Opinion
Are agrochemicals the cause of the Rajarata Kidney Disease?

By Dr Parakrama Waidyanatha
Various reports in the media yet claim that the Rajarata kidney disease, scientifically defined as the chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu), is caused by agrochemicals whereas the overwhelming evidence is that it is caused by hard water and fluoride prevalent in dug wells on high ground. Further it claimed that the number of patients is on the increase whereas published evidence is that it has been decreasing from 2016.
Agrochemicals are not the cause
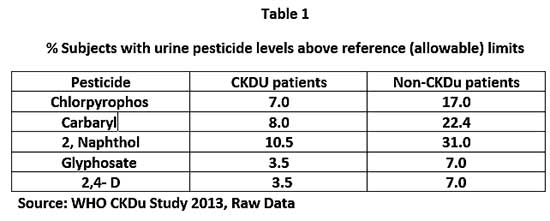
An exhaustive study carried out by the World Health Organization under the aegis of the National Science Foundation of Sri Lanka (NSF)was published in 2013. Although it failed to bring out conclusive evidence as to the etiology, it suggested an involvement of pesticides in the causation of the disease in that residues of some pesticides were above reference levels in the urine of CKDu patients. However, the pesticides residues of subjects in a non CKDu, control area (Hambantota) were also measured but the report failed to quote that data. The writer was able to get the raw data of the urine pesticide residues of Hambantota from the NSF, and to his dismay it was found that the residue levels were far higher in the urine of non-CKDu subjects of Hambantota as seen in Table 1 .As per the grapevine, the draft Report did not come up with any firm conclusions but at the insistence of the then political authority they were compelled to make some conclusions. So, it was vaguely concluded that agrochemicals probably played a role in the etiology of the disease. It is probably why the data of the non-CKDu patients were not reported!
A report entitled “Health effects of fertilis ers and pesticides” was submitted to the authorities on 22-October-2021 by none other than Dr S. H. Munasinghe, Secretary, Ministry of Health. Therein he has clearly stated that there is no evidence for a direct link between the kidney disease and agrochemicals. The report may be read at: https://dh-web.org/place.names/posts/Ministry of HealthReviewAgroChem2021.pdf. (See Table 1)
There have been various other unsubstantiated claims for a link between agrochemicals and the kidney disease. For example, a research paper in an open-access (fee levying) journal, titled ‘International Journal of Public Health, Prof. Channa Jayasumana and two other authors hypothesised that glyphosate forms complexes with heavy metals such as cadmium and arsenic in hard water causing the kidney disease. No evidence has been established to prove the formation of such complexes. However, the claim that glyphosate is a probable etiolating agent led to the then government to ban glyphosate which caused serious hardships in weed management in crops. The ban was finally lifted initially for tea and later for all crops!
The claim that agrochemicals are the cause of many health problems have let to the coining of the term wasa visa to agrochemicals. It has also been purported that Sri Lanka is the country that uses the highest quantities of fertilisers and pesticides in the world! However, the available evidence as shown in Table 2 clearly establishes that Sri Lanka is one of the countries using the least amounts of both fertilisers and pesticides. (See Table 2)
Hard water and fluoride are the key causes for the disease
Not agrochemicals but fluoride and hard water are the causes for the kidney disease have been now well established. Apartment from several quality publications, a dramatic study compared two adjacent villages in Girandurukotte, namely, Badulupura, on high ground where the people exclusively drank water from dug wells and Sarabhumi in the plain where the people drank water from the river, reservoir or wells dug close to their homes. The Badulupura people contracted the disease, while affecting virtually none from Sarabhumi. Analysis of the water in the wells in the Badulupura and Sarabhumi revealed that the Badulupura water was hard and heavily contaminated with fluoride, a highly nephrotoxic chemical. However, there was no evidence of any agrochemicals above safety limits in the Badulupura waters. Further evidence for a role for fluoride in the disease is that CKD patients also often have dental fluorosis.
That people living in the planes and consuming water from reservoirs and rivers do not contaminate the disease is further exemplified by the fact that people in the Anuradhapura city and consuming tap water from the reservoirs do not contaminate the disease.
Commencing in the mid 2010-decade, community-based reverse osmosis (RO) water treatment plants were established as an interim measure for producing safe drinking water for the endemic areas of the kidney disease in the rural dry zone of Sri Lanka. It was reported that RO –treated water diminished progression of the disease. In addition, during the same period rain water harvesting and consumption were introduced to the Badulupura people, and it has now been reported there has been a diminution of the occurrence of the disease in the village. However, a formal study yet needs to be done to confirm this observation.
Moreover, a study published in the journal, Science of the Total Environment( Vol. 745, 2020) by a Japanese team of scientists in collaboration with some Sri Lankan scientists established that alkalinity, hardness and microbial parameters in the ground waters exceeded the maximum allowable limits(MAL) for drinking water in all disease affected study areas. Also, Magnesium exceeded the minimum allowable limit exclusively in the disease prevalent areas.
A further study involving feeding Wistar rats undertaken at the University of Peradeniya and reported in an issue of Ceylon Medical Journal in 2017 established that high fluoride, hard water and other undetected toxins in shallow dug wells may be the causative factor for renal and liver lesions that were detected in these rats. (Figure 01)
In vegetable growing areas of the upcountry and Puttalam where agrochemical use has been far more than in the Rajarata, no CKD has been reported. Moreover, in Mulaitive, a hard water area where no agrochemicals had been hardly used due to unavailability during the Tamil rebellion which lasted over two decades, no CKD has been reported.
Evidence is thus, overwhelming that the chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKD) is related to drinking hard water containing fluoride and magnesium. Some 176,000 such wells are reported to be present in the Rajarata.
The disease in the early stages of research towards detection of its etiology was referred to it as ‘the chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology’ (CKDu). But now with a firm understanding of the cause of the disease the ‘u’ has been dropped and the disease should be referred to as the chronic kidney disease (CKD).
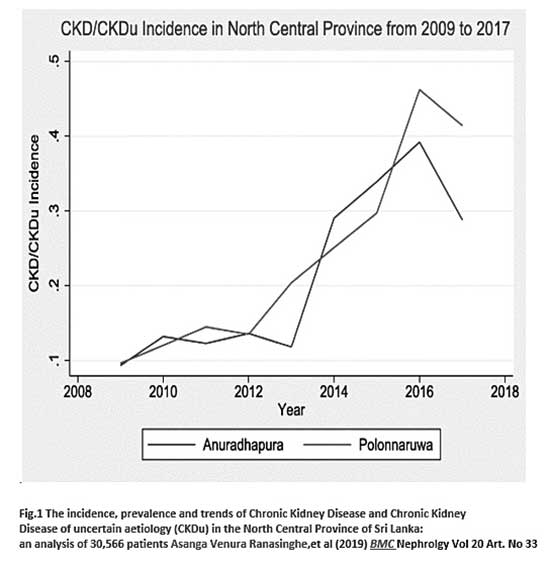
However, there are also recent claims that the numbers of CKD patients are on the increase. On the other hand the Figure 1. Clearly shows that the numbers of new patients are on the decline after the introduction of RO filters and rainwater harvesting. Regrettably, it appears that the health authorities have not published the data after 2017.
Although adequate supplies of safe drinking water may not be available in all CKD endemic areas, the people are now amply aware that the disease is caused by the consumption of hard water from wells on high ground containing fluoride and magnesium, and they avoid drinking such water.
Opinion
Structural Failures and Economic Consequences in Sri Lanka – Part II

Research and Development in Crisis:
(Part I of this article appeared in The Island of 07. 12. 2025)
China and India as Unequal Competitors
China and India did not emerge as global economic powers through unrestricted exposure to international competition. Their industrial sectors benefited from decades of state support, protected domestic markets, subsidised inputs, and coordinated innovation policies. Public investment in R&D, infrastructure, and human capital created conditions for large-scale, low-cost production.
Sri Lankan producers, by contrast, operate in a vastly different environment. They face high energy costs, limited access to capital, weak logistics, and minimal state support. Expecting them to compete directly with Chinese or Indian manufacturers without comparable policy backing is economically unrealistic and strategically unsound. Treating global competition as inherently fair ignores structural asymmetries. Without deliberate policy intervention, Sri Lanka will remain a consumption-oriented economy dependent on external production. Recognising unequal competition is the first step toward designing realistic, protective, and development-oriented R&D policies.
University Research Under Structural Threat
University-based research in Sri Lanka is facing a structural crisis that threatens its long-term viability. Universities remain the primary centers of knowledge generation, yet they are constrained by rigid administrative systems, inadequate funding, and limited autonomy. Academic research is often treated as an auxiliary activity rather than a core institutional mandate, resulting in heavy teaching loads that leave minimal time for meaningful research engagement.
A major challenge is that university innovations frequently remain confined to academic outputs with little societal or economic impact. Research success is measured primarily through publications rather than problem-solving or commercialisation. This disconnect discourages applied research and weakens university-industry linkages. Consequently, many promising innovations never progress beyond the proof-of-concept stage, despite strong potential for real-world application.
Publication itself has become a financial burden for researchers. The global shift toward open-access publishing has transferred costs from readers to authors, with publication fees commonly ranging from USD 3,000 to 4,500. For Sri Lankan academics, these costs are prohibitive. The absence of national publication support mechanisms forces researchers to either publish in low-visibility outlets or self-finance at personal financial risk, further marginalising Sri Lankan scholarship globally.
Limited Access to International Conferences
International conferences play a critical role in the research ecosystem by facilitating knowledge exchange, collaboration, and visibility. They provide platforms for researchers to present findings, receive peer feedback, and establish professional networks that often lead to joint projects and external funding. However, Sri Lankan researchers face severe constraints in accessing these opportunities due to limited institutional and national funding.
Conference participation is frequently viewed as discretionary rather than essential. Funding allocations, where they exist, are insufficient to cover registration fees, travel, and accommodation. As a result, researchers often rely on personal funds or forego participation altogether. This disproportionately affects early-career researchers, who most need exposure and mentorship to establish themselves internationally.
The cumulative effect of limited conference participation is scientific isolation. Sri Lankan research becomes less visible, collaborations decline, and awareness of emerging global trends weakens. Over time, this isolation reduces competitiveness in grant applications and limits the country’s ability to integrate into global research networks, further entrenching systemic disadvantage.
International Patents and Missed Global Markets
Given the limitations of the domestic market, international markets offer a vital opportunity for Sri Lankan innovations. However, accessing these markets requires robust intellectual property protection beyond national borders. International patenting is expensive, complex, and legally demanding, placing it beyond the reach of most individual researchers and institutions in Sri Lanka.
Without state-backed support mechanisms, local innovators struggle to file, maintain, and enforce patents in foreign jurisdictions. Costs associated with Patent Cooperation Treaty applications, national phase entries, and legal representation are prohibitive. As a result, many innovations are either not patented internationally or are disclosed prematurely through publication, rendering them vulnerable to appropriation by foreign entities.
This failure to protect intellectual property globally results in lost export opportunities and diminished national returns on research investment. Technologies with potential relevance to global markets particularly in agriculture, veterinary science, and biotechnology remain underexploited. A systematic approach to international patenting is essential if Sri Lanka is to transition from a knowledge generator to a knowledge exporter.
Bureaucratic Barriers to International Collaboration
International research collaboration is increasingly essential in a globalized scientific environment. Partnerships with foreign universities, research institutes, and funding agencies provide access to advanced facilities, diverse expertise, and external funding. However, Sri Lanka’s bureaucratic processes for approving international collaborations remain excessively slow and complex.
Memoranda of Understanding with foreign institutions often require multiple layers of approval across ministries, departments, and governing bodies. These procedures can take months or even years, by which time funding windows or collaborative opportunities have closed. Foreign partners, accustomed to efficient administrative systems, frequently withdraw due to uncertainty and delay.
This bureaucratic inertia undermines Sri Lanka’s credibility as a research partner. In a competitive global environment, countries that cannot respond quickly lose opportunities. Streamlining approval processes through delegated authority and single-window mechanisms is critical to ensuring that Sri Lanka remains an attractive destination for international research collaboration.
Research Procurement and Audit Constraints
Rigid procurement regulations pose one of the most immediate operational challenges to research in Sri Lanka. Scientific research often requires highly specific reagents, equipment, or consumables that are available only from selected suppliers. Standard procurement rules, which mandate multiple quotations and lowest-price selection, are poorly suited to the realities of experimental science.
In biomedical and veterinary research, for example, reproducibility often depends on using antibodies, kits, or reagents from the same manufacturer. Substituting products based solely on price can alter experimental outcomes, compromise data integrity, and invalidate entire studies. Even though procurement officers and auditors frequently lack the scientific background to appreciate these nuances.
Lengthy procurement processes further exacerbate the problem. Delays in acquiring time-sensitive materials disrupt experiments, extend project timelines, and increase costs. For grant-funded research with fixed deadlines, such delays can result in underperformance or loss of funding. Procurement reform tailored to research needs is therefore essential.
Audit Practices Misaligned with Research and Innovation
While financial accountability is essential in publicly funded research, audit practices in Sri Lanka often fail to recognize the distinctive and uncertain nature of scientific and innovation-driven work. Auditors trained primarily in general public finance frequently apply rigid procedural interpretations that are poorly aligned with research timelines, intellectual property development, and iterative experimentation. This disconnect results in frequent audit queries that challenge legitimate scientific, technical, and strategic decisions made by research teams.
There are documented instances where principal investigators and research teams are questioned by auditors regarding the timing of patent applications, perceived delays in filing, or outcomes of the patent review process. In such cases, responsibility is often inappropriately placed on investigators, rather than on structural inefficiencies within patent authorities, institutional IP offices, or prolonged examination timelines beyond researchers’ control. This misallocation of accountability creates an environment where researchers are penalized for systemic failures, discouraging engagement with the patenting process altogether.
Lengthy patent application review periods often extending beyond the duration of time-bound, grant-funded projects can result in incomplete, weakened, or abandoned patents. When reviewer feedback or amendment requests arrive after project closure, research teams typically lack funding to conduct additional validation studies, refine claims, or seek legal assistance. Despite these structural constraints, audit queries may still cite “delays” or “non-compliance” by investigators, further exacerbating institutional risk aversion and undermining innovation incentives.
Beyond patent-related issues, researchers are compelled to spend substantial time responding to audit observations, justifying procurement decisions, or explaining complex methodological choices to non-specialists. This administrative burden diverts time and intellectual energy away from core research activities and contributes to frustration, demoralization, and reduced productivity. In extreme cases, fear of audit repercussions leads researchers to avoid ambitious, interdisciplinary, or translational projects that carry higher uncertainty but greater potential impact.
The absence of structured dialogue between auditors, patent authorities, institutional administrators, and the research community has entrenched mistrust and inefficiency. Developing research-sensitive audit frameworks, training auditors in the fundamentals of scientific research and intellectual property processes, and clearly distinguishing individual responsibility from systemic institutional failures would significantly improve accountability without undermining innovation. Effective accountability mechanisms should enable scientific excellence and economic translation, not constrain them through procedural rigidity and misplaced blame.
Limited Training and Capacity-Building Opportunities
Continuous training and capacity building are essential for maintaining a competitive research workforce in a rapidly evolving global knowledge economy. Advances in methodologies, instrumentation, data analytics, and regulatory standards require researchers to update their skills regularly. However, opportunities for structured training, advanced short courses, and technical skill enhancement remain extremely limited in Sri Lanka.
Funding constraints significantly restrict access to international training programs and specialized workshops. Overseas short courses, laboratory attachments, and industry-linked training are often beyond institutional budgets, while national-level training programs are sporadic and narrow in scope. As a result, many researchers rely on self-learning or informal knowledge transfer, which cannot fully substitute for hands-on exposure to cutting-edge techniques.
The absence of systematic capacity-building initiatives creates a widening skills gap between Sri Lankan researchers and their international counterparts. This gap affects research quality, competitiveness in grant applications, and the ability to absorb advanced foreign technologies. Without sustained investment in human capital development, even increased research funding would yield limited returns.
From Discussion to Implementation
Sri Lanka does not lack policy dialogue on research and innovation. Numerous reports, committee recommendations, and strategic plans have repeatedly identified the same structural weaknesses in funding, commercialization, governance, and market access. What is lacking is decisive implementation backed by political commitment and institutional accountability.
Protecting locally developed R&D products during their infancy, reforming procurement and audit systems, stabilizing fiscal policy, and supporting publication and conference participation are not radical interventions. They are well-established policy instruments used by countries that have successfully transitioned to innovation-led growth. The failure lies not in policy design but in execution and continuity. Implementation requires a shift in mindset from viewing R&D as a cost to recognizing it as a strategic investment. This shift must be reflected in budgetary priorities, administrative reforms, and measurable performance indicators. Without such alignment, discussions will continue to cycle without tangible impact on the ground.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Dependence and Innovation
Sri Lanka stands at a critical crossroads in its development trajectory. Continued neglect of research and development will lock the country into long-term technological dependence, import reliance, and economic vulnerability. In such a scenario, local production capacity will continue to erode, skilled human capital will migrate, and national resilience will weaken. Alternatively, strategic investment in R&D, coupled with protective and enabling policies, can unlock Sri Lanka’s latent innovation potential. Sustained funding, institutional reform, quality enforcement, and market protection for locally developed products can transform research outputs into engines of growth. This path demands patience, policy consistency, and political courage.
As Albert Einstein aptly has aptly us, “The true failure of research lies not in unanswered questions, but in knowledge trapped by institutional, financial, and systemic barriers to dissemination.” The choice before Sri Lanka is therefore not between consumers and producers, nor between openness and protection. It is between short-term convenience and long-term national survival. Without decisive action, Sri Lanka risks outsourcing not only its production and innovation, but also its future.
Prof. M. P. S. Magamage is a senior academic and former Dean of the Faculty of Agricultural Sciences at the Sabaragamuwa University of Sri Lanka. He has also served as Chairman of the National Livestock Development Board of Sri Lanka and is an accomplished scholar with extensive national and international experience. Prof. Magamage is a Fulbright Scholar, Indian Science Research Fellow, and Australian Endeavour Fellow, and has served as a Visiting Professor at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, USA. He has published both locally and internationally reputed journals and has made significant contributions to research commercialization, with patents registered under his name. His work spans agricultural sciences, livestock development, and innovation-led policy engagement. E-mail: magamage@agri.sab.ac.lk
by Prof. M. P. S. Magamage
Sabaragamuwa University of
Sri Lanka
Opinion
Why do we have to wait in queues?

Queues! Not the temporary ones for fuel or rice that appear from time to time, but the permanent queues we encounter at places like the passport office, identity card office, and hospital clinics. People often gather at these institutions well before opening hours, crowding the premises unnecessarily.
Why don’t the officers in charge take steps to reduce these waiting times? In most of these places, the rush subsides within two or three hours after opening. If the public were properly informed of the operating hours, they could arrive at a reasonable time instead of crowding from early morning.
Consider two examples: A couple visited the passport office around 10 a.m. to apply for their first passport (not the one-day service). Only two people were ahead of them. Within 45–50 minutes, all formalities were completed. Yet, prior-advice from friends had been to be there by 7:30 a.m.
• At Apeksha Hospital, a patient arrived at 7 a.m. for his first appointment and joined the crowd. By the time he finished around 10:30 a.m., the premises were almost deserted.
What do these incidents reveal? That much of the crowding is unnecessary, caused by misinformation and habit rather than actual demand. Public awareness campaigns could encourage people to come during staggered times.
Moreover, institutions like the passport office could introduce structured systems to manage attendance—for example:
• Appointments booked in advance
• Allocating days by alphabetical order (e.g., names starting with A–E on Mondays, F–J on Tuesdays, and so on)
Another form of time-wasting occurs at doctor channelling centres, and this is even more inhumane because it involves ailing patients. Doctors, knowing well the time they can realistically arrive, allow centres to advertise a starting time that misleads patients. Worse still, doctors who visit multiple centres fix times for their second or third visits without accounting for delays at the earlier centre.
This lack of coordination results in sick patients waiting for hours unnecessarily. Such practices must be regularised. After all, neither doctors nor channelling centres provide their services free of charge. In fact, this may be the only place where the customer is not treated as king.
Whether at government offices or private medical centres, the common thread is inefficiency and disregard for the public’s time. By introducing appointment systems, staggered schedules, and stricter regulation of medical channelling centres, we can reduce queues, ease patient suffering, and restore dignity to public services.
D R
Opinion
Retaining retired professionals for Presidential TF

I write further to the recent public discourse surrounding the Presidential Task Force appointed to oversee rehabilitation, recovery, and reconstruction following the devastation caused by the recent cyclonic event.
At the outset, I wish to place on record my appreciation of the speed, resolve, and sense of urgency demonstrated by President Anura Kumara Dissanayake in establishing a high-powered coordination mechanism at this critical juncture. In a country still emerging from the after-effects of a severe financial crisis, such decisive leadership has provided reassurance and direction to the nation.
A feature article published in a leading newspaper by Dr. C. Narayanasami, a former member of the Ceylon Civil Service and retired senior professional of the Asian Development Bank, makes an observation that merits serious consideration. He rightly notes that the ultimate success of the Task Force will hinge not merely on its mandate, but on the technical competence, experience, and delivery capacity of those entrusted with implementation.
It is an uncomfortable but widely acknowledged reality that the present public service—through no fault of many dedicated officers—has been weakened over time by capacity erosion, skills gaps, and systemic constraints. The magnitude, complexity, and urgency of the post-cyclone reconstruction effort demand expertise that goes beyond routine administrative functions and requires seasoned judgment, sectorial depth, and crisis-tested leadership.
In this context, I urge the government to consider formally engaging retired subject-matter specialists from both the public and private sectors, locally and overseas, on a short-term or task-based basis to support the work of the Task Force and its sub-committees. Sri Lanka possesses a considerable pool of retired engineers, planners, economists, administrators, project managers, and development professionals who have previously led large-scale reconstruction, infrastructure, and emergency-response programs, both nationally and internationally.
Such engagement would:
• strengthen technical decision-making and implementation capacity;
• reduce pressure on an already stretched public service;
• accelerate delivery without significant fiscal burden; and
• send a strong signal of inclusivity and national mobilization in a time of crisis.
Many of these professionals would, I believe, be willing to serve on modest terms—motivated less by remuneration and more by a sense of duty to contribute to national recovery at a critical moment.
The President can harness this reservoir of experience in support of the government’s rebuilding agenda. The judicious blending of existing public-sector structures with retired expertise could significantly enhance delivery outcomes and public confidence.
Having handled large-scale projects funded by the International Funding Agencies and with my experience spanning over five decades as a project consultant, I may also be able to help the Task Force in this difficult hour.
I offer these thoughts in a spirit of constructive engagement and deep respect for the immense responsibilities currently borne by the government.
J .A. A. S. Ranasinghe
Colombo 5.
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoInterception of SL fishing craft by Seychelles: Trawler owners demand international investigation
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoBroad support emerges for Faiszer’s sweeping proposals on long- delayed divorce and personal law reforms
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoPrivate airline crew member nabbed with contraband gold
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoPrez seeks Harsha’s help to address CC’s concerns over appointment of AG
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoGovt. exploring possibility of converting EPF benefits into private sector pensions
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoEducational reforms under the NPP government
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoHealth Minister sends letter of demand for one billion rupees in damages
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoPharmaceuticals, deaths, and work ethics