Business
A cut tree, a dead elephant, is a lost tourism dollar in the future

by Michel Nugawela and Pesala Karunaratna
Four decades of inaction since introduction of open economy – Sri Lanka has never missed an opportunity to miss an opportunity
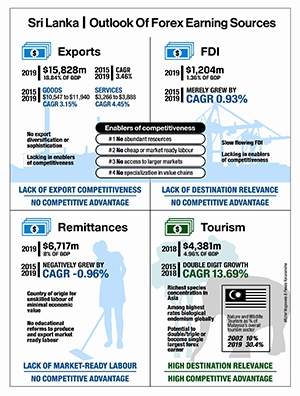
Globally and regionally, country is unplanned and unprepared to drive forex earnings; exports, FDIs, and foreign-earned wage remittances record very slow growth rates below CAGR 5%
With CAGR 13.69%, tourism sector shows resilience despite no concentrated effort or national strategy; emerges as priority sector in medium-term to be No 1 forex earner
Nature and wildlife tourism has most potential to drive Sri Lanka as a hot destination for high value travellers as global mobility returns in 2021
A single elephant, alive, contributes $0.16mn a year or $11mn over its lifetime to tourism sector; 350 elephant deaths in 2019 amount to economic value of $3.9bn had they lived their lives fully
Forest cover reduced by 130,349 hectares from 2010-2019 reflecting a sharp increase of 8.6% of net forest change
 The coronavirus crisis throws into sharp relief the tenuous state of Sri Lanka’s economy. The government is committed to export expansion but remains handicapped by decades of unpreparedness in strengthening the underlying enablers of competitiveness.
The coronavirus crisis throws into sharp relief the tenuous state of Sri Lanka’s economy. The government is committed to export expansion but remains handicapped by decades of unpreparedness in strengthening the underlying enablers of competitiveness.
This opinion paper proposes a refocus on tourism as the priority sector to drive growth as Sri Lanka begins the difficult and lengthy task of reforming, restructuring, and strengthening national competitiveness. This will require shifting away from one-size-fits-all marketing under the mass tourism model to developing a product differentiation strategy that targets the best tourists – the high value traveller – with our best assets – nature and wildlife. This broad and diverse segment of travellers outspend mass tourists by 3-4 times and will be the first to travel and visit other countries once global mobility returns in 2021.
However, the high rate of deforestation dismantles the only competitive advantage Sri Lanka has to compete internationally and increase its exports of services. By stripping away nature and wildlife assets, the destination will be left with only its beaches and reputation for cheap sea-sun-sand tourism in the future.
Stagnant exports of goods and services
Exports of goods and services (% of GDP) was reported at 18.8% in 2019 of which goods accounted for 14.2% and services for 4.6%. In the years 2015-2019, total exports of goods grew from $10,547mn to $11,940mn – CAGR 3.15% – while total exports of services increased from $3,266mn to $3,888mn – just CAGR 4.45%.
Sri Lanka continues to lag other emerging economies in Asia that have successfully transitioned from an overreliance on primary goods to achieve export diversification and sophistication. In 1989, our total exports of goods and services as a percentage of GDP was 21.4% against Vietnam’s 16.5%. Thirty years later, our exports had shrunk to 18.8% as Vietnam’s increased to 119.3%. The reasons for this disparity can be found in the underlying enablers of export competitiveness where Sri Lanka’s capabilities are weak or entirely lacking.
Enabler #1 – Resource abundance
We have none. Consider the example of India’s BPO industry which is around 1% of the country’s GDP and 6% share of global BPO, directly and indirectly employing 10mn people. According to Tholons and AT Kearney Indexes of 2019, India remains the leading country to outsource because of cheap labour costs, a huge talent pool of skilled, English-speaking professionals (India’s English proficiency: #35/100 in the world and #5/25 in Asia), and tech-savvy manpower, despite competition from The Philippines, Vietnam and other Asian countries.
Enabler #2 – Price and contribution of unskilled or market-ready labour
We are stagnating at middle-income levels. The unskilled labour market demands higher wages and Sri Lanka lacks a pool of skilled market-ready workers (unlike the example of India, above).
Enabler #3 – Trade agreements that give producers access to a larger market
Domestic interest groups in Sri Lanka have opposed and successfully pressured governments to abandon free trade agreements. Meanwhile, emerging economies like Vietnam have made huge economic advances through trade liberalization and global integration. Since its Doi Moi reforms, the country has signed 12 (mostly bilateral) FTAs that have increased trade by ten-fold – from US$30bn in 2000 to almost US$300bn by 2014 – shifting it away from exports of primary goods and low-tech manufacturing products to more complex high-tech goods like electronics, machinery, vehicles and medical devices. The competitiveness of its exports will continue to increase, firstly, through more diversified input sources from larger trade networks and cheaper imports of intermediate goods from partner countries, and secondly, through partnerships with foreign firms that transfer the know-how and technology that is needed to leap into higher valued-added production.
Enabler #4 – Ability to enter, establish or move up regional or global value chains and production networks
Today, global firms optimize resources by investing or outsourcing the design, procurement, production, or distribution stages of their value chain activities across different countries. Yet since 1978, Sri Lanka has only captured share in the manufacturing and design stages of the global apparel value chain. The examples of Vietnam and Thailand demonstrate how both economies have become integral to different stages of the smartphone and automobile value chains for Samsung and Toyota.
Vietnam:
Vietnam attracted Samsung at the early stages of smartphone evolution. Samsung established its first factory in Vietnam in 2008, when smartphone penetration was 10.8% globally; today it has three factories in Vietnam and world smartphone penetration is at 41%. Samsung remains the single largest foreign investor in Vietnam, with investments totaling $17bn (20% of Sri Lanka’s GDP) whilst Vietnam’s exports of smartphones and spare parts, mostly produced by Samsung Electronics, account for $51.38bn (20% of Vietnam’s GDP). On top of the current $220mn Samsung R&D center, Vietnamese Prime Minister Nguyen Xuan Phuc has requested Samsung Chairman Lee Jae-yong to next invest in a chip manufacturing plant, further strengthening the country’s competitiveness and sophistication in exports.
Thailand:
Toyota’s decision to enter the Thai automobile market in 1962 was largely due to the country’s industrial policy regime. Today – after 6 decades of concentrated effort between the Thai government and Toyota – Thailand is becoming a global passenger car production hub. Toyota’s investments have also helped to transfer knowledge and technology into Thailand, strengthening the R&D capabilities of Thai engineers. Toyota Thailand president Michinobu Sugata has expressed complete confidence in both Thailand and the company’s future direction in the country.
Since 1978, Sri Lanka has repeatedly missed opportunities to enter or establish itself in global value chains and production networks. We continue to be unplanned and unprepared in strengthening the underlying enablers of export competitiveness. Expect meagre export growth to continue.
Slow flowing foreign direct investment
These enablers of competitiveness are also the most important considerations to increase foreign direct investment. Inflows between 2015-2019 totalled $6.4bn, averaging $1.2bn every year and merely growing by CAGR 0.93% (this excludes the 99-year lease of Hambantota port to China in exchange for $1.1bn). Without improving supply-side constraints, international investors will remain reluctant to sink substantial resources in the country.
Strengthening the underlying enablers of competitiveness will take time. Expect stagnation in FDI inflows to continue.
Sluggish foreign worker remittances
Sri Lanka has become a major country of origin for unskilled workers with minimal economic value. Wage receipts, which amounted to $6,717mn in 2019 or 8% of GDP, negatively grew by CAGR -0.96% between the years 2015-2019. In 2019, the highest inflow ($3,459mn) came from the Middle East, a segment that participates in the lowest economic positions and lacks the skills, abilities and qualifications to mitigate any downturn in value in remittance flows.
However, the demographics are changing for neighbouring countries like India, where an increasing number of skilled white-collar workers (a growing cohort of professionals in the IT and engineering fields, according to MoneyGram) are quadrupling the average volume per each remittance.
To export quality human capital and increase our share of foreign-earned wages, Sri Lanka must introduce transformational policy reforms in education. Our university system – supported by proactive primary and secondary education systems – must be restructured to produce market-ready workers with the skills and adaptability to learn, grow and respond to change.
Reforms in the education sector will take time. Improving value in wage receipts remains a remote opportunity in the near future.
Amid no support or concentrated effort, tourism receipts grow double-digit
Tourism continued to expand and record double-digit growth of CAGR 13.69% between the years 2015-2018, despite the absence of a national strategy and a high percentage of low-income visitors. As a single sector, tourism receipts amounted to $4,381mn in 2018 or 4.96% of GDP and trended towards topping that in 2019. As Sri Lanka is weak or entirely lacking in the underlying enablers of competitiveness, and continues to be unplanned and unprepared in all other means of earning foreign exchange, tourism is the priority sector to drive economic growth in the short to medium-term.
The myth of mass tourism
For Sri Lanka, mass tourism has its advantages; it produces high revenues at high seasons by attracting tourists looking for the cheapest way to holiday (Sri Lanka’s largest inbound mass tourist markets are India, Britain, China, Germany, France, Australia, Russia, the US, the Maldives, and Canada). The mass tourism sector is also one of the largest employers in the country, providing direct and indirect employment to about 400,000 people.
But there are inherent constraints to the mass tourism model – such as its high seasonality, low average length of stay and low occupancy rates – which accelerate a downward pressure on prices. By repeatedly discounting for shrinking tourism dollars, mass tourism suppliers attract tourists who don’t spend (enough) and the tourism product stagnates: service quality decreases and consumer dissatisfaction increases over time. Finally, the destination gains popularity and is promoted for inexpensive travel.
Business
NDB reports all-time high earnings; doubles PAT on a normalised basis

National Development Bank PLC (hereinafter ‘the Bank’) announced its results for the financial year ended December 31, 2025 to the Colombo Stock Exchange recently. Full year results tabled by the Bank showcase a strong growth across all business lines with Net Banking Revenue increasing by a 45.2% on a comparable basis.
Like most other peers, the Bank’s 2024 financial performance was positively impacted following the successful conclusion of the ISB debt restructure with a one-off impact on interest income, fee income and net impairments amounting to LKR 1.4 billion, LKR 0.7 billion and LKR 9.4 billion, respectively for the said year.
Fund based income
Net interest income (NII), which accounts for close to 75.0% of Bank’s total operating income, grew by 6.5% on a normalised basis. Despite pressure on interest-earning assets arising from the lower interest rate environment, the Bank’s disciplined margin management helped stabilise Net Interest Margin (NIM) at 4.0% for the year. On a comparable basis, excluding one-off exceptional items, NIM stood at 4.2%, compared to 4.3% for both scenarios in 2024. By the end of the year, the Bank had close to LKR 29.3 billion in Loans and Deposits under a special arrangement with its customer(s) with a netting-off feature (end 2024: LKR 19.6 billion).
Non-fund based income
Net fee and commission income reached LKR 8.1 billion for the year – representing a growth of 14.3% from LKR 7.1 billion in 2024 excluding ISB restructuring related fees. Key growth drivers for the current year were trade finance, credit and lending, digital banking and credit and debit cards.
Credit and operating costs
Credit costs for the year amounted to LKR 5.7 billion, reflecting a substantial reduction of 57.1% compared to LKR 13.2 billion in 2024, a testament to the Bank’s strong credit underwriting practices and focused efforts on collections and recoveries. The Bank’s success on account of the latter is best reflected in notably improved stage 2 and 3 loan stock which stood at 7.9% and 10.8% respectively at end 2025 as compared with 16.6% and 14.0% at end 2024. Stage 3 provision coverage also saw further improvement to 59.1% from 54.5% during 2024 showcasing the Bank’s prudent management of credit risk.
Operating expenses closed at LKR 19.0 billion for the year, marking a 13.1% YoY increase. This increase was primarily driven by routine staff-related increments and necessary market realignments, along with higher investments in IT infrastructure and business development undertaken during the year.(NDB)
Business
PMF Finance appoints Nishani Perera as Non-Executive Independent Director

PMF Finance PLC has announced the appointment of Ms. Nishani Perera as a Non-Executive Independent Director, further strengthening the Company’s strategic oversight, governance framework, and board-level expertise as it continues to advance its transformation and long-term growth agenda.
Ms. Perera is a Fellow Member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of Sri Lanka and brings over 19 years of experience across audit, assurance, advisory, risk management, and corporate governance. She currently serves as Partner – Audit & Assurance at Moore Aiyar and as Director of Moore Consulting (Pvt) Ltd.
Over the course of her career, Ms. Perera has gained substantial exposure to listed companies, banks, finance companies, and other regulated entities. Her areas of expertise include financial reporting under SLFRS/LKAS, audit and risk oversight, regulatory compliance, and the implementation of quality management standards. She has worked closely with Boards of Directors and Audit Committees on matters relating to financial reporting integrity, internal control frameworks, enterprise risk governance, and adherence to evolving regulatory requirements.
Ms. Perera holds a Master of Laws (LL.M.) from Cardiff Metropolitan University in the United Kingdom and a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration (Special) from the University of Sri Jayewardenepura. She is also an Associate Member of ACCA and CMA Sri Lanka, and a Fellow Member of AAT Sri Lanka.
Business
Capital Alliance deepens capital market presence with third Closed-End Fund Listing at the CSE

The units of the “CAL Three Year Closed End Fund” were officially listed on the Colombo Stock Exchange (CSE) recently. Accordingly, a total of 841,263,375 units of the ‘CAL Three Year Closed End Fund’ were listed by Capital Alliance Investments Ltd (CALI), a member of the Capital Alliance Ltd Group (CAL Group). The listing was commemorated by way of a special bell ringing ceremony on the CSE trading floor.
CSE CEO Rajeeva Bandaranaike speaking at the occasion remarked upon the rising demand for Unit Trusts: “When you look at funds, particularly unit trusts in today’s active capital market, we see a lot of domestic interest in the market with more investors entering. Funds, not only fixed income funds but also growth and balanced funds, can be the ideal vehicle through which new investors can enter the market. We see this interest reflected in the success of CAL’s Three Year Closed End Fund. More people are seeking to invest their money through professional fund managers.”
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoWhy does the state threaten Its people with yet another anti-terror law?
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoReconciliation, Mood of the Nation and the NPP Government
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoVictor Melder turns 90: Railwayman and bibliophile extraordinary
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoLOVEABLE BUT LETHAL: When four-legged stars remind us of a silent killer
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoVictor, the Friend of the Foreign Press
-

 Latest News6 days ago
Latest News6 days agoNew Zealand meet familiar opponents Pakistan at spin-friendly Premadasa
-

 Latest News6 days ago
Latest News6 days agoTariffs ruling is major blow to Trump’s second-term agenda
-

 Latest News6 days ago
Latest News6 days agoECB push back at Pakistan ‘shadow-ban’ reports ahead of Hundred auction













