Department of Buildings (NP)
40. A. Antony Pilinton, David Peris Company, Jaffna
41. A. Muralietharan, Social Activist
42. Sinthuja Sritharan, Independent Researcher
43. T. Sritharan, Social Activist
44. Ms. Gnasakthi Sritharan, Social Activist
45. P. Thevatharsan, Management Service Officer
46. . S. Mohan, Social Activist
47. K. Jeyakumaran, Social Activist
48. Dr. N. Nithianandan, Chairman, Ratnam Foundation
49. George Antony Cristy, Social Activist
50. S. Thangarasa, Social Activist
51. N. Bhavan, Retd. Deputy Principal, Mahajana College
52. P. Muthulingam, Executive Director, Institute of Social Development, Kandy
53. M.K. Sivarajah, Social Activist
54. Mr. V. Sivalingam, Human Rights Activist
55. S. Jeyaganeshan, Samuthi Development Officer
-

 Editorial4 days ago
Editorial4 days agoIllusory rule of law
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoUNDP’s assessment confirms widespread economic fallout from Cyclone Ditwah
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoKoaloo.Fi and Stredge forge strategic partnership to offer businesses sustainable supply chain solutions
-

 Editorial5 days ago
Editorial5 days agoCrime and cops
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoDaydreams on a winter’s day
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoThe Chakka Clash
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoSurprise move of both the Minister and myself from Agriculture to Education
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoExtended mind thesis:A Buddhist perspective













