Features
China’s Belt and Road Initiative: Kenya and a railway to nowhere

The first section of Kenya’s Chinese-built railway was opened with much fanfare in 2017 – but two years later work on the tracks stopped in the middle of the country and the master plan of linking it to other landlocked countries in East Africa seems to have derailed.
This means the project is not bringing as much money as was hoped at this stage, while Kenya is left servicing loans totalling around $4.7bn (£3.9bn), mainly borrowed from Chinese banks.
Yet it is hard to believe that Kenya’s Standard Gauge Railway (SGR) is not a success when passengers disgorge from a packed train of around 12 carriages at the Syokimau railway terminus in the capital, Nairobi – the last service of the day.
They have travelled non-stop from the port city of Mombasa, 470km (290 miles) away on the Indian Ocean. “It’s great,” 53-year-old commuter Pauline Echesa told me. The four-and-a-half hour journey gives her the bonus of watching wildlife along the way as the railway cuts through national parks, she says.
A 30-year-old commuter found the experience a little more exhausting, saying the seats were not that comfortable but the journey saved her money compared to other ways of travelling from the coast.
There is no doubt the passenger side of the business is doing well and is fully booked, but it cannot pay back the loans on its own – and it was never meant to do so.
This burden falls to the cargo side of the business – bringing inland the containers that arrive at Mombasa port. It was intended that they would reach Uganda, Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
The problem is that they can go only go as far as the Kenyan town of Naivasha – 120km from Nairobi but still far from the Ugandan border – on the SGR. Most of the freight trains then return to Mombasa empty, a huge loss of potential income.
“It will be more productive for us to continue with the project,” Kenya’s Transport Cabinet Secretary Kipchumba Murkomen told the BBC. “But the financing part is actually our challenge.” He says the government would be exploring options for funding the construction of the remaining portion of the railway during the upcoming Belt and Road Summit in China.
Launched in 2013, China’s massive Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has stretched across the globe and noticeably changed the landscape of infrastructure across Africa. But its future is a matter of debate now as China continues to scale down funding and African countries face the reality of growing debt that in some cases threatens to destabilise their economies.
American think-tank the Council on Foreign Relations argues that some BRI investments have involved opaque bidding processes and required use of Chinese firms leading to inflated costs which have in some cases resulted in the cancellation of projects and a political backlash.
Internal issues that have affected the Chinese economy have also led to hugely diminished funding, says Nigeria’s former Deputy Central Bank Governor, Kingsley Moghalu. “The funding levels in the past couple of years have not been more than $2bn across the continent,” he says – down, he estimates, from between $10bn and $20bn a decade ago. Kenya’s SGR is one of those to have suffered.

Kenya is hoping to find backing to build the SGR line to the Ugandan border at the Belt and Road Summit in China (pic BBC)
But Mr Murkomen says Kenya is open to options: “We have private sector players in China who have said they are willing to put their own resources as long as we can have a conversation about how they’ll recoup their finances.” One could be a grace period to allow the country to first service the loans taken to finance the sections of the railway that are complete, he explains.
An admission that the government is seeking more funding may not sit well with many in the country who already reeling from tax hikes introduced by President William Ruto since he came into office a year ago.
Kenyans are concerned that debt repayments are exerting significant pressure on the country’s economy. Government figures from the end of June 2022 showed that China was Kenya’s third biggest external creditor – accounting for 19.4% of the country’s debt.
“Right now, the debt profile of the country is quite heavy,” says Kenyan economist Ken Gichinga, explaining that next June is when Kenya must repay a $2bn Eurobond. “And there is also a feeling that not all that money went to building the railway,” says Mr Gichinga.
The opacity in the deals countries like Kenya have signed with China is a matter of concern to their own citizens as well as critics abroad.
The Council on Foreign Relations assessment notes that loan terms are rarely made public and “because China refused to join the Paris Club of major official creditors”, Chinese banks are under no pressure to cap lending rates or share information.
This, it concludes, means the risks for both the US and recipient countries “considerably outweighed its benefits”.

Critics are concerned that the details of China’s loans are rarely publicly disclosed (pic BBC)
For Kenya’s railway to reap the benefits that were envisioned at its inception, it needs to go transnational. “Uganda really needs to also be onboard,” argues Mr Gichinga. But that ambition looks shaky.
The original East Africa Transport Master Plan, proposed by the East Africa Community around two decades ago, wanted two routes into landlocked countries from the coast – one coming from Kenya, known as the northern corridor, and another from Tanzania, dubbed the central corridor. It then had connections to South Sudan and DR Congo.
However Uganda may decide to push its business towards Tanzania. Its railway project has cost way less to build and offers higher speeds as the line is electrified.
Former Tanzanian President John Magufuli tore up the deal that had been signed by his predecessor with China to build the railway and chose to get funding instead from Turkey and Portugal to finance the first leg of the project.
Tanzania also appears on track to connect to Rwanda, Burundi and DR Congo – with China coming onboard in latter sections.
Mr Moghalu argues that, like Tanzania, countries on the continent “should be drivers of their own destiny”. “African countries need a mental repositioning and not feel like an abused spouse that they should be grateful to China because their former spouse, the West, did not treat them well.”
Western countries have recently been trying to counter BRI, including US President Joe Biden’s Build Back Better World Initiative, launched in 2021 in collaboration with G7 economies. But there is general acknowledgement that China still can offer more in terms of long-term development.
For the Nairobi-Mombasa commuters, such investments for the country’s future are definitely worthwhile. “Let us sacrifice to pay the debt and get more for such projects,” Ms Echesa told the BBC.
The Kenyan government will be hoping it can convince China, and its banks, that the SGR railway will be profitable if it gets to the border and beyond.
(BBC)
Features
Misinterpreting President Dissanayake on National Reconciliation

President Anura Kumara Dissanayake has been investing his political capital in going to the public to explain some of the most politically sensitive and controversial issues. At a time when easier political choices are available, the president is choosing the harder path of confronting ethnic suspicion and communal fears. There are three issues in particular on which the president’s words have generated strong reactions. These are first with regard to Buddhist pilgrims going to the north of the country with nationalist motivations. Second is the controversy relating to the expansion of the Tissa Raja Maha Viharaya, a recently constructed Buddhist temple in Kankesanturai which has become a flashpoint between local Tamil residents and Sinhala nationalist groups. Third is the decision not to give the war victory a central place in the Independence Day celebrations.
Even in the opposition, when his party held only three seats in parliament, Anura Kumara Dissanayake took his role as a public educator seriously. He used to deliver lengthy, well researched and easily digestible speeches in parliament. He continues this practice as president. It can be seen that his statements are primarily meant to elevate the thinking of the people and not to win votes the easy way. The easy way to win votes whether in Sri Lanka or elsewhere in the world is to rouse nationalist and racist sentiments and ride that wave. Sri Lanka’s post independence political history shows that narrow ethnic mobilisation has often produced short term electoral gains but long term national damage.
Sections of the opposition and segments of the general public have been critical of the president for taking these positions. They have claimed that the president is taking these positions in order to obtain more Tamil votes or to appease minority communities. The same may be said in reverse of those others who take contrary positions that they seek the Sinhala votes. These political actors who thrive on nationalist mobilisation have attempted to portray the president’s statements as an abandonment of the majority community. The president’s actions need to be understood within the larger framework of national reconciliation and long term national stability.
Reconciler’s Duty
When the president referred to Buddhist pilgrims from the south going to the north, he was not speaking about pilgrims visiting long established Buddhist heritage sites such as Nagadeepa or Kandarodai. His remarks were directed at a specific and highly contentious development, the recently built Buddhist temple in Kankesanturai and those built elsewhere in the recent past in the north and east. The temple in Kankesanturai did not emerge from the religious needs of a local Buddhist community as there is none in that area. It has been constructed on land that was formerly owned and used by Tamil civilians and which came under military occupation as a high security zone. What has made the issue of the temple particularly controversial is that it was established with the support of the security forces.
The controversy has deepened because the temple authorities have sought to expand the site from approximately one acre to nearly fourteen acres on the basis that there was a historic Buddhist temple in that area up to the colonial period. However, the Tamil residents of the area fear that expansion would further displace surrounding residents and consolidate a permanent Buddhist religious presence in the present period in an area where the local population is overwhelmingly Hindu. For many Tamils in Kankesanturai, the issue is not Buddhism as a religion but the use of religion as a vehicle for territorial assertion and demographic changes in a region that bore the brunt of the war. Likewise, there are other parts of the north and east where other temples or places of worship have been established by the military personnel in their camps during their war-time occupation and questions arise regarding the future when these camps are finally closed.
There are those who have actively organised large scale pilgrimages from the south to make the Tissa temple another important religious site. These pilgrimages are framed publicly as acts of devotion but are widely perceived locally as demonstrations of dominance. Each such visit heightens tension, provokes protest by Tamil residents, and risks confrontation. For communities that experienced mass displacement, military occupation and land loss, the symbolism of a state backed religious structure on contested land with the backing of the security forces is impossible to separate from memories of war and destruction. A president committed to reconciliation cannot remain silent in the face of such provocations, however uncomfortable it may be to challenge sections of the majority community.
High-minded leadership
The controversy regarding the president’s Independence Day speech has also generated strong debate. In that speech the president did not refer to the military victory over the LTTE and also did not use the term “war heroes” to describe soldiers. For many Sinhala nationalist groups, the absence of these references was seen as an attempt to diminish the sacrifices of the armed forces. The reality is that Independence Day means very different things to different communities. In the north and east the same day is marked by protest events and mourning and as a “Black Day”, symbolising the consolidation of a state they continue to experience as excluding them and not empathizing with the full extent of their losses.
By way of contrast, the president’s objective was to ensure that Independence Day could be observed as a day that belonged to all communities in the country. It is not correct to assume that the president takes these positions in order to appease minorities or secure electoral advantage. The president is only one year into his term and does not need to take politically risky positions for short term electoral gains. Indeed, the positions he has taken involve confronting powerful nationalist political forces that can mobilise significant opposition. He risks losing majority support for his statements. This itself indicates that the motivation is not electoral calculation.
President Dissanayake has recognized that Sri Lanka’s long term political stability and economic recovery depend on building trust among communities that once peacefully coexisted and then lived through decades of war. Political leadership is ultimately tested by the willingness to say what is necessary rather than what is politically expedient. The president’s recent interventions demonstrate rare national leadership and constitute an attempt to shift public discourse away from ethnic triumphalism and toward a more inclusive conception of nationhood. Reconciliation cannot take root if national ceremonies reinforce the perception of victory for one community and defeat for another especially in an internal conflict.
BY Jehan Perera
Features
Recovery of LTTE weapons

I have read a newspaper report that the Special Task Force of Sri Lanka Police, with help of Military Intelligence, recovered three buried yet well-preserved 84mm Carl Gustaf recoilless rocket launchers used by the LTTE, in the Kudumbimalai area, Batticaloa.
These deadly weapons were used by the LTTE SEA TIGER WING to attack the Sri Lanka Navy ships and craft in 1990s. The first incident was in February 1997, off Iranativu island, in the Gulf of Mannar.
Admiral Cecil Tissera took over as Commander of the Navy on 27 January, 1997, from Admiral Mohan Samarasekara.
The fight against the LTTE was intensified from 1996 and the SLN was using her Vanguard of the Navy, Fast Attack Craft Squadron, to destroy the LTTE’s littoral fighting capabilities. Frequent confrontations against the LTTE Sea Tiger boats were reported off Mullaitivu, Point Pedro and Velvetiturai areas, where SLN units became victorious in most of these sea battles, except in a few incidents where the SLN lost Fast Attack Craft.

Carl Gustaf recoilless rocket launchers
The intelligence reports confirmed that the LTTE Sea Tigers was using new recoilless rocket launchers against aluminium-hull FACs, and they were deadly at close quarter sea battles, but the exact type of this weapon was not disclosed.
The following incident, which occurred in February 1997, helped confirm the weapon was Carl Gustaf 84 mm Recoilless gun!
DATE: 09TH FEBRUARY, 1997, morning 0600 hrs.
LOCATION: OFF IRANATHIVE.
FACs: P 460 ISRAEL BUILT, COMMANDED BY CDR MANOJ JAYESOORIYA
P 452 CDL BUILT, COMMANDED BY LCDR PM WICKRAMASINGHE (ON TEMPORARY COMMAND. PROPER OIC LCDR N HEENATIGALA)
OPERATED FROM KKS.
CONFRONTED WITH LTTE ATTACK CRAFT POWERED WITH FOUR 250 HP OUT BOARD MOTORS.
TARGET WAS DESTROYED AND ONE LTTE MEMBER WAS CAPTURED.
LEADING MARINE ENGINEERING MECHANIC OF THE FAC CAME UP TO THE BRIDGE CARRYING A PROJECTILE WHICH WAS FIRED BY THE LTTE BOAT, DURING CONFRONTATION, WHICH PENETRATED THROUGH THE FAC’s HULL, AND ENTERED THE OICs CABIN (BETWEEN THE TWO BUNKS) AND HIT THE AUXILIARY ENGINE ROOM DOOR AND HAD FALLEN DOWN WITHOUT EXPLODING. THE ENGINE ROOM DOOR WAS HEAVILY DAMAGED LOOSING THE WATER TIGHT INTEGRITY OF THE FAC.
THE PROJECTILE WAS LATER HANDED OVER TO THE NAVAL WEAPONS EXPERTS WHEN THE FACs RETURNED TO KKS. INVESTIGATIONS REVEALED THE WEAPON USED BY THE ENEMY WAS 84 mm CARL GUSTAF SHOULDER-FIRED RECOILLESS GUN AND THIS PROJECTILE WAS AN ILLUMINATER BOMB OF ONE MILLION CANDLE POWER. BUT THE ATTACKERS HAS FAILED TO REMOVE THE SAFETY PIN, THEREFORE THE BOMB WAS NOT ACTIVATED.

Sea Tigers
Carl Gustaf 84 mm recoilless gun was named after Carl Gustaf Stads Gevärsfaktori, which, initially, produced it. Sweden later developed the 84mm shoulder-fired recoilless gun by the Royal Swedish Army Materiel Administration during the second half of 1940s as a crew served man- portable infantry support gun for close range multi-role anti-armour, anti-personnel, battle field illumination, smoke screening and marking fire.
It is confirmed in Wikipedia that Carl Gustaf Recoilless shoulder-fired guns were used by the only non-state actor in the world – the LTTE – during the final Eelam War.
It is extremely important to check the batch numbers of the recently recovered three launchers to find out where they were produced and other details like how they ended up in Batticaloa, Sri Lanka?
 By Admiral Ravindra C. Wijegunaratne
By Admiral Ravindra C. Wijegunaratne
WV, RWP and Bar, RSP, VSV, USP, NI (M) (Pakistan), ndc, psn, Bsc (Hons) (War Studies) (Karachi) MPhil (Madras)
Former Navy Commander and Former Chief of Defence Staff
Former Chairman, Trincomalee Petroleum Terminals Ltd
Former Managing Director Ceylon Petroleum Corporation
Former High Commissioner to Pakistan
Features
Yellow Beatz … a style similar to K-pop!
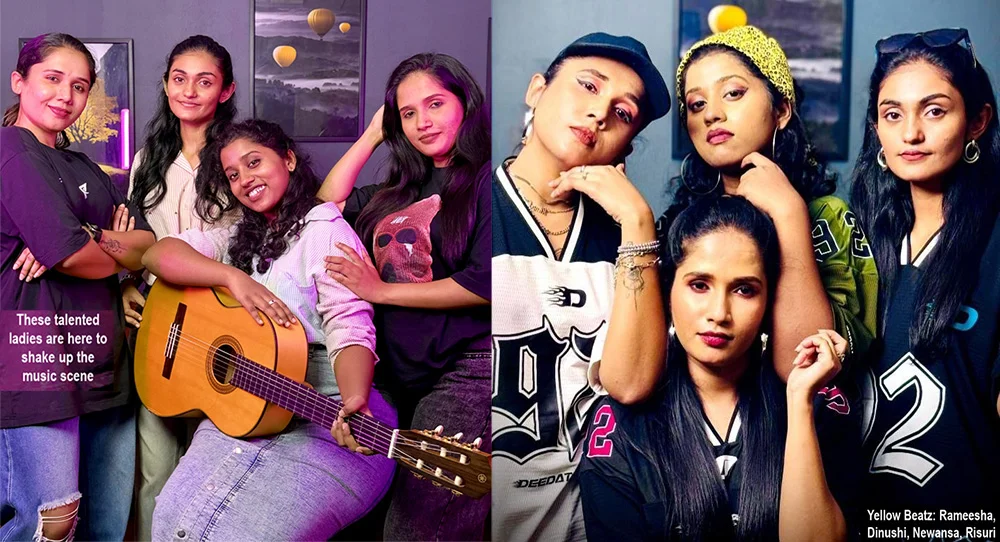
 Yes, get ready to vibe with Yellow Beatz, Sri Lanka’s awesome girl group, keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-pop!
Yes, get ready to vibe with Yellow Beatz, Sri Lanka’s awesome girl group, keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-pop!
With high-energy beats and infectious hooks, these talented ladies are here to shake up the music scene.
Think bold moves, catchy hooks, and, of course, spicy versions of old Sinhala hits, and Yellow Beatz is the package you won’t want to miss!
According to a spokesman for the group, Yellow Beatz became a reality during the Covid period … when everyone was stuck at home, in lockdown.
“First we interviewed girls, online, and selected a team that blended well, as four voices, and then started rehearsals. One of the cover songs we recorded, during those early rehearsals, unexpectedly went viral on Facebook. From that moment onward, we continued doing cover songs, and we received a huge response. Through that, we were able to bring back some beautiful Sri Lankan musical creations that were being forgotten, and introduce them to the new generation.”
The team members, I am told, have strong musical skills and with proper training their goal is to become a vocal group recognised around the world.
Believe me, their goal, they say, is not only to take Sri Lanka’s name forward, in the music scene, but to bring home a Grammy Award, as well.
“We truly believe we can achieve this with the love and support of everyone in Sri Lanka.”
The year 2026 is very special for Yellow Beatz as they have received an exceptional opportunity to represent Sri Lanka at the World Championships of Performing Arts in the USA.
Under the guidance of Chris Raththara, the Director for Sri Lanka, and with the blessings of all Sri Lankans, the girls have a great hope that they can win this milestone.
“We believe this will be a moment of great value for us as Yellow Beatz, and also for all Sri Lankans, and it will be an important inspiration for the future of our country.”
Along with all the preparation for the event in the USA, they went on to say they also need to manage their performances, original song recordings, and everything related.

The year 2026 is very special for Yellow Beatz
“We have strong confidence in ourselves and in our sincere intentions, because we are a team that studies music deeply, researches within the field, and works to take the uniqueness of Sri Lankan identity to the world.”
At present, they gather at the Voices Lab Academy, twice a week, for new creations and concert rehearsals.
This project was created by Buddhika Dayarathne who is currently working as a Pop Vocal lecturer at SLTC Campus. Voice Lab Academy is also his own private music academy and Yellow Beatz was formed through that platform.
Buddhika is keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-Pop and Yellow Beatz began as a result of that vision. With that same aim, we all work together as one team.
“Although it was a little challenging for the four of us girls to work together at first, we have united for our goal and continue to work very flexibly and with dedication. Our parents and families also give their continuous blessings and support for this project,” Rameesha, Dinushi, Newansa and Risuri said.
Last year, Yellow Beatz released their first original song, ‘Ihirila’ , and with everything happening this year, they are also preparing for their first album.
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoGREAT 2025–2030: Sri Lanka’s Green ambition meets a grid reality check
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoAll’s not well that ends well?
























