Features
The failure of political leadership

Dr. Nihal Jayawickrema
(Continued from last week)
If the health of the nation has been seriously compromised, it is principally due to the failure of its political leadership, all of whom represent, or have represented predominantly Sinhalese electorates. For them, the constituency is essentially Sinhalese in race, Buddhist in religion, and Mahawamsa in mindset. Under pressure from the Tamil political leadership or faced with the threat of satyagraha or civil disobedience campaigns, or occasionally when driven to seek the support of the Tamil members of parliament to form an administration, successive Sinhalese political parties have entered into formal or informal agreements with representatives of the Tamil people. These were rarely honoured. The responses were determined purely by political expediency.
For example, in 1957, the Bandaranaike – Chelvanayakam Pact provided for the establishment of Regional Councils and for the use of Tamil in the northern and eastern provinces. Nine months later, under pressure from the Eksath Bhikku Peramuna and from the UNP led by J.R. Jayewardene which organized a 72-mile march from Colombo to the Temple of the Tooth “to save the Sinhala race”, S.W.R.D. Bandaranaike announced that the pact which bore his signature as Prime Minister was incapable of being implemented.
In 1958, Mr Bandaranaike enacted the Tamil Language (Special Provisions) Act but failed in his lifetime to make the regulations which would have made that law operative. When in 1966, Dudley Senanayake attempted to make these regulations, Opposition parties led by Mrs Bandaranaike demonstrated against that move on the streets of Colombo and took an oath at the statue of Vihara Maha Devi to oppose the division of the country. Dudley Senanayake, fortified by a state of emergency, proceeded to make the regulations, but did not implement them in the remaining four years of his government.
In 1965, Dudley Senanayake signed an agreement with S.J.V. Chelvanayakam in which he promised to establish District Councils. A Bill for this purpose was prepared but was never introduced in Parliament. Meanwhile, a White Paper on the subject, promising less than what Mr Bandaranaike had offered in 1957, was publicly and ceremonially burnt on the steps of parliament building by members of the SLFP and other Opposition parties.
In 1970, Mrs Bandaranaike invited the Federal Party members to the Constituent Assembly to help draft a new constitution which would “serve to build a nation ever more strongly consciousness of its oneness amidst the diversity imposed upon it by history”. When they responded positively and suggested that that goal be reached through federalism, they were ruled out of order and left with no alternative but to withdraw from the exercise.
In 1977, the UNP manifesto promised to summon an All-Party Conference to consider the problems of non-Sinhala speaking people, but conveniently forgot that promise once the general election was won, and it took several years of terrorist activity and military reprisals, hundreds of deaths, the burning of the Jaffna public library, and the events of July 1983, to convince the government that that promise ought to be kept. When that All-Party Conference eventually met (but without the SLFP leader on whom civil disabilities had been imposed and expelled from parliament), the much-maligned Annexure C, which the Tamil political leadership claimed contained the agenda they had been invited to discuss, continued to lie on the table in the manner of an illegitimate child abandoned by its mother.
Meanwhile, the Sixth Amendment to the Constitution, which required all members of parliament to take a loyalty oath to an indivisible Sri Lanka, which the TULF refused to do, resulted in the moderate political wing of the Tamil community losing their political influence and becoming irrelevant in any negotiations. That, in brief and in outline, is a case study of the failure of political leadership.
HEALING THE NATION
Transitional justice
The problem of healing the nation today is two-fold. On the one hand, there is the issue of governance which our political leaders have failed to resolve for nearly 60 years. On the other hand, there is the issue of justice, reparation, and reconciliation, which has been brought to the fore through the actions of a succession of Presidents who set out to resolve a political and human rights problem, conveniently dubbed “the terrorist problem”, through the application of military firepower. It was President Jayewardene who, in October 1979, directed the Army Commander to proceed to the north with absolute authority to eliminate by any means whatsoever all forms of terrorism he may encounter; the final solution was to be achieved by Christmas of that year. For decades thereafter, a daily sacrificial offering was made of thousands of idealistic young Sinhalese men in the prime of their lives who journeyed to the north and the east in the confident hope that before they laid down their own lives, they would be able to kill a few equally idealistic young Tamil men and women, and thereby make this thrice blessed isle a safer, happier, and more righteous place for all of us to live in.
The poet John Donne reminds us that ‘No man is an island, entire of itself. Every man is piece of the continent, a part of the main’. How a nation treats its nationals is no longer a matter exclusively within its own concern. There are now norms and standards which form part of a growing body of international law. Therefore, a government’s behaviour towards its own nationals is now regulated by international treaties. In 1981, the Government of Sri Lanka brought itself within the jurisdiction of international human rights law when it subscribed to, and ratified, the two international human rights covenants.
Sri Lanka is believed to have one of the highest rates of reported cases of enforced disappearances in the world, and yet no tangible steps have been taken for several years even in respect of the much-publicised Ekneligoda disappearance. Over 300 political killings in 2005, and over 700 extra-judicial executions in the next two years have been recorded, with no action being taken to investigate them. The high-profile killings of Lakshman Kadirgamar in August 2005 in circumstances that are still classified and shrouded in mystery; of Joseph Pararajasingham at a Christmas Eve church service in Batticaloa in 2005; of five Tamil university students in Trincomalee in January 2006; of 17 ACF workers in Muttur in August 2006; and of Lasantha Wickrematunge within a high security zone in January 2009; have all remained uninvestigated or not effectively investigated. Some military personnel have been charged with the killing of Nadarajah Raviraj in Colombo in November 2006, but has it been ascertained why they committed that crime? The Rajapaksa Government clearly demonstrated that it lacked the will or the desire to hold persons who have perpetrated such serious crimes accountable for their actions. Even if the present Government wishes to reverse this culture of impunity, does it have at its disposal the expertise to successfully investigate several thousand cases of enforced disappearance and extra-judicial execution?
In 2015, the Human Rights Council published the findings of the investigation on Sri Lanka conducted by three distinguished legal experts, the former President of Finland, the former Governor-General of New Zealand and the former President of the Human Rights Commission of Pakistan. That commission had gathered information of unlawful killings of civilians by security forces and paramilitary groups; extrajudicial execution of identified LTTE cadres and unidentified individuals at the very end of the fighting, including those who were known to have surrendered to the Sri Lankan military; arbitrary arrests and abductions; enforced disappearances; torture and other forms of cruel, inhuman and degrading treatment; sexual and gender-based violence; forced recruitment of children for use in hostilities; denial of humanitarian assistance; and the deprivation of liberty of internally displaced persons.
The government has announced its intention to establish a Truth Commission, which is a healing process that offers victims and perpetrators an opportunity to outline details of past crimes. It is a mechanism that has been attempted, with some degree of success, in South Africa and in several Latin American countries such as Argentina, Chile, El Salvador and Guatemala. I once witnessed the proceedings of a truth commission in Nigeria. It is based on the Christian concept of confession. Whether it would be appropriate for Sri Lanka is an open question. The government is reportedly taking steps to provide restitution, compensation, and rehabilitation. However, a pre-condition for reconciliation is accountability. Without accountability, there can be no reconciliation in any society.
The UN High Commissioner for Human Rights recommended the establishment of a hybrid court which is a unique element in the human rights-based approach to transitional justice in a post-conflict situation. By including international judges, prosecutors, lawyers and investigators, a hybrid court is designed to deal with those who bear the greatest responsibility for serious crimes arising from or during the conflict, such as war crimes or crimes against humanity, including sexual crimes and crimes against children. President Sirisena has repeatedly asserted that, under no circumstances, will he agree to the participation of foreigners in the accountability process in Sri Lanka. He has claimed that Sri Lanka has an independent judiciary which is quite capable of addressing the issues of accountability without any foreign assistance. It is perhaps time that his advisers briefed him on the real position.
In many significant respects, the Sri Lankan legal and judicial system has, in the past few decades, failed its multi-ethnic and multi-religious population, and has demonstrated that it lacks the will and the capacity to address such serious crimes. War Crimes and Crimes against Humanity, as well as Enforced Disappearances, have not been criminalized in Sri Lanka. Neither the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (which the Jayewardene Government acceded to) and its Optional Protocol (which the Kumaratunge Government ratified), nor the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, have yet been incorporated in our law. No effective mechanism has yet been established for the protection of witnesses and victims of crime. In 2006, Chief Justice Sarath Silva suspended the application to Sri Lanka of international human rights treaties, holding that their ratification was an infringement of the Constitution. His judgment was described by a world-renowned jurist as “an example of judicial waywardness” or “judicial eccentricity”. Another referred to it as “Alice in Wonderland reasoning”. Therefore, we lack the legal framework within which accountability can be established for such crimes. The process of remedying that deficiency may benefit from expertise, whether international or otherwise.
The judicial culture of the Supreme Court, especially evident in the past decade, has been one of extreme deference to the presidential executive. Whenever fundamental rights were invoked, the court, composed as it was of judges appointed by President Rajapaksa, often from among his contemporaries at Law College, would, more often than not, capitulate to executive assertions of state security. Political opponents of the previous government and members of ethnic minorities, and indeed civil society, have rarely, if ever, obtained any relief. The judgments of the Supreme Court, especially in matters affecting individual rights, reveal an astounding ignorance or unfamiliarity with contemporary developments in the law in other jurisdictions.
The Attorney-General’s Department, which remained embedded in the Presidential Secretariat from 2011 to 2015, did not possess the capacity or the inclination to view, with independence and impartiality, the crimes allegedly committed with the knowledge or connivance of those at the highest levels of the then government. Instead, its senior officers travelled annually to Geneva to deny before the international community that any such crimes had ever been committed. An Attorney General himself uttered what was later proved to be a lie regarding a disappeared journalist. Is it being seriously suggested that these same officers should now be entrusted with the task of presenting the evidence which the OHCHR claims it has, and which they have so strenuously repudiated for decades? The apparent indifference with which investigations that commenced after the change of government are being handled by those in the commanding heights of that department suggests that the culture in that department remains the same.
Sri Lanka’s inability to conduct credible investigations through quasi-judicial bodies has also been demonstrated by the performance of a succession of commissions of inquiry headed by retired judicial officers. The Udalagama Commission lost its credibility very early in its proceedings. The Paranagama Commission keeps rolling along, from month to month, year to year, signifying the urgency it attaches to Enforced Disappearances. The performance of the previous Human Rights Commission, which had the duty to investigate infringements of fundamental rights, was so abysmal that the United Nations downgraded its status for lack of balance and objectivity.
The question which the government will need to address is whether it has, with the resources available to it, the capacity to effectively investigate, prosecute and try the serious allegations referred to in the report of the OHCHR investigation on Sri Lanka, including war crimes and crimes against humanity. To admit that we cannot undertake these tasks alone is not an admission of weakness. On the contrary, it will be a sincere and genuine commitment to achieving the objective of accountability on behalf of those who laid down their lives and the families who continue to live in grief. In respect of war crimes and crimes against humanity, the expertise of lawyers skilled in dealing with such crimes, military analysts, crime scene investigators, trauma experts, psychological counsellors, and a host of others who are competent to address issues of victim needs and rights, witness preparation and protection, are essential, and international assistance in that regard ought to be welcomed.
Power sharing at the centre
One inescapable fact that emerges from the post-Independence history of Sri Lanka is that the Sinhalese political leadership is unwilling to share political power with the Tamil political leadership. For the past fifty years, since the emergence of the Federal Party, negotiations between Sinhalese and Tamil political leaders have focused on the unit of devolution. Should it be district, provincial or regional? Fear has been created in Sinhalese minds that any such form of devolution would eventually lead to a separate state. In this connection, I wish to refer to two principles of international human rights law which now regulate the relationship between the government and the different ethnic groups living in Sri Lanka. These are the principles of non-discrimination and self-determination.
The principle of non-discrimination means that as between the citizens of Sri Lanka, neither law nor executive action may discriminate on the basis of race, religion, language, sex, political or other opinion, national or social origin, birth or other status. The principle of self-determination is contained in both human rights covenants to which the Government of Sri Lanka has committed itself. It means that cohesive ethnic groups have the right to choose for themselves a form of political organization, and through such organization to freely pursue their economic, social, and cultural development. That choice may take one of several forms. It could be independence as a separate state; or association with other ethnic groups in a federal state; or autonomy or assimilation in a unitary state. However, if the ethnic group concerned already has a home within territorial boundaries of a sovereign and independent state, (which the Tamil community has); and if that state has a government which is representative of all the people irrespective of race, (which the Sri Lankan government is not}; and if that government respects the twin principles of non-discrimination and self-determination, (which Sri Lankan governments have not}; the choice of that ethic group does not extend to the creation of a separate state.
Therefore, it seems to me that, whatever agreement may be reached regarding governance at the periphery, it is vital and fundamental that there should be power sharing at the centre. This is not a matter that should be left for negotiation at the conclusion of a general election. That has led in the past to the inclusion of Colombo-based token Tamils in the Cabinet, such as C. Kumarasuriar and Lakshman Kadirgamar, who represented none but themselves. Power sharing at the centre is a requirement that should be incorporated in the Constitution. Whichever political party forms the government, it should be mandatory for the different ethnic groups to be represented in the Cabinet, at least in proportion to the number of such members elected to Parliament. Thereby, the minority communities will be constitutionally guaranteed not of token but of genuine representation, both in the legislature and in the government. Policy formation will thereafter be by consensus of the different ethnic groups, which is how it should be in a multi-ethnic, multi-religious and multi-linguistic country as Sri Lanka.
Entering the global community
After almost 60 years of isolationist policies, it is time that we entered the global community. We cannot do that if we are unable to communicate with others outside our island home. Lee Kuan Yew had the foresight to retain the use of the English language in Singapore, as did many of Africa’s national leaders. At a meeting in Thailand last year, the Thai Foreign Secretary informed me that his country had begun using English as the medium of instruction in schools. When I expressed some surprise, he explained that Thailand did not want to send its citizens out as menial workers. By retaining, or adopting, English – now the acknowledged international language, these countries have ensured that their peoples can communicate with the world beyond their geographical boundaries and acquire the new knowledge that now emerges as rapidly as the old is debunked and equip themselves to serve the global community in capacities other than as domestic helpers and semi-skilled workers. I think it would be a reality check for our politicians if they were to ask the youth of this country which language they wish to be educated in. Language is not only a mode of communication; it is also the medium through which knowledge is acquired. It is unfortunate, but true, that Sinhala does not serve either purpose adequately.
Conclusion
I do not wish to conclude my presentation by leaving the impression that Sri Lanka has been devoid of any manifestation of leadership. Of course, not. In the 1920s, A.E. Goonesinha provided the leadership for the working people to organize themselves, and for the youth to agitate for the immediate relief of social problems. In the 1930s, a group of young Ceylonese intellectuals on their return from universities abroad, influenced deeply by the ideas of Karl Marx – Dr S.A. Wickremasinghe, Dr N.M. Perera, Dr Colvin R de Silva, Leslie Goonewardene and Philip Gunewardene – provided the leadership to the formation of the left movement in Ceylon. In the 1940s, D.S. Senanayake and Sir Oliver Goonetilleke provided the leadership to the negotiations with the British Government that secured self-government for Ceylon without shedding a single drop of blood. On the long night of January 27, 1962, Felix Dias Bandaranaike, almost single-handedly, saved not only a great many lives, but also the social and political fabric of our society by aborting the first ever attempt to overthrow the lawfully established government of this country.
In April 1971, barely two weeks into the JVP insurgency, with the military ready to launch an offensive, Mrs Bandaranaike called upon combatants to surrender at check points manned by public servants, guaranteeing them safe conduct, an appeal to which nearly 10,000 young persons responded. In 1978, J.R. Jayewardene gave a whole new direction to our economy, lifting it out of the shackles of outmoded socialism. In 2002, Ranil Wickremasinghe had the courage and the vision to enter into a ceasefire agreement with the LTTE to bring an end to the hostilities as a means to establishing a positive atmosphere in which steps towards negotiations on a lasting solution could be taken. These were all examples of leadership.
In conclusion, may I adopt and adapt the words of the present Chief Justice of Kenya in reminding ourselves that we must fully discharge our obligations to each other as individuals who are part of a common polity.
These obligations start from the basic requirements: respect for each other as individuals, as well as respect for communities and other identity groups. It is socially obnoxious, politically reckless, and economically ignorant to cheapen the presence of any community in this country. It is only the weak-minded people incapable of comprehending the origins of the modern state, its philosophy, its instruments, and its edicts, that resort to such approaches in managing the expression of disagreement. Just as a fish that grows in a pond may consider itself the king of the sea until it is introduced into the ocean, we too must also awaken to the reality that our ethnic and sectarian interests may only matter if we are disconnected from the rest of the world. Unless we all recognize that we are a confederation of cultures, languages and interests, we shall never be able to cultivate the sensitivity and respect for one another that is necessary to hold us together. We might never live up to true greatness as a member of the community of nations because we overstayed our welcome in the pond when the ocean beckoned. The things that are seen to divide us – ethnicity, religion, race, class, clan, region, occupation, sexual identity, generation, disability – are also the raw materials needed to create the mosaic of one nation.
(Concluded)
Features
Cyclones, greed and philosophy for a new world order

Further to my earlier letter titled, “Psychology of Greed and Philosophy for a New World Order” (The Island 26.11.2025) it may not be far-fetched to say that the cause of the devastating cyclones that hit Sri Lanka and Indonesia last week could be traced back to human greed. Cyclones of this magnitude are said to be unusual in the equatorial region but, according to experts, the raised sea surface temperatures created the conditions for their occurrence. This is directly due to global warming which is caused by excessive emission of Greenhouse gases due to burning of fossil fuels and other activities. These activities cannot be brought under control as the rich, greedy Western powers do not want to abide by the terms and conditions agreed upon at the Paris Agreement of 2015, as was seen at the COP30 meeting in Brazil recently. Is there hope for third world countries? This is why the Global South must develop a New World Order. For this purpose, the proposed contentment/sufficiency philosophy based on morals like dhana, seela, bhavana, may provide the necessary foundation.
Further, such a philosophy need not be parochial and isolationist. It may not be necessary to adopt systems that existed in the past that suited the times but develop a system that would be practical and also pragmatic in the context of the modern world.
It must be reiterated that without controlling the force of collective greed the present destructive socioeconomic system cannot be changed. Hence the need for a philosophy that incorporates the means of controlling greed. Dhana, seela, bhavana may suit Sri Lanka and most of the East which, as mentioned in my earlier letter, share a similar philosophical heritage. The rest of the world also may have to adopt a contentment / sufficiency philosophy with strong and effective tenets that suit their culture, to bring under control the evil of greed. If not, there is no hope for the existence of the world. Global warming will destroy it with cyclones, forest fires, droughts, floods, crop failure and famine.
Leading economists had commented on the damaging effect of greed on the economy while philosophers, ancient as well as modern, had spoken about its degenerating influence on the inborn human morals. Ancient philosophers like Plato, Aristotle, and Epicurus all spoke about greed, viewing it as a destructive force that hindered a good life. They believed greed was rooted in personal immorality and prevented individuals from achieving true happiness by focusing on endless material accumulation rather than the limited wealth needed for natural needs.
Jeffry Sachs argues that greed is a destructive force that undermines social and environmental well-being, citing it as a major driver of climate change and economic inequality, referencing the ideas of Adam Smith, John Maynard Keynes, etc. Joseph Stiglitz, a Nobel Laureate economist, has criticised neoliberal ideology in similar terms.
In my earlier letter, I have discussed how contentment / sufficiency philosophy could effectively transform the socioeconomic system to one that prioritises collective well-being and sufficiency over rampant consumerism and greed, potentially leading to more sustainable economic models.
Obviously, these changes cannot be brought about without a change of attitude, morals and commitment of the rulers and the government. This cannot be achieved without a mass movement; people must realise the need for change. Such a movement would need leadership. In this regard a critical responsibility lies with the educated middle class. It is they who must give leadership to the movement that would have the goal of getting rid of the evil of excessive greed. It is they who must educate the entire nation about the need for these changes.
The middle class would be the vanguard of change. It is the middle class that has the capacity to bring about change. It is the middle class that perform as a vibrant component of the society for political stability. It is the group which supplies political philosophy, ideology, movements, guidance and leaders for the rest of the society. The poor, who are the majority, need the political wisdom and leadership of the middle class.
Further, the middle class is the font of culture, creativity, literature, art and music. Thinkers, writers, artistes, musicians are fostered by the middle class. Cultural activity of the middle class could pervade down to the poor groups and have an effect on their cultural development as well. Similarly, education of a country depends on how educated the middle class is. It is the responsibility of the middle class to provide education to the poor people.
Most importantly, the morals of a society are imbued in the middle class and it is they who foster them. As morals are crucial in the battle against greed, the middle class assume greater credentials to spearhead the movement against greed and bring in sustainable development and growth. Contentment sufficiency philosophy, based on morals, would form the strong foundation necessary for achieving the goal of a new world order. Thus, it is seen that the middle class is eminently suitable to be the vehicle that could adopt and disseminate a contentment/ sufficiency philosophy and lead the movement against the evil neo-liberal system that is destroying the world.
The Global South, which comprises the majority of the world’s poor, may have to realise, before it is too late, that it is they who are the most vulnerable to climate change though they may not be the greatest offenders who cause it. Yet, if they are to survive, they must get together and help each other to achieve self-sufficiency in the essential needs, like food, energy and medicine. Trade must not be via exploitative and weaponised currency but by means of a barter system, based on purchase power parity (PPP). The union of these countries could be an expansion of organisations,like BRICS, ASEAN, SCO, AU, etc., which already have the trade and financial arrangements though in a rudimentary state but with great potential, if only they could sort out their bilateral issues and work towards a Global South which is neither rich nor poor but sufficient, contented and safe, a lesson to the Global North. China, India and South Africa must play the lead role in this venture. They would need the support of a strong philosophy that has the capacity to fight the evil of greed, for they cannot achieve these goals if fettered by greed. The proposed contentment / sufficient philosophy would form a strong philosophical foundation for the Global South, to unite, fight greed and develop a new world order which, above all, will make it safe for life.
by Prof. N. A. de S. Amaratunga
PHD, DSc, DLITT
Features
SINHARAJA: The Living Cathedral of Sri Lanka’s Rainforest Heritage

When Senior biodiversity scientist Vimukthi Weeratunga speaks of Sinharaja, his voice carries the weight of four decades spent beneath its dripping emerald canopy. To him, Sri Lanka’s last great rainforest is not merely a protected area—it is “a cathedral of life,” a sanctuary where evolution whispers through every leaf, stream and shadow.
“Sinharaja is the largest and most precious tropical rainforest we have,” Weeratunga said.
“Sixty to seventy percent of the plants and animals found here exist nowhere else on Earth. This forest is the heart of endemic biodiversity in Sri Lanka.”
A Magnet for the World’s Naturalists
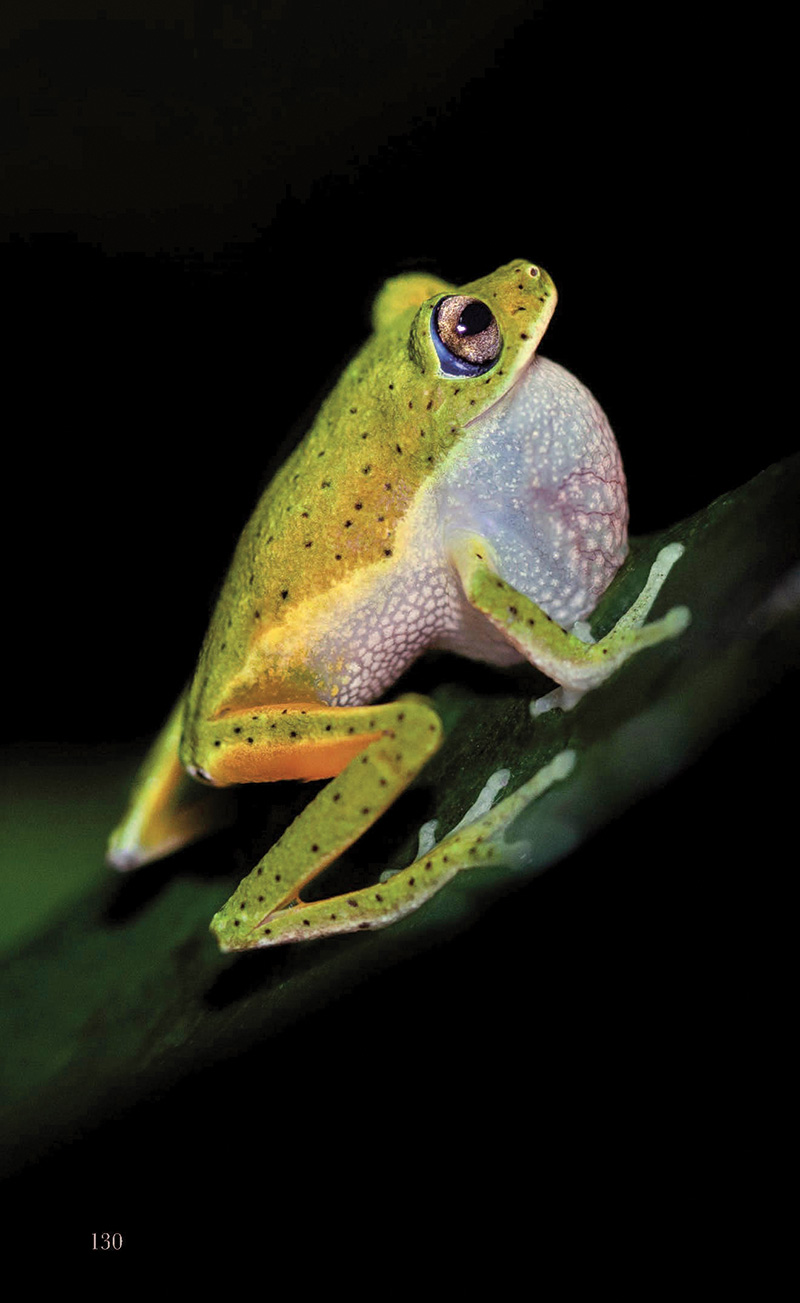
Sinharaja’s allure lies not in charismatic megafauna but in the world of the small and extraordinary—tiny, jewel-toned frogs; iridescent butterflies; shy serpents; and canopy birds whose songs drift like threads of silver through the mist.
“You must walk slowly in Sinharaja,” Weeratunga smiled.
“Its beauty reveals itself only to those who are patient and observant.”
For global travellers fascinated by natural history, Sinharaja remains a top draw. Nearly 90% of nature-focused visitors to Sri Lanka place Sinharaja at the top of their itinerary, generating a deep economic pulse for surrounding communities.
A Forest Etched in History
Centuries before conservationists championed its cause, Sinharaja captured the imagination of explorers and scholars. British and Dutch botanists, venturing into the island’s interior from the 17th century onward, mapped streams, documented rare orchids, and penned some of the earliest scientific records of Sri Lanka’s natural heritage.
These chronicles now form the backbone of our understanding of the island’s unique ecology.
The Great Forest War: Saving Sinharaja
But Sinharaja nearly vanished.
In the 1970s, the government—guided by a timber-driven development mindset—greenlit a Canadian-assisted logging project. Forests around Sinharaja fell first; then, the chainsaws approached the ancient core.
“There was very little scientific data to counter the felling,” Weeratunga recalled.
- Poppie’s shrub frog
- Endemic Scimitar babblers
- Blue Magpie
“But people knew instinctively this was a national treasure.”
The public responded with one of the greatest environmental uprisings in Sri Lankan history. Conservation icons Thilo Hoffmann and Neluwe Gunananda Thera led a national movement. After seven tense years, the new government of 1977 halted the project.
What followed was a scientific renaissance. Leading researchers—including Prof. Savithri Gunathilake and Prof. Nimal Gunathilaka, Prof. Sarath Kottagama, and others—descended into the depths of Sinharaja, documenting every possible facet of its biodiversity.
“Those studies paved the way for Sinharaja to become Sri Lanka’s very first natural World Heritage Site,” Weeratunga noted proudly.
- Vimukthi
- Nadika
- Janaka
A Book Woven From 30 Years of Field Wisdom
For Weeratunga, Sinharaja is more than academic terrain—it is home. Since joining the Forest Department in 1985 as a young researcher, he has trekked, photographed, documented and celebrated its secrets.
Now, decades later, he joins Dr. Thilak Jayaratne, the late Dr. Janaka Gallangoda, and Nadika Hapuarachchi in producing, what he calls, the most comprehensive book ever written on Sinharaja.
“This will be the first major publication on Sinharaja since the early 1980s,” he said.
“It covers ecology, history, flora, fauna—and includes rare photographs taken over nearly 30 years.”
Some images were captured after weeks of waiting. Others after years—like the mysterious mass-flowering episodes where clusters of forest giants bloom in synchrony, or the delicate jewels of the understory: tiny jumping spiders, elusive amphibians, and canopy dwellers glimpsed only once in a lifetime.
The book even includes underwater photography from Sinharaja’s crystal-clear streams—worlds unseen by most visitors.
A Tribute to a Departed Friend
Halfway through the project, tragedy struck: co-author Dr. Janaka Gallangoda passed away.
“We stopped the project for a while,” Weeratunga said quietly.
“But Dr. Thilak Jayaratne reminded us that Janaka lived for this forest. So we completed the book in his memory. One of our authors now watches over Sinharaja from above.”
An Invitation to the Public
A special exhibition, showcasing highlights from the book, will be held on 13–14 December, 2025, in Colombo.
“We cannot show Sinharaja in one gallery,” he laughed.
“But we can show a single drop of its beauty—enough to spark curiosity.”
A Forest That Must Endure
What makes the book special, he emphasises, is its accessibility.
“We wrote it in simple, clear language—no heavy jargon—so that everyone can understand why Sinharaja is irreplaceable,” Weeratunga said.
“If people know its value, they will protect it.”
To him, Sinharaja is more than a rainforest.
It is Sri Lanka’s living heritage.
A sanctuary of evolution.
A sacred, breathing cathedral that must endure for generations to come.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
How Knuckles was sold out

Leaked RTI Files Reveal Conflicting Approvals, Missing Assessments, and Silent Officials
“This Was Not Mismanagement — It Was a Structured Failure”— CEJ’s Dilena Pathragoda
An investigation, backed by newly released Right to Information (RTI) files, exposes a troubling sequence of events in which multiple state agencies appear to have enabled — or quietly tolerated — unauthorised road construction inside the Knuckles Conservation Forest, a UNESCO World Heritage site.
At the centre of the unfolding scandal is a trail of contradictory letters, unexplained delays, unsigned inspection reports, and sudden reversals by key government offices.
“What these documents show is not confusion or oversight. It is a structured failure,” said Dilena Pathragoda, Executive Director of the Centre for Environmental Justice (CEJ), who has been analysing the leaked records.
“Officials knew the legal requirements. They ignored them. They knew the ecological risks. They dismissed them. The evidence points to a deliberate weakening of safeguards meant to protect one of Sri Lanka’s most fragile ecosystems.”
A Paper Trail of Contradictions
RTI disclosures obtained by activists reveal:
Approvals issued before mandatory field inspections were carried out
Three departments claiming they “did not authorise” the same section of the road
A suspiciously backdated letter clearing a segment already under construction
Internal memos flagging “missing evaluation data” that were never addressed
“No-objection” notes do not hold any legal weight for work inside protected areas, experts say.
One senior officer’s signature appears on two letters with opposing conclusions, sent just three weeks apart — a discrepancy that has raised serious questions within the conservation community.
“This is the kind of documentation that usually surfaces only after damage is done,” Pathragoda said. “It shows a chain of administrative behaviour designed to delay scrutiny until the bulldozers moved in.”
The Silence of the Agencies
Perhaps, more alarming is the behaviour of the regulatory bodies.
Multiple departments — including those legally mandated to halt unauthorised work — acknowledged concerns in internal exchanges but issued no public warnings, took no enforcement action, and allowed machinery to continue operating.
“That silence is the real red flag,” Pathragoda noted.
“Silence is rarely accidental in cases like this. Silence protects someone.”
On the Ground: Damage Already Visible
Independent field teams report:
Fresh erosion scars on steep slopes
Sediment-laden water in downstream streams
Disturbed buffer zones
Workers claiming that they were instructed to “complete the section quickly”
Satellite images from the past two months show accelerated clearing around the contested route.
Environmental experts warn that once the hydrology of the Knuckles slopes is altered, the consequences could be irreversible.
CEJ: “Name Every Official Involved”
CEJ is preparing a formal complaint demanding a multi-agency investigation.
Pathragoda insists that responsibility must be traced along the entire chain — from field officers to approving authorities.
“Every signature, every omission, every backdated approval must be examined,” she said.
“If laws were violated, then prosecutions must follow. Not warnings. Not transfers. Prosecutions.”
A Scandal Still Unfolding
More RTI documents are expected to come out next week, including internal audits and communication logs that could deepen the crisis for several agencies.
As the paper trail widens, one thing is increasingly clear: what happened in Knuckles is not an isolated act — it is an institutional failure, executed quietly, and revealed only because citizens insisted on answers.
by Ifham Nizam
-
News6 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 News14 hours ago
News14 hours agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
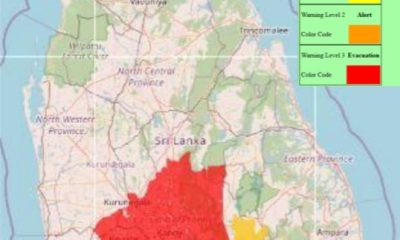
 News4 days ago
News4 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-
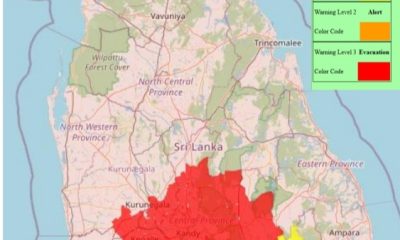
 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoLevel III landslide early warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoDitwah: An unusual cyclone
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady