Features
Birth of Bangladesh
By Jayantha Somasundaram
“My greatest strength is the love for my people,
My greatest weakness is that I love them too much.”
– Sheikh Mujibur Rahman
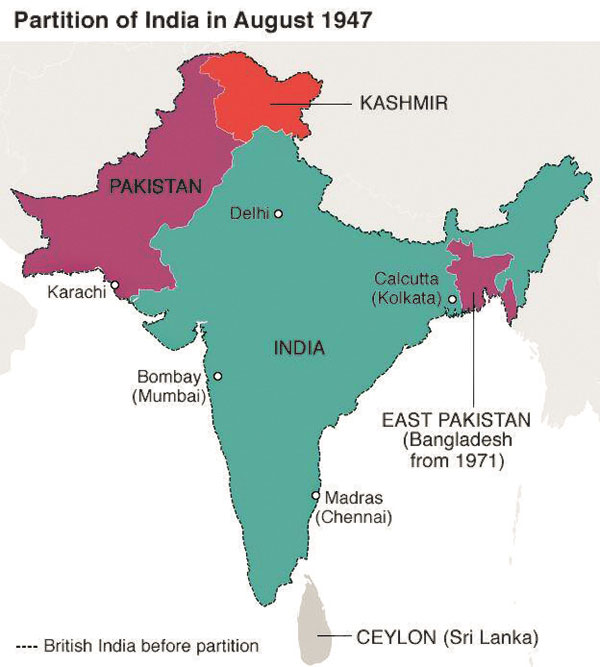
On December 16, 1971, Lieutenant General Amir Abdullah Khan Niazi, Pakistan’s Eastern Commander, surrendered to India’s Lieutenant General Jagjit Singh Aurora, bringing to an end the war that completed the bifurcation of Pakistan, in order to create the new state of Bangladesh. This war of independence had been a brutally bitter conflict that had lasted almost a year.
When dominion status was granted in August 1947, Pakistan was made up of two enclaves, separated by a thousand miles of Indian territory. Muslim-majority East Bengal made up East Pakistan while the other Muslim-majority areas in the west comprised West Pakistan. In 1971 East Pakistan with 73 million had a larger population than West Pakistan which had 57 million.
At the end of over a decade of military rule in Pakistan, General Yahya Khan held parliamentary elections in December 1970. The poll resulted in the Awami League securing nearly all the seats in East Pakistan. The All Pakistan Awami (People’s) League was founded in 1949 by Bengali nationalists as a counter to the Muslim League which sought centralisation of political power and the imposition of Urdu as the national language. The Awami League had gone to the election on a Six Point Plan to gain Bengali control of everything except defence and foreign affairs.
 However, overlooking the claims of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, the leader of the Awami League, President Yahya Khan appointed Zulficar Ali Bhutto as Prime Minister, and refused to summon the newly elected parliament, the National Assembly of Pakistan.
However, overlooking the claims of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, the leader of the Awami League, President Yahya Khan appointed Zulficar Ali Bhutto as Prime Minister, and refused to summon the newly elected parliament, the National Assembly of Pakistan.
In response, Mujibur Rahman on March 7, 1971 at a public rally in Dacca, attended by two million Bengalis, called for civil disobedience, armed resistance and Bengali independence. The result was a civil disobedience campaign which took the form of a general strike, non-payment of taxes, closure of schools and courts; and for the next three weeks East Bengal was a de facto independent state ruled by the Awami League.
Sahabzada Lieutenant General Yaqub Ali Khan was commander of the Pakistan Army’s Eastern Command in Dacca and Governor of East Pakistan. He opposed the use of military force to settle the Bengali issue and when ordered to do so, he refused and resigned his position. He was replaced by Lieutenant General Tikka Khan. His use of force led to criticism even in West Pakistan and in August he was recalled.
Independence declared
On March 25 Mujibur declared Bangladesh independent. That night the West Pakistani armed forces attacked the police barracks at Rajarbagh and the East Pakistan Rifles, a 15,000 strong paramilitary force based in Dacca. Debasish Roy Chowdhury in The Asia Times (23/6/05) claims that, “The military now decided enough was enough. At a meeting of the military top brass, Yahya declared: Kill three million of them and the rest will eat out of our hands.” Islamabad responded with Operation Searchlight on 26, a lightning military move aimed at taking all major Eastern cities. It included the arrest of Sheikh Mujibur who was thereafter imprisoned in Karachi in the West.
In addition, Islamabad banned the Awami League and arrested its leaders. The Awami League described it as genocide, targeting in particular their leadership and supporters as well as Bengali intellectuals and the destruction of their economy.
The New York Times
reported on March 30, “In two days and nights of shelling by the Pakistan Army perhaps seven thousand Bengalis died in Dacca alone. The Army which attacked without warning with American-supplied M24 Chaffee tanks destroyed large parts of the City.” A subsequent report published in the Times on April 14 said, “The Central Government forces killed East PakistanArmy officers and soldiers who were unable to break out and join the guerrillas when the Army offensive began on 25th March.”
Responding to the claim that Ceylon provided refuelling facilities for Pakistani military planes carrying troops to the East to suppress the uprising, Leslie Goonewardena, Minister of Communications stated, “in March 1971 sixteen east-bound and fifteen west-bound Pakistan Air Force planes touched down at the Bandaranaike International Airport.”
Provisional Government established
The Provisional Government of Bangladesh was established on April 17 when the 469 Bengali parliamentarians elected in December 1970, to the National and Provincial assemblies, formed the Constituent Assembly of Bangladesh and drew up an interim constitution. In the absence of Mujibur, Syed Nazrul Islam was appointed Acting President. In the months that followed it is alleged that anything up to three million Bengalis were killed, including students, intellectuals, politicians and Hindus in what is referred to as the 1971 Bangladesh Genocide. The post war Hamoodur Rahman Commission appointed by Islamabad concluded that there were only 26,000 civilian deaths.
Anthony Mascarenhas was a Karachi-based reporter who was one of eight Pakistani journalists given a tour of the East by the Government. Appalled by what he learnt he fled to London with his family and broke his story in an article published in The Sunday Times on June 13. Under the headline ‘Genocide’ it began with: “Abdul Bari had run out of luck. Like thousands of other people in East Bengal, he had made the mistake – the fatal mistake – of running within sight of a Pakistani patrol. He was 24 years old, a slight man surrounded by soldiers. He was trembling because he was about to be shot.”
“…I have heard the screams of men bludgeoned to death in the compound of the Circuit House (civil administrative headquarters) in Comilla. I have seen truckloads of other human targets and those who had the humanity to try to help them hauled off ‘for disposal’ under the cover of darkness and curfew…I have witnessed the brutality of ‘kill and burn missions’ as the army units, after clearing out the rebels, pursued the pogrom in the towns and villages. I have seen whole villages devastated by ‘punitive action’. And in the officer’s mess at night I have listened incredulously as otherwise brave and honourable men proudly chewed over the day’s kill. ‘How many did you get?’ The answers are seared in my memory.”
Ten years ago on the anniversary of these events the BBC said: “There is little doubt that Mascarenhas’ reportage played its part in ending the war. It helped turn world opinion against Pakistan and encouraged India to play a decisive role….In the first of many notorious war crimes, soldiers attacked Dhaka University, lining up and executing students and professors….Their campaign of terror then moved into the countryside, where they battled local troops who had mutinied.”
In an article titled ‘Pakistan: The Ravaging of Golden Bengal’ on August 2, Time reported that “In Dacca, where soldiers set sections of the Old City ablaze with flamethrowers and then machine-gunned thousands as they tried to escape the cordon of fire, nearly 25 blocks have been bulldozed clear, leaving open areas set incongruously amid jam-packed slums.” It quoted a senior US official as saying, “It is the most incredible, calculated thing since the days of the Nazis in Poland.”
Archer Blood, US Consul-General in Dacca criticised Washington for supporting Islamabad, in an official cable subsequently known as the Blood Telegram. “Our government has failed to denounce the suppression of democracy,” the telegram said. “Our government has failed to denounce atrocities….Our government has evidenced what many will consider moral bankruptcy.”
By April 10, the West Pakistani Army had control of Dacca and Operation Searchlight, and the military control of all of Bangladesh by Pakistan was successfully completed in less than two months. In the civil war that ensued 300,000 Bengalis died. And by August there were seven million Bangladeshi refugees in India.
(To be continued)
Features
The call for review of reforms in education: discussion continues …

 The hype around educational reforms has abated slightly, but the scandal of the reforms persists. And in saying scandal, I don’t mean the error of judgement surrounding a misprinted link of an online dating site in a Grade 6 English language text book. While that fiasco took on a nasty, undeserved attack on the Minister of Education and Prime Minister Harini Amarasuriya, fundamental concerns with the reforms have surfaced since then and need urgent discussion and a mechanism for further analysis and action. Members of Kuppi have been writing on the reforms the past few months, drawing attention to the deeply troubling aspects of the reforms. Just last week, a statement, initiated by Kuppi, and signed by 94 state university teachers, was released to the public, drawing attention to the fundamental problems underlining the reforms https://island.lk/general-educational-reforms-to-what-purpose-a-statement-by-state-university-teachers/. While the furore over the misspelled and misplaced reference and online link raged in the public domain, there were also many who welcomed the reforms, seeing in the package, a way out of the bottle neck that exists today in our educational system, as regards how achievement is measured and the way the highly competitive system has not helped to serve a population divided by social class, gendered functions and diversities in talent and inclinations. However, the reforms need to be scrutinised as to whether they truly address these concerns or move education in a progressive direction aimed at access and equity, as claimed by the state machinery and the Minister… And the answer is a resounding No.
The hype around educational reforms has abated slightly, but the scandal of the reforms persists. And in saying scandal, I don’t mean the error of judgement surrounding a misprinted link of an online dating site in a Grade 6 English language text book. While that fiasco took on a nasty, undeserved attack on the Minister of Education and Prime Minister Harini Amarasuriya, fundamental concerns with the reforms have surfaced since then and need urgent discussion and a mechanism for further analysis and action. Members of Kuppi have been writing on the reforms the past few months, drawing attention to the deeply troubling aspects of the reforms. Just last week, a statement, initiated by Kuppi, and signed by 94 state university teachers, was released to the public, drawing attention to the fundamental problems underlining the reforms https://island.lk/general-educational-reforms-to-what-purpose-a-statement-by-state-university-teachers/. While the furore over the misspelled and misplaced reference and online link raged in the public domain, there were also many who welcomed the reforms, seeing in the package, a way out of the bottle neck that exists today in our educational system, as regards how achievement is measured and the way the highly competitive system has not helped to serve a population divided by social class, gendered functions and diversities in talent and inclinations. However, the reforms need to be scrutinised as to whether they truly address these concerns or move education in a progressive direction aimed at access and equity, as claimed by the state machinery and the Minister… And the answer is a resounding No.
The statement by 94 university teachers deplores the high handed manner in which the reforms were hastily formulated, and without public consultation. It underlines the problems with the substance of the reforms, particularly in the areas of the structure of education, and the content of the text books. The problem lies at the very outset of the reforms, with the conceptual framework. While the stated conceptualisation sounds fancifully democratic, inclusive, grounded and, simultaneously, sensitive, the detail of the reforms-structure itself shows up a scandalous disconnect between the concept and the structural features of the reforms. This disconnect is most glaring in the way the secondary school programme, in the main, the junior and senior secondary school Phase I, is structured; secondly, the disconnect is also apparent in the pedagogic areas, particularly in the content of the text books. The key players of the “Reforms” have weaponised certain seemingly progressive catch phrases like learner- or student-centred education, digital learning systems, and ideas like moving away from exams and text-heavy education, in popularising it in a bid to win the consent of the public. Launching the reforms at a school recently, Dr. Amarasuriya says, and I cite the state-owned broadside Daily News here, “The reforms focus on a student-centered, practical learning approach to replace the current heavily exam-oriented system, beginning with Grade One in 2026 (https://www.facebook.com/reel/1866339250940490). In an address to the public on September 29, 2025, Dr. Amarasuriya sings the praises of digital transformation and the use of AI-platforms in facilitating education (https://www.facebook.com/share/v/14UvTrkbkwW/), and more recently in a slightly modified tone (https://www.dailymirror.lk/breaking-news/PM-pledges-safe-tech-driven-digital-education-for-Sri-Lankan-children/108-331699).
The idea of learner- or student-centric education has been there for long. It comes from the thinking of Paulo Freire, Ivan Illyich and many other educational reformers, globally. Freire, in particular, talks of learner-centred education (he does not use the term), as transformative, transformative of the learner’s and teacher’s thinking: an active and situated learning process that transforms the relations inhering in the situation itself. Lev Vygotsky, the well-known linguist and educator, is a fore runner in promoting collaborative work. But in his thought, collaborative work, which he termed the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) is processual and not goal-oriented, the way teamwork is understood in our pedagogical frameworks; marks, assignments and projects. In his pedagogy, a well-trained teacher, who has substantial knowledge of the subject, is a must. Good text books are important. But I have seen Vygotsky’s idea of ZPD being appropriated to mean teamwork where students sit around and carry out a task already determined for them in quantifying terms. For Vygotsky, the classroom is a transformative, collaborative place.
But in our neo liberal times, learner-centredness has become quick fix to address the ills of a (still existing) hierarchical classroom. What it has actually achieved is reduce teachers to the status of being mere cogs in a machine designed elsewhere: imitative, non-thinking followers of some empty words and guide lines. Over the years, this learner-centred approach has served to destroy teachers’ independence and agency in designing and trying out different pedagogical methods for themselves and their classrooms, make input in the formulation of the curriculum, and create a space for critical thinking in the classroom.
Thus, when Dr. Amarasuriya says that our system should not be over reliant on text books, I have to disagree with her (https://www.newsfirst.lk/2026/01/29/education-reform-to-end-textbook-tyranny ). The issue is not with over reliance, but with the inability to produce well formulated text books. And we are now privy to what this easy dismissal of text books has led us into – the rabbit hole of badly formulated, misinformed content. I quote from the statement of the 94 university teachers to illustrate my point.
“The textbooks for the Grade 6 modules . . . . contain rampant typographical errors and include (some undeclared) AI-generated content, including images that seem distant from the student experience. Some textbooks contain incorrect or misleading information. The Global Studies textbook associates specific facial features, hair colour, and skin colour, with particular countries and regions, and refers to Indigenous peoples in offensive terms long rejected by these communities (e.g. “Pygmies”, “Eskimos”). Nigerians are portrayed as poor/agricultural and with no electricity. The Entrepreneurship and Financial Literacy textbook introduces students to “world famous entrepreneurs”, mostly men, and equates success with business acumen. Such content contradicts the policy’s stated commitment to “values of equity, inclusivity and social justice” (p. 9). Is this the kind of content we want in our textbooks?”
Where structure is concerned, it is astounding to note that the number of subjects has increased from the previous number, while the duration of a single period has considerably reduced. This is markedly noticeable in the fact that only 30 hours are allocated for mathematics and first language at the junior secondary level, per term. The reduced emphasis on social sciences and humanities is another matter of grave concern. We have seen how TV channels and YouTube videos are churning out questionable and unsubstantiated material on the humanities. In my experience, when humanities and social sciences are not properly taught, and not taught by trained teachers, students, who will have no other recourse for related knowledge, will rely on material from controversial and substandard outlets. These will be their only source. So, instruction in history will be increasingly turned over to questionable YouTube channels and other internet sites. Popular media have an enormous influence on the public and shapes thinking, but a well formulated policy in humanities and social science teaching could counter that with researched material and critical thought. Another deplorable feature of the reforms lies in provisions encouraging students to move toward a career path too early in their student life.
The National Institute of Education has received quite a lot of flak in the fall out of the uproar over the controversial Grade 6 module. This is highlighted in a statement, different from the one already mentioned, released by influential members of the academic and activist public, which delivered a sharp critique of the NIE, even while welcoming the reforms (https://ceylontoday.lk/2026/01/16/academics-urge-govt-safeguard-integrity-of-education-reforms). The government itself suspended key players of the NIE in the reform process, following the mishap. The critique of NIE has been more or less uniform in our own discussions with interested members of the university community. It is interesting to note that both statements mentioned here have called for a review of the NIE and the setting up of a mechanism that will guide it in its activities at least in the interim period. The NIE is an educational arm of the state, and it is, ultimately, the responsibility of the government to oversee its function. It has to be equipped with qualified staff, provided with the capacity to initiate consultative mechanisms and involve panels of educators from various different fields and disciplines in policy and curriculum making.
In conclusion, I call upon the government to have courage and patience and to rethink some of the fundamental features of the reform. I reiterate the call for postponing the implementation of the reforms and, in the words of the statement of the 94 university teachers, “holistically review the new curriculum, including at primary level.”
(Sivamohan Sumathy was formerly attached to the University of Peradeniya)
Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.
By Sivamohan Sumathy
Features
Constitutional Council and the President’s Mandate

The Constitutional Council stands out as one of Sri Lanka’s most important governance mechanisms particularly at a time when even long‑established democracies are struggling with the dangers of executive overreach. Sri Lanka’s attempt to balance democratic mandate with independent oversight places it within a small but important group of constitutional arrangements that seek to protect the integrity of key state institutions without paralysing elected governments. Democratic power must be exercised, but it must also be restrained by institutions that command broad confidence. In each case, performance has been uneven, but the underlying principle is shared.
Comparable mechanisms exist in a number of democracies. In the United Kingdom, independent appointments commissions for the judiciary and civil service operate alongside ministerial authority, constraining but not eliminating political discretion. In Canada, parliamentary committees scrutinise appointments to oversight institutions such as the Auditor General, whose independence is regarded as essential to democratic accountability. In India, the collegium system for judicial appointments, in which senior judges of the Supreme Court play the decisive role in recommending appointments, emerged from a similar concern to insulate the judiciary from excessive political influence.
The Constitutional Council in Sri Lanka was developed to ensure that the highest level appointments to the most important institutions of the state would be the best possible under the circumstances. The objective was not to deny the executive its authority, but to ensure that those appointed would be independent, suitably qualified and not politically partisan. The Council is entrusted with oversight of appointments in seven critical areas of governance. These include the judiciary, through appointments to the Supreme Court and Court of Appeal, the independent commissions overseeing elections, public service, police, human rights, bribery and corruption, and the office of the Auditor General.
JVP Advocacy
The most outstanding feature of the Constitutional Council is its composition. Its ten members are drawn from the ranks of the government, the main opposition party, smaller parties and civil society. This plural composition was designed to reflect the diversity of political opinion in Parliament while also bringing in voices that are not directly tied to electoral competition. It reflects a belief that legitimacy in sensitive appointments comes not only from legal authority but also from inclusion and balance.
The idea of the Constitutional Council was strongly promoted around the year 2000, during a period of intense debate about the concentration of power in the executive presidency. Civil society organisations, professional bodies and sections of the legal community championed the position that unchecked executive authority had led to abuse of power and declining public trust. The JVP, which is today the core part of the NPP government, was among the political advocates in making the argument and joined the government of President Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga on this platform.
The first version of the Constitutional Council came into being in 2001 with the 17th Amendment to the Constitution during the presidency of Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga. The Constitutional Council functioned with varying degrees of effectiveness. There were moments of cooperation and also moments of tension. On several occasions President Kumaratunga disagreed with the views of the Constitutional Council, leading to deadlock and delays in appointments. These experiences revealed both the strengths and weaknesses of the model.
Since its inception in 2001, the Constitutional Council has had its ups and downs. Successive constitutional amendments have alternately weakened and strengthened it. The 18th Amendment significantly reduced its authority, restoring much of the appointment power to the executive. The 19th Amendment reversed this trend and re-established the Council with enhanced powers. The 20th Amendment again curtailed its role, while the 21st Amendment restored a measure of balance. At present, the Constitutional Council operates under the framework of the 21st Amendment, which reflects a renewed commitment to shared decision making in key appointments.
Undermining Confidence
The particular issue that has now come to the fore concerns the appointment of the Auditor General. This is a constitutionally protected position, reflecting the central role played by the Auditor General’s Department in monitoring public spending and safeguarding public resources. Without a credible and fearless audit institution, parliamentary oversight can become superficial and corruption flourishes unchecked. The role of the Auditor General’s Department is especially important in the present circumstances, when rooting out corruption is a stated priority of the government and a central element of the mandate it received from the electorate at the presidential and parliamentary elections held in 2024.
So far, the government has taken hitherto unprecedented actions to investigate past corruption involving former government leaders. These actions have caused considerable discomfort among politicians now in the opposition and out of power. However, a serious lacuna in the government’s anti-corruption arsenal is that the post of Auditor General has been vacant for over six months. No agreement has been reached between the government and the Constitutional Council on the nominations made by the President. On each of the four previous occasions, the nominees of the President have failed to obtain its concurrence.
The President has once again nominated a senior officer of the Auditor General’s Department whose appointment was earlier declined by the Constitutional Council. The key difference on this occasion is that the composition of the Constitutional Council has changed. The three representatives from civil society are new appointees and may take a different view from their predecessors. The person appointed needs to be someone who is not compromised by long years of association with entrenched interests in the public service and politics. The task ahead for the new Auditor General is formidable. What is required is professional competence combined with moral courage and institutional independence.
New Opportunity
By submitting the same nominee to the Constitutional Council, the President is signaling a clear preference and calling it to reconsider its earlier decision in the light of changed circumstances. If the President’s nominee possesses the required professional qualifications, relevant experience, and no substantiated allegations against her, the presumption should lean toward approving the appointment. The Constitutional Council is intended to moderate the President’s authority and not nullify it.
A consensual, collegial decision would be the best outcome. Confrontational postures may yield temporary political advantage, but they harm public institutions and erode trust. The President and the government carry the democratic mandate of the people; this mandate brings both authority and responsibility. The Constitutional Council plays a vital oversight role, but it does not possess an independent democratic mandate of its own and its legitimacy lies in balanced, principled decision making.
Sri Lanka’s experience, like that of many democracies, shows that institutions function best when guided by restraint, mutual respect, and a shared commitment to the public good. The erosion of these values elsewhere in the world demonstrates their importance. At this critical moment, reaching a consensus that respects both the President’s mandate and the Constitutional Council’s oversight role would send a powerful message that constitutional governance in Sri Lanka can work as intended.
by Jehan Perera
Features
Gypsies … flying high
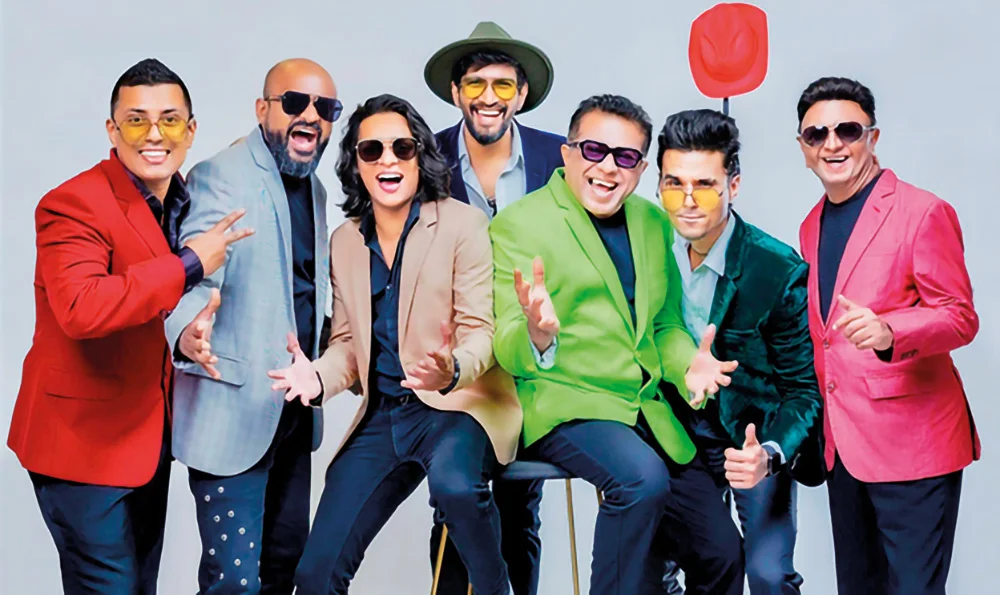

 The scene has certainly changed for the Gypsies and today one could consider them as awesome crowd-pullers, with plenty of foreign tours, making up their itinerary.
The scene has certainly changed for the Gypsies and today one could consider them as awesome crowd-pullers, with plenty of foreign tours, making up their itinerary.
With the demise of Sunil Perera, music lovers believed that the Gypsies would find the going tough in the music scene as he was their star, and, in fact, Sri Lanka’s number one entertainer/singer,
Even his brother Piyal Perera, who is now in charge of the Gypsies, admitted that after Sunil’s death he was in two minds about continuing with the band.
However, the scene started improving for the Gypsies, and then stepped in Shenal Nishshanka, in December 2022, and that was the turning point,
With Shenal in their lineup, Piyal then decided to continue with the Gypsies, but, he added, “I believe I should check out our progress in the scene…one year at a time.”
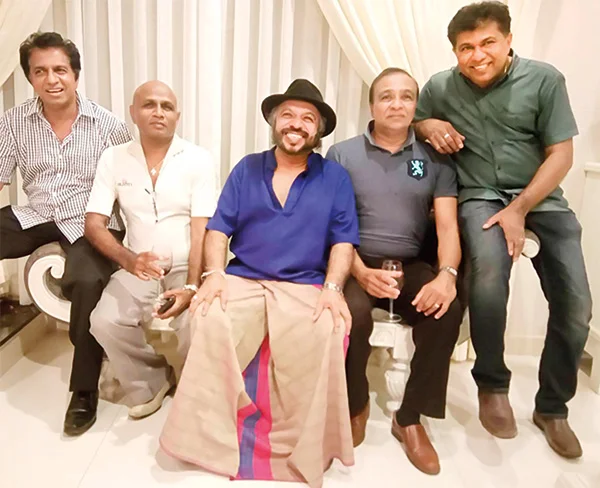

The original Gypsies: The five brothers Lal, Nimal, Sunil, Nihal and Piyal
They had success the following year, 2023, and then decided that they continue in 2024, as well, and more success followed.
The year 2025 opened up with plenty of action for the band, including several foreign assignments, and 2026 has already started on an awesome note, with a tour of Australia and New Zealand, which will keep the Gypsies in that part of the world, from February to March.
Shenal has already turned out to be a great crowd puller, and music lovers in Australia and New Zealand can look forward to some top class entertainment from both Shenal and Piyal.
Piyal, who was not much in the spotlight when Sunil was in the scene, is now very much upfront, supporting Shenal, and they do an awesome job on stage … keeping the audience entertained.
Shenal is, in fact, a rocker, who plays the guitar, and is extremely creative on stage with his baila.
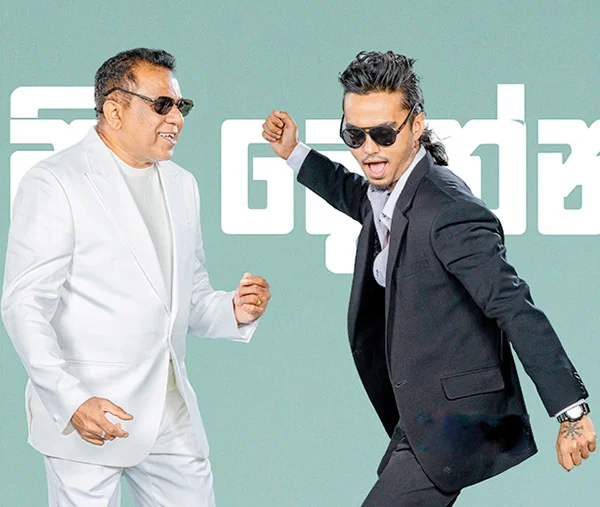

‘Api Denna’ Piyal and Shenal
Piyal and Shenal also move into action as a duo ‘Api Denna’ and have even done their duo scene abroad.
Piyal mentioned that the Gypsies will feature a female vocalist during their tour of New Zealand.
“With Monique Wille’s departure from the band, we now operate without a female vocalist, but if a female vocalist is required for certain events, we get a solo female singer involved, as a guest artiste. She does her own thing and we back her, and New Zealand requested for a female vocalist and Dilmi will be doing the needful for us,” said Piyal.
According to Piyal, he originally had plans to end the Gypsies in the year 2027 but with the demand for the Gypsies at a very high level now those plans may not work out, he says.
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoSri Lanka, the Stars,and statesmen
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoClimate risks, poverty, and recovery financing in focus at CEPA policy panel
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHayleys Mobility ushering in a new era of premium sustainable mobility
-

 Business23 hours ago
Business23 hours agoSLIM-Kantar People’s Awards 2026 to recognise Sri Lanka’s most trusted brands and personalities
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoAdvice Lab unveils new 13,000+ sqft office, marking major expansion in financial services BPO to Australia
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoArpico NextGen Mattress gains recognition for innovation
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoAltair issues over 100+ title deeds post ownership change
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoSri Lanka opens first country pavilion at London exhibition



















