Business
Bridging conservation and livelihoods: Addressing the Human-Elephant Conflict in Sri Lanka on World Elephant Day
By Ruwan Samaraweera
Written ahead of World Elephant Day, observed on 12 August 2023.
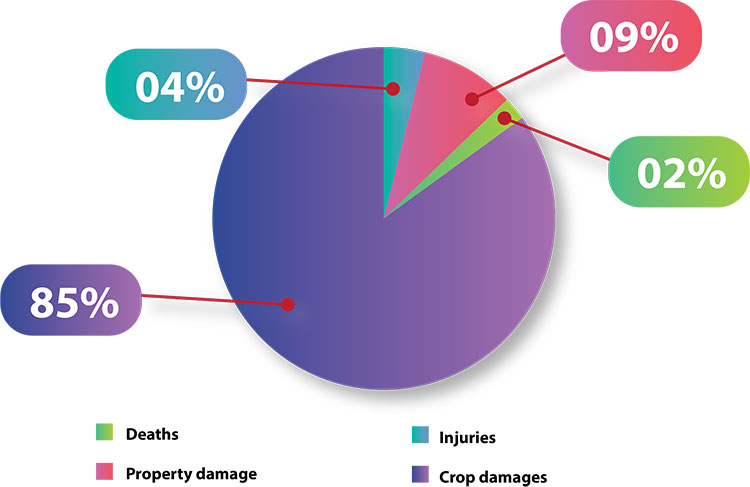
On World Elephant Day, attention turns to the unique challenges faced by Sri Lanka in the realm of human-elephant conflict (HEC). HEC’s escalating toll paints a stark reality. Human communities endure property damage, crop loss, and tragic fatalities, amplifying poverty and socio-economic instability. In 2022, as per the Department of Wildlife Conservation (DWC), Sri Lanka documented a total of 145 human fatalities resulting from HEC. Simultaneously, elephants face habitat loss, injuries, and mortality due to retaliatory killings and encounters with human settlements. DWC reported a substantial rise in elephant mortality, reaching a peak with a recorded total of 433 deaths in 2022. Therefore, the urgent need for implementing effective solutions to minimise HEC in the country becomes paramount.
Understanding the Conflict
 The HEC is one of the widespread environmental issues with severe socio-economic and political implications in Sri Lanka. It arises from numerous reasons, wherein the competition for resources and land between humans and elephants being the most prominent. Rapid urbanisation, encroachment into elephant habitats, conversion of forests for agriculture, and other infrastructure development projects like road infrastructure have disrupted the elephants’ traditional migration patterns and fragmented their habitats. Consequently, elephants often venture into human settlements in search of sustenance, leading to conflicts that endanger both elephants’ and human lives.
The HEC is one of the widespread environmental issues with severe socio-economic and political implications in Sri Lanka. It arises from numerous reasons, wherein the competition for resources and land between humans and elephants being the most prominent. Rapid urbanisation, encroachment into elephant habitats, conversion of forests for agriculture, and other infrastructure development projects like road infrastructure have disrupted the elephants’ traditional migration patterns and fragmented their habitats. Consequently, elephants often venture into human settlements in search of sustenance, leading to conflicts that endanger both elephants’ and human lives.
Sumanadasa, a farmer in Galgamuwa, shares his experience of frequent elephant raids on their crop lands. He says, “As a farmer, my family depends on the crops we cultivate for our livelihood. However, the constant raids by elephants have taken a toll on our lives. We wake up each morning with anxiety, not knowing if our fields will be destroyed overnight. Our hard work and investment go in vain as elephants trample and devour our crops. It has become a struggle to provide for our family and maintain a sustainable income.”
These heart-wrenching stories highlight the profound impact of the HEC on individuals and communities. Beyond the economic losses, the emotional trauma and loss of human lives are immeasurable. The alarming increase in human and elephant fatalities resulting from HEC in Sri Lanka underscores the gravity of the situation. The average annual human death rate due to HEC increased by approximately 42% from 1992 to 2021, with the 2021 figure reaching 142 deaths. Despite fluctuations, the number of HEC-caused human deaths has consistently exceeded 100 per year over the last three years, resulting in a total of 2,111 human and 5,954 elephant casualties within the last 30 years. Apart from that, as already mentioned, crop damages emerge as a pervasive and severe issue. An IPS study revealed that among the crops grown in HEC-prone areas, paddy is the most vulnerable crop for elephant attacks, following coconut and banana. Furthermore, farmers have altered their cropping seasons due to this wild elephant risk.
Recognising the urgency of addressing the HEC, Sri Lanka has undertaken various policy initiatives and conservation efforts. Some of these are institutionally arranged measures while some are voluntary adjustments by affected communities. The DWC plays a crucial role in mitigating conflicts, implementing institutionally arranged measures such as creating elephant corridors, elephant drives, thunder flashes distribution, habitat enrichments and installing electric fences to reduce human-elephant interactions. Additionally, community-based conservation projects involving local communities in decision-making have shown promising results in promoting peaceful coexistence in some parts of the country. As a multifaceted approach to mitigating HEC, DWC has been implementing the “GajaMituro‟ programme since 2008. Under this, the DWC launched the aforementioned mitigating measures in 58 Divisional Secretariat Divisions (DSD) of 18 Districts. Similarly, residents in affected areas practice numerous voluntary measures to deter problems from elephants. Some examples of voluntary measures include erecting watch huts, creating noise (e.g., firing thunder flashes, shouting), establishing biological fences, and using lighting methods such as fires, kerosene lamps, flares, and flashlights to frighten and chase away the elephants. However, none of the mitigation measures has given a perfect solution due to various limitations. For instance, some elephants develop adaptive behaviours to actions such that thunder flashes, thus making those no longer effective against them.
Hence, to effectively manage the HEC, innovative solutions are imperative, and the government, academia, and other interested stakeholders continue to actively pursue innovative approaches and optimal strategies to effectively tackle the issue of HEC in Sri Lanka. Technology-driven approaches, including using infrared cameras, drones, sensor-based systems, and satellite imagery to detect habitat monitoring and elephant movements and then using mobile communication systems to alert nearby communities in real-time (early warning system), can help prevent conflicts. Through educational programmes in schools and community outreach initiatives, a sense of responsibility can be instilled while highlighting innovative market-based solutions like insurance. An IPS study found that insurance as a market-based solution can deliver promising results. These solutions can be complemented by agro-ecological practices such as cultivating elephant-resistant crops, bee-fencing and establishing community-managed buffer zones around protected areas.
Conclusion
As World Elephant Day serves as a powerful global platform for raising awareness on elephant conservation, Sri Lanka can capitalise on this occasion to promote understanding, empathy, and conservation values within local communities.
It is crucial to acknowledge that no single solution can entirely address the complexities of the HEC issue, given its regional variations, changes in elephant behaviour, and diverse human activities. Therefore, adopting a holistic approach that combines suitable traditional methods alongside innovative strategies, involving local communities, and considering the conflict’s ecological, economic, and social aspects becomes essential for effective and sustainable HEC mitigation. Collaboration among government agencies, conservation organisations, and local communities becomes paramount in achieving a harmonious coexistence where elephants roam freely, and humans thrive.
By adopting this comprehensive approach, Sri Lanka can strive towards a future where both elephants and humans coexist peacefully, safeguarding the well-being of these majestic creatures for generations to come. World Elephant Day serves as a poignant reminder that collective action and shared responsibility are crucial in preserving the rich biodiversity and cultural heritage that define this island nation.
Link to blog: https://www.ips.lk/talkingeconomics/2023/08/10/bridging-conservation-and-livelihoods-addressing-the-human-elephant-conflict-in-sri-lanka-on-world-elephant-day/
Ruwan Samaraweera is a Research Officer at IPS with a background in entrepreneurial agriculture. He holds a Bachelor’s in Export Agriculture from Uva Wellassa University of Sri Lanka. His research interests are environmental economics, agricultural economics, macroeconomic policy and planning, labour and migration, and poverty and development policy. (Talk to Ruwan – ruwan@ips.lk)
Business
Binance signals a maturing Crypto pitch in Sri Lanka
Frames crypto investing as a ‘measured journey rooted in knowledge and security’
In an industry often characterised by velocity, volatility and viral marketing, Binance’s latest community activation in Sri Lanka suggested a deliberate recalibration of its investor messaging.At its #BinanceHODLove event held at One Galle Face Mall, the world’s largest crypto exchange by trading volume chose a Valentine’s-themed slogan that stood out for its restraint: “Real Love Doesn’t Rush, Neither Should Crypto: A Valentine’s Message for Smart Investors.”
Behind the seasonal branding lies a more strategic theme – one that aligns with the crypto industry’s post-cycle shift toward compliance, literacy and risk awareness.
Sri Lanka’s retail investor base has demonstrated periodic interest in digital assets, particularly during phases of currency pressure and global crypto rallies. Yet market participation has also exposed gaps in financial literacy and susceptibility to high-yield promises.
Binance’s messaging at the event leaned heavily into investor caution. Participants were reminded to scrutinise unsolicited offers, avoid guarantees of quick returns, and protect sensitive information such as private keys and passwords. In a market where informal crypto schemes have occasionally surfaced, such emphasis reflects reputational risk management as much as community engagement.
The company also spotlighted Binance Academy, its educational platform, positioning knowledge acquisition as foundational to long-term participation in blockchain ecosystems.
While the event featured raffles and consumer electronics giveaways to drive footfall, the broader objective appeared to be brand consolidation at the grassroots level. Physical activations in high-traffic urban centres suggested a hybrid strategy: digital scale complemented by localised trust-building.
For a global exchange operating in increasingly scrutinised regulatory environments, nurturing responsible retail participation is both a defensive and expansionary move. By framing crypto investing as a “measured journey rooted in knowledge and security,” Binance is aligning itself with the industry’s pivot toward sustainability rather than speculative exuberance.
The subtext of the campaign was clear: growth in emerging markets like Sri Lanka will depend less on price momentum and more on credibility.
Binance’s Valentine’s message, therefore, may be less about romance and more about risk calibration. In that sense, the slogan captured a broader industry truth: endurance, not impulse, will define the next phase of digital asset adoption.
By Sanath Nanayakkare
Business
Unlisted tax jitters frizzle CSE rally; analysts flag spillover fears

Morning gains on the Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE) evaporated sharply in afternoon trade yesterday, as a wave of nervous selling swept through the market triggered by speculation that the government is mooting a fresh 10-15 percent tax on unlisted corporates. Although the proposed levy is currently targeted at entities outside the CSE purview, market participants grew wary that the measure could signal a broader shift in fiscal policy, stoking fears of future tax hikes that may eventually engulf listed companies and dent corporate earnings.
Amid those developments, the turnover was capped at a mere Rs 369 million despite fourteen crossings.
The top seven crossings mainly contributed to the turnover were Commercial Bank 1.60 million shares crossed to the tune of Rs 359.7 million and its share price traded at Rs 223, Renuka Foods 2.7 million shares crossed to the tune of Rs 179.6 million and its share price traded at Rs 63.50, LOLC Holdings 300,000 shares crossed to the tune of Rs 171.9 million and its share price traded at Rs 573, Sampath Bank 821,000 shares crossed to the tune of Rs 132 million and its share price traded at Rs 161, Commercial Bank (Non-Voting) 484,000 shares crossed to the tune of Rs 98.9 million and its share price traded at Rs 204, Sierra Cables two million shares crossed to the tune of Rs 69.6 million and its share price traded at Rs 34.80 and Citizens Developments Business Bank (Non-Voting) 200,000 shares crossed to the tune of Rs 62.9 million and its share price traded at Rs 324.
In the retail market top seven companies that have mainly contributed to the turnover were Renuka Agri Rs 1.14 billion (82.4 million shares traded), Softlogic Finance Rs 653.9 million (115 million shares traded), Sampath Bank Rs 270.8 million (1.65 million shares traded), Softlogic Capital Rs 230 million (19.3 million shares traded), JKH Rs 201 million (nine million shares traded) ,LOLC Holdings Rs 171.9 million (297,000 shares traded) and LMF Rs 171 million (1.8 million shares traded). During the day 369 million shares volumes changed hands in 39059 transactions.
It is said that banking and agriculture related companies performed well. In the banking sector Sampath Bank and Commercial Bank performed well. Further manufacturing sector especially JKH also significantly active in the market.
By Hiran H Senewiratne
Business
ComBank loan book grows by Rs. 541bn to top Rs. 2tn

The Commercial Bank of Ceylon achieved another performance milestone in 2025, becoming the first private sector bank in the country to expand its loan book beyond Rs. 2 Tn., with a growth of Rs. 541 Bn. over 12 months at a monthly average of over Rs. 45 Bn., demonstrating its commitment to national economic resurgence.
Recording the highest annual loan growth in absolute terms in the history of the institution, the Bank said gross loans and advances for the year ending 31st December 2025 grew by 36.37% to Rs. 2.028 Tn., taking total assets to Rs. 3.258 Tn. This reflected an increase of Rs. 468 Bn. or 16.78% and demonstrated more than double the growth recorded in 2024. The Bank’s net assets value per share improved to Rs. 198.30 from Rs. 170.94 at end 2024.
Deposits grew by 16.65% or Rs. 372 Bn. over the 12 months to end the year at Rs. 2.6 Tn., reflecting an average deposit growth of over Rs. 30 Bn. per month despite relatively lower interest rates, the Bank said. The CASA ratio of the Bank, which is considered to be the industry’s best, stood at 39.65% from 38.07% as at 31st December 2024.
Sharhan Muhseen, Chairman of Commercial Bank said: “We remain focused on the fundamentals that sustain shareholder value: earnings resilience, balance sheet strength, disciplined risk management and a strategy that is responsive to evolving customer and market needs. Our 2025 performance affirms the value of that focus.”
Sanath Manatunge, Managing Director/CEO of Commercial Bank said: “In 2025, we proved that scale and discipline can move together, growing lending and accelerating digital activity while strengthening asset quality and balance sheet resilience.”
In a filing with the Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE) the Bank said it recorded gross income of Rs. 354.81 Bn. for the year ending 31st December 2025 reflecting growth of 13.70% over the normalised figure for 2024, after adjusting for the impacts of restructuring of Sri Lanka International Sovereign Bonds (SLISBs) accommodated in that year, in order to avoid potential distortion of growth figures. Net gains / (losses) from derecognition of financial assets in the Income Statement for 2024 (as reported) included a derecognition loss on restructuring of SLISBs amounting to Rs. 45.108 Bn.
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoWhy does the state threaten Its people with yet another anti-terror law?
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoReconciliation, Mood of the Nation and the NPP Government
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoVictor Melder turns 90: Railwayman and bibliophile extraordinary
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoLOVEABLE BUT LETHAL: When four-legged stars remind us of a silent killer
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoVictor, the Friend of the Foreign Press
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoSeeing is believing – the silent scale behind SriLankan’s ground operation
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoBathiya & Santhush make a strategic bet on Colombo
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBarking up the wrong tree













