Features
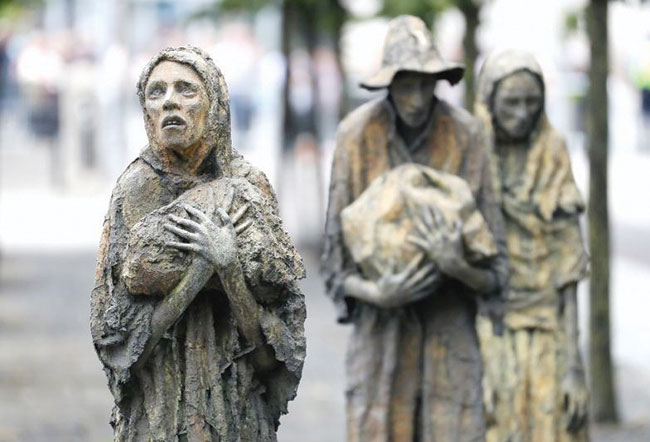
Are we heading for an unprecedented disaster like the Irish Potato Famine?

by Dr Parakrama Waidyanatha
When the potato crop, the staple diet then in Ireland, began to totally fail with a fungal infestation that lead to the historic Irish famine (1845-1852), the Irish leaders in Dublin turned to Queen Victoria and the British Parliament for redress. However, the British government under which Ireland was then a colony, acted negatively repealing certain laws and tariffs that made food such as corn and bread prohibitively expensive. Tenant farmers were unable even to produce enough food for themselves, and hundreds of thousands died of starvation and diseases caused by malnutrition!
The exact role of the British government in the Potato Famine and its aftermath—whether it ignored the plight of Ireland’s poor out of malice, or if their collective inaction and inadequate response could be attributed to incompetence—is still being debated. However, even during the famine some food items were exported out of Ireland. Our situation looks very comparable to the Irish fiasco except that our leaders are not acting with malice but with foolish obstinacy, not analysing the issues at stake, not consulting experts in the subject and sticking coherently to their policy of organic farming with unattainable goals.
Our rice farmers may yet not be starving because they have at least the last Yala rice crop which has been reasonable despite the fertilizer and other agrochemical shortages. On the other hand, tea and vegetable farmers appear to be the most hit. Many tea smallholders complain that without adequate nitrogen fertilizer their crops have declined immensely and some are not even harvesting the meagre flush as it can hardly meet even the workers wages. The seriousness of the situation is further aggravated by our losing the markets which the industry claims can be substantial.
At the same time, for the general public, sky-rocketing prices of food and other essentials are unbearable. Our women won’t be able even to emulate what the French women did during the days of the French Revolution due to inflation, carrying the money in the shopping bags and bringinging back the purchases in their purses, because they have no money to carry.
It is regrettable that the President did not consult the agricultural experts in deciding to rush to convert the country entirely to organic from conventional farming within one season.He has not positively responded to the current fiasco of neither chemical nor organic fertilizer being available. His main consultants on matter appear to be a pediatrician who wants to go back to traditional rice varieties which yield less than half the new improved varieties and a professor of agriculture who identified sorghum as a rice variety, Swayanjatha wee’, with which, he claims, King Dutugamunu fed his ‘Dasa Maha Yodayas.’ There are many other ‘yes men’ behind him nodding their heads to every thing he says.
The President should be mindful that the world moved away from organic farming from about the 1850s to conventional farming because even in that era organic farming could not meet the food demand. The writer hopes that he would at least look at Table 1 here which shows how chemical fertilizers and new high yielding varieties pushed production from essentially organic farming and traditional rice to chemical farming and new varieties by three to four fold across many countries. Distinguished Professor Vaclav Smil, University of Manitoba calculated that 40% of the global population in 1999 would not have lived if urea fertilizer had not been invented.
Table 1. Comparative Rice
Production (Million MT)
Country 1960 1999
China 48 170
India 46 112
Sri Lanka 1.1 3.4
The transition from traditional agriculture where fertilizer comprised essentially farmyard manure(FYM) and green manures, to conventional agriculture(CF), as we know it today, took place in the mid 19th century with two ground breaking inventions , the synthesis of soluble (super) phosphate(John Lawes,1814 to 1900) and the need for chemical nitrogenous fertilizer for crop growth (Justus von Liebig,1803-1873) by two great scientists. In 1909, another great German scientist, Fritz Haber (1868-1934) successfully synthesized ammonia by combining atmospheric nitrogen and hydrogen which revolutionized the production of urea and other commercial nitrogenous fertilizers.
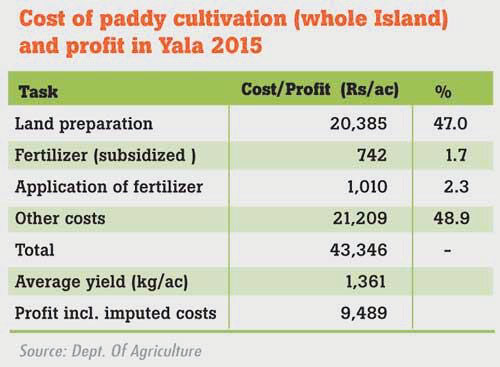
These inventions and the rapidly growing knowledge then in plant chemistry led to the substitution of natural dung with chemical fertilizer. The third important element, potassium, was provided largely by potash, a substance that had been known from antiquity. It has been said that without these inventions, the industrial countries of Western Europe could not have supported the dense population growth of the 19th century. It is the same reason that later led to the Green Revolution. This is ironically the fundamental question that we should ask: is there adequate organic matter and associated technologies to “go green” fully, as the President calls it, now, if it was not possible then with much lower populations but more farmlands. Sir John Russell (1942), the reputed British soil scientist, in an article titled British Agriculture states that: “it is difficult for us in this distance in time to recapture the feelings with which the farmers received the information that a powder made in a factory and applied out of a bag at the rate of only a few hundred weights per acre could possibly act as well as farmyard manure put on the land as dressings of tons to meet the nutrient demands of crops’. The question then is if organic matter was inadequate to meet the fertilizer requirements then, can it do so now on a global scale?
The main blame of the President and his cabinet colleagues is on health hazzards of agrochemicals. There is no argument that there are risks largely due to misuse of agrochemicals. One serious problem recently has been phosphate pollution of the Rajarata water bodies due to excessive application of phosphate fertilizers in the upcountry vegetable farms. On the other hand, no comprehensive studies reveal pollution of water or soil with heavy metals or pesticides, a subject much spoken about. Farmer training on judicious use can greatly reduce the risk of agrochemical misuse which sadly is not happening with the very ineffective extension services of the day. Strengthening this service is matter of highest priority.
On the other hand hardly any politician utters a word about ambient air pollution, which is a far more serious problem than agrochemical pollution. Records reveal that it caused 3.5 million premature, non-communicable disease- deaths, globally in 2017. These were from stroke, ischemic heart disease non chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, respiratory infections, and diabetes. Local health records reveal that our situation is no better.
The President and many of his cabinet colleagues including the Minister of Agriculture continue to lay the blame on agrochemicals for the kidney disease in the Rajarata and other non- communicable diseases, apparently the main reason for the President ‘going green.’ At some public meeting the President was heard to say that if he gives ‘chemical fertilizer with one hand he will have to give a kidney’ to the farmer with the other. He was prompted to say so by one of his key advisors in agriculture, a pediatrician turned agriculture expert. Sadly he has not sought advice from the health authorities as to the causation of the kidney disease. Numerous knowledgeable scientists and publications have revealed beyond doubt that hardwater and fluoride are the cause of the disease, and a recent comprehensive report by the Health Ministry reveals that there is no evidence to implicate agrochemicals in the causation of the disease.
In this crisis situation, of diminishing food production, the President does not appear to have sought the advise of real agriculture experts. In fact a letter delivered to him over a month ago with some 140 signatures of qualified agriculture researchers and academics seeking an opportunity to discuss the current agricultural calamity has fallen on deaf ears. Let alone the local expert knowledge, he should have sought evidence from what happens elsewhere in the world. Many countries are only gradually expanding their organic crop cover which, however, yet stands at 1.5 % of the total global croplands expanding annually at a meagre 2% per annum.Only 16 countries have exceeded 10 % of the crop cover in organic farming, and in nearly all them the major extents are in pasture fertilized with farmyard manure.
Policy blunders continue to be committed. To meet the rice fertilizer needs the government claims importing 2.1 million litres of nano fertilizer at a cost of USD 12 per litre. It appears to be nano urea although the Minister of Agriculture vehemently claims that it is not nano urea but ‘nanonitrogen’ to give it an organic stance. Urea is not allowed in organic farming. The authorities claim that the cost of a litre is USD 12, and it has 4% nitrogen, meaning there are 40 grams nitrogen/litre. As average rice crop of 5 tons/ha removes over 100kg nitrogen , meaning to meet the crop demand the farmers should spray 2,500 bottles of which the theoretical cost should be USD 30,000. However, the government makes the ridiculous claim that five litres/ha of nanonitrogen is adequate to meet the crop demand. God save the farmers!
The global synthetic urea prices have soared to about USD 750 per metric ton from about USD500 last November. Assuming that a farmer applies 100kg nitrogen/ha with urea (46% N) his cost should be Rs 32,608 without subsidy; and assuming he sells his crop of five tons at Rs 60/kg, his gross income should be Rs 300,000, and the cost of urea alone should be over 10.6% of the gross income. On the other hand, with the huge fertilizer subsidy in previous years the total fertilizer cost for rice farming was a mere 2 to 3% of the total cost of production or about 1.5% of the gross return. Incisive thinking on fertilizer subsidy is another matter that needs state attention.
The need for a national advisory body like the one in India set up by Nehru in 1963, which still continues with a name change made by Prime Minister Modi to give it more emphasis on technologies. Modi also recently reported repealing antiquated regulations that are adversely affecting small farmers. Moreover, whereas we have rushed to ban palm oil imports (now reversed) and oil palm cultivation, promoting coconut cultivation to meet the national oil yields despite it yielding only 20% of oil as oil palm, Modi has engaged in a policy of expanding oil palm cultivation extending it to irrigated lands and replacing some of the low-yielding arable oil crops. His target is to expand the oil palm cover from the current level of about 400,000 ha to a million by 2025. This writer repeats that our leaders should look at what happens elsewhere in the world apart from listening to proven experts in the respective fields.
Features
How many more must die before Sri Lanka fixes its killer roads?

On the morning of May 11, 2025, the quiet hills of Ramboda were pierced by the wails of sirens and the cries of survivors. A Sri Lanka Transport Board (SLTB) bus, en route from Kataragama to Kurunegala via Nuwara Eliya, veered off the winding road and plunged down a deep precipice in the Garandiella area. At least 23 people lost their lives and more than 35 were injured—some critically.
The nation mourned. But this wasn’t merely an isolated accident. It was a brutal reminder of Sri Lanka’s long-standing and worsening road safety crisis––one where the poor pay the highest price, and systemic neglect continues to endanger thousands every day.
A national epidemic
According to the Central Bank of Sri Lanka’s 2023 Road Safety Report, buses and other passenger vehicles are involved in 60% of fatalities while motorcycles account for 35% of reported accidents. Though three-wheelers are often criticised in the media, they contribute to only 12% of all accidents. The focus, however, remains disproportionately on smaller vehicles—ignoring the real danger posed by larger, state-run and private buses.
The Ramboda incident reflects what transport experts and road safety advocates have long warned about: that Sri Lanka’s road accident problem is not primarily about vehicle type, but about systemic failure. And the victims—more often than not—are those who rely on public transport because they have no other choice.
One of the biggest contributors to the frequency and severity of road accidents is Sri Lanka’s crumbling infrastructure. A 2023 report by the Sri Lanka Road Development Authority (SLRDA) noted that nearly 40% of the country’s road network is in poor or very poor condition. In rural and hilly areas, this figure is likely higher. Potholes, broken shoulders, eroded markings, and inadequate lighting are all too common. In mountainous terrain like Ramboda, these conditions can be fatal.
Even worse, since 2015, road development has effectively stagnated. Although the Mahinda Rajapaksa administration was often criticised for its ambitious infrastructure drive, it left behind a network of wide, well-lit highways and urban improvements. The subsequent administrations not only failed to continue this momentum, but actively reversed course in some instances—most notably, with the cancellation of the Light Rail Transit (LRT) project in Colombo, which had been poised to modernise urban mobility and reduce congestion.
Instead of scaling up, Sri Lanka scaled down. Maintenance budgets were slashed, long-term projects shelved, and development planning took a back seat to short-term political calculations. Roads deteriorated, traffic congestion worsened, and safety standards eroded.
Dangerous drivers
Infrastructure is only part of the story. Human behaviour plays a significant role too—and Sri Lanka’s roads often mirror the lawlessness that prevails off them.
A 2022 survey by the Sri Lanka Road Safety Council revealed alarming patterns in driver behaviour: 45% of accidents involved drivers under the influence of alcohol or drugs, and 40% were attributed to speeding. These figures reflect not just recklessness, but a dangerous culture of impunity.
The legal blood alcohol limit for drivers in Sri Lanka is 0.08%, but enforcement remains lax, particularly in rural areas and during off-peak hours. There is no consistent system of random breath testing, and police checkpoints are often limited to high-profile holidays or urban areas.
The same lack of enforcement applies to speeding, tailgating, overtaking on blind corners, and ignoring traffic signals. While the law technically provides for penalties, in practice, enforcement is selective at best. Even SLTB bus drivers—tasked with transporting hundreds daily—are known for aggressive and erratic driving. The Ramboda bus is reported to have been speeding on a dangerously narrow bend, a pattern that has become disturbingly common.
Public buses, both state-run and private, are some of the most dangerous vehicles on the road today—not just due to their size, but because of operational cultures that prioritise speed over safety. Competition for passengers, poor driver training, minimal vehicle maintenance, and weak regulatory oversight have created a deadly combination.
Do they not deserve better?
Most people who travel in SLTB buses are from lower-income backgrounds. They rely on public transportation not by choice, but by necessity. A factory worker in Nuwara Eliya, a schoolteacher in Bandarawela, or a daily wage earner commuting between towns—all are bound to a public transport system that is increasingly unreliable and unsafe.
Sri Lanka’s social contract has failed its most vulnerable. The poor are expected to brave substandard buses on crumbling roads, driven by underpaid and undertrained drivers, often in hazardous weather and terrain. In many rural areas, buses are lifelines. When one crashes, it is not merely a tragedy—it’s a profound injustice.
Had the LRT system gone forward, had road maintenance been prioritised, had reckless drivers been reined in through strict enforcement, how many lives could have been saved?
Experts agree that the solution lies in a combination of infrastructure investment, driver education, and law enforcement reform. The Sri Lanka Road Safety Council has repeatedly called for mandatory road safety training, particularly for commercial drivers. Such training should cover not just traffic laws, but also defensive driving, fatigue management, and the dangers of DUI.
Enforcement, too, needs a dramatic overhaul. License suspensions, large fines, and jail time for repeat offenders must become the norm—not the exception. A centralised traffic violation database could prevent habitual offenders from slipping through the cracks.
And critically, investment in infrastructure must resume—not in flashy mega-projects for political gain, but in safe, functional, and equitable roads and transit systems. The re-introduction of the LRT or similar mass transit projects should be seriously reconsidered, especially in urban centers where congestion is growing and road space is limited.
The misunderstood three-wheeler
On the other hand, while three-wheelers are frequently vilified in public discourse and media narratives for reckless driving, the data tells a different story. According to the Central Bank’s 2023 Road Safety Report, they account for just 12% of all road accidents—a fraction compared to the 60% involving buses and other passenger vehicles, and the 35% attributed to motorcycles. Yet, disproportionate attention continues to be directed at three-wheelers, conveniently shifting focus away from the far greater risks posed by large, state-run and private buses.
What often goes unacknowledged is the essential role three-wheelers play in Sri Lanka’s transport ecosystem, particularly in remote and rural areas where reliable public transport is virtually nonexistent. For residents of small towns and isolated villages in the hill country, three-wheelers are not a luxury—they are a necessity. Affordable, nimble, and capable of navigating narrow, winding roads where buses cannot operate, these vehicles have become the primary mode of short-distance travel for countless Sri Lankans.
Even more importantly, in the aftermath of road accidents—especially in remote regions like Ramboda—it is often the three-wheeler drivers who are the first to respond. When tragedy strikes, they ferry the injured to hospitals, assist with rescue efforts, and offer immediate aid long before official emergency services arrive. This community-centered, grassroots role is rarely acknowledged in national conversations about road safety, yet it remains a vital, life-saving contribution.
Rather than treating three-wheelers as a problem to be blamed, the government should recognise their indispensable value and work towards integrating them more effectively and safely into the national transport framework. Regularising the sector through measures such as mandatory driver training programmes, periodic vehicle safety checks, and the enforcement of standardised operating licenses could improve safety without displacing an essential service. Additionally, designating official three-wheeler stands, particularly in high-risk or high-traffic areas, and incentivising drivers who maintain clean safety records would help create a safer, more accountable environment for both passengers and pedestrians.
Moving beyond the blame game
It is time for us to move beyond the tired narrative that blames specific vehicles—motorcycles, three-wheelers, or buses—for the carnage on Sri Lanka’s roads. The problem is not the mode of transport. It is the system that surrounds it.
When buses are poorly maintained, roads are not repaired, drivers are not trained, and laws are not enforced, tragedy becomes inevitable. Blaming a single vehicle type does nothing to address these root causes.
The real question is: Do we have the political will to fix this? Or will Sri Lanka continue to count the dead—accident after accident—while doing little more than issuing condolences?
The Ramboda accident was not the first. It won’t be the last. But it should be the turning point.Let this be the moment we stop pointing fingers—and start fixing the road.
(The writer is an Attorney-at-Law with over a decade of experience specializing in civil law, a former Board Member of the Office of Missing Persons, and a former Legal Director of the Central Cultural Fund. He holds an LLM in International Business Law and resides in Battaramulla, where he experiences the daily challenges of commuting to Hulftsdorp, providing him with a unique perspective on Sri Lanka’s road safety issues.)
By Sampath Perera
Features
J’accuse – Need for streamlined investigation of corruption in former President’s office

Though the government is moving more slowly on corruption than I would have liked, it is moving, which is more than can be said for its predecessors. I remember how sad I was when Yahapalanaya did very little, except for political advantage, about the corruption it had highlighted in the election campaign in which I had so foolishly joined; but the reason became clear with the bond scam, when the Ranil Wickremesinghe administration rose to heights of corruption that surpassed, in convoluted ingenuity, anything the Mahinda Rajapaksa government could have achieved. Thus far the present government is clean, and that will make its task much easier.
I hope then that the slow but steady progress of this government in investigation will bear fruit. But at the same time, I think it would also be good if it looked at instances when corruption was avoided. The horrors of the visa scam, in which the Controller General of Immigration seems to have connived with his political masters, suggest how important it is to also praise those civil servants who resist pressures.
With regard to the visa scam, I had thought Tiran Alles largely responsible, but perhaps I have done the man an injustice – if that were conceivable – and the fountainhead of the matter was the President. I now think this the more likely, having heard about a Civil Servant who did stand up against the political pressures brought upon him. If this government were to look into the matter, and recognise his integrity and courage, perhaps that would prompt the former Controller General of Immigration and Emigration too to come clean and turn Crown Witness, having accepted a compounded penalty for anything he might have done wrong.
It can be difficult to resist pressure. That must be understood though it is no reason to excuse such conduct. But it is therefore more essential to praise the virtuous, such as the former Secretary to the Ministry of Health, Dr Palitha Mahipala. I had heard of him earlier, and I am sorry he was removed, though I have also heard good things about his successor, so there is no reason to bring him back. But perhaps he could be entrusted with greater responsibilities, and awarded some sort of honour in encouragement of those with courage.
One of the notable things Dr Mahipala did was to resist pressure brought upon him to award a contract to Francis Maude, a British crony of the President. This was to design a supply chain management for pharmaceuticals. A system for this was already being designed by the Asian Development Bank, but when told about this the authorities had nevertheless insisted.
The then Secretary to the Prime Minister cannot absolve himself of the responsibility for having asked the Ministry of Health to prepare a stunningly expensive MoU that was quite unnecessary.
But his claim was that he had been introduced to the Britisher by a top aide of the President. This rings true for it was the President who first wished Maude upon the country. It was after all Ranil Wickremesinghe who, a year after he became President, announced that, to boost state revenue, Maude had been invited ‘to visit Sri Lanka and share his insights on sectoral reform’.
When he became a Minister under David Cameron, Maude’s responsibilities included ‘public service efficiency and transparency’. There seems to have been nothing about revenue generation, though the President’s statement claimed that ‘Sri Lanka must explore new avenues for increasing income tax revenues…He expressed concern over not only the neglect of public revenue but also the unrestricted spending of public funds on non-beneficial activities’.
He ‘called for an extensive media campaign to educate the public’ but this did not happen, doubtless because transparency went by the board, in his antics, including the demand, whoever prompted it, that Maude be to do something already done. Surely, this comes under the heading of unrestricted spending of public funds on non-beneficial activities, and it is difficult to believe that top government officials connived at promoting this while Ranil would have expressed concern had he known what they were up to.
Nothing further is recorded of Ranil’s original trumpeting of Maude’s virtues, and far from being there to provide advice on the basis of his experience in government, he seems to have been trawling for business for the firm he had set up on leaving politics, for it was with that private agency that the MoU was urged.
Thankfully, Dr Mahipala resisted pressure, and that plot came to nothing. But it should not be forgotten, and the government would do well to question those responsible for what happened, after speaking to Dr Mahipala and looking at the file.
Indeed, given the amount of corruption that can be traced to the President’s Office, it would make sense for the government to institute a Commission of Inquiry to look into what happened in that period of intensive corruption. It should be subject to judicial appeal, but I have no doubt that incisive questioning of those who ran that place would lead to enough information to institute prosecutions, and financial recompense for the abuses that occurred.
by Prof. Rajiva Wijesinha
Features
Trump’s Press Secretary; no attention to the health crisis

 In her Cry on 25 April, Cassandra wrote this in her section on Trump’s moves to Make America Great Again – MAGA. “The latest was heard on BBC news on Wednesday 16. A fluff of a blonde White House press secretary by name of Karoline Leavitt announces that President Trump expects Harvard University to apologise to him for the continuing tolerance of anti-Semitism by the university. And that little blonde fluff adds ‘And they should.’ Didn’t Cass guffaw, but bitterly. That’s Trump vs Harvard.”
In her Cry on 25 April, Cassandra wrote this in her section on Trump’s moves to Make America Great Again – MAGA. “The latest was heard on BBC news on Wednesday 16. A fluff of a blonde White House press secretary by name of Karoline Leavitt announces that President Trump expects Harvard University to apologise to him for the continuing tolerance of anti-Semitism by the university. And that little blonde fluff adds ‘And they should.’ Didn’t Cass guffaw, but bitterly. That’s Trump vs Harvard.”
Karoline Leavitt
This young blonde has been making waves ever since, so much so that night shows in the US have spoken of her, and not well. Jimmy Kimmel arranged a dialogue between Karoline and Mark Carney, PM of Canada, when he recently visited the US. She insulted him by saying he did not know what democracy was and that Canada would benefit by becoming the 51st of the US. Carney vowed Canada was not for sale and never would be. The interview which was described in a video which I watched got hotter, Carney became cooler and Karoline rattled until she shot up and left the room. The usually noisy crowd that collects to listen to Kimmel roared – disdain.
Cass had to ferret more about her, so she went to the Internet. Born in 1997, Karoline Leavitt studied politics and communication at Saint Anselm College, which she entered on a games scholarship. She interned in the White House as an apprentice press secretary and was named a press secretary in Trump‘s first term. After Trump’s loss in 2020, she became a communications director for New York. She was the Republican candidate in the US House of Reps election for New Hampshire in 2022 but lost. She was much in Trump’s campaign against Biden’s winning and then served as a spokeswoman for MAGA Inc. In November 2024, Trump named her his White House Press Secretary, the youngest to hold this post in US history. All this seems to have gone to her blonde head!
Mosquitoes making life hell in Colombo
These pests are breeding like mad in and around Colombo and other parts of the country too. We can be tolerant of nature and its creatures, but the mosquito now is deadly. She passes on the dreaded diseases of chikungunya and dengue; the former debilitating for months after the grueling ache in bones is abated as the infection recedes. Dengue can be fatal if one’s platelet count goes below the red line.
The crux of the near pandemic of these two diseases is that infection and prevalence of the two could be greatly reduced by control of the carrier of the infection – The Mosquito. And on whom rests the responsibility of controlling the breeding of mosquitoes? On You and Me. But both of these entities are often careless, and totally non-caring about keeping their premises clean and of course eliminating all breeding spots for flying pests. Does the responsibility end there? Not upon your life! The buck moves on and lands on the public health inspectors, the garbage removers, the fumigators. Their boss who sees to them working properly is the Medical Officer of Health. And he is part of the Colombo Municipal Council that has the responsibility of looking to the health of people within the MC.
The spread of the two diseases mentioned is proof that the above persons and establishments are NOT doing the work they should be doing.
It is a proven fact that just before a change in personnel in the country, or a MC or a Pradeshiya Sabha, with a general election or local government election in the near future, most work stops in government offices or in local government establishments as the case may be. Workers get the disease of ennui; do minimum work until new bosses take over.
This definitely has happened in Colombo. Cass lives in Colombo 3. Quite frequent fumigation stopped some time ago. About two weeks ago she heard the process and smelled the fumes. Then nothing and mosquitoes breeding with the infrequent rain and no repellents or cleaning of premises. She phoned the MOH’s office on Thursday last week. Was promised fumigation. Nothing.
We are in a serious situation but no Municipal Council action. Politics is to blame here too. The SJB is trying to grab control of the Colombo MC and people are falling prey to the two diseases. All politicians shout it’s all for the people they enter politics, etc. The NPP has definitely shown concern for the public and have at least to a large extent eliminated corruption in public life. They have a woman candidate for Mayor who sure seems to be able to do a very good job. Her concern seems to be the people. But no. A power struggle goes on and its root cause: selfishness and non-caring of the good of the people. And for more than a week, the personnel from the MOH are looking on as more people suffer due to dirty surroundings.
Garbage is collected from her area on Tuesdays and Saturdays with paper, etc., on Thursdays. Tuesday 13 was a holiday but garbage was put out for collection. Not done. At noon, she phoned a supervisor of the cleaning company concerned only to ask whether the workers had a day off. Garbage was removed almost immediately. That is concern, efficiency and serving the public.
As Cass said, Colombo is in near crisis with two mosquito borne diseases mowing down people drastically. And nothing is being done by the officers who are given the responsibility of seeing to the cleanliness of the city and its suburbs.
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoSAITM Graduates Overcome Adversity, Excel Despite Challenges
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoDrs. Navaratnam’s consultation fee three rupees NOT Rs. 300
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoDestined to be pope:Brother says Leo XIV always wanted to be a priest
-

 Foreign News7 days ago
Foreign News7 days agoMexico sues Google over ‘Gulf of America’ name change
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoASBC Asian U22 and Youth Boxing Championships from Monday
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoChampioning Geckos, Conservation, and Cross-Disciplinary Research in Sri Lanka
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDilmah – HSBC future writers festival attracts 150+ entries
-

 Midweek Review3 days ago
Midweek Review3 days agoBronze statue for P’karan, NPP defeat in the North and 16th anniversary of triumph over terrorism












