Midweek Review
EPIC-MEMORY and BRECHT

by Laleen Jayamanne
‘Memory of the World’
UNESCO established the Memory of the World Programme in 1992 to preserve for posterity the audio-visual heritage of humankind, stating that war, social upheaval and lack of resources have accelerated its destruction.
“Significant collections worldwide have suffered a variety of fates. Looting and dispersal, illegal trading, destruction, inadequate housing and funding have all played a part. Much has vanished forever; much is endangered. Happily, missing documentary heritage is sometimes
rediscovered.” UNESCO
 UNESCO has also promoted the preservation (through revival), of the vital endangered category of human culture it calls, ‘The Intangible Heritage of Mankind’; the ancient arts of music, dance, theatre and ritual. As temporal arts, they are ephemeral by nature, passed through guru-shishya parampara transmission encoded in bodies through practice, in what used to be called the Third World.
UNESCO has also promoted the preservation (through revival), of the vital endangered category of human culture it calls, ‘The Intangible Heritage of Mankind’; the ancient arts of music, dance, theatre and ritual. As temporal arts, they are ephemeral by nature, passed through guru-shishya parampara transmission encoded in bodies through practice, in what used to be called the Third World.
Thanks to the availability of digital technological tools of preservation, exhibition and connectivity, the work of these visionary programmes has been considerably enhanced. Now, the fragile celluloid film, which was once the medium of preservation of artefacts, has itself been saved, restored and preserved digitally. Apart from this kind of essential programme of preservation, the very idea of attributing memory to the ‘world’, in the UNESCO formulation, is fascinating to speculate on because we usually think of memory as an inalienable human organic faculty of the mind without which we would live in a perpetual state of amnesia, in a timeless and depleted present. It seems to me that ‘memory of the world’ as an idea can also be imagined as something more than historical memory, which by definition is the written record, usually organised chronologically. ‘The world’ can now also suggest not only the human but also the earth itself and all that it sustains, plants and animals and even microbes and fossils and minerals and the cosmos, too. This is the zone that some artists have begun to explore within a ‘deep-ecological’ consciousness of what is known as the Anthropocene – the epoch of man-made ecological devastation.
‘Epic-Memory’
Walter Benjamin, the German theorist of culture, in his essay, The Story Teller, described another kind of memory, created by humans over millennia, which he called ‘epic memory.’ He invites us to imagine how to think about an idea of memory that’s more ample than our personal memory, by offering a dazzling image of ‘epic memory.’
“One must imagine the transformation of epic forms occurring in rhythms comparable to those of the change that has come over the earth’s surface in the course of thousands of centuries. Hardly any other forms of human communications have taken shape more slowly, been lost more slowly.
Memory is the epic faculty par excellence.
Memory creates the chain of tradition which passes a happening on from generation to generation.”
What Benjamin calls the ‘chain of tradition’ has been severed or partially lost in societies subject to colonisation and the forces of modernity have also destroyed many traditions. So we are looking for ways in which an expansive mode of remembering might be generated by artists through creative work, especially in the post-war situation of Sri Lanka where experiences of loss and trauma are widespread and some of their causes left unaddressed, forgotten, repressed, for many reasons. And now especially, with Sri Lanka in a state of profound crisis open to new possibilities of collective life free of ethnic nationalism and violence, an idea of epic memory might be of some use. It is the case that we don’t have ancient epics like India’s, Silappatikaram, Mahabharata and the Ramayana or the Greek ones, the Iliad and the Odyssey. Yet a modern idea of epic memory can perhaps still be formulated with what we do have.
The epic form was originally an oral form, which required from the bards a prodigious memory, trained through repeated recitation, which is why the muse of the epic form was called Mnemosyne, meaning epic memory in Greek. The written form of the epic came into being much later in history, based on the much older collective oral poetry of legends and myths of ‘the people’ handed down orally. Both in the UNESCO idea of ‘memory of the world’ and Benjamin’s definition of ‘epic memory,’ what is clear is that memory is a collective creation, taking shape over vast epochs. According to Greek myth, Mnemosyne, is the mother of the nine muses, and the word mouseion in Greek (from which the word museum is derived) means the dwelling place of the muses, who are the inspiration for the different art forms. This is a rich vital aesthetic image of the museum which is worth thinking about.
Then, one might be tempted to think that this is the same as the idea of ‘civilization’, which is the sum total of a culture’s pre-history and history as expressed in artefacts and written record. Usually this is indeed how nation states constitute themselves and give themselves an identity formulated on ethnicity, language, religion, custom, myths, etc. This is dangerous territory because states have deployed their myths to justify authoritarian and racist policies to divide and rule multi-ethnic, multi-religious, multi-linguistic societies such as Lanka. The Rajapaksa regime mobilised the Mahavansa narrative of Sinhala-Buddhist hegemony of Lanka to secure its own rule and some artists joined in with the mythic-epic genre films and shows. But I think the UNESCO idea is counter-hegemonic because it’s not created by a centralising state. Its memories may not fit easily into a master narrative of mythic inevitability. There is an element of chance and the possibility of ‘minor narratives’ emerging, which can’t be totalised into primordial myths.
Brecht’s Theory of Epic Theatre
To create a clearer picture of how to craft an idea of memory with great amplitude and rich potential, we can start with a modern example, the work of Bertolt Brecht, which Lankans have been quite familiar with (since the mid 1960’s), in all three languages. He famously created an ‘epic theatre’ and a theory of modern epic practice, as opposed to the traditional ‘dramatic theatre’. He called traditional dramatic theatre Aristotelian because it followed the basic structures analysed by the Greek philosopher in his Poetics. Walter Benjamin wrote several essays defending Brecht’s idea of epic theatre because what Brecht did was something quite unusual within the history of European theatre at the time. Instead of following the 1920s avant-garde German Expressionist theatre or French Surrealist theatre or constructivist Soviet practice, he looked to classical Asiatic theatrical forms such as Peking opera and its conventions of staging and highly formalised abstract forms of acting, to create a modern epic practice. For some artists of the left, Brecht’s theory appeared to be a strange move, looking to traditional Asian practice of the deep feudal past – not at all modern. Benjamin showed how Brecht’s modern epic form was suited to their time of the rise of fascism in Germany and its appeal to irrational emotions and ideas of racial purity and superiority. According to Aristotle the epic form contains three genres in one. That is, the lyric or ‘first person’ expression of subjective feeling as in love poetry, the dramatic as in actions and reactions organised in dialogue, in ‘second person’ and narration, which is the power to tell a story or narrate in ‘third person’. Therefore the ample epic mode can combine all three genres with ease, which means that it has the power to shift focus from one to the other, in complex combinations.
The traditional idea of ‘epic memory’ itself has an act of performance built into it through what is sung and is not something private and personal but consists of mythic stories, legends common to a people. But there is a crucial distinction Brecht and Benjamin made here between myth, on the one hand, and the epic form, on the other. The epic as a genre is a much later historical development from myth and though it does deploy myth, it does so on its own terms. Because, historically speaking, the epic is a later human achievement than myth, it also has had the rational power to comment on the myths it uses. That is to say, the epic form, with its many flexible techniques, has the power to create a sense of distance from the mythic universe of the ancients, which appears irrational and fated.
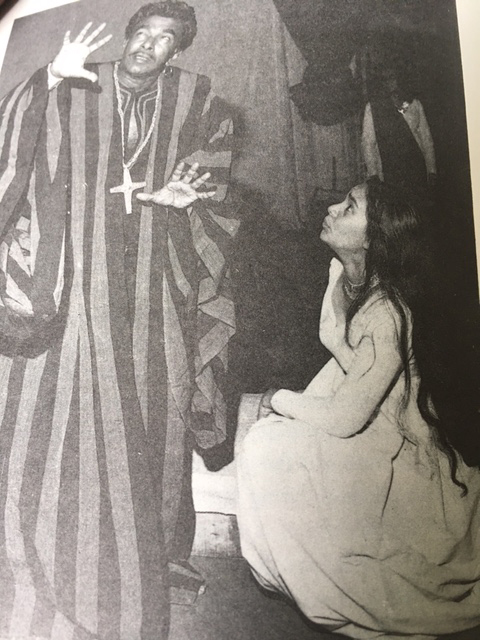
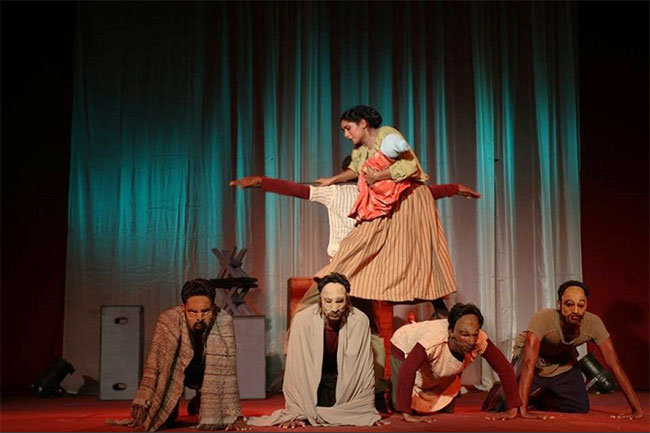
This idea of a historical ‘distance’ of the epic form (from the original myths), was taken up by Brecht and made into a method of constructing his epic drama. He called it, using a long German compound word, ‘verfremdungseffect’, variously translated as ‘distanciation’ or ‘Alienation-effect’ or ‘de-familiarisation’ or ‘making-strange’. Fine scholarship is available on this idea, my favourite was developed by Eugenio Barba and his Odin Theatret in Denmark. To create a dramatic situation which can immediately be ‘frozen’ and turned into a scene which is narrated and commented on, is one of the well-known ways in which Brecht’s Caucasian Chalk Circle was performed in Colombo, in the 1965 by Ernest Macintyre’s ‘Stage and Set’ production. The tender scene of a lyrical song sung by Grusha to her adopted infant son, can swiftly change to a bawdy commentary by the chorus. Sudden changes of point of view, mood and tone, are calibrated to give the spectator a chance to perceive a situation from more than one angle. It’s a way to introduce the exercise of reason into the spectacle of theatre, according to Brecht, to break its spell even as it is deployed. Brecht was here influenced by Eisenstein’s theory of montage, which he introduced into theatre. Eisenstein’s theory of montage created a clash between one shot and another, so as to produce a new idea in the mind of the spectator. So the continuously flowing conventional dramatic action could be interrupted, fragmented and anything-what-ever from ‘the memory of the world’ could be inserted to break the flow. So it’s the introduction of a radical film technique, montage, into theatre to make the mind constantly alert and instantly beguiled and then relaxed by the commentary of the chorus. These disjunctions can be very subtle or very direct depending on the skill of both actor and director.
Professor Saumya Liyanage’s recent article, on the play ‘Sanga Veda Guru Govi Kamkaru’, clearly indicated that the brilliant young playwright-director Chamila Priyanka had created an epic mode of theatre, which the judges of the drama competition failed to understand, (The Island, 11/5). Liyanage said that there is a to and fro movement between empathy and distance in the way the play was constructed and directed. The current Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe referred to Brecht in parliament, comparing his current task (to save Lanka), to that of the selfless Grusha’s action of saving the baby, treading on the rickety bridge. Whether he wanted empathy or analytical distance by offering this parable from the Caucasian Chalk Circle we don’t know, but he could assume that Lankans at large would know the reference. But we also know the play well enough to see what a thoughtless comparison it was.
The Artists’ Protest March

I saw a Brechtian epic mode in full flight in the artists’ protest march (#GotaGoGama), the other day on the streets of Colombo, which converged on Gall Face. Actors wearing handmade cardboard masks of the various yakas and the sunniyas were doing wild dancing moves using these marvellous creatures of the folk imagination of Lanka to exorcise the political demons sucking the people’s life-blood. These performers were such a refreshing counter to the expensive kitsch fascist-mythic-nationalist spectacles and films made under the Rajapaksa regime. And to see and hear a group of women walking rhythmically and playing the heavy drums slung across their bodies strung from their necks or tied at the waist, was a powerful moment for me, as I never imagined that Lankan women would be allowed to play these ritual drums belonging to a male tradition of such vitality. Traditionally, women only played raban pada! While the documentary camera excitedly cut between many performances very fast, I got the sense of an epic vision being performed as street theatre. Gamini Hattotuwegama’s pioneering street theatre work of the 70’s and 80’s seems to have taken on an unimaginable mass form, matured, diversified, loosening up and airing so many different stratified and compacted layers of the blood-soaked earth, of this famed ‘island of Dhamma’, Sri Lanka.
Perhaps artists can generate some ideas from these two modes of imagining memory (‘memory of the world’ and Brecht’s epic mode), which are quite distinct from personal memory. Artists working on traumatic experiences of the civil war and the formidable state ideologies that led to and orchestrated it, may find it useful to try to mobilise an ample epic mode of perception. I think so because it has this flexible montage structure, not tied to a strict linear chronology. ‘Montage’ is a term taken from engineering, of fitting different pieces of machinery together, so it contains the idea of assembling something with different components, stuff, to make something happen. While one might work on oneself and one’s sense of loss and a host of other urgent feelings that resist linguistic expression, one can also create certain disjunctions, breaks, (distanciation, make-strange the familiar), through an epic mode of composition. The need to repeatedly go back to the traumatic moment is often limitless, with no end in sight. Each repetition yields less as it becomes routine with no exit. Whereas, epic vision-memory, understood in a Brechtian way, is centrifugal not centripetal, it ripples out. It is not centred on man and nor is its vision cut to the measure of MAN. It is non-anthropocentric and non-anthropomorphic. Epic vision-memory helps us to see and feel and understand that we are part of something vaster and also much finer and subtle than ourselves. Epic vision gives us antennae like insects have. Tantric Buddhist idea of a ‘subtle body’ (Sukshama Dehaya) might be a line of investigation for those attracted to the rich visual traditions of Mahayana Buddhism which include vast scroll paintings which visually activate ‘nadi’ or a nervous system that connects many life forms too.
Brecht’s epic vision, in not giving ‘happy endings’ or resolving all the dramatic conflicts, leave us with an ability to discuss alternatives, as in say The Good Woman of Szechwan (Hita Honda Ammandi). I think the famous Chennai bonze statues of poets, (including a female one), and scholars (including an English scholar-missionary), and the epic heroine of Silappatikāram, Kannagi, lining the ocean front of the Marina really is a marvellous epic configuration that could also be understood in the Brechtian modern sense of the epic as well. They are positioned against the background of the ocean and address the people of Tamil Nadu evoking epic memory. The idea of debate so dear to Brecht also was staged when the Kannagi statue built by the Karunanidi’s DMK government was removed from her pedestal by Jaylalitha as Chief Minister, inaugurating a statue ‘battle’ and then returned from a museum, back again to her pedestal, with a change of government. There appears to be a sense of humour too in these serious political moves and counter moves, a marvellous sense of epic performance. This kind of jostling, argumentative, magnificent vision evoked by these bronze statues of Tamil Nadu is surely a modern mode of epic memory conjoined with the ocean, the sand and the sky – a memory of the world for sure.
Epic form is not the same as mythic form. The epic is Janus-faced (has two faces) facing two opposed directions. One face is turned toward myth and the other faces history. And situated in between the two, it has ample space-time to play and shuttle between the two modes of knowledge by making sure that history itself is not allowed to turn into myth.
And Laughter?
I saw on YouTube a well-known Sinhala actor perform a strange oration of excessive praise, a Rajapaksha varnanawa, invoking the glory days of Dutugamunu. What struck me was how much the brothers Mahinda and Gotabhaya laughed when they were praised in more and more exaggerated ways (drawing on the heroic parallels), by the actor who appeared to be carried away by his own brilliance at flattery and histrionic performance. I couldn’t help but think that the two brothers were looking at each other in a certain way and laughing, as much as to say, ‘does he really believe this stuff he’s spouting, what an idiot!’ They appeared to know that these were stupid but useful myths that they had themselves mobilised as history for their gain, but the true believers and the fools were the people themselves. This is just my reading of laughter of the two authoritarian brothers. Laughter is a tricky involuntary human impulse hard to control and pin down rationally. But one hopes that the last laugh will not be theirs’ to enjoy.
Features
Remembering Ernest MacIntyre’s Contribution to Modern Lankan Theatre & Drama

Humour and the Creation of Community:
“As melancholy is sadness that has taken on lightness,
so humour is comedy that has lost its bodily weight”. Italo Calvino on ‘Lightness’ (Six Memos for the New Millennium (Harvard UP, 1988).
With the death of Ernest Thalayasingham MacIntyre or Mac, as he was affectionately known to us, an entire theatrical milieu and the folk who created and nourished Modern Lankan Theatre appear to have almost passed away. I have drawn from Shelagh Goonewardene’s excellent and moving book, This Total Art: Perceptions of Sri Lankan Theatre (Lantana Publishing; Victoria, Australia, 1994), to write this. Also, the rare B&W photographs in it capture the intensity of distant theatrical moments of a long-ago and far-away Ceylon’s multi-ethnic theatrical experiments. But I don’t know if there is a scholarly history, drawing on oral history, critical reviews, of this seminal era (50s and 60s) written by Lankan or other theatre scholars in any of our languages. It is worth remembering that Shelagh was a Burgher who edited her Lankan journalistic reviews and criticism to form part of this book, with new essays on the contribution of Mac to Lankan theatre, written while living here in Australia. It is a labour of love for the country of her birth.
Here I wish to try and remember, now in my old age, what Mac, with his friends and colleagues from the University of Ceylon Drama Society did to create the theatre group called Stage & Set as an ‘infrastructure of the sensible’, so to speak, for theatrical activity in English, centred around the Lionel Wendt Theatre in Colombo 7 in the 60s. And remarkably, how this group connected with the robust Sinhala drama at the Lumbini Theatre in Colombo 5.
Shelagh shows us how Bertolt Brecht’s plays facilitated the opening up of a two-way street between the Sinhala and English language theatre during the mid-sixties, and in this story, Mac played a decisive role. I will take this story up below.
I was an undergraduate student in the mid-sixties who avidly followed theatre in Sinhala and English and the critical writings and radio programmes on it by eminent critics such as Regi Siriwardena and A. J. Gunawardana. I was also an inaugural student at the Aquinas University’s Theatre Workshop directed by Mac in late 1968, I think it was. So, he was my teacher for a brief period when he taught us aspects of staging (composition of space, including design of lighting) and theatre history, and styles of acting. Later in Australia, through my husband Brian Rutnam I became friends with Mac’s family including his young son Amrit and daughter Raina and followed the productions of his own plays here in Sydney, and lately his highly fecund last years when he wrote (while in a nursing home with his wife and comrade in theatre, Nalini Mather, the vice-principal of Ladies’ College) his memoir, A Bend in the River, on their University days. In my review in The Island titled ‘Light Sorrow -Peradeniya Imagination’ I attempted to show how Mac created something like an archaeology of the genesis of the pivotal plays Maname and Sinhabahu by Ediriweera Sarachchandra in 1956 at the University with his students. Mac pithily expressed the terms within which such a national cultural renaissance was enabled in Sinhala; it was made possible, he said, precisely because it was not ‘Sinhala Only’! The ‘it’ here refers to the deep theatrical research Sarachchandra undertook in his travels as well as in writing his book on Lankan folk drama, all of which was made possible because of his excellent knowledge of English.
The 1956 ‘Sinhala Only’ Act of parliament which abolished the status of Tamil as one of the National languages of Ceylon and also English as the language of governance, violated the fundamental rights of the Tamil people of Lanka and is judged as a violent act which has ricocheted across the bloodied history of Lanka ever since.
Mac was born in Colombo to a Tamil father and a Burgher mother and educated at St Patrick’s College in Jaffna after his father died young. While he wrote all his plays in English, he did speak Tamil and Sinhala with a similar level of fluency and took his Brecht productions to Jaffna. I remember seeing his production of Mother Courage and Her Children in 1969 at the Engineering Faculty Theatre at Peradeniya University with the West Indian actress Marjorie Lamont in the lead role.
Stage & Set and Brecht in Lanka
The very first production of a Brecht play in Lanka was by Professor E.F. C. Ludowyk (Professor of English at Peradeniya University from 1933 to 1956) who developed the Drama Society that pre-existed his time at the University College by expanding the play-reading group into a group of actors. This fascinating history is available through the letter sent in 1970 to Shelagh by Professor Ludowyk late in his retirement in England. In this letter he says that he produced Brecht’s The Good Woman of Szechwan with the Dram Soc in 1949. Shelagh who was directed by Professor Ludowyk also informs us elsewhere that he had sent from England a copy of Brecht’s Caucasian Chalk Circle to Irangani (Meedeniya/Serasinghe) in 1966 and that she in turn had handed it over to Mac, who then produced it in a celebrated production with her in the role of Grusha, which is what opened up the two way-street between the English language theatre of the Wendt and the Lumbini Theatre in Sinhala. Henry Jayasena in turn translated the play into Sinhala, making it one of the most beloved Sinhala plays. Mac performed in Henry’s production as the naughty priest who has the memorable line which he was fond of reciting for us in Sinhala; ‘Dearly beloved wedding and funeral guests, how varied is the fate of man…’. The idiomatic verve of Henry’s translation was such that people now consider the Caucasian Chalk Circle a Sinhala play and is also a text for high school children, I hear. Even a venal president recently quoted a famous line of the selfless Grusha in parliament assuming urbanely that folk knew the reference.
Others will discuss in some detail the classical and modern repertoire of Western plays that Mac directed for Stage & Set and the 27 plays he wrote himself, some of which are published, so that here I just want to suggest the sense of excitement a Stage & Set production would create through the media. I recall how characters in Mac’s production of Othello wore costumes made of Barbara Sansoni’s handloom material crafted specially for it and also the two sets of lead players, Irangani and Winston Serasinghe and Shelagh and Chitrasena. While Serasinghe’s dramatic voice was beautifully textured, Chitrasena with his dancer’s elan brought a kinetic dynamism not seen in a dramatic role, draped in the vibrant cloaks made of the famous heavy handloom cotton, with daring vertical black stripes – there was electricity in the air. Karan Breckenridge as the Story Teller in the Chalk Circle and also as Hamlet, Alastair Rosemale-Cocq as Iago were especially remarkable actors within the ensemble casts of Stage & Set. When Irangani and Winston Serasinghe, (an older and more experienced generation of actors than the nucleus of Stage & Set), joined the group they brought a gravitas and a sense of deep tradition into the group as Irangani was a trained actor with a wonderful deep modulated voice rare on our stage. The photographs of the production are enchanting, luminous moments of Lankan theatre. I had a brief glimpse of the much loved Arts Centre Club (watering hole), where all these people galvanised by theatre, – architects, directors, photographers, artists, actors, musicians, journalists, academics, even the odd senator – all met and mingled and drank and talked regularly, played the piano on a whim, well into the night; a place where many ideas would have been hatched.
A Beckett-ian Couple: Mac & Nalini
In their last few years due to restricted physical mobility (not unlike personae in Samuel Beckett’s last plays), cared for very well at a nursing home, Mac and Nalini were comfortably settled in two large armchairs daily, with their life-long travelling-companion- books piled up around them on two shelves ready to help. With their computers at hand, with Nalini as research assistant with excellent Latin, their mobile, fertile minds roamed the world.
It is this mise-en-scene of their last years that made me see Mac metamorphose into something of a late Beckett dramatis persona, but with a cheeky humour and a voracious appetite for creating scenarios, dramatic ones, bringing unlikely historical figures into conversation with each other (Galileo and Aryabhatta for example). The conversations, rather more ludic and schizoid and yet tinged with reason, sweet reason. Mac’s scenarios were imbued with Absurdist humour and word play so dear to Lankan theatre of a certain era. Lankans loved Waiting for Godot and its Sinhala version, Godot Enakan. Mac loved to laugh till the end and made us laugh as well, and though he was touched by sorrow he made it light with humour.
And I feel that his Memoir was also a love letter to his beloved Nalini and a tribute to her orderly, powerful analytical mind honed through her Classics Honours Degree at Peradeniya University of the 50s. Mac’s mind however, his theatrical imagination, was wild, ‘unruly’ in the sense of not following the rules of the ‘Well-Made play’, and in his own plays he roamed where angels fear to tread. Now in 2026 with the Sinhala translation by Professor Chitra Jayathilaka of his 1990 play Rasanayagam’s Last Riot, audiences will have the chance to experience these remarkable qualities in Sinhala as well.
Impossible Conversations
In the nursing home, he was loved by the staff as he made them laugh and spoke to one of the charge nurses, a Lankan, in Sinhala. Seated there in his room he wrote a series of short well-crafted one-act plays bristling with ideas and strange encounters between figures from world history who were not contemporaries; (Bertolt Brecht and Pope John Paul II, and Galileo Galilei and a humble Lankan Catholic nun at the Vatican), and also of minor figures like poor Yorik, the court jester whom he resurrects to encounter the melancholic prince of Denmark, Hamlet.
Community of Laughter: The Kolam Maduwa of Sydney
A long life-time engaged in theatre as a vital necessity, rather than a professional job, has gifted Mac with a way of perceiving history, especially Lankan history, its blood-soaked post-Independence history and the history of theatre and life itself as a theatre of encounters; ‘all the world’s a stage…’. But all the players were never ‘mere players’ for him, and this was most evident in the way Mac galvanised the Lankan diasporic community of all ethnicities in Sydney into dramatic activity through his group aptly named the Kolam Maduwa, riffing on the multiple meanings of the word Kolam, both a lusty and bawdy dramatic folk form of Lanka and also a lively vernacular term of abuse with multiple shades of meaning, unruly behaviour, in Sinhala.
The intergenerational and international transmission of Brecht’s theatrical experiments and the nurturing of what Eugenio Barba enigmatically calls ‘the secret art of the performer’, given Mac’s own spin, is part of his legacy. Mac gave a chance for anyone who wanted to act, to act in his plays, especially in his Kolam Maduwa performances. He roped in his entire family including his two grand-children, Ayesha and Michael. What mattered to him was not how well someone acted but rather to give a person a chance to shine, even for an instance and the collective excitement, laughter and even anguish one might feel watching in a group, a play such as Antigone or Rasanayagam’s Last Riot.
A colleague of mine gave a course in Theatre Studies at The University of California at Berkeley on ‘A History of Bad Acting’ and I learnt that that was his most popular course! Go figure!
Mac never joined the legendary Dram Soc except in a silent walk-on role in Ludowyk’s final production before he left Ceylon for good. In this he is like Gananath Obeyesekere the Lankan Anthropologist who did foundational and brilliant work on folk rituals of Lanka as Dionysian acts of possession. While Gananath did do English with Ludowyk, he didn’t join the Dram Soc and instead went travelling the country recording folk songs and watching ritual dramas. Mac, I believe, did not study English Lit and instead studied Economics but at the end of A Bend in the River when he and his mates leave the hall of residence what he leaves behind is his Economics text book but instead, carries with him a copy of the Complete Works of Shakespeare.
I imagine that there was a ‘silent transmission of the secret’ as Mac stood silently on that stage in Shaw’s Androcles and the Lion; the compassionate lion. Mac understood why Ludowyk chose that play to be performed in 1956 as his final farewell to the country he loved dearly. Mac knew (among others), this gentle and excellent Lankan scholar’s book The Foot Print of the Buddha written in England in 1958.
Both Gananath and Mac have an innate sense of theatre and with Mac it’s all self-taught, intuitive. He was an auto-didact of immense mental energy. In his last years Mac has conjured up fantastic theatrical scenarios for his own delight, untrammelled by any spatio-temporal constraints. And so it happens that he gives Shakespeare, as he leaves London, one last look at his beloved Globe theatre burnt down to ashes, where ‘all that is solid melts into air’.
However, I wish to conclude on a lighter note touched by the intriguing epigram by Calvino which frames this piece. It is curious that as a director Mac was drawn to Shakespearean tragedy (Hamlet, Othello), rather than comedy. And it becomes even curiouser because as a playwright-director his own preferred genre was comedy and even grotesque-comedy and his only play in the tragic genre is perhaps Irangani. Though the word ‘Riot’ in Rasanayagam’s Last Riot refers to the series of Sinhala pogroms against Tamils, it does have a vernacular meaning, say in theatre, when one says favourably of a performance, ‘it was a riot!’, lively, and there are such scenes even in that play. So then let me end with Calvino quoting from Shakespeare’s deliciously profound comedy As You Like It, framed by his subtle observations.
‘Melancholy and humour, inextricably intermingled, characterize the accents of the Prince of Denmark, accents we have learned to recognise in nearly all Shakespeare’s plays on the lips of so many avatars of Hamlet. One of these, Jacques in As You Like It (IV.1.15-18), defines melancholy in these terms:
“But it is a melancholy of mine own, compounded of many simples, extracted from many objects, and indeed the sundry contemplation of my travels, in which my often rumination wraps me in a most humorous sadness.”’
Calvino’s commentary on Jacques’ self-perception is peerless:
‘It is therefore not a dense, opaque melancholy, but a veil of minute particles of humours and sensations, a fine dust of atoms, like everything else that goes to make up the ultimate substance of the multiplicity of things.’
Ernest Thalayasingham MacIntyre certainly was attuned to and fascinated to the end by the ‘fine dust of atoms, by the veil of minute particles of humours and sensations,’ but one must also add to this, laughter.
by Laleen Jayamanne ✍️
Features
Lake-Side Gems

With a quiet, watchful eye,
The winged natives of the sedate lake,
Have regained their lives of joyful rest,
Following a storm’s battering ram thrust,
Singing that life must go on, come what may,
And gently nudging that picking up the pieces,
Must be carried out with the undying zest,
Of the immortal master-builder architect.
By Lynn Ockersz ✍️
Features
IPKF whitewashed in BJP strategy
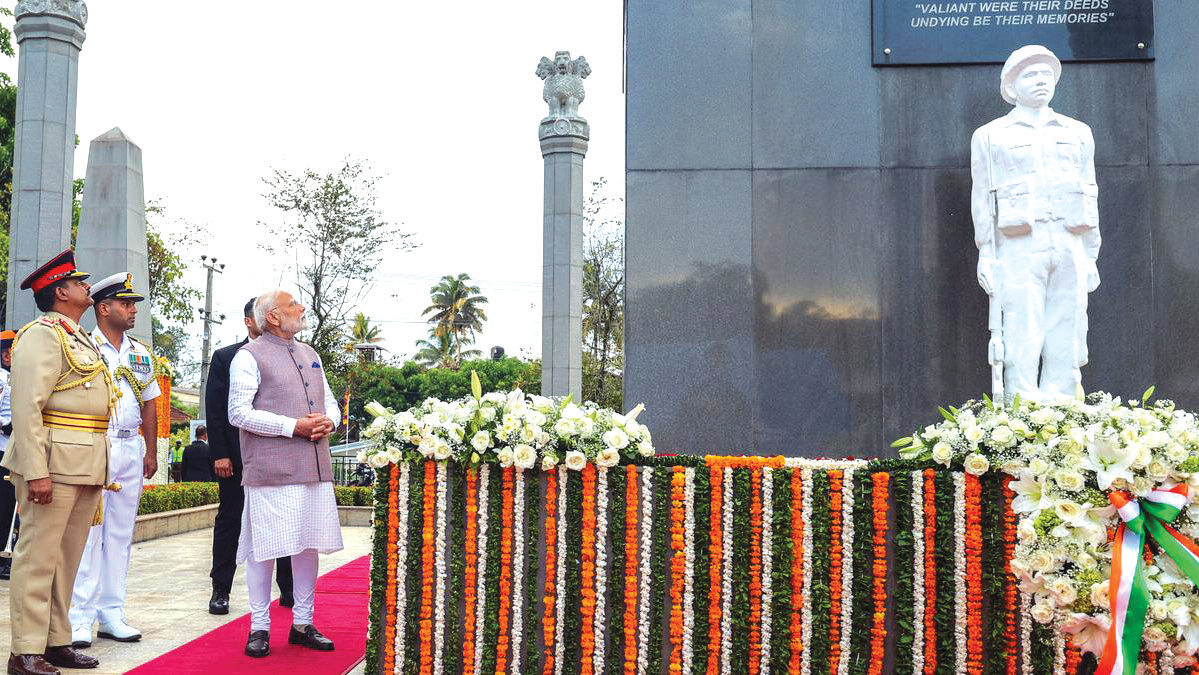

A day after the UN freshly repeated the allegation this week that sexual violence had been “part of a deliberate, widespread, and systemic pattern of violations” by the Sri Lankan military and “may amount to war crimes and crimes against humanity,” India praised its military (IPKF) for the operations conducted in Sri Lanka during the 1987-1990 period.
Soon after, as if in an echo, Human Rights Watch (HRW) in a statement, dated January 15, 2026, issued from Geneva, quoted Meenakshi Ganguly, Deputy Asia Director at the organisation, as having said: “While the appalling rape and murder of Tamil women by Sri Lankan soldiers at the war’s end has long been known, the UN report shows that systematic sexual abuse was ignored, concealed, and even justified by Sri Lankan government’s unwillingness to punish those responsible.”
Ganguly, who had been with the Western-funded HRW since 2004 went on to say: “Sri Lanka’s international partners need to step up their efforts to promote accountability for war crimes in Sri Lanka.”
To point its finger at Sri Lanka, or for that matter any other weak country, HRW is not that squeaky clean to begin with. In 2012, Human Rights Watch (HRW) accepted a $470,000 donation from Saudi billionaire Mohamed Bin Issa Al Jaber with a condition that the funds are not be used for its work on LGBT rights in the Middle East and North Africa. The donation was kept largely internal until it was revealed by an internal leak published in 2020 by The Intercept. Its Executive Director Kenneth Roth got exposed for taking the kickback. It refunded the money to Al Jaber only after the sordid act was exposed.
The UN, too, is no angel either, as it continues to play deaf, dumb and blind at an intrepid pace to the continuing unprecedented genocide against Palestinians and other atrocities being committed in West Asia and other parts of the world by Western powers.
The HRW statement was headlined ‘Sri Lanka: ‘UN Finds Systemic Sexual Violence During Civil War’, with a strap line ‘Impunity Prevails for Abuses Against Women, Men; Survivors Suffer for Years’
HRW reponds
The HRW didn’t make any reference to the atrocities perpetrated during the Indian Army deployment here.
The Island sought Ganguly’s response to the following queries:
* Would you please provide the number of allegations relating to the period from July 1987 to March 1990 when the Indian Army had been responsible for the Northern and Eastern Provinces of Sri Lanka and the Sri Lanka military confined to their camps, in terms of the Indo-Lanka accord.
* Have you urged the government of India to take tangible measures against the Indian Army personnel for violations perpetrated in Sri Lanka?
* Would you be able to provide the number of complaints received from foreign citizens of Sri Lankan origin?
Meenakshi responded: Thanks so much for reaching out. Hope you have been well? We can’t speak about UN methodology. Please could you reach out to OHCHR. I am happy to respond regarding HRW policies, of course. We hope that Sri Lankan authorities will take the UN findings on conflict-related sexual violence very seriously, regardless of perpetrator, provide appropriate support to survivors, and ensure accountability.
Mantri on IPKF
The Indian statement, issued on January 14, 2026, on the role played by its Army in Sri Lanka, is of significant importance at a time a section of the international community is stepping up pressure on the war-winning country on the ‘human rights’ front.
Addressing about 2,500 veterans at Manekshaw Centre, New Delhi, Indian Defence Minister Raksha Mantri referred to the Indian Army deployment here whereas no specific reference was made to any other conflicts/wars where the Indian military fought. India lost about 1,300 officers and men here. At the peak of Indian deployment here, the mission comprised as many as 100,000 military personnel.
According to the national portal of India, Raksha Mantri remembered the brave ex-servicemen who were part of Operation Pawan launched in Sri Lanka for peacekeeping purposes as part of the Indian Peacekeeping Force (IPKF) almost 40 years ago. Mantri’s statement verbatim: “During the operation, the Indian forces displayed extraordinary courage. Many soldiers laid down their lives. Their valour, sacrifices and struggles did not receive the respect they deserved. Today, under the leadership of PM Modi, our government is not only openly acknowledging the contributions of the peacekeeping soldiers who participated in Operation Pawan, but is also in the process of recognising their contributions at every level. When PM Modi visited Sri Lanka in 2015, he paid his respects to the Indian soldiers at the IPKF Memorial. Now, we are also recognising the contributions of the IPKF soldiers at the National War Memorial in New Delhi and giving them the respect they deserv.e” (https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleseDetailm.aspx?PRID=2214529®=3&lang=2)
One-time President of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), and ex-Home Minister Mantri received the Defence Portfolio in 2019. There hadn’t been a similar statement from any Modi appointed Defence Minister since he became the Prime Minister in 2014.
Perhaps, we should remind Mantri that Operation Pawan hadn’t been launched for peacekeeping purposes and the Indian Army deployment here cannot be discussed without examining the treacherous Indian destabilisation project launched in the early ’80s.
Nothing can be further from the truth than the attempt to describe Operation Pawan as a peacekeeping mission. India destabilised and terrorised Sri Lanka to its heart’s content that the then President JRJ had no option but to accept the so-called Indo-Lanka accord and the deployment of the Indian Army here to supervise the disarming of terrorist groups sponsored by India. Once the planned disarming of terrorist groups went awry in August, 1987 and the LTTE engineered a mass suicide of a group of terrorists who had been held at Palaly airbase, thereby Indian peacekeeping mission was transformed to a military campaign.
Mantri, in his statement, referred to the Indian Army memorial at Battaramulla put up by Sri Lanka years ago. The Indian Defence Minister seems to be unaware of the first monument installed here at Palaly in memory of 33 Indian commandos of the 10 Indian Para Commando unit, including Lieutenant Colonel Arun Kumar Chhabra who died in a miscalculated raid on the Jaffna University at the commencement of Operation Pawan.
BJP politics
Against the backdrop of Mantri’s declaration that India recognised the IPKF at the National War Memorial in New Delhi, it would be pertinent to ask when that decision was taken. The BJP must have decided to accommodate the IPKF at the National War Memorial in New Delhi recently. Otherwise Mantri’s announcement would have been made earlier. Obviously, Modi, the longest serving non-Congress Prime Minister of India, didn’t feel the need to take up the issue vigorously during his first two terms. Modi won three consecutive terms in 2014, 2019 and 2024. Congress great Jawaharlal Nehru is the only other to win three consecutive parliamentary elections in 1951, 1957 and 1962.
The issue at hand is why India failed to recognise the IPKF at the National War Memorial for so long. The first National War Memorial had been built and inaugurated in January 1972 following the Indo-Pakistan war of 1971, but under Modi’s direction India set up a new memorial, spread over 40 acres of land near India Gate Circle. Modi completed the National War Memorial project during his first term.
No one would find fault with India for honouring those who paid the supreme sacrifice in Sri Lanka, but the fact that the deployment of the IPKF took place here under the overall destabilisation project cannot be forgotten. India cannot, under any circumstances, absolve itself of the responsibility for the death and destruction caused as a result of the decision taken by Indira Gandhi, in her capacity as the Prime Minister, to intervene in Sri Lanka. Her son Rajiv Gandhi, in his capacity as the Prime Minister, dispatched the IPKF here after Indian,trained terrorists terrorised the country. India exercised terrorism as an integral part of their overall strategy to compel Sri Lanka to accept the deployment of Indian forces here under the threat of forcible occupation of the Northern and Eastern provinces.
India could have avoided the ill-fated IPKF mission if Premier Rajiv Gandhi allowed the Sri Lankan military to finish off the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) in 1987. Unfortunately, India carried out a forced air-drop over the Jaffna peninsula in June, 1987 to compel Sri Lanka to halt ‘Operation Liberation,’ at that time the largest ever ground offensive undertaken against the LTTE. Under Indian threat, Sri Lanka amended its Constitution by enacting the 13th Amendment that temporarily merged the Eastern Province with the Northern Province. That had been the long-standing demand of those who propagated separatist sentiments, both in and outside Parliament here. Don’t forget that the merger of the two provinces had been a longstanding demand and that the Indian Army was here to install an administration loyal to India in the amalgamated administrative unit.
The Indian intervention here gave the Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna (JVP) with an approving wink from Washington as India was then firmly in the Soviet orbit, an opportunity for an all-out insurgency burning anything and everything Indian in the South, including ‘Bombay onions’ as a challenge to the installation of the Eelam People’s Revolutionary Liberation front (EPRLF)-led administration in the North-East province in November 1988. How the Indian Army installed ex-terrorist Varatharaja Perumal’s administration and the formation of the so-called Tamil National Army (TNA) during the period leading to its withdrawal made the Indian military part of the despicable Sri Lanka destabilisation project.
The composition of the first NE provincial council underscored the nature of the despicable Indian operation here. The EPRLF secured 41 seats, the Sri Lanka Muslim Congress (SLMC) 17 seats, Eelam National Democratic Liberation Front (ENDLF) 12 and the United National Party (UNP) 1 in the 71-member council.
The Indian intelligence ran the show here. The ENDLF had been an appendage of the Indian intelligence and served their interests. The ENDLF that had been formed in Chennai (then Madras) by bringing in those who deserted EPRLF, PLOTE (People’s Liberation Organisation of Tamil Eelam) and Three Stars, a PLOTE splinter group led by Paranthan Rajan was accused of committing atrocities. Even Douglas Devananda, whose recent arrest over his failure to explain the disappearance of a weapon provided to him by the Sri Lanka Army, captured media attention, too, served the ENDLF for a short period. The ENDLF also contested the parliamentary polls conducted under Indian Army supervision in February 1989.
The ENDLF, too, pulled out of Sri Lanka along with the IPKF in 1990, knowing their fate at the hands of the Tigers, then honeymooning with Premadasa.
Dixit on Indira move
The late J.N. Dixit who was accused of behaving like a Viceroy when he served as India’s High Commissioner here (1985 to 1989) in his memoirs ‘Makers of India’s Foreign Policy: Raja Ram Mohun Roy to Yashwant Sinha’ was honest enough to explain the launch of Sri Lanka terrorism here.
In the chapter that also dealt with Sri Lanka, Dixit disclosed the hitherto not discussed truth. According to Dixit, the decision to militarily intervene had been taken by the late Indira Gandhi who spearheaded Indian foreign policy for a period of 15 years – from 1966 to 1977 and again from 1980 to 1984 (Indira was assassinated by her Sikh bodyguards in that year). That disastrous decision that caused so much death and destruction here and the assassination of her son Rajiv Gandhi had been taken during her second tenure (1980 to 1984) as the Prime Minister.
The BJB now seeking to exploit Indira Gandhi’s ill-fated decision probably taken at the onset of her second tenure as the Premier, came into being in 1980. Having described Gandhi’s decision to intervene in Sri Lanka as the most important development in India’s regional equations, one-time Foreign Secretary (December 1991 to January 1994) and National Security Advisor (May 2004 to January 2005) declared that Indian action was unavoidable.
Dixit didn’t mince his words when he mentioned the two major reasons for Indian intervention here namely (1) Sri Lanka’s oppressive and discriminating policies against Tamils and (2) developing security relationship with the US, Pakistan and Israel. Dixit, of course, didn’t acknowledge that there was absolutely no need for Sri Lanka to transform its largely ceremonial military to a lethal fighting force if not for the Indian destabilisation project. The LTTE wouldn’t have been able to enhance its fighting capabilities to wipe out a routine army patrol at Thinnaveli, Jaffna in July 1983, killing 13 men, including an officer, without Indian training. That was the beginning of the war that lasted for three decades.
Anti-India project
Dixit also made reference to the alleged Chinese role in the overall China-Pakistan project meant to fuel suspicions about India in Nepal and Bangladesh and the utilisation of the developing situation in Sri Lanka by the US and Pakistan to create, what Dixit called, a politico-strategic pressure point in Sri Lanka.
Unfortunately, Dixit didn’t bother to take into consideration Sri Lanka never sought to expand its armed forces or acquire new armaments until India gave Tamil terrorists the wherewithal to challenge and overwhelm the police and the armed forces. India remained as the home base of all terrorist groups, while those wounded in Sri Lanka were provided treatment in Tamil Nadu hospitals.
At the concluding section of the chapter, titled ‘AN INDOCENTRIC PRACTITIONER OF REALPOLITIK,’ Dixit found fault with Indira Gandhi for the Sri Lanka destabilisation project. Let me repeat what Dixit stated therein. The two foreign policy decisions on which she could be faulted are: her ambiguous response to the Russian intrusion into Afghanistan and her giving active support to Sri Lanka Tamil militants. Whatever the criticisms about these decisions, it cannot be denied that she took them on the basis of her assessments about India’s national interests. Her logic was that she could not openly alienate the former Soviet Union when India was so dependent on that country for defense supplies and technologies. Similarly, she could not afford the emergence of Tamil separatism in India by refusing to support the aspirations of Sri Lankan Tamils. These aspirations were legitimate in the context of nearly fifty years of Sinhalese discrimination against Sri Lankan Tamils.
The writer may have missed Dixit’s invaluable assessment if not for the Indian External Affairs Ministry presenting copies of ‘Makers of India’s Foreign Policy: Raja Ram Mohun Roy to Yashwant Sinha’ to a group of journalists visiting New Delhi in 2006. New Delhi arranged that visit at the onset of Eelam War IV in mid-2006. Probably, Delhi never considered the possibility of the Sri Lankan military bringing the war to an end within two years and 10 months. Regardless of being considered invincible, the LTTE, lost its bases in the Eastern province during the 2006-2007 period and its northern bases during the 2007-2009 period. Those who still cannot stomach Sri Lanka’s triumph over separatist Tamil terrorism, propagate unsubstantiated allegations pertaining to the State backing excesses against the Tamil community.
There had been numerous excesses and violations on the part of the police and the military. There is no point in denying such excesses happened during the police and military action against the JVP terrorists and separatist Tamil terrorists. However, sexual violence hadn’t been State policy at any point of the military campaigns or post-war period. The latest UN report titled ‘ACCOUNTABILITY FOR CONFLICT RELATED VIOLENCE IN SRI LANKA’ is the latest in a long series of post-war publications that targeted the war-winning military. Unfortunately, the treacherous Sirisena-Wickremesinghe Yahapalana government endorsed the Geneva accountability resolution against Sri Lanka in October 2015. Their despicable action caused irreversible damage and the ongoing anti-Sri Lanka project should be examined taking into consideration the post-war Geneva resolution.
By Shamindra Ferdinando ✍️
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoExtended mind thesis:A Buddhist perspective
-

 Business21 hours ago
Business21 hours agoComBank advances ForwardTogether agenda with event on sustainable business transformation
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoAmerican rulers’ hatred for Venezuela and its leaders
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoRemembering Cedric, who helped neutralise LTTE terrorism
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoCORALL Conservation Trust Fund – a historic first for SL
-
 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoA puppet show?
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoHistory of St. Sebastian’s National Shrine Kandana
-

 Opinion21 hours ago
Opinion21 hours agoConference “Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill: Neither Here, Nor There”














