Features
BEYOND REASONABLE DOUBT?

The killing of a Prime Minister
by Sanjiva Senanayake
(PART I)
Many people ‘know’ the conventional tale about the assassination of the Prime Minister of Ceylon, S.W.R.D. Bandaranaike, 62 years ago. However, they each have a slightly different take and theory about the facts, the reasons, the conspiracy theories and who ‘actually’ did it. Those then unborn or too young to have been aware of it at the time, have heard about it from older people. We have to assume that the intrinsic Lankan sense of rumour would have spiced up the details as time went by.
There is a common belief that the standards of general governance, integrity and legal processes were much higher back then, in Ceylon, than now. Bolstering this justifiable belief, adjudication was done by the Supreme Court (SC), the verdict was confirmed in the Court of Criminal Appeal and accepted by the Privy Council in London. Therefore, the predominant view continues to be that justice was served objectively and impartially.
However, there were many controversial interpretations and theories that circulated before, during and after the Bandaranaike trials. There were several aspects of the conduct of the trial and the actual evidence presented that raised questions about the guilt of the alleged assassin and, as a consequence, the guilt of the others.
Articles about those traumatic events of long ago have been published periodically, but they have progressively reverted to recounting and sometimes sensationalizing the standard version, and have not adequately addressed the many controversial questions.
This article focuses specifically on the alleged murderer and the most critical of the controversies, based on the ‘eye-witness’ evidence led at the SC trial – was Somarama proved to be the assassin beyond reasonable doubt? If there is any doubt, it opens up the possibility of a different, politically motivated conspiracy, especially since Bandaranaike was the Prime Minister during turbulent times.
THE STORY IN SUMMARY
The PM was shot several times with a revolver at his residence ‘Tintagel’ – 65, Rosmead Place – at around 10 am on September 25, 1959. Despite appearing to recover somewhat by evening following surgery, and even dictating a message to the nation from hospital, he died the next morning. The only thing Bandaranaike said about the identity of the gunman was that he was “a foolish man dressed in the robes of a monk”. This was the first major targeted political assassination in post-independence Ceylon, one that changed the future course of the country.
A Buddhist monk, Talduwe Somarama, was immediately arrested in the house, with a gun in hand, on suspicion of being the assailant. He was a hitherto low-profile Buddhist monk who was an eye specialist at the College of Indigenous Medicine in Rajagiriya.
After several days another monk, the politically powerful Mapitigama Buddharakkitha, was arrested in addition to several other individuals alleged to have assisted Buddharakkitha as part of a year-long conspiracy to kill Bandaranaike using Somarama as the assassin. Buddharakkitha, although only 38-years old, was the chief monk of the important Kelaniya Temple and, as the head of the Eksath Bhikkhu Peramuna (EBP), the most politically powerful monk in the country at the time. He was also headstrong, impulsive and confrontational – certainly not a pious monk. Although the EBP helped bring Bandaranaike to power in 1956, by 1959 Buddharakkitha was antagonistic toward the PM for being too ‘soft’ in pushing a more aggressive Sinhala Buddhist agenda. Buddharakkitha was aligned with the right-wing of the government and his antagonism toward the leftists (and vice versa) in the government was public knowledge.

After exhaustive investigations and a long trial in the SC, a special jury found both monks and H.P. Jayawardena, a close associate of Buddharakkitha, guilty of the conspiracy, and Somarama guilty of committing the murder, and all three were sentenced to death. The convictions were upheld in the Court of Criminal Appeal, but due to an inadvertent omission in intervening legislative change, Buddharakkitha and Jayawardena were sentenced to life in prison for conspiring to commit murder. An appeal to the Privy Council in London failed, and Somarama was subsequently executed.
There the matter rested and most people forgot about the details of the case with the passage of time. Other dramatic political events followed thereafter leading to an attempted coup d’etat on January 27, 1962 to overthrow the government of Bandaranaike’s widow. Resort to violence for political purposes became more prevalent from the 1970s, and targeted assassinations of political leaders more frequent.
Only two books have been written in English about the assassination; one by the late Justice A.C. Alles and the other by the late Lucian Weeramantry, who was Somarama’s counsel in the trial. It is surprising that more books and academic studies do not seem to have been published specifically about the assassination, an important event in our post-Independence history.
Justice Alles’ book provides a lot of relevant background material but, judging by assertions made and conclusions drawn, it appears to have been written on the assumption that the conspiracy allegedly planned by Buddharakkitha was true and the verdicts just, although he does refer to some questionable issues.
Weeramantry restricts himself to the procedures followed, the evidence led and the submissions made in the SC, to demonstrate that there was more than ‘reasonable doubt’ about the convictions. He argues that the prosecution of the case was politically influenced and not neutral.
It is a fascinating case with many twists and turns as well as contradictions. A critical reading of the above books is recommended to anyone who is interested in digging further into the unusual events specifically pertinent to the murder and trial. A deeper understanding of contemporary political and social developments also helps.
BACKGROUND IN BRIEF
Bandaranaike left the United National Party (UNP) in 1951 and formed the Sri Lanka Freedom Party (SLFP). His party lost badly at the next general election in March 1952 and it appeared that his political career was doomed. In the meantime, political pressures by Sinhalese and Buddhist groups for affirmative action had been intensifying since Independence to redress what was perceived as historical discrimination against them from colonial times. The UNP was rather indifferent to these forces but Bandaranaike decided to channel them and was supported strongly by the ‘pancha maha balavegaya’ consisting of Buddhist monks, Ayurveda practitioners, vernacular teachers, peasants and workers.
The SLFP then formed a coalition called the Mahajana Eksath Peramuna (MEP) with a leftist party headed by Philip Gunawardena and a small party
led by W. Dahanayake, to contest the general election of April 1956. A key election slogan was ‘Sinhala-Only in 24 hours’, a potent rallying cry that meant different things to different people. The UNP too adopted the slogan prior to the election when it realised its electoral potential, but its late volte-face lacked credibility and the MEP won by a landslide.
However, the very next year, Bandaranaike initiated discussions with Tamil political leaders to provide devolution of some powers through the establishment of Regional Councils and the so-called Bandaranaike-Chelvanayakam Pact was signed in July 1957. It was a compromise on both sides, which the PM likened to the Buddha’s Middle Way, but most of the politicians of the time were focused on short-term gains and not inclined to compromise for stability and longer-term progress. There were opposition and agitation from both sides and some avoidable incidents occurred in the process. Eventually, the pact was abrogated under severe pressure in April 1958, with the EBP too playing a major role.
The antagonistic posturing did not cease and this led to one week of intense conflict at the end of May, the so-called Sinhala-Tamil riots that left long-lasting social scars. The PM’s rule was seen as weak and indecisive in bringing the riots under control and the Governor General, Sir Oliver Goonetilleke, played a major role in quelling it.
Despite all this, Bandaranaike introduced the Tamil Language (Special Provisions) Act No. 28 of 1958 less than three months later in August 1958 as a compromise measure to accommodate Tamil demands regarding matters such as education, public service entrance examinations and the administration of the north and east. This too was criticized by extremists on both sides.
Ceylon in 1959, a decade after Independence but still looking for direction, was a hotbed of political turmoil. Agitations and strikes were rampant, with the constant interplay of all the emotion-rousing political forces of the time – urban vs. rural; westernized vs. nationalist; capitalist vs. socialist; Buddhist vs. Catholic; Sinhala vs. Tamil; rich vs. poor – trying to quickly carve pieces out of the emerging national pie. The old order was dying and a new one was being born.
In April 1959, Bandaranaike had a difference of opinion with the Inspector General of Police, Osmund de Silva and decided to replace him. The PM had been previously warned by various Buddhist leaders and MEP coalition partners in Parliament about a right-wing conspiracy to topple his administration with the involvement of the police and armed forces. Although Osmund de Silva was a Buddhist, all the senior Police officers next in line were not and, despite protests from within the Police, Bandaranaike decided to appoint M.W.F Abeykoon, an administrative officer from outside the Police service, angering several senior officers.
That was not all. The urban elites, more inclined to western lifestyles, accustomed to calling the shots politically and economically, and linguistically quite alienated from the masses, were becoming increasingly alarmed at the turn of events since the debacle in 1956 of their preferred political party, the UNP. The growing influence of more aggressive Sinhalese and Buddhist groups was causing concern among the established organizations and social groups.
There was an international dimension too. Despite the intense Cold War then raging, the Bandaranaike government had established diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union in December 1956 and signed an economic and technical cooperation agreement in 1958. The previous UNP government had recognized the People’s Republic of China in January 1950, supported China’s entry to the United Nations and entered into the historic Rubber-Rice barter agreement in 1952. The Bandaranaike government established full diplomatic relations with China in 1957.
The government’s plans to nationalize State-assisted private schools and foreign businesses such as the oil companies, and its decision in October 1957 to abrogate the Defence Pact with Britain and take back control of Trincomalee harbour and the RAF airbase at Katunayake, were all loud alarm bells.
By the latter half of 1959 the PM was into the fourth year of his five-year term, and already the coalition was fraying. The leftist faction, led by Philip Gunawardena, resigned from the government in April 1959 due to pressure from the coalition’s right wing regarding socialist measures such as the Paddy Lands Act, which included land reform. Strikes became more frequent and intense.
In this milieu, there were many disparate groups that could have had reasons to eliminate Bandaranaike, and perhaps get a bonus by pinning the blame on Buddharakkitha to neutralize a powerful, antagonistic group such as the EBP and the growing direct involvement of Buddhist monks in politics.
THE SHOOTING
Unlike today, firearms were not easily available and targeted political killings were extremely rare. The level of security considered necessary was quite basic and Bandaranaike himself was not keen on too many guards. Access to his residence was freely available during the morning to all and sundry. The shooting at close quarters happened on the verandah of the PM’s private residence with at least 30 people in the immediate vicinity.
Somarama was seated at one end of the outside verandah. There was another monk (Niwanthidiye Ananda) seated about 10 feet away from Somarama and more to the centre of the verandah, near the entrance to the corridor that led from the front porch into the interior of the house. Several others were standing around including a teacher named Gunaratne who was opposite Ananda.
The PM first spoke with Ananda and gave him some instructions. He then moved along the verandah toward Somarama and, as he bent and worshipped him in greeting, a gunshot was heard. Bandaranaike cried out in pain, turned and tried to run back into the house. Further shots were heard, and the PM was hit in the chest and abdomen. Altogether he was hit by four bullets, the first one glancing his left wrist and three entering his torso as he staggered into the house. Gunaratne, who should have had a clear view of the shooting, was also shot in the neck area by a fifth bullet as Bandaranaike stumbled past him to escape into the house along the central corridor.
In the utter confusion that followed, Somarama followed the PM into the house carrying a revolver and was then assaulted by several people who came from other parts of the house before he could say anything. In the melee the revolver went off once, the last bullet, but no one was hurt. The World War I vintage revolver, in rather poor condition, that had been used was recovered by the police.
Somarama’s version was that someone dressed in robes shot repeatedly at the PM from the garden just below the verandah, threw the revolver on to the verandah and then ran off toward the road. He then involuntarily picked up the gun and followed the PM into the house to hand it over to someone responsible.
In the meantime, PC Samarakoon, who was the sentry at the main gate, rushed to the house and shot at Somarama, injuring him in the thigh and groin area. The PM was sent to hospital by car and, soon after that, DIG Sidney de Zoysa, who had a prior appointment to meet the PM, arrived and took control of the chaotic situation. In fact, de Zoysa passed the PM’s car going toward the hospital on his way to the house, but didn’t realise the injured PM was in it. Some time after de Zoysa’s arrival, a bleeding Somarama in obvious pain was, for some inexplicable reason, despatched to the Harbour Police station on the other side of the city and detained there for around two hours before being taken to hospital where he underwent an operation to remove one of his testicles.
The firing of the first five bullets was rapid and probably took less than 10 seconds, since the PM was also moving away. The despatch of the PM by car and the arrival of Sidney de Zoysa would probably have happened within 10-15 minutes thereafter.
It seems, at first glance, to be a straightforward case. The alleged assailant, the weapon, the victim and witnesses were all readily available, and it happened in the heart of Colombo, in a narrow space, in broad daylight. On the face of it, only the motive and the possible involvement of others had to be discerned. But in political murders things are not always what they seem.
THE LEGAL PROCESS
Buddharakkitha and Jayawardena were arrested on October 14, 1959 and held in remand custody, along with Somarama. Following intensive investigations by the police, the magisterial inquiry started on December 14, 1959, less than three months after the murder, and went on until July 27, 1960. At the end of the almost seven month-long hearings, five people were named to stand trial in the SC.
1. Mapitigama Buddharakkitha thero
2. H.P. Jayawardena
3. Anura de Silva
4. Talduwe Somarama thero
5. Newton Perera
All the accused were to be charged with conspiracy to murder the PM, and the fourth with murder as well. The indictment read as follows:
That between the 25th of August, 1958, and the 26th of September, 1959, at Kelaniya, Wellampitiya, Rajagiriya, Colombo and other places within the jurisdiction of this Court, you did agree to commit or abet or act together with the common purpose of committing or abetting an offence, to wit, the murder of Solomon West Ridgeway Dias Bandaranaike, and that you are thereby guilty of the offence of conspiracy to commit or abet the said offence of murder, in consequence of which conspiracy the said offence of murder was committed, and that you have thereby committed an offence punishable under section 296 read with sections 113B and 102 of the Penal Code.
It specifically mentioned a date 13 months earlier (August 25, 1958) as the origin of the conspiracy. This was the date on which the PM, on the advice of senior technocrats of the Ministry of Finance, decided not to award a shipping contract to a company in which Buddharakkitha’s brother had a significant interest. The direct implication is that Buddharakkitha’s resentment due to this act was the trigger for a year-long conspiracy that led to the assassination.
The defence counsel made a request for a Special Jury at the start of the SC trial due to the highly politically-charged nature of the case. They requested that government employees should be excluded but, in the end, the Foreman of the English-speaking jury was a public servant. As a matter of interest, six members were Christians and the seventh was a Buddhist, and all were from Colombo. However, the integrity of the members of the jury was never questioned.
During the SC trial it became apparent that the third accused was an insignificant character and he was finally acquitted unanimously. It was not clear why he was charged at all, or placed ahead of the alleged murderer Somarama, if there was indisputable evidence against Somarama.
Newton Perera, a police officer, allegedly procured the revolver and ammunition used in the killing. He was also accused of training Somarama to shoot, but this was not established. He was subsequently found not guilty in the SC with the jury divided five to two.
The SC trial commenced seven months later, on February 22, 1961 before Justice T.S. Fernando, and went on till May 12, 1961. The government retained George Chitty QC, a prominent criminal defence lawyer from the private Bar, to lead the prosecution in the SC, by-passing the Attorney General’s Department. The Deputy Solicitor General, A.C.M. Ameer, who was the prosecutor in the Magistrate’s Court, resigned in protest.
There were criticisms that the prosecutor for the State focused more on getting judgements against the accused who were charged, rather than seeking the truth via a broader inquiry to get to the bottom of who actually killed the PM of the country, and why. Some of the defence counsel, including Phineas Quass QC, who came over from the UK to defend Buddharakkitha and Jayawardena, also alluded to this during the trial.
The prosecution did not call Gunaratne who was in a perfect position to see the shooting at close quarters. Neither did the prosecution call key witnesses DIG Sidney de Zoysa or any of the senior (Gazetted) police officers who investigated the case. De Zoysa was called instead by Weeramantry, Somarama’s counsel. There was a lot of evidence led by the prosecution that did not appear to have relevance. The government even paid to bring down a ‘witness’ from the UK (Bruno Perera), who only served to distract attention. He was reprimanded and fined by the Judge at the end of the trial.
The seven members of the Special Jury were the final arbiters of the judgement rather than the Judge. They would have had a tedious task in assessing the oral evidence, unravelling the many counsel’s interventions and addresses, absorbing the Judge’s directions on points of law, and then arriving at a decision in a short while. In those non-computerized days, the jury had to rely only on what they heard in the courts almost every day for 55 days and make a decision on a matter of life and death, without the advantage of printed transcripts of evidence. A total of 97 witnesses testified and the typed record of the proceedings ran into 3,536 pages.
(Note: typed transcripts of the day’s proceedings were, however, made available to the Judge and counsel the following day)
TO BE CONTINUED …..
Features
Sheer rise of Realpolitik making the world see the brink
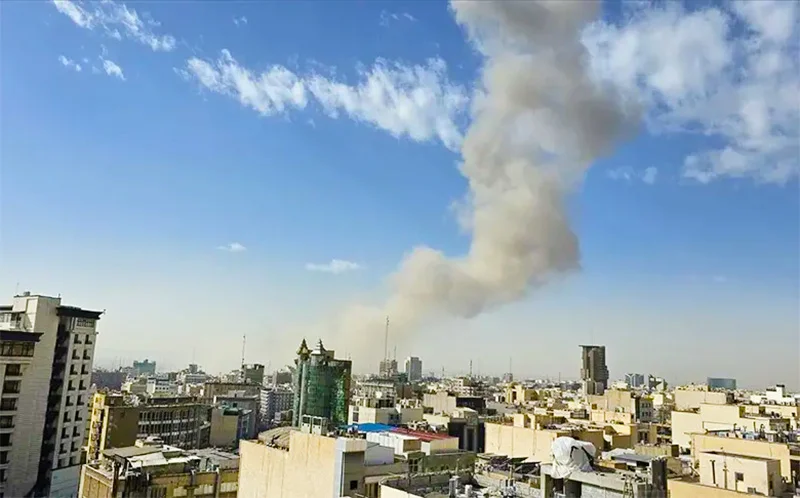

 The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
As matters stand, there seems to be no credible evidence that the Indian state was aware of the impending torpedoing of the Iranian vessel but these acerbic-tongued politicians of Sri Lanka’s South would have the local public believe that the tragedy was triggered with India’s connivance. Likewise, India is accused of ‘embroiling’ Sri Lanka in the incident on account of seemingly having prior knowledge of it and not warning Sri Lanka about the impending disaster.
It is plain that a process is once again afoot to raise anti-India hysteria in Sri Lanka. An obligation is cast on the Sri Lankan government to ensure that incendiary speculation of the above kind is defeated and India-Sri Lanka relations are prevented from being in any way harmed. Proactive measures are needed by the Sri Lankan government and well meaning quarters to ensure that public discourse in such matters have a factual and rational basis. ‘Knowledge gaps’ could prove hazardous.
Meanwhile, there could be no doubt that Sri Lanka’s sovereignty was violated by the US because the sinking of the Iranian vessel took place in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While there is no international decrying of the incident, and this is to be regretted, Sri Lanka’s helplessness and small player status would enable the US to ‘get away with it’.
Could anything be done by the international community to hold the US to account over the act of lawlessness in question? None is the answer at present. This is because in the current ‘Global Disorder’ major powers could commit the gravest international irregularities with impunity. As the threadbare cliché declares, ‘Might is Right’….. or so it seems.
Unfortunately, the UN could only merely verbally denounce any violations of International Law by the world’s foremost powers. It cannot use countervailing force against violators of the law, for example, on account of the divided nature of the UN Security Council, whose permanent members have shown incapability of seeing eye-to-eye on grave matters relating to International Law and order over the decades.
The foregoing considerations could force the conclusion on uncritical sections that Political Realism or Realpolitik has won out in the end. A basic premise of the school of thought known as Political Realism is that power or force wielded by states and international actors determine the shape, direction and substance of international relations. This school stands in marked contrast to political idealists who essentially proclaim that moral norms and values determine the nature of local and international politics.
While, British political scientist Thomas Hobbes, for instance, was a proponent of Political Realism, political idealism has its roots in the teachings of Socrates, Plato and latterly Friedrich Hegel of Germany, to name just few such notables.
On the face of it, therefore, there is no getting way from the conclusion that coercive force is the deciding factor in international politics. If this were not so, US President Donald Trump in collaboration with Israeli Rightist Premier Benjamin Natanyahu could not have wielded the ‘big stick’, so to speak, on Iran, killed its Supreme Head of State, terrorized the Iranian public and gone ‘scot-free’. That is, currently, the US’ impunity seems to be limitless.
Moreover, the evidence is that the Western bloc is reuniting in the face of Iran’s threats to stymie the flow of oil from West Asia to the rest of the world. The recent G7 summit witnessed a coming together of the foremost powers of the global North to ensure that the West does not suffer grave negative consequences from any future blocking of western oil supplies.
Meanwhile, Israel is having a ‘free run’ of the Middle East, so to speak, picking out perceived adversarial powers, such as Lebanon, and militarily neutralizing them; once again with impunity. On the other hand, Iran has been bringing under assault, with no questions asked, Gulf states that are seen as allying with the US and Israel. West Asia is facing a compounded crisis and International Law seems to be helplessly silent.
Wittingly or unwittingly, matters at the heart of International Law and peace are being obfuscated by some pro-Trump administration commentators meanwhile. For example, retired US Navy Captain Brent Sadler has cited Article 51 of the UN Charter, which provides for the right to self or collective self-defence of UN member states in the face of armed attacks, as justifying the US sinking of the Iranian vessel (See page 2 of The Island of March 10, 2026). But the Article makes it clear that such measures could be resorted to by UN members only ‘ if an armed attack occurs’ against them and under no other circumstances. But no such thing happened in the incident in question and the US acted under a sheer threat perception.
Clearly, the US has violated the Article through its action and has once again demonstrated its tendency to arbitrarily use military might. The general drift of Sadler’s thinking is that in the face of pressing national priorities, obligations of a state under International Law could be side-stepped. This is a sure recipe for international anarchy because in such a policy environment states could pursue their national interests, irrespective of their merits, disregarding in the process their obligations towards the international community.
Moreover, Article 51 repeatedly reiterates the authority of the UN Security Council and the obligation of those states that act in self-defence to report to the Council and be guided by it. Sadler, therefore, could be said to have cited the Article very selectively, whereas, right along member states’ commitments to the UNSC are stressed.
However, it is beyond doubt that international anarchy has strengthened its grip over the world. While the US set destabilizing precedents after the crumbling of the Cold War that paved the way for the current anarchic situation, Russia further aggravated these degenerative trends through its invasion of Ukraine. Stepping back from anarchy has thus emerged as the prime challenge for the world community.
Features
A Tribute to Professor H. L. Seneviratne – Part II

A Living Legend of the Peradeniya Tradition:
(First part of this article appeared yesterday)
H.L. Seneviratne’s tenure at the University of Virginia was marked not only by his ethnographic rigour but also by his profound dedication to the preservation and study of South Asian film culture. Recognising that cinema is often the most vital expression of a society’s aspirations and anxieties, he played a central role in curating what is now one of the most significant Indian film collections in the United States. His approach to curation was never merely archival; it was informed by his anthropological work, treating films as primary texts for understanding the ideological shifts within the subcontinent
The collection he helped build at the UVA Library, particularly within the Clemons Library holdings, serves as a comprehensive survey of the Indian ‘Parallel Cinema’ movement and the works of legendary auteurs. This includes the filmographies of directors such as Satyajit Ray, whose nuanced portrayals of the Indian middle class and rural poverty provided a cinematic counterpart to H.L. Seneviratne’s own academic interests in social change. By prioritising the works of figures such as Mrinal Sen and Ritwik Ghatak, H.L. Seneviratne ensured that students and scholars had access to films that wrestled with the complex legacies of colonialism, partition, and the struggle for national identity.
These films represent the ‘Parallel Cinema’ movement of West Bengal rather than the commercial Hindi industry of Mumbai. H.L. Seneviratne’s focus initially cantered on those world-renowned Bengali masters; it eventually broadened to encompass the distinct cinematic languages of the South. These films refer to the specific masterpieces from the Malayalam and Tamil regions—such as the meditative realism of Adoor Gopalakrishnan or the stylistic innovations of Mani Ratnam—which are culturally and linguistically distinct from the Bengali works. Essentially, H.L. Seneviratne is moving from the specific (Bengal) to the panoramic, ensuring that the curatorial work of H.L. Seneviratne was not just a ‘Greatest Hits of Kolkata’ but a truly national representation of Indian artistry. These films were selected for their ability to articulate internal critiques of Indian society, often focusing on issues of caste, gender, and the impact of modernisation on traditional life. Through this collection, H.L. Seneviratne positioned cinema as a tool for exposing the social dynamics that often remain hidden in traditional historical records, much like the hidden political rituals he uncovered in his early research.
Beyond the films themselves, H.L. Seneviratne integrated these visual resources into his curriculum, fostering a generation of scholars who understood the power of the image in South Asian politics. He frequently used these screenings to illustrate the conflation of past and present, showing how modern cinema often reworks ancient myths to serve contemporary political agendas. His legacy at the University of Virginia therefore encompasses both a rigorous body of writing that deconstructed the work of the kings and a vivid archive of films that continues to document the work of culture in a rapidly changing world.
In his lectures on Sri Lankan cinema, H.L. Seneviratne has frequently championed Lester James Peries as the ‘father of authentic Sinhala cinema.’ He views Peries’s 1956 film Rekava (Line of Destiny) as a watershed moment that liberated the local industry from the formulaic influence of South Indian commercial films. For H.L. Seneviratne, Peries was not just a filmmaker but an ethnographer of the screen. He often points to Peries’s ability to capture the subtle rhythms of rural life and the decline of the feudal elite, most notably in his masterpiece Gamperaliya, as a visual parallel to his own research into the transformation of traditional authority. H.L. Seneviratne argues that Peries provided a realistic way of seeing for the nation, one that eschewed nationalist caricature in favour of complex human emotion.
However, H.L. Seneviratne’s praise for Peries is often tempered by a critique of the broader visual nationalism that followed. He has expressed concern that later filmmakers sometimes misappropriated Peries’s indigenous style to promote a narrow, majoritarian view of history. In his view, while Peries opened the door to an authentic Sri Lankan identity, the state and subsequent commercial interests often used that same door to usher in a simplified, heroic past. This critique aligns with his broader academic stance against the rationalization of culture for political ends.
Constitutional Governance:
H.L. Seneviratne’s support for independent commissions is best described as a hopeful pragmatism; he views them as essential, albeit fragile, instruments for diffusing the hyper-concentration of executive power. Writing to Colombo Page and several news tabloids, H.L. Seneviratne addresses the democratic deficit by creating a structural buffer between partisan interests and public institutions, theoretically ensuring that the judiciary, police, and civil service operate on merit rather than political whim. However, he remains deeply aware that these commissions are not a panacea and are indeed inherently susceptible to the ‘politics of patronage.’
In cultures where power is traditionally exercised through personal loyalties, there is a constant risk that these bodies will be subverted through the appointment of hidden partisans or rendered toothless through administrative sabotage. Thus, while H.L. Seneviratne advocates for them as a means to transition a state from a patron-client culture to a rule-of-law framework, his anthropological lens suggests that the success of such commissions depends less on the law itself and more on the sustained pressure of civil society to keep them honest.
Whether discussing the nuances of a film’s narrative or the complexities of a constitutional clause, H.L. Seneviratne’s approach remains consistent in its focus on the spirit behind the institution. He maintains that a healthy democracy requires more than just the right laws or the right symbols; it requires a citizenry and a clergy capable of critical self-reflection. His career at the University of Virginia and his continued engagement with Sri Lankan public life stand as a testament to the idea that the intellectual’s work is never truly finished until the work of the people is fully realized.
In the context of H.L. Seneviratne’s philosophy, as discussed in his work of the kings ‘the work of the people’ is far more than a populist catchphrase; it represents the practical application of critical consciousness within a democracy. Rather than defining ‘work’ as labour or voting, H.L. Seneviratne views it as the transition of a population from passive subjects to an active, self-reflective citizenry. This means that a democracy is only truly ‘realized’ when the public possesses the intellectual autonomy to look beyond the ‘right laws’ or ‘right symbols’ and instead engage with the underlying spirit of their institutions. For H.L. Seneviratne, this work is specifically tied to the ability of the people—including influential groups like the clergy—to perform rigorous self-critique, ensuring that they are not merely following tradition or authority, but are actively sustaining the ethical health of the nation. It is a perpetual process of civic education and moral vigilance that moves a society from the ‘paper’ democracy of a constitution to a lived reality of accountability and insight.
This decline of the ‘intellectual monk’ had a catastrophic impact on the political landscape, particularly surrounding the watershed moment of 1956 and the ‘Sinhala Only’ movement. H.L. Seneviratne posits that when the Sangha exchanged their role as impartial moral advisors for that of political kingmakers, they became the primary obstacle to ethnic reconciliation. He suggests that politicians, fearing the immense grassroots influence of the monks, entered a state of monachophobia, where they felt unable to propose pluralistic or fair policies toward minority communities for fear of being branded as traitors to the faith. In H.L. Seneviratne’s framework, the monk’s transition from a social servant to a political vanguard effectively trapped the state in a cycle of majoritarian nationalism from which it has yet to escape.
H.L. Seneviratne’s work serves as a multifaceted critique of the modern Sri Lankan state and its cultural foundations. Whether he is dissecting what he sees as the betrayal of the monastic ideal or celebrating the humanistic vision of an Indian filmmaker, his goal remains the same: to champion a world where intellect and compassion are not sacrificed on the altar of political power. His legacy at the University of Virginia and his continued voice in Sri Lankan discourse remind us that the work of the intellectual is to provide a moral compass even, indeed especially, when the nation has lost its way.
(Concluded)
by Professor
M. W. Amarasiri de Silva
Features
Musical journey of Nilanka Anjalee …

 Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe is, in fact, a reputed doctor, but the plus factor is that she has an awesome singing voice, as well., which stands as a reminder that music and intellect can harmonise beautifully.
Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe is, in fact, a reputed doctor, but the plus factor is that she has an awesome singing voice, as well., which stands as a reminder that music and intellect can harmonise beautifully.
Well, our spotlight today is on ‘Nilanka – the Singer,’ and not ‘Nilanka – the Singing Doctor!’
Nilanka’s journey in music began at an early age, nurtured by an ear finely tuned to nuance and a heart that sought expression beyond words.
Under the tutelage of her singing teachers, she went on to achieve the A.T.C.L. Diploma in Piano and the L.T.C.L. Diploma in Vocals from Trinity College, London – qualifications recognised internationally for their rigor and artistry.
These achievements formally certified her as a teacher and performer in both opera singing and piano music, while her Performer’s Certificate for singing attested to her flair on stage.
Nilanka believes that music must move the listener, not merely impress them, emphasising that “technique is a language, but emotion is the message,” and that conviction shines through in her stage presence –serene yet powerful, intimate yet commanding.
Her YouTube channel, Facebook and Instagram pages, “Nilanka Anjalee,” have become a window into her evolving artistry.
Here, audiences find not only her elegant renditions of local and international pieces but also her original songs, which reveal a reflective and modern voice with a timeless sensibility.
Each performance – whether a haunting ballad or a jubilant interpretation of a traditional hymn – carries her signature blend of technical finesse and emotional depth.
Beyond the concert hall and digital stage, Nilanka’s music is driven by a deep commitment to meaning.
Her work often reflects her belief in empathy, inner balance, and the beauty of simplicity—values that give her performances their quiet strength.
She says she continues to collaborate with musicians across genres, composing and performing pieces that reflect both her classical discipline and her contemporary outlook.
Widely acclaimed for her ability to adapt to both formal and modern stages, with equal grace, and with her growing repertoire, Nilanka has become a sought-after soloist at concerts and special events,
For those who seek to experience her artistry, firsthand, Nilanka Anjalee says she can be contacted for live performances and collaborations through her official channels.
Her voice – refined, resonant, and resolutely her own – reminds us that music, at its core, is not about perfection, but truth.
Dr. Nilanka Anjalee Wickramasinghe also indicated that her newest single, an original, titled ‘Koloba Ahasa Yata,’ with lyrics, melody and singing all done by her, is scheduled for release this month (March)
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoPeradeniya Uni issues alert over leopards in its premises
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoFemale lawyer given 12 years RI for preparing forged deeds for Borella land
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoLibrary crisis hits Pera university
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days ago‘IRIS Dena was Indian Navy guest, hit without warning’, Iran warns US of bitter regret
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoSri Lanka evacuates crew of second Iranian vessel after US sunk IRIS Dena