Features
From Pettah to Cotta

By Uditha Devapriya
Historically, the city of Colombo always faced a conflict, or contradiction, between an almost endless set of high-rise buildings and largely poorly constructed streets. As far back as 1907, for instance, it was observed that “large improvements would have to be carried out in the direction of widening such streets, while legislation by the Municipal Council should be enacted to “fix the line of streets and prevent encroachment thereon”, which would have saved money spent on buying buildings, “the erection of which ought never have been allowed.” The gap between the affluent and depressed wards not surprisingly became a cause for worry: the “native wards” were all “deficient”, with the exception of the European and chief residential quarters, which appeared “well provided.”.
There was, of course, a Colombo that existed before all this. The Rajavaliya referred to it as “Kalan Thota” or “Kelani Ferry.” Emerson Tennent has noted that the Moors, who took over the coast and harbour in the 12th and 13th centuries, renamed it as “Kalambu” or “a good harbour.” It gained prominence gradually thereafter: Ibn Batuta would describe it as “the finest town in Serendib.” The town remained under the control of a Muslim Vizier named Jalestie. Tennent observed that this was because the Sinhalese were uninterested in trade, which is somewhat true: as K. M. de Silva notes in A History of Sri Lanka, the principal source of royal income in Kotte was not trade, but rather land revenue.
Kotte would, of course, bear witness to two wars of succession, both compounded by Portuguese presence in the island. The latter were concerned with two priorities: gaining a monopoly over the cinnamon trade, and establishing commerce in Colombo.
According to de Silva, the first objective was generally considered less important than the first, but it nevertheless was crucial for the ambitious imperialists to gain control over the area; to this end they established an unfortified fort in Colombo for trading purposes. It is with the advent of the Portuguese, moreover, that Kalambu became Colombo: a name that more or less “approached that of Columbus”. But it was more than a change of name: as the Census of 1946 notes, under the Portuguese the city transformed from “a small stockade of wood” to “a gallant city fortified with a dozen bastions.”
But the Portuguese and the Dutch after them had to contend with two seemingly never-ending conflicts in the country: between the Kotte Kingdom and colonial authorities on the one hand and the Kotte Kingdom and pretenders from Sitawaka and Kandy on the other. The wars of succession weakened Kotte, and the Sinhalese monarchs, whose interest in trade depleted, in effect handed over commercial matters to colonial authorities. Despite this, however, authorities were never able to expand the city beyond Pettah, “between the lake at one side and the rocks, which form the harbour, on the other.” It was left to British officials to develop Colombo into more than just a military enclave.
To begin with, the British made use of what the Portuguese and the Dutch had left behind. The former especially had turned Colombo into a fortress. After the conquest of Kandy in 1815, the British began tapping into the region’s commercial potential in a way their predecessors had not. Once again it was the port which facilitated this shift in policy; by 1907 it had become “one of the principal ports of call of the world”, and was described as “the Clapham Junction of the East.” The British added a railway system to the shipping line; here too Colombo became the centre. Over the years the Fort area changed: it became a hub for government establishments, banking houses, and European businesses.
Interestingly, despite its veneer of sophistication and grace, British officials were not impressed with the new capital. “Colombo presents little to attract a stranger,” noted Tennent in 1859, and he had much to complain about: “the prevalence of damp”, “the nightly serenade of frogs”, and worst of all, “the tormenting profusion of mosquitoes” which had lead to outbreaks of dengue that had never visited the better developed areas of the municipality. Through all this, incidentally, a gap emerged between the centre and the periphery, in effect between the affluent and the indigent wards.
At first it was the areas developed by the Portuguese and Dutch which became hotspots for the colonial officials and the native elite. The area from Fort to Hulftsdorp, which James Cordiner had once described as “a more comfortable residence for a garrison than any other military station in India”, would in 40 years turn into what Prince Alexey Saltykov described as “a botanical garden on a gigantic scale.” This was facilitated by several factors: the breakdown of the old order, the shift from the interior to the littoral, and the emergence of a plantation economy. Moreover, Prince Saltykov made his remark about Colombo at a time when the old elite was yielding place to a new bourgeoisie.
The transition from a mercantilist to a semi-feudal economy in the first half of the 19th century was accompanied by the rise of a new colonial bourgeoisie. While the traditional elite had depended on the patronage of the British officials in terms of land bequests and perpetuation of familial dynasties (which led to the concentration of power within the Bandaranaike-Obeyesekere clique), the bourgeoisie took advantage of favourable economic conditions and prospered through capitalist-rentier enterprises.

Arrack renting became the main avenue of growth for the nouveau riche; by 1876 the annual rents from this trade amounted to £ 218,600 (£ 28,035,560 or Rs. 12,093,260,379 when adjusted for inflation). Profits from the arrack trade, however, were never invested in productive enterprises (as they were in other colonies) and were instead invested in coffee, coconut, graphite, and plumbago on the one hand and items of conspicuous consumption which helped distinguish them from the rest of the country on the other. Property in this regard was seen as paramount; it had a say in how the “posh neighbourhoods” shifted from Pettah, Hulftsdorp, and Maradana to Cotta, Colpetty, and Cinnamon Gardens.
Initially, the elite purchased land in the Pettah-Maradana-Kotahena-Mutwal area. Even in the last few decades of the century these places were at the forefront of British colonial activity in terms of commerce and education: all the major credit institutions were in the Pettah, while the two biggest schools in the country (one public, the other private) were established there: the Colombo Academy in Hill Street (the first batch of which consisted of 21 students from elite Burgher families within the neighbourhood, among them Richard Morgan, Charles Loos, and Christoffel de Saram) in 1836, and S. Thomas’ College in Mutwal 17 years later. This is certainly not to forget the Medical College and the Law College, built respectively in 1870 and 1874.
These trends were reflected in the lands purchased and palatial residences built during the period: Solomon Dias Bandaranaike, S. C. Obeyesekere, and G. G. Ponnambalam all built their manors in Hulftsdorp. Vinod Moonesinghe contends that long before Cinnamon Gardens became a plush neighbourhood, “the prime residential areas were Mutwal (for Europeans) and Kotahena (for locals), plus Grandpass for ‘country homes’.”
According to Moonesinghe, land values in Cinnamon Gardens rose after the Race Course moved from Galle Face, and the “process of gentrification” in the area culminated when Royal College shifted to its current location in 1912. But even then, this process was not fully complete: as Denham notes in Ceylon at the Census of 1911, while land in Cinnamon Gardens fetched Rs. 5,000 per acre, land near the Slave Island, Maradana, and Pettah stations fetched more than four times that amount. In other words, it would take another 30 years for the shift from one part of Colombo to another to complete.
The writer is an international relations analyst, researcher, and columnist who can be reached at udakdev1@gmail.com
Features
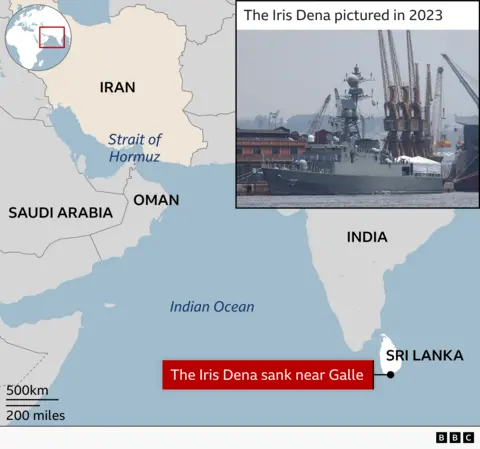
The final voyage of the Iranian warship sunk by the US
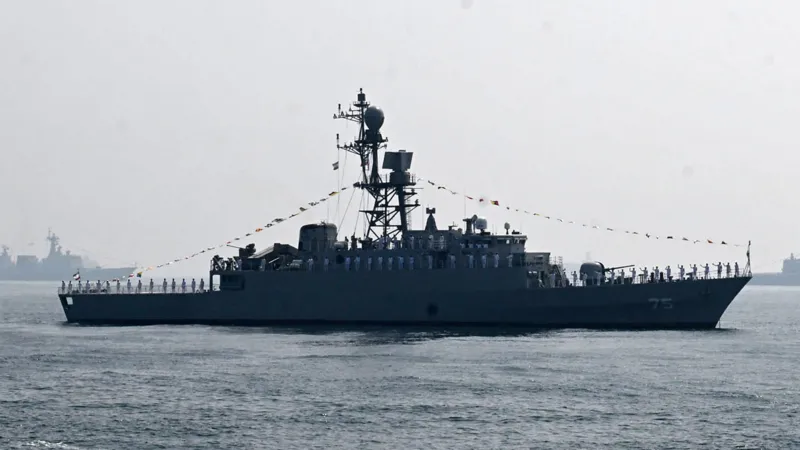

On 17 February, the Indian Navy posted a cheerful message on X.
“Welcome!” it wrote, greeting the Iranian warship Iris Dena as it steamed into the port of Visakhapatnam to join an international naval gathering.
Photographs showed sailors in crisp whites and a grey frigate gliding in the sea harbour on a clear day. The hashtags spoke of “Bridges of Friendship” and “United Through Oceans”.
Two weeks later the ship, carrying 130 sailors, lay at the bottom of the Indian Ocean. It had been torpedoed by a US submarine off Sri Lanka’s southern coast on 4 March.
Commissioned in 2021, the Dena was a relatively new vessel – a Moudge-class frigate of Iran’s Southern Fleet, which patrols the Strait of Hormuz and the Gulf of Oman.
According to US Defence Secretary Pete Hegseth, the vessel “thought it was safe in international waters” but instead “died a quiet death”. Rescue teams from Sri Lanka have recovered at least 87 bodies. Only 32 sailors survived.
The sinking marks a dramatic widening of the war between America, Israel and Iran. And, though it occurred in international waters of the Indian Ocean and outside India’s jurisdiction, it is an awkward moment for Delhi.
“The war has come to our doorsteps. That is not a good thing,” says retired Vice Admiral Arun Kumar Singh.
For some strategists, the episode carries broader implications for India’s regional standing.
Indian strategic affairs expert Brahma Chellaney wrote on X that the US torpedoing of the Iranian warship in India’s “maritime neighbourhood” was “more than a battlefield episode” – calling it a “strategic embarrassment” for Delhi.
“By sinking a vessel returning from an Indian-hosted multilateral exercise, Washington effectively turned India’s maritime neighbourhood into a war zone, raising uncomfortable questions about India’s authority in its own backyard,” Chellaney wrote.
Just days before its destruction, the Dena had been a diplomatic guest of the Indian Navy.
The ship had travelled to Visakhapatnam, a sun-washed port city on India’s east coast, to participate in the International Fleet Review 2026 and Exercise Milan, a large multilateral naval exercise meant to showcase India’s growing maritime leadership.
Seventy-four countries and 18 warships took part in the events, which Delhi described as a demonstration of its ambition to become the Indian Ocean’s “preferedsecurity partner”.
Visiting ships at such multilateral exercises usually do not carry a full combat load of live munitions, unless scheduled for a live-fire drill, according to Chellaney. Even during the sea phase, when drills and live firing take place, ships carry only tightly controlled ammunition limited to the specific exercises.
Singh, an invitee to the event, recalls seeing the warship and its Iranian sailors in Visakhapatnam just days before its fate changed.
“I saw the boys marching in front of me,” he says of the Iranian naval contingent during the parade along the seafront, just 10m away. “All young people. I feel very sad.”
He says on 21 February, the assembled ships – including the Iranian vessel – sailed out for the sea phase of Exercise Milan, scheduled to run until 25 February.
“What happened next is less clear: the ship may have returned to port or peeled away after exercises. Either way, the waters where it was later sunk – off Galle in Sri Lanka – lie only two to three days’ sailing from India’s east coast,” Singh says. What the ship was doing in the 10-12 days in between is not clear.
Singh, who has commanded submarines, believes the sequence leading up to the attack was probably straightforward.
The US, he notes, tracks vessels across the world’s oceans. “They would have known exactly when the ship left and where it was heading,” he says. A fourth of America’s submarine fleet of 65-70 is at sea at any given time, according to analysts.
According to the Indian Navy, the Iranian warship had been operating about 20 nautical miles west of Galle – roughly 23 miles (37km) – in waters that fall under Sri Lanka’s designated search-and-rescue zone.
The attack, Singh says, appears to have involved a single Mark-48 torpedo, a heavyweight weapon carrying about 650 pounds of high explosive, capable of snapping a ship in two. Video footage suggests the submarine may have fired from 3-4km away, around 05:30 local time.
The aftermath was grim and swift.
The warship reportedly sank within two to three minutes, leaving little time for rescue. “It’s a miracle they managed to send an SOS,” Singh says, which was picked up by the Sri Lanka Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre in Colombo.
According to the Indian Navy, a distress call from the Iranian warship was picked up by Colombo in the early hours of 4 March, triggering a regional search-and-rescue effort.
The navy said in a statement that Sri Lanka’s navy began rescue operations first, while India moved to assist later.
The Indian Navy deployed a long-range maritime patrol aircraft to support the search and kept another aircraft with air-droppable life rafts on standby.
A naval vessel already operating nearby reached the area by late afternoon. Another ship, which sailed from the southern Indian port city of Kochi to join the effort, continues to comb the waters for survivors and debris.

Under the Second Geneva Convention, countries at war are required to take “all possible measures” to rescue wounded or shipwrecked sailors after a naval attack. In practice, however, this duty applies only if a rescue can be attempted without putting the attacking vessel in serious danger.
Singh says submarines are rarely able to help.
“Submarines don’t surface,” he says. “If you surface and give up your position, someone else can sink you.”
Singh suspects the speed of the sinking – and possibly sparse shipping in the area at the time – meant few nearby vessels could respond. “A ship breaking up that fast leaves almost no chance,” he says.
In a shooting war, Singh says, the legal position is blunt.
Fighting between the United States and Iran had been under way since 28 February, with claims that 17 Iranian naval vessels had already been destroyed.
“When a shooting war is on, any ship of a belligerent country becomes fair game,” he says.
Many questions remain. Why was the Iranian warship still in waters near Sri Lanka nearly two weeks after leaving India’s naval exercise? Was it heading home, or on another mission? And how long had the US submarine been tracking it before firing?
For Delhi, the episode is diplomatically awkward.
India has drawn closer to Washington on defence while maintaining long-standing political and economic ties with Tehran – a balancing act the war has made harder.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi has called broadly for “dialogue and diplomacy” to resolve conflicts, but has neither addressed the sinking of the Iranian vessel directly nor criticised the American strike.
Iran’s Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi described the attack as “an atrocity at sea” and stressed that the frigate had been “a guest of India’s Navy”. Meanwhile Sri Lanka has taken control of another Iranian naval vessel off its coast after an engine failure forced it to seek port, a day after the US attack.
The episode has nonetheless sparked debate within India’s strategic community.
Kanwal Sibal, a veteran diplomat, argued that India’s responsibility may not be legal, but it is moral.

“The Iranian ship would not have been where it was had India not invited it to the Milan exercise,” he wrote on X. “A word of condolence at the loss of lives of those who were our invitees would be in order.”
Others like Chellaney have framed the issue in more strategic terms.
He described the strike as a blow to India’s maritime diplomacy. The torpedoing of the frigate in “India’s maritime backyard”, he argued, punctured Delhi’s carefully cultivated image as a “preferred security partner” in the Indian Ocean.
“In one torpedo strike, American hard power has punctured India’s carefully cultivated soft power,” says Chellaney.
As the debate gathered pace in strategic circles, India’s official response remained cautious.
External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar said on X that he had held a telephone conversation with Araghchi, and also posted a photograph of a meeting with Iran’s Deputy Foreign Minister Saeed Khatibzadeh at a foreign policy summit in Delhi.
For military historian Srinath Raghavan, the legal position is clear: once the Iranian vessel left India’s shores, Delhi had no formal responsibility.
The strategic message, however, is harder to ignore.
“First, the spreading geography of this war. Second, India’s limited ability to manage its fallout,” says Raghavan.
“Indeed, the US Navy has fired a shot across the bow aimed at all regional players, including India.”
[BBC]
Features
End of ‘Western Civilisation’?

“All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others” ––George Orwell, Animal Farm
 When I wrote in this column an essay on 4th February 2026 titled, the ‘Beginning of Another ‘White Supremacist’ World Order?’, my focus was on the hypocrisy of Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney’s Davos address on 20 January 2026 to the World Economic Forum. It was embraced like the gospel by liberal types and the naïve international relations ‘experts’ in our country and elsewhere. My suspicion of Carney’s words stemmed from the consistent role played by countries like Canada and others which he called ‘middle powers’ or ‘intermediate powers’ in the world order he critiqued in Davos. He wanted such countries, particularly Canada, “to live the truth?” which meant “naming reality” as it exists; “acting consistently” towards all in the world; “applying the same standards to allies and rivals” and “building what we claim to believe in, rather than waiting for the old order to be restored.” These are some memorable pieces of Carney’s mantra.
When I wrote in this column an essay on 4th February 2026 titled, the ‘Beginning of Another ‘White Supremacist’ World Order?’, my focus was on the hypocrisy of Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney’s Davos address on 20 January 2026 to the World Economic Forum. It was embraced like the gospel by liberal types and the naïve international relations ‘experts’ in our country and elsewhere. My suspicion of Carney’s words stemmed from the consistent role played by countries like Canada and others which he called ‘middle powers’ or ‘intermediate powers’ in the world order he critiqued in Davos. He wanted such countries, particularly Canada, “to live the truth?” which meant “naming reality” as it exists; “acting consistently” towards all in the world; “applying the same standards to allies and rivals” and “building what we claim to believe in, rather than waiting for the old order to be restored.” These are some memorable pieces of Carney’s mantra.
Yet unsurprisingly, it only took the Trump-Netanyahu illegal war against Iran to prove the hollowness in Carney’s words. If he placed any premium on his own words, he should have at least voiced his concern against the continuing atrocities in the Middle East unilaterally initiated by the US and Israel. But his concern is only about Iran’s seemingly indiscriminate attacks across the region targeting US and Israeli installations and even civilian locations in countries allied with the Us-Israel coalition.
Issuing a statement on 3 March 2026 from Sydney he noted, “Canada has long seen Iran as the principal source of instability and terror in the Middle East” and “despite more than two decades of negotiations and diplomatic efforts, Iran has not dismantled its nuclear programme, nor halted its enrichment activities.” A sensible observer would note how the same statement would also apply to Israel. In fact, Israel has been the bigger force of instability in the Middle East surpassing Iran. After all, it has exiled an entire population of people — the Palestinians — from their country to absolute statelessness has not halted its genocide of the same people unfortunate enough to find themselves in Gaza after their homeland was taken over to create Israel in 1948 and their properties to build illegal Jewish settlements in more recent times. And then there is the matter of nuclear weapons. Israel has never been hounded to stop its nuclear programme unlike Iran. There is, in the world order Carney criticixed and the one in his fantasy, a fundamental difference between a ‘Jewish bomb’ and a ‘Muslim bomb’ in the ‘clash of civilisations’ as imagined by Samuel P. Huntington and put into practice by the likes of Messers Trump, Netanyahu, and Carney. That is, the Jewish bomb is legitimate, and the Muslim one is not, which to me evokes the commandments in the dystopian novella Animal Farm.
But Carney, in his new rhetoric closely echoing those of the leaders of Germany, UK and France, did not completely forget his Davos words too. He noted, in the same statement, “we take this position with regret, because the current conflict is another example of the failure of the international order.” But in reality, it is not the failure of the current international order, but its reinforcement by the likes of Mr Carney, reiterating why it will not change.
Coming back to the US-Israel attack on Iran, anyone even remotely versatile in the craft of warfare should have known, sooner or later, the rapidly expanding theatre of devastation in the Middle East was likely to happen for two obvious reasons. One, Iran had warned of this outcome if attacked as it considered those countries hosting US and Israeli bases or facilities as enemies. This is military common sense. Two, this was also likely because it is the only option available for a country under attack when faced with superior technology, firepower and the silence of much of the world. I cannot but feel deep shame about the lukewarm and generic statements urging restraint issued by our political leaders notwithstanding the support of Iran to our country in many times of difficulty at the hands of this very same world order.
When I say this, I am not naïvely embracing Iran as a shining example of democracy. I am cognizant of the Iranian regime’s maltreatment of some of its own citizens, stifling of dissent within the country and its proxy support for armed groups in the region. But in real terms, this is no different from similar actions of Israel and the US. The difference is, the actions of these countries, particularly of the US, have been far more devastating for the world than anything Iran has done or could do. US’s misadventures in Vietnam, Iraq, Syria, and Afghanistan come to mind — to take only a handful of examples.
But it is no longer about Carney and the hollowness of his liberal verbal diarrhoea in Davos. What is of concern now is twofold. One is the unravelling fiction of what he called the ‘new world order’ in which he located countries like Canada at the helm. And the second is the reality of continuing to live in the same old world order where countries like Canada and other middle and intermediate powers will continue to do the bidding of powerful aggressors like the US and Israel as they have done since the 20th century.
Yet, one must certainly thank Trump and Mr Natenyahu for one thing. That is, they have effectively exposed the myth of what used to be euphemistically called the ‘western civilisation.’ Despite its euphemism, the notion and its reality were omnipresent and omnipotent, because of the devastating long term and lingering consequences of its tools of operation, which were initially colonialism and later postcolonial and neocolonial forms of control to which all of us continue to be subjected.
One thing that was clearly lacking in the long and devastating history of the ‘western civilisation’ in so far as it affected the lives of people like us is its lack of ‘civilisation’ and civility at all times. Therefore, Trump and Mr Netanyahu must be credited for exposing this reality in no uncertain terms.
But what does illegal and unprovoked military action and the absence so far of accountability mean in real terms? It simply means that rules no longer matter. If Israel and the US can bomb and murder heads of state of a sovereign country, its citizens including children, cause massive destruction claiming a non-existent imminent threat violating both domestic and international law, it opens a wide playing field for the powerful and the greedy. Hypothetically, in this free-for-all, China can invade India through Arunachal Pradesh and occupy that Indian state which it calls Zangnan simply because it has been claiming the territory of itself for a very long time and also simply because it can. India can invade and occupy Sri Lanka, if it so wishes because this can so easily be done and also because it is part of the extended neighbourhood of the Ramayana and India’s ‘Akhand Bharat’ political logic. Sri Lanka can perhaps invade and occupy the Maldives if it wants a free and perennial supply of Maldive Fish. Incidentally, the Sri Lankan Tamil guerrilla group, People’s Liberation Organization of Tamil Eelam nearly succeeded in doing so 1988.
Sarcasm aside, even more dangerous is the very real possibility of this situation opening the doors for small, violent and mobile militant groups to target citizens of these aggressor countries and their allies as we saw in the late 1960s and 1970s. This will occur because in this kind of situation, many people would likely believe this form of asymmetric warfare is the only avenue of resistance open to them. It is precisely under similar conditions that the many Palestinian armed factions and Lebanese militia groups emerged in the first place. If this happens, the victims will not be the fathers and the vociferous supporters of the present aggression but all of us including those who had nothing to do with the atrocities or even opposed it in their weak and inaudible voices.
If I may go back to Carney’s Davos words, what would “to live the truth?”, “naming reality”, “acting consistently” and “applying the same standards to allies and rivals” mean in the emerging situation in the Middle East? Would this kind of hypocrisy, hyperbole, choreographed silence and selective accusations only end if a US invasion of Greenland, an integral part of the ‘White Supremacist’ World Order’ takes place? By then, however, all of us would have been well-trained in the art of feeling numb. By that time, we too would have forgotten yet another important line in Animal Farm: “No animal shall kill any other animal without cause.”
Features
Silence is not protection: Rethinking sexual education in Sri Lanka

Sexual education is a vital component of holistic education, contributing to physical health, emotional well-being, gender equality, and social responsibility. Despite its importance, sexual education remains a sensitive and often controversial subject in many societies, particularly in culturally conservative contexts. In Sri Lanka, discussions around sexuality are frequently avoided in formal and informal settings, leaving young people to rely on peers, social media, or misinformation. This silence creates serious social, health, and psychological consequences. By examining the Sri Lankan context alongside international examples, the importance of comprehensive and age-appropriate sexual education becomes clear.
Understanding Sexual Education
Sexual education goes beyond biological explanations of reproduction. Comprehensive sexual education includes knowledge about human anatomy, puberty, consent, relationships, emotional health, gender identity, sexual orientation, reproductive rights, contraception, prevention of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and personal safety. Importantly, it also promotes values such as respect, responsibility, dignity, and mutual understanding. When delivered appropriately, sexual education empowers individuals to make informed decisions rather than encouraging early or risky sexual behavior.
The Sri Lankan Context: Silence and Its Consequences
In Sri Lanka, sexual education is included in school curricula mainly through subjects such as Health Science and Life Competencies, however the content is often limited and taught with hesitation. Many teachers feel uncomfortable discussing sexual topics openly due to cultural norms, religious sensitivities, and fear of parental backlash. As a result, lessons are rushed, skipped, or delivered in a purely biological manner without addressing emotional, social, or ethical dimensions.
This lack of open education has led to several social challenges. Teenage pregnancies, although less visible, remain a significant issue, particularly in rural and estate sectors. Young girls who become pregnant often face school dropouts, social stigma, and limited future opportunities. Many of these pregnancies occur due to lack of knowledge about contraception, consent, and bodily autonomy.
Another serious concern in Sri Lanka is child sexual abuse. Numerous reports indicate that many children do not recognize abusive behaviour or lack the confidence and language to report it. Proper sexual education, especially lessons on body boundaries and consent, can help children identify inappropriate behavior and seek help early. In the Sri Lankan context, where respect for elders often discourages questioning authority, this knowledge is especially crucial.
Furthermore, misinformation about menstruation, nocturnal emissions, and bodily changes during puberty causes anxiety and shame among adolescents. Many Sri Lankan girls experience menarche without prior knowledge, leading to fear and confusion. Similarly, boys often receive no guidance about emotional or physical changes, reinforcing unhealthy notions of masculinity and silence around mental health.
Cultural Resistance and Misconceptions
Opposition to sexual education in Sri Lanka often stems from the belief that it promotes immoral behaviour or encourages premarital sex. However, international research consistently shows the opposite: young people who receive comprehensive sexual education tend to delay sexual initiation and engage in safer behaviours. The resistance is therefore rooted more in cultural fear than empirical evidence.
Religious and cultural values are important, but they need not conflict with sexual education. In fact, sexual education can be framed within moral discussions about responsibility, respect, family values, and care for others principles shared across Sri Lanka’s major religious traditions. Ignoring sexuality does not protect cultural values; rather, it leaves young people vulnerable.
International Evidence: Lessons from Other Countries
Several countries demonstrate how effective sexual education contributes to positive social outcomes.
In the Netherlands, sexual education begins at an early age and is age-appropriate, focusing on respect, relationships, and communication rather than explicit sexual activity. As a result, the Netherlands has one of the lowest rates of teenage pregnancy and STIs in the world. Young people are encouraged to discuss feelings, boundaries, and consent openly, both in schools and at home.
Similarly, Sweden introduced compulsory sexual education as early as the 1950s. Swedish programs emphasise gender equality, reproductive rights, and sexual health. This long-term commitment has contributed to high levels of sexual health awareness, low maternal mortality among young mothers, and strong societal acceptance of gender diversity. Sexual education in Sweden is also closely linked to public health services, ensuring access to counseling and contraception.
In many developing contexts, international organisations have supported sexual education as a tool for social development. UNESCO promotes Comprehensive Sexuality Education (CSE) globally, emphasising that it equips young people with knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values that enable them to protect their health and dignity. Studies supported by UNESCO show that CSE reduces risky behaviours, improves academic outcomes, and supports gender equality.
In countries such as Rwanda and South Africa, sexual education has been integrated with HIV/AIDS prevention programs. These initiatives demonstrate that sexual education is not a luxury of developed nations but a necessity for public health and social stability.
Comparing Sri Lanka with International Models
When compared with international examples, Sri Lanka’s challenges are not due to lack of capacity but lack of open dialogue and political will. Sri Lanka has a strong education system, high literacy rates, and an extensive public health network. These strengths provide an excellent foundation for implementing comprehensive sexual education that is culturally sensitive yet scientifically accurate.
Unlike the Netherlands or Sweden, Sri Lanka may not adopt early-age sexuality discussions in the same manner, but age-appropriate education during late primary and secondary school is both feasible and necessary. Topics such as puberty, menstruation, consent, online safety, and respectful relationships can be introduced gradually without violating cultural norms.
Sexual Education in the Digital Era
The urgency of sexual education has increased in the digital age. Sri Lankan adolescents are exposed to sexual content through social media, films, and online platforms, often without guidance. Pornography frequently becomes a primary source of sexual knowledge, leading to unrealistic expectations, objectification, and distorted ideas about consent and relationships.
Sexual education can counter these influences by developing critical thinking, media literacy, and ethical understanding. Teaching young people how to navigate digital relationships, cyber harassment, and online exploitation is now an essential component of sexual education.
Gender Equality and Social Change
Sexual education also plays a crucial role in promoting gender equality. In Sri Lanka, traditional gender roles often limit open discussion about female sexuality while excusing male dominance. Comprehensive sexual education challenges these norms by emphasizing mutual respect, shared responsibility, and equality in relationships.
Educating boys about consent and emotional expression helps reduce gender-based violence, while educating girls about bodily autonomy strengthens empowerment. In the long term, this contributes to healthier families and more equitable social structures.
The Way Forward for Sri Lanka
For sexual education to be effective in Sri Lanka, several steps are necessary. Teachers must receive proper training to handle the subject confidently and sensitively. Parents should be engaged through awareness programs to reduce fear and misconceptions. Curriculum developers must ensure that content is age-appropriate, culturally grounded, and scientifically accurate.
Importantly, sexual education should not be treated as a one-time lesson but as a continuous process integrated into broader life skills education. Collaboration between schools, healthcare providers, religious leaders, and community organisations can help normalise discussions around sexual health while respecting cultural values.
Finally , sexual education is not merely about sex; it is about health, dignity, safety, and responsible citizenship. The Sri Lankan experience demonstrates how silence and taboo can lead to misinformation, vulnerability, and social harm. International examples from the Netherlands, Sweden, and global initiatives supported by UNESCO clearly show that comprehensive sexual education leads to positive individual and societal outcomes.
For Sri Lanka, embracing sexual education does not mean abandoning cultural values. Rather, it means equipping young people with knowledge and ethical understanding to navigate modern social realities responsibly. In an era of rapid social and technological change, sexual education is not optional it is essential for building a healthy, informed, and compassionate society.
by Milinda Mayadunna ✍️
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoLegal experts decry move to demolish STC dining hall
-

 News1 day ago
News1 day agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoA life in colour and song: Rajika Gamage’s new bird guide captures Sri Lanka’s avian soul
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoCabinet nod for the removal of Cess tax imposed on imported good
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoOverseas visits to drum up foreign assistance for Sri Lanka
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoSri Lanka to Host First-Ever World Congress on Snakes in Landmark Scientific Milestone