News
AI: Authorities must refrain from use of military to police protests

The Sri Lankan authorities must not impose a blanket order authorising use of force during the state of emergency that has been announced and refrain from use of the armed forces to police people’s protest, said Amnesty International following a new order empowering armed forces to maintain law and order in Colombo.
“The recent escalation of the authorities’ response to protests by calling in the armed forces, firing at protestors and excessive use of tear gas which resulted in the death of one person yesterday is deeply worrying,” said Yamini Mishra, Amnesty International’s South Asia Regional Director.
On the morning of 13 July 2022, thousands of protestors started making their way towards the Prime Minister’s office and the Parliament in Colombo. After an angry face-off, protesters breached the gates and took over the Prime Minister’s office. Amnesty International staff present at the protest location confirmed that law enforcement officers fired volleys of teargas against people, including children and journalists some of whom were seen escaping the plumes while coughing and sputtering. Dozens of protesters were injured, and one was reported dead. At Galle Face, helicopters flew low overhead, where a rolling peaceful protest site had been established three months ago in the prolonged agitation over the economic crisis in the country. At another protest near the Parliament later the same day, more than 80 people were reported to be injured and admitted to hospital.
At 3pm the Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe delivered a televised address in which he said he had ordered the military to “do whatever is necessary to restore order”. On 14 July 2022, a press release was issued by the army announcing a warning that they will use force to restore law and order in the country.
Any blanket order authorising use of force by armed forces is problematic even during times of emergency. The armed forces should not be involved in the policing of public assemblies, since they are trained to fight against enemies and not to protect and control civilians.
Amnesty calls upon law enforcement agencies to act with restraint to avoid further serious injury and loss of life. They may only use the minimum level of force necessary force to bring a situation under control where doing so is strictly necessary and proportionate. Even in instances where some parts of a protests turn violent, law enforcement must assess the situation on a case-by-case basis with use of force only where absolutely necessary and only against those engaged in violence. It must be strictly proportionate to the situation faced by law enforcement, which means authorities must not cause more harm than they seek to avert.
“At a time when the country is facing a dire economic crisis and protests are growing in scale, authorities must make comprehensive efforts to de-escalate the situation and focus resources on ensuring people can access essential goods and services, in line with international human rights law and standards,” said Yamini Mishra.
Latest News
President chairs Nuwara Eliya District Special Coordinating Committee Meeting

A special District Coordinating Committee meeting, convened to review the damage caused to the agricultural sector in the Nuwara Eliya District due to Cyclone Ditwah and to discuss the urgent measures required, was held this morning (08) at the Nuwara Eliya District Secretariat. The meeting was chaired by President Anura Kumara Dissanayake, with the participation of the relevant responsible officials.
Due to adverse weather conditions, 1,421 hectares of vegetable cultivation in the Nuwara Eliya District has been damaged. President Anura Kumara Dissanayake instructed the relevant officials to take the necessary measures to provide compensation to farmers without delay.
Officials stated that although there has been crop damage, the reduction in the vegetable harvest in the Nuwara Eliya District would be around 25%. They added that Nuwara Eliya district would be able to meet the daily demand, but a decrease in the daily demand has been observed.
Officials further pointed out to the President that the reason for this decline is the spread of false information claiming a vegetable shortage in the Nuwara Eliya District and that prices have excessively increased.
News
Jetstar to launch Australia’s only low-cost direct flights to Sri Lanka, with fares from just $315^

It has been announced that Jetstar will take off for the first time from Australia to Sri Lanka in August next year, with the launch of the only direct low-cost service from Melbourne to the South Asian nation’s capital, Colombo.
From 25 August 2026, Jetstar will become the first Australian airline to operate this route, flying three times a week between Melbourne and Colombo and offering more than 100,000 low-fare seats a year on the new route.
Upgraded aircraft
This year-round service will be operated by Jetstar’s fleet of 11 widebody Boeing 787 Dreamliners which are progressively being upgraded from early next year to overhaul both the economy and business class cabins*.
The interior refit includes more than doubling the number of business class seats and installing Wi-Fi so customers can stream entertainment to their own devices.
The addition of a new lie-flat crew rest area to allow flights of up to 16 hours will open the door to even more incredible long-haul destinations in the future. The first of the upgraded aircraft is due to touchdown in Melbourne in late March 2026.
Sale fares
The countdown is on to these new flights going on sale at midday today (8 December).
At that time, Jetstar will launch a 24-hour Route Launch Sale with one-way fares available between Melbourne (Tullamarine) and Colombo from only $315^ at jetstar.com.
Jetstar’s growth
The launch of Melbourne to Colombo flights comes during one of the most exciting growth periods in Jetstar’s almost 22-year history.
Over the past two years, the airline has announced 26 new routes and welcomed 13 new aircraft, allowing travellers to take off more, for less.
2025 has been a standout year, with 14 new routes announced – nine of them international – with more exciting growth plans in coming years.
This year the Melbourne based carrier is also celebrating 10 years of operating domestically from Melbourne’s T4, having carried more than 50 million customers through the terminal.
Holiday peak travel
The new route announcement comes as Jetstar prepares for its biggest Christmas ever.
Jetstar is forecast to carry a record of almost six million passengers across its Australian, New Zealand, Japan and international network throughout December and January.
This includes a record 1.7 million passengers flying through Melbourne alone across the summer peak.
Jetstar CEO Stephanie Tully said the airline’s Melbourne to Colombo route will give Australians a new direct and affordable way to take off more to Sri Lanka.
“Colombo is an incredible destination, and from August next year, we’re excited to be making it easier for Aussies to experience everything the beautiful country of Sri Lanka has to offer.
“This new route out of our home base of Melbourne is part of a huge growth phase for Jetstar. We’ve added new destinations, more aircraft and we’re continuing to expand our international network to give travellers even more choice and opportunities to take off for less.”
Melbourne Airport Chief Executive Officer, Lorie Argus, welcomed Jetstar’s new flights to Sri Lanka as the airport and airline celebrate 10 years since the opening of Terminal 4.
“We’re thrilled to see Sri Lanka, one of the region’s fastest-growing destinations, become Jetstar’s 10th international destination from Melbourne.
“More Jetstar flights mean more legendary low fares – making it easier than ever for Victorians to explore this part of the world for leisure or to visit family and relatives.
“We’re marking a major milestone as we celebrate a decade since Jetstar moved into its home at Terminal 4 and it’s fantastic to see how our partnership has strengthened. A decade on, we’re proud to be Jetstar’s largest hub.”
Flight schedules
From 25 August 2026**
| Flight | Frequency | Depart | Arrive |
| JQ5
Melbourne – Colombo |
Tuesday, Thursday and Saturday | 12:00 | 17:50 |
| JQ6
Colombo – Melbourne |
Tuesday, Thursday and Saturday | 19:50 | 10:00+1 |
**Schedule valid for 25 August – 03 Oct 2026, other periods vary based on daylight savings.
*As the upgraded 787 are progressively rolled out, some flights will operate with upgraded aircraft and others with our existing 787 aircraft.
^Sale ends 12.00pm AEDT Tuesday 9 December 2025, unless sold out. Excludes checked bags. Prices based on payment by PayID, Jetstar voucher, Jetstar Gift Card, or bookings redeemed only in Qantas Points through jetstar.com. For other options, a Payment Fee applies. See jetstar.com/fees. Travel dates and other conditions apply. Flights from Melbourne (Tullamarine) to Colombo are subject to Government and Regulatory approval.
Latest News
Laws to curb unauthorised constructions to be strengthened

The President emphasised that no room will be given in the future for unauthorised constructions and that the laws relating to them will be strengthened. The President further pointed out that failure to do so would lead the country to face an even greater disaster.
President Dissanayake stated that a separate unit will be established under the Reconstruction Presidential Task Force, which is to be set up shortly, to formulate legal policies and that this will enable long-term solutions to these issues.
President Anura Kumara Dissanayake made these remarks on Sunday (07) afternoon while participating in the Special District Coordination Committee meeting held at the Kurunegala District Secretariat.
The President instructed the relevant authorities to restore all damaged provincial roads and local council roads in the Kurunegala District to full functionality and reopen them for public use within the next two weeks.
He further stated that the allocations already set aside for this purpose should be utilized and that any roads that cannot be completed before 31 December, along with the required allocations, should be reported. The necessary funds will be allocated for these in the 2026 budget.
The district has recorded damage to 1,181l ‘A’ and ‘B’ grade provincial roads due to the disaster, along with 35 bridges, 162 culverts and one embankment. Detailed discussions were held on restoring them urgently.
The President separately reviewed the measures taken to restore essential infrastructure including electricity, water supply and communication facilities that had been disrupted in the district due to the disaster. He emphasised that delivering services up to the end user is the responsibility of the service-providing institutions and highlighted the need for strong coordination among these institutions to overcome existing obstacles.
Officials reported that 12,729 hectares of paddy land in the Kurunegala District were fully damaged due to the disaster, of which 7,215 hectares remain cultivable, while 5,514 hectares cannot be cultivated.
The President instructed the Water Supply Board to provide temporary water where cultivation is hindered due to lack of irrigation water and directed authorities to minimise the extent of uncultivable land as much as possible to ensure harvesting. He also inquired into the programme for supplying paddy seeds and fertiliser to farmers.
Damage caused to maize, vegetables and other supplementary crops, as well as the compensation process for affected farmers, was also reviewed.
The President informed local council Chairpersons that a main responsibility for well-cleaning activities lies with the local councils and instructed them to expedite the work with the assistance of the Tri-Forces and voluntary organisations.
Highlighting the need for maintaining accurate data on livestock farms across the country, the President pointed out that existing laws may be insufficient for this purpose and stressed the need to revise them. He also noted that the lack of proper registration of livestock farms causes issues when granting compensation and other assistance.
Therefore, the President instructed officials to bring all livestock-related data into a single system, review it and promptly make policy decisions regarding compensation.
There were also discussions on reviving the inland fisheries industry, healthcare requirements and the reopening of schools.
Extensive discussions were held on identifying land for resettlement and granting compensation for damaged houses. The President instructed that Divisional Secretaries must play a major role in compensation payments and resettlement activities.
Meanwhile, Venerable Aluthgama Mangala Thero, Chief Incumbent of Maddeketiya, Gokarella Sangamu Raja Maha Viharaya has allocated 20 acres of temple land for the resettlement of affected families. The relevant documentation was handed over to the President.
A financial donation of Rs. 10 million from the North Western Provincial Cooperative Societies, associations and members coordinated by the North Western Provincial Cooperative Development Department along with a donation from S.M. Wasantha Samarakoon, owner of Gokarella Rice Mill, was also handed over to the President.
Minister of Public Security and Parliamentary Affairs, Ananda Wijepala, Deputy Minister of Agriculture and Livestock, Namal Karunaratne, Deputy Minister of Women and Child Affairs , Namal Sudarshana, North Western Province Governor, Tissa Warnasuriya, district MPs from both government and opposition, local council Chairpersons, Secretary to the Treasury, Dr Harshana Suriyapperuma , Ministry Secretaries, Kurunegala District Secretary, Chandana Dissanayake, senior government officials and security forces leaders were present on this occasion.
-
News6 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 News12 hours ago
News12 hours agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
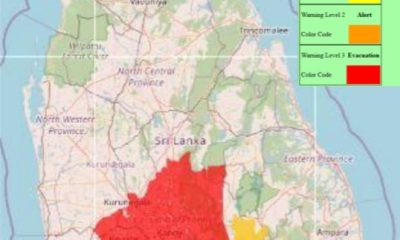
 News4 days ago
News4 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-
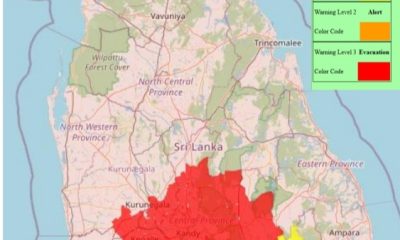
 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoLevel III landslide early warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoDitwah: An unusual cyclone
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady













