Features
Buddhist Theory of Kamma

by Venerable Narada Maha Thera
Kamma is the law of moral causation. The theory of kamma is a fundamental doctrine in Buddhism. This belief was prevalent in India before the advent of the Buddha. Nevertheless, it was the Buddha who explained and formulated this doctrine in the complete form in which we have it today.
What is the cause of inequality that exists among mankind?
Why should one person be brought up in the lap of luxury, endowed with fine mental, moral and physical qualities, and another in absolute poverty, steeped in misery?
Why should one person be a mental prodigy and another an idiot’?
Why should one person be born with saintly characteristics and another with criminal tendencies?
Why should some be linguistic, artistic, mathematically inclined, or musical from the very cradle.
Why should others be congenitally blind, deaf, or deformed? Why should some be blessed and others cursed from their births?
Either this inequality of mankind has a cause or it is purely accidental. No sensible person would think of attributing this unevenness, this inequality, and this diversity to blind chance or pure accident.
In this world nothing happens to a person that he does not for some reason or other deserve. Usually, men of ordinary intellect cannot comprehend the actual reason or reasons. The definite invisible cause or causes of the visible effect is not necessarily confined to the present life, they may be traced to a proximate or remote past birth.
According to Buddhism, this inequality is due not only to heredity, environment, “nature and nurture”, but also to kamma. In other words, it is the result of our own past actions and our own present doings. We ourselves are responsible for our own happiness and misery. We create our own Heaven. We create our own Hell. We are the architects of our own fate.
Perplexed by the seemingly inexplicable, apparent disparity that existed among humanity, a young truth-seeker approached the Buddha and questioned him regarding this intricate problem of inequality:
“What is the cause, what is the reason, 0 Lord,” questioned lie, “that we find amongst mankind the short-lived and long-lived, the healthy and the diseased, the ugly and beautiful, those lacking influence and the powerful, the poor and the rich, the low-born and the high-born, and the ignorant and the wise?”
The Buddha’s reply was:
“All living beings have actions (Kamma) as their own, their inheritance, their congenital cause, their kinsman, their refuge. It is kamma that differentiates beings into low and high states.”
The Buddha then explained the cause of such differences in accordance with the law of cause and effect.
Certainly we are born with hereditary characteristics. At the same time we possess certain innate abilities that science cannot adequately account for. To our parents we are indebted for the gross sperm and ovum that form the nucleus of this so-called being. They remain dormant within each parent until this potential germinal compound is vitalised by the karmic energy needed for the production of the foetus. kamma is therefore the indispensable conceptive cause of this being.
The accumulated karmic tendencies, inherited in the course of previous lives, at times play a far greater role than the hereditary parental cells and genes in the formation of both physical and mental characteristics.
The Buddha for instance, inherited, like every other person, the reproductive cells and genes from his parents. But physically, morally and intellectually there was none comparable to him in his long line of Royal ancestors. In the Buddha’s own words, he belonged not to the Royal lineage, but to that of the Aryan Buddhas. He was certainly a superman, an extraordinary creation of his own kamma.
According to the Lakkhana Sutta of Digha Nikaya, the Buddha inherited exceptional features, such as the 32 major marks, as the result of his past meritorious deeds. The ethical reason for acquiring each physical feature is clearly explained in the Sutta.
It is obvious from this unique case that karmic tendencies could not only influence our physical organism, but also nullify the potentiality of the parental cells and genes – hence the significance of the Buddha’s enigmatic statement, – “We are the heirs of our own actions.”
Dealing with this problem of variation, the Atthasalini, being a commentary on the Abhidharma, states:
“Depending on this difference in Karma appears the differences in the birth of beings, high and low, base and exalted, happy and miserable. Depending on the difference in karma appears the difference in the individual features of beings as beautiful and ugly, high-born or low born, well-built or deformed. Depending on the difference in karma appears the difference in worldly conditions of beings, such as gain and loss, and disgrace, blame and praise, happiness and misery. “
Thus, from a Buddhist point of view, our present mental, moral intellectual and temperamental differences are, for the most part, due to our own actions and tendencies, both past and present.
Although Buddhism attributes this variation to kamma as being the chief cause among a variety, it does not, however, assert that everything is due to kamma. The law of kamma, important as it is, is only one of the twenty-four conditions described in Buddhist Philosophy.
Refuting the erroneous view that “whatsoever fortune or misfortune experienced is all due to some previous action”, the Buddha said:
“So, then, according to this view owing to previous actions men will become murderers, thieves, unchaste, liars, slanderers, covetous, malicious and perverts. Thus, for those who fall back on the former deeds as the essential reason, there is neither the desire to do, nor effort to do, nor necessity to do this deed, or abstain from this deed. “
It was this important text, which states the belief that all physical circumstances and mental attitudes spring solely from past kamma that Buddha contradicted. If the present life is totally conditioned or wholly controlled by our past actions, then certainly kamma is tantamount to fatalism or determinism or predestination. If this were true, free will would be an absurdity. Life would be purely mechanistic, not much different from a machine. Being created by an Almighty God who controls our destinies and predetermines our future, or being produced by an irresistible kamma that completely determines our fate and controls our life’s course, independent of any free action on our part, is essentially the same. The only difference lies in the two words God and kamma. One could easily be substituted for the other, because the j ultimate operation of both forces would be identical.
Such a fatalistic doctrine is not the Buddhist law of kamma, Five Processes for Kamma Niyama.
According to Buddhism, there are five orders or processes (niyama) which operate in the physical and mental realms.
They are:
1. Utu Niyama –
physical inorganic order, e.g. seasonal phenomena of winds and rains. The unerring order of seasons, characteristic seasonal changes and events, causes of winds and rains, nature of heat, etc., all belong to this group.
2. Beeja Niyama –
order of germs and seeds (physical organic order), e.g. rice produced from rice-seed, sugary taste from sugar-cane or honey, peculiar characteristics of certain fruits, etc. The scientific theory of cells and genes and the physical similarity of twins may be ascribed to this order.
3. Kamma Niyama –
order of act and result, e.g., desirable and undesirable acts produce corresponding good and bad results. As surely as water seeks its own level so does kamma, given opportunity, produce its inevitable result, not in the form of a reward or punishment but as an innate sequence. This sequence of deed and effect is as natural and necessary as the way of the sun and the moon.
4. Dhamma Niyama –
order of the norm, e.g. the natural phenomena occurring at the advent of a Bodhisattva in his last birth. Gravitation and other similar laws of nature. The natural reason for being good and so forth, many be included in this group.
5. Citta Niyama –
order or mind or psychic law, e.g., processes of consciousness, arising and perishing of consciousness, constituents of consciousness, power of mind, etc. including telepathy, telaesthesia, retro-cognition, premonition, clairvoyance, clairaudience, thought-reading and such other psychic phenomena which are inexplicable to modern science.
Every mental or physical phenomenon could be explained by these all-embracing five orders or processes which are laws in themselves. kamma as such is only one of these five orders. Like all other natural laws they demand no lawgiver.
Of these five, the physical inorganic order and the order of the norm are more or less mechanistic, though they can be controlled to some extent by human ingenuity and the power of mind. For example, fire normally burns, and extreme cold freezes, but man has walked scatheless over fire and meditated naked on Himalayan snows; horticulturists have worked marvels with flowers and fruits; Yogis have performed levitation. Psychic law is equally mechanistic, but Buddhist training aims at control of mind, which ispossible by right understanding and skilful volition. The kamma law operates quite automatically and, when the kamma is powerful, man cannot interfere with its inexorable result though he may desire to do so; but here also right understanding and skilful volition can accomplish much and mould the future. Good kamma, persisted in, can thwart the reaping of bad kamma, or as some Western scholars prefer to say ‘action influence’, is certainly an intricate law whose working is fully comprehended only by a Buddha. The Buddhist aims at the final destruction of all kamma.
WHAT IS KAMMA?
The Pali term kamma literally means action or doing. Any kind of intentional action whether mental, verbal, or physical, is regarded as kamma. It covers all that is included in the phrase “thought, word and deed”. Generally speaking, all good and bad action constitutes kamma. In its ultimate sense kamma means all moral and immoral volition. Involuntary, unintentional or unconscious actions, though technically deeds, do not constitute kamma, because volition, the most important factor in determining kamma, is absent.
The Buddha says :
“I declare, 0 Bhikkhus, that volition is kamma, having willed one acts by body, speech, and thought. ” (Anguttara Nikaya)
Every volitional action of individuals, save those of the Buddhas and Arahants, is called kamma. The exception made in their case is because they are delivered from both good and evil; they have eradicated ignorance and craving, the roots of kamma.
“Destroyed are their germinal seeds (Khina beeja); selfish desires no longer grow,” states the Ratans Sutta of the Sutta nipata.
This does not mean that the Buddha and Arahantas are passive. They are tirelessly active in working for the real well being and happiness of all. Their deeds ordinarily accepted as good or moral, lack creative power as regards themselves, Understanding things as they truly are, they have finally shattered their cosmic fetters – the chain of cause and effect.
Kamma does not necessarily mean past actions. It embraces both past and present deeds. Hence in one sense, we are the result of what we were; we will be the result of what we are.
In another sense, it should be added, we are not totally the result of what we were; we will not absolutely be the result of what we arc. The present is no doubt the offspring of the past and is the present of the future, but the present is not always a true index of either the past or the future; so complex is the working of kamma.
It is this doctrine of kamma that the mother teaches her child when she says “Be good and you will be happy and we will love you; but if you are bad, you will be unhappy and we will not love you.” In short, kamma is the law of cause and effect in the ethical realm.
KAM MA AND VIPAKA
Kamma is action, and Vipaka, fruit or result, is its reaction.
Just as every object is accompanied by a shadow, even so every volitional activity is inevitably accompanied by its due effect.
kamma is like potential seed: Vipaka could be likened to the fruit arising from the tree – the effect or result. Anisamsa and Adinaya are the leaves, flowers and so forth that correspond to external differences such as health, sickness and poverty-these are inevitable consequences, which happen at the same time. Strictly speaking, both kamma and Vipaka pertain to the mind.
As kamma may be good or bad, so may Vipaka, – the fruit – is good or bad. As kamma is mental so Vipaka is mental (of the mind). It is experienced as happiness, bliss, unhappiness or misery, according to the nature of the kamma seed. Anisainsa are the concomitant advantages material things such as prosperity, health and longevity. When Vipaka’s concomitant material things are disadvantageous, they arc known as Adairaja, full of wretchedness, and appear as poverty, ugliness, disease, short life-span and so forth.
As we sow, we reap somewhere and sometime, in this life or in a future birth. What we reap today is what we have sown either in the present or in the past.
The Samyutta Nikaya states :
“According to the seed that’s sown, So is the fruit you reap there from, Doer of good will gather good,
Doer of evil, evil reaps,
Down is the seed and thou shalt taste The fruit there of”
Kamma is a law in itself, which operates in its own field without the intervention of any external, independent ruling agency.
Happiness and misery, which are the common lot of humanity, are the inevitable effects of causes. From a Buddhist point of view, they are not rewards and punishments, assigned by a supernatural, omniscient ruling power to a soul that has done good or evil. Theists, who attempt to explain everything in this and temporal life and in the eternal future life, ignoring a past, believe in a ‘postmortem’ justice, and may regard present happiness and misery as blessings and curses conferred on His creation by an omniscient and omnipotent Divine Ruler who sits in heaven above controlling the destinies of the human race. Buddhism, which emphatically denies such an Almighty, All merciful God-Creator and an arbitrarily created immortal soul, believes in natural law and justice which cannot be suspended by either an Almighty God or an All-compassionate Buddha. According to this natural law, acts bear their own rewards and punishments to the individual doer whether human justice finds out or not.
There are some who criticise thus: “So, you Buddhists, too, administer capitalistic opium to the people, saying: “You are born poor in this life on account of your past evil kamma. He is born rich on account of his good kamma. So, be satisfied with your humble lot; but do good to be rich in your next life. You are being oppressed now because of your past evil kamma. There is your destiny. Be humble and bear your sufferings patiently. Do good now. You can be certain of a better and happier life after death.”
The Buddhist doctrine of kamma does not expound such ridiculous fatalistic views. Nor does it vindicate a postmortem justice. The All-Merciful Buddha, who had no ulterior selfish motives, did not teach this law of kamma to protect the rich and comfort the poor by promising illusory happiness in an after-life.
While we are born to a state created by ourselves, yet by our own self-directed efforts there is every possibility for us to create new, favourable environments even here and now. Not only individually, but also, collectively, we are at liberty to create fresh kamma that leads either towards our progress or downfall in this very life.
According to the Buddhist doctrine of kamma, one is not always compelled by an ‘iron necessity’, for Kamma is neither fate, nor predestination imposed upon us by some mysterious unknown power to which we must helplessly submit ourselves. It is one’s own doing reacting on oneself, and so one has the possibility to divert the course of one’s kamma to some extent. How far one diverts it depends on oneself.
Is one bound to reap all that one has sown in just proportion?
The Buddha provides an answer:
“if anyone says that a man or woman must reap in this life according to his present deeds, in that case there is no religious life, nor is an opportunity, afforded for the entire extinction of sorrow But if anyone says that what a man or woman reaps in this and future lives accords with his or her deeds present and past, in that case there is a religious life, and an opportunity is afforded for the entire extinction of ‘a sorrow” (Anguttara Nikaya)
Although it is stated in the Dhammapada that “not in the sky, nor in mid-ocean, or entering a mountain cave is found that place on earth where one may escape from (the consequences of) an evil deed”, yet one is not bound to pay all the past arrears of one’s kamma. If such were the case emancipation would be impossibility. Eternal recurrence would be the unfortunate result.
Features
Ranking public services with AI — A roadmap to reviving institutions like SriLankan Airlines

Efficacy measures an organisation’s capacity to achieve its mission and intended outcomes under planned or optimal conditions. It differs from efficiency, which focuses on achieving objectives with minimal resources, and effectiveness, which evaluates results in real-world conditions. Today, modern AI tools, using publicly available data, enable objective assessment of the efficacy of Sri Lanka’s government institutions.
Among key public bodies, the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka emerges as the most efficacious, outperforming the Department of Inland Revenue, Sri Lanka Customs, the Election Commission, and Parliament. In the financial and regulatory sector, the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) ranks highest, ahead of the Securities and Exchange Commission, the Public Utilities Commission, the Telecommunications Regulatory Commission, the Insurance Regulatory Commission, and the Sri Lanka Standards Institution.
Among state-owned enterprises, the Sri Lanka Ports Authority (SLPA) leads in efficacy, followed by Bank of Ceylon and People’s Bank. Other institutions assessed included the State Pharmaceuticals Corporation, the National Water Supply and Drainage Board, the Ceylon Electricity Board, the Ceylon Petroleum Corporation, and the Sri Lanka Transport Board. At the lower end of the spectrum were Lanka Sathosa and Sri Lankan Airlines, highlighting a critical challenge for the national economy.
Sri Lankan Airlines, consistently ranked at the bottom, has long been a financial drain. Despite successive governments’ reform attempts, sustainable solutions remain elusive.
Globally, the most profitable airlines operate as highly integrated, technology-enabled ecosystems rather than as fragmented departments. Operations, finance, fleet management, route planning, engineering, marketing, and customer service are closely coordinated, sharing real-time data to maximise efficiency, safety, and profitability.
The challenge for Sri Lankan Airlines is structural. Its operations are fragmented, overly hierarchical, and poorly aligned. Simply replacing the CEO or senior leadership will not address these deep-seated weaknesses. What the airline needs is a cohesive, integrated organisational ecosystem that leverages technology for cross-functional planning and real-time decision-making.
The government must urgently consider restructuring Sri Lankan Airlines to encourage:
=Joint planning across operational divisions
=Data-driven, evidence-based decision-making
=Continuous cross-functional consultation
=Collaborative strategic decisions on route rationalisation, fleet renewal, partnerships, and cost management, rather than exclusive top-down mandates
Sustainable reform requires systemic change. Without modernised organisational structures, stronger accountability, and aligned incentives across divisions, financial recovery will remain out of reach. An integrated, performance-oriented model offers the most realistic path to operational efficiency and long-term viability.
Reforming loss-making institutions like Sri Lankan Airlines is not merely a matter of leadership change — it is a structural overhaul essential to ensuring these entities contribute productively to the national economy rather than remain perpetual burdens.
By Chula Goonasekera – Citizen Analyst
Features
Why Pi Day?

International Day of Mathematics falls tomorrow
The approximate value of Pi (π) is 3.14 in mathematics. Therefore, the day 14 March is celebrated as the Pi Day. In 2019, UNESCO proclaimed 14 March as the International Day of Mathematics.
Ancient Babylonians and Egyptians figured out that the circumference of a circle is slightly more than three times its diameter. But they could not come up with an exact value for this ratio although they knew that it is a constant. This constant was later named as π which is a letter in the Greek alphabet.
It was the Greek mathematician Archimedes (250 BC) who was able to find an upper bound and a lower bound for this constant. He drew a circle of diameter one unit and drew hexagons inside and outside the circle such that the sides of each hexagon touch the sides of the circle. In mathematics the circle passing through all vertices of a polygon is called a ‘circumcircle’ and the largest circle that fits inside a polygon tangent to all its sides is called an ‘incircle’. The total length of the smaller hexagon then becomes the lower bound of π and the length of the hexagon outside the circle is the upper bound. He realised that by increasing the number of sides of the polygon can make the bounds get closer to the value of Pi and increased the number of sides to 12,24,48 and 60. He argued that by increasing the number of sides will ultimately result in obtaining the original circle, thereby laying the foundation for the theory of limits. He ended up with the lower bound as 22/7 and the upper bound 223/71. He could not continue his research as his hometown Syracuse was invaded by Romans and was killed by one of the soldiers. His last words were ‘do not disturb my circles’, perhaps a reference to his continuing efforts to find the value of π to a greater accuracy.
Archimedes can be considered as the father of geometry. His contributions revolutionised geometry and his methods anticipated integral calculus. He invented the pulley and the hydraulic screw for drawing water from a well. He also discovered the law of hydrostatics. He formulated the law of levers which states that a smaller weight placed farther from a pivot can balance a much heavier weight closer to it. He famously said “Give me a lever long enough and a place to stand and I will move the earth”.
Mathematicians have found many expressions for π as a sum of infinite series that converge to its value. One such famous series is the Leibniz Series found in 1674 by the German mathematician Gottfried Leibniz, which is given below.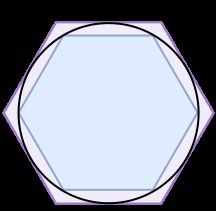
π = 4 ( 1 – 1/3 + 1/5 – 1/7 + 1/9 – ………….)
The Indian mathematical genius Ramanujan came up with a magnificent formula in 1910. The short form of the formula is as follows.
π = 9801/(1103 √8)
For practical applications an approximation is sufficient. Even NASA uses only the approximation 3.141592653589793 for its interplanetary navigation calculations.
It is not just an interesting and curious number. It is used for calculations in navigation, encryption, space exploration, video game development and even in medicine. As π is fundamental to spherical geometry, it is at the heart of positioning systems in GPS navigations. It also contributes significantly to cybersecurity. As it is an irrational number it is an excellent foundation for generating randomness required in encryption and securing communications. In the medical field, it helps to calculate blood flow rates and pressure differentials. In diagnostic tools such as CT scans and MRI, pi is an important component in mathematical algorithms and signal processing techniques.
This elegant, never-ending number demonstrates how mathematics transforms into practical applications that shape our world. The possibilities of what it can do are infinite as the number itself. It has become a symbol of beauty and complexity in mathematics. “It matters little who first arrives at an idea, rather what is significant is how far that idea can go.” said Sophie Germain.
Mathematics fans are intrigued by this irrational number and attempt to calculate it as far as they can. In March 2022, Emma Haruka Iwao of Japan calculated it to 100 trillion decimal places in Google Cloud. It had taken 157 days. The Guinness World Record for reciting the number from memory is held by Rajveer Meena of India for 70000 decimal places over 10 hours.
Happy Pi Day!
The author is a senior examiner of the International Baccalaureate in the UK and an educational consultant at the Overseas School of Colombo.
by R N A de Silva
Features
Sheer rise of Realpolitik making the world see the brink

 The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
As matters stand, there seems to be no credible evidence that the Indian state was aware of the impending torpedoing of the Iranian vessel but these acerbic-tongued politicians of Sri Lanka’s South would have the local public believe that the tragedy was triggered with India’s connivance. Likewise, India is accused of ‘embroiling’ Sri Lanka in the incident on account of seemingly having prior knowledge of it and not warning Sri Lanka about the impending disaster.
It is plain that a process is once again afoot to raise anti-India hysteria in Sri Lanka. An obligation is cast on the Sri Lankan government to ensure that incendiary speculation of the above kind is defeated and India-Sri Lanka relations are prevented from being in any way harmed. Proactive measures are needed by the Sri Lankan government and well meaning quarters to ensure that public discourse in such matters have a factual and rational basis. ‘Knowledge gaps’ could prove hazardous.
Meanwhile, there could be no doubt that Sri Lanka’s sovereignty was violated by the US because the sinking of the Iranian vessel took place in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While there is no international decrying of the incident, and this is to be regretted, Sri Lanka’s helplessness and small player status would enable the US to ‘get away with it’.
Could anything be done by the international community to hold the US to account over the act of lawlessness in question? None is the answer at present. This is because in the current ‘Global Disorder’ major powers could commit the gravest international irregularities with impunity. As the threadbare cliché declares, ‘Might is Right’….. or so it seems.
Unfortunately, the UN could only merely verbally denounce any violations of International Law by the world’s foremost powers. It cannot use countervailing force against violators of the law, for example, on account of the divided nature of the UN Security Council, whose permanent members have shown incapability of seeing eye-to-eye on grave matters relating to International Law and order over the decades.
The foregoing considerations could force the conclusion on uncritical sections that Political Realism or Realpolitik has won out in the end. A basic premise of the school of thought known as Political Realism is that power or force wielded by states and international actors determine the shape, direction and substance of international relations. This school stands in marked contrast to political idealists who essentially proclaim that moral norms and values determine the nature of local and international politics.
While, British political scientist Thomas Hobbes, for instance, was a proponent of Political Realism, political idealism has its roots in the teachings of Socrates, Plato and latterly Friedrich Hegel of Germany, to name just few such notables.
On the face of it, therefore, there is no getting way from the conclusion that coercive force is the deciding factor in international politics. If this were not so, US President Donald Trump in collaboration with Israeli Rightist Premier Benjamin Natanyahu could not have wielded the ‘big stick’, so to speak, on Iran, killed its Supreme Head of State, terrorized the Iranian public and gone ‘scot-free’. That is, currently, the US’ impunity seems to be limitless.
Moreover, the evidence is that the Western bloc is reuniting in the face of Iran’s threats to stymie the flow of oil from West Asia to the rest of the world. The recent G7 summit witnessed a coming together of the foremost powers of the global North to ensure that the West does not suffer grave negative consequences from any future blocking of western oil supplies.
Meanwhile, Israel is having a ‘free run’ of the Middle East, so to speak, picking out perceived adversarial powers, such as Lebanon, and militarily neutralizing them; once again with impunity. On the other hand, Iran has been bringing under assault, with no questions asked, Gulf states that are seen as allying with the US and Israel. West Asia is facing a compounded crisis and International Law seems to be helplessly silent.
Wittingly or unwittingly, matters at the heart of International Law and peace are being obfuscated by some pro-Trump administration commentators meanwhile. For example, retired US Navy Captain Brent Sadler has cited Article 51 of the UN Charter, which provides for the right to self or collective self-defence of UN member states in the face of armed attacks, as justifying the US sinking of the Iranian vessel (See page 2 of The Island of March 10, 2026). But the Article makes it clear that such measures could be resorted to by UN members only ‘ if an armed attack occurs’ against them and under no other circumstances. But no such thing happened in the incident in question and the US acted under a sheer threat perception.
Clearly, the US has violated the Article through its action and has once again demonstrated its tendency to arbitrarily use military might. The general drift of Sadler’s thinking is that in the face of pressing national priorities, obligations of a state under International Law could be side-stepped. This is a sure recipe for international anarchy because in such a policy environment states could pursue their national interests, irrespective of their merits, disregarding in the process their obligations towards the international community.
Moreover, Article 51 repeatedly reiterates the authority of the UN Security Council and the obligation of those states that act in self-defence to report to the Council and be guided by it. Sadler, therefore, could be said to have cited the Article very selectively, whereas, right along member states’ commitments to the UNSC are stressed.
However, it is beyond doubt that international anarchy has strengthened its grip over the world. While the US set destabilizing precedents after the crumbling of the Cold War that paved the way for the current anarchic situation, Russia further aggravated these degenerative trends through its invasion of Ukraine. Stepping back from anarchy has thus emerged as the prime challenge for the world community.
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoWinds of Change:Geopolitics at the crossroads of South and Southeast Asia
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoProf. Dunusinghe warns Lanka at serious risk due to ME war
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoRoyal start favourites in historic Battle of the Blues
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoThe 147th Royal–Thomian and 175 Years of the School by the Sea
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoHistoric address by BASL President at the Supreme Court of India
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoSeven decades of sartorial excellence: The legacy of Linton Master Tailors in Kandy
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoCEBEU warns of operational disruptions amid uncertainty over CEB restructuring




















