Business
Special goods and services tax: Issues and concerns

By Dr Roshan Perera & Naqiya Shiraz
The new bill titled ‘Special Goods and Services Tax’ was published by gazette dated 07 January 2022.1 The Special Goods and Services Tax (SGST) was originally proposed in Budget speech 2021 but was not implemented. It has once again been presented in Budget 2022. The SGST aims to consolidate taxes on manufacturing and importing cigarettes, liquor, vehicles and assembly parts, while also consolidating taxes on telecommunication and betting and gaming (see table 1 for existing taxes on these products and table 2 for taxes consolidated into the SGST as per the schedule in the gazette). The rationale for this new tax as per the bill is “…to promote self-compliance in the payment of taxes in order to ensure greater efficiency in relation to the collection and administration on such taxes by avoiding the complexities associated with the application and administration of a multiple tax regime on specified goods and services.”
Given the multiplicity of taxes and the complexity of the current tax system as a whole, rationalising taxes is necessary to improve collection. However, whether the proposed SGST simplifies the tax system, while ensuring revenue neutrality or even improving revenue collection, needs to be carefully examined.
The SGST Bill is silent on the treatment of the existing VAT on these goods and services. However, according to the Value Added Tax (Amendment) Bill also gazetted on 07 January 2022,1 liquor, cigarettes and motor vehicles will be exempted from VAT while telecommunications and betting and gaming services will still be subject to VAT.
While the gazetted Bill sets out some of the features of the proposed SGST there are many important areas not covered in the Bill. These are expected to be gazetted as and when required by the Minister in charge.
Issues & Concerns
The motivation behind SGST is the simplification of the tax system. Although the objective of introducing the SGST is to improve efficiency by reducing the complexity of the tax system there are many issues and concerns with this proposed tax.
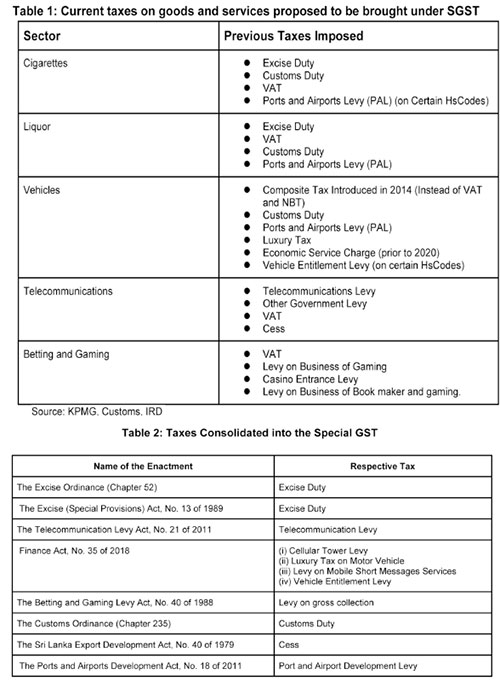
Revenue
Tax revenue which was 13% of GDP in 2010, declined to 8% in 2020. Ad hoc policy changes and weak administration contributed to the decline in tax revenue collection. This continuous decline in tax revenue has led to widening fiscal deficits and increasing debt. One of the main reasons for the current macroeconomic crisis is low tax revenue collection. Hence, any change to the existing tax system should be with the primary objective of raising more revenue.
According to the budget speech the SGST is estimated to bring in an additional Rs. 50 billion in revenue in 2022.1 Revenue from taxes proposed to be consolidated under the SGST has significantly declined over the past 3 years. Given the already difficult macroeconomic environment, along with ad hoc tax policy changes raising the additional revenue estimated at Rs. 50 billion seems a difficult task.
Tax Base and Rate
For the SGST to raise taxes in excess of what is already being collected through the existing taxes, the rate and the base for the SGST needs to be carefully and methodically calculated. Further, the existing taxes have different bases of taxation. For instance the basis of taxation of motor vehicles is both on an ad valorem1 basis and a quantity basis while the basis of taxation of cigarettes and liquor is quantity.2 In light of this, the basis of taxation on which SGST isapplied becomes an issue. Having different bases and different rates for various goods and services would complicate the implementation of the tax These issues need to be carefully considered to ensure the new tax is revenue neutral or be able to enhance revenue collection.
Efficiency
One possible revenue benefit of this proposal is the inability to claim input tax credits on the sectors exempted from VAT. However, the issue is the cascading effect that would result where there would be a tax on tax with the end consumer paying taxes on already paid taxes. If the idea was to raise additional revenue by limiting tax credits, it would have been simpler to raise the tax rates on the existing taxes rather than introduce a new tax.
4. Administration
According to the bill, SGST will now be collected through a new unit set up under the General Treasury where a Designated Officer (DO) will be in charge of the administration, collection and accountability of the tax. The existing revenue collection agencies, such as the Inland Revenue Department (IRD) or the Excise Department will not be primarily responsible for the collection of this tax. By removing the IRD and Excise Department, a parallel bureaucracy will be created, at a time when public spending needs to be carefully managed. The General Treasury also has no previous experience and expertise in direct revenue collection. Weak administration is one of the key reasons for the low tax collection and success of this tax would depend on the strength of its administration.
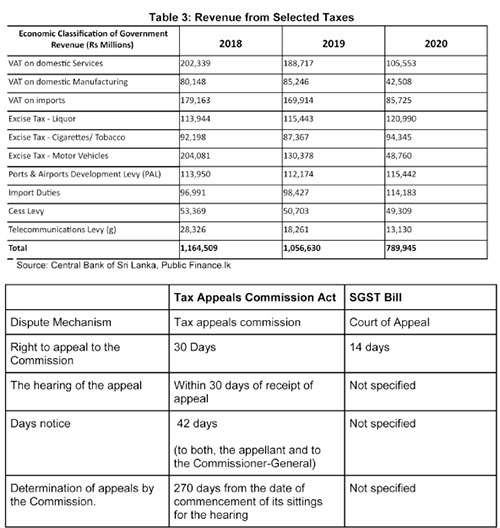
In addition to the above mentioned concerns, as per the Bill the minister in charge of the SGST has been vested with the power to set the rates, the base and grant exemptions. Accordingly, Parliamentary oversight over fiscal matters is weakened under this proposed Bill.
It could also lead to a time lag between the gazetting and implementing of changes to the SGST (such as the rate, base etc) and obtaining Parliamentary approval for those changes.
Dispute resolution
The SGST Bill also focuses on the dispute resolution mechanism. Under the present tax system, with the enactment of the Tax Appeals Commission Act, No. 23 in 2011 the Tax Appeals Commission has the “responsibility of hearing all appeals in respect of matters relating to imposition of any tax, levy or duty”.1 The most recent amendment to the Tax Appeal
Commissions act (2013)1 seeks to address the large number (495) of cases pending before the Tax Appeals Commision2 by increasing the number of panels to hear the appeals.
Under the proposed SGST disputes will be handled through the court of appeal. However, the time period by which specific actions need to be taken is not provided in the bill. In addition, disputes have to be taken to the court of appeal. Hence, the entire process will be more time consuming. This could result in revenue lags and difficulties in revenue estimation until disputes are resolved.
Additionally, in the case that no valid appeal has been lodged within 14 days, any remaining payments would be considered to be in default. Thereafter, the responsibility is shifted to the Commissioner General of the IRD to recover the dues. Given the IRD is completely removed from the normal collection process, the rationale for bringing defaults under the IRD is not clear.
III. Policy Recommendations
As discussed, the SGST Bill has several limitations and much of this is due to the ambiguities in the Bill.
If the tax is implemented, the rate and basis of taxation needs to be revenue neutral to ensure tax collection is maximised and administrative costs minimised.
The rates, basis of taxation, exemptions etc should be specified in the Bill, as done in most other Acts. This would avoid the power for discretionary changes to the tax being placed in the hands of the minister in charge.
Given the already weak tax administration, it would be more sensible to strengthen the existing revenue collecting agencies and address the weaknesses in the existing system without creating a parallel bureaucracy.
In the case where VAT is consolidated into the proposed GST, the issue of cascading effect of input tax credits needs to be addressed. This is relevant particularly in the case of capital expenditure.
Given the critical state of revenue collection in the country the question to ask is whether this is the best time to introduce a new tax. Focus should be on fixing issues in the existing tax system to ensure revenue is maximised. The VAT is the least distortionary tax and it is the easiest to administer. Given these features it can be a very efficient revenue generator for a country. Therefore instead of introducing a new tax, capitalising on systems that are already in place and amending the VAT rate, threshold and exemptions may be a more practical solution to the revenue problem that the country is currently facing.
Dr. Roshan Perera is a Senior Research Fellow at the Advocata Institute and the former Director of the Central Bank of Sri Lanka.
Naqiya Shiraz is a Research Analyst at the Advocata Institute.
The opinions expressed are the author’s own views. They may not necessarily reflect the views of the Advocata Institute, or anyone affiliated with the institute.
Business
Norochocholai coal-fired power complex seen as facing staggering financial losses

Sri Lanka’s first and largest coal-fired power complex at Norochcholai is staring at mounting financial losses running into millions of rupees as low-quality coal imports, rejected shipments and unusable stockpiles disrupt operations and expose deep flaws in coal procurement, power sector and environmental experts warned yesterday.
Energy sector sources told The Island Financial Review the economic damage has already begun, with rejected coal stocks, delayed payments and declining plant efficiency forcing the system to absorb losses from under-performance, additional handling costs and the risk of turning to more expensive backup generation.
Insiders estimate that continued reliance on sub-standard coal could result in tens of millions of rupees in losses per day, once reduced output, higher fuel burn and maintenance costs are factored in.
At the centre of the controversy is a recent coal shipment procured by the Lanka Coal Company (LCC), which has come under intense scrutiny after laboratory tests reportedly showed ash content of around 21%, far exceeding the 16% maximum allowed under tender conditions.
While parliamentary debate has focused narrowly on whether the coal meets the required calorific value, experts stress that excessive ash alone is sufficient grounds for outright rejection, regardless of calorific performance.
The situation worsened after coal stocks at the Norochcholai Coal-Fired Power Complex were recently rejected, leaving shipments in limbo and payments withheld. Power sector officials say this has resulted in logistical losses, demurrage risks and operational uncertainty, while existing low-quality coal stockpiles continue to deteriorate in storage.
“Coal that does not meet specifications is not just unusable — it becomes a financial liability, a senior electrical engineer said.
High-ash coal reduces boiler efficiency, increases fly ash generation and accelerates wear on ash handling systems, electrostatic precipitators and boilers — translating into higher maintenance costs and forced outages. Industry analysts warn that these hidden costs ultimately find their way into CEB losses or consumer tariffs.
Environmental Scientist Hemantha Withanage warned that accepting or burning such coal would push Norochcholai into a new environmental crisis, with serious consequences for communities in Norochcholai, Puttalam and surrounding areas.
“This is not just about calorific value. High ash coal means significantly more fly ash, Withanage told The Island Financial Review. “With low moisture and excessive ash, particulate matter spreads easily, contaminating air, soil and water. This is a massive ecological threat that will directly affect public health.”
He stressed that fly ash contains toxic heavy metals and fine particulates linked to respiratory illness and long-term environmental degradation. “If tender conditions are ignored, the cost will be paid by communities, not the suppliers, Withanage said.
Critics say the crisis exposes serious weaknesses in coal procurement oversight, with questions now being raised about supplier selection, quality verification and accountability. They argue that repeatedly importing low-quality coal — only to reject it or burn it at reduced efficiency — amounts to systemic mismanagement of public funds.
By Ifham Nizam
Business
IRCSL launches ambitious mission to transform Sri Lanka’s insurance sector

In a groundbreaking initiative, Insurance Regulatory Commission of Sri Lanka (IRCSL), announced an ambitious mission aimed at transforming the insurance industry into a cornerstone of national economic resilience and social stability.
To address this, the IRCSL will launch a nationwide education campaign titled “Insurance for All: For a Secure Future,” focusing on enhancing financial literacy across the country said Dr. Ajith Raveendra De Mel, the newly appointed Chairman IRCSL. Few sample events have already commenced last year in Matara, Jaffna and Kilinochchi that have set a strong precedent for future initiatives. “The positive response from participants highlighted the strong need for direct engagement and community-level awareness,” he said.
The IRCSL has also partnered with the Ministry of Education to integrate insurance literacy into the national curriculum, starting as early as Grade 5. This initiative aims to embed core concepts of risk management and financial protection, preparing students for future roles in the insurance industry. Complementing educational efforts, the IRCSL is also hosting an Inter-University Quiz Competition focused on insurance and financial literacy, aiming to engage university students and cultivate future thought leaders in the sector. Additionally, an e-Newsletter will keep stakeholders informed about industry updates and regulatory developments.
Dr. De Mel emphasized that this transformation it is not just about increasing insurance penetration, currently at a mere 1.1%, but about fostering a financially literate society where every citizen, family, and business is shielded from unforeseen risks. He said “Our mission is to cultivate a fully insured, financially literate, and future-ready society. The journey ahead involves profound regulatory, technological, and educational reform to create a modern, transparent, and robust regulatory environment that earns public trust while promoting innovation and sustainable growth in the industry.”
He pointed out the critical need for awareness, noting that many Sri Lankans perceive insurance as complex or exclusive to the wealthy. “We need to change how people think about insurance. Our goal is to make it simple, relatable, and accessible to everyone, particularly in rural and underserved communities,” he explained. The IRCSL will collaborate closely with the Insurance Association of Sri Lanka (IASL), the Sri Lanka Insurance Brokers Association (SLIBA), and the Sri Lanka Insurance Institute (SLII) to ensure that the message of financial preparedness reaches all corners of the nation. As Sri Lanka stands on the brink of an insurance transformation, Dr. De Mel’s vision promises a secure future driven by informed financial decisions and enhanced protection against life’s uncertainties.
The IRCSL is also focusing on digital transformation, enhancing operational excellence within the insurance sector. Key initiatives include establishing a Centralized Motor Insurance Database to improve transparency and efficiency in motor insurance, and advancing health insurance through digital integration, including standardized disease coding and electronic health records.
To ensure global competitiveness, the IRCSL is benchmarking against international best practices. A recent study tour to India has provided valuable insights into implementing risk-based supervision and capital frameworks, as well as developing accessible insurance products for underserved communities.
As the IRCSL approaches its 25th anniversary, it emphasizes the importance of staff development and alignment with other financial regulatory bodies to maintain high professional standards. The upcoming OECD/ADBI Roundtable on Insurance and Retirement Savings in Asia will further position Sri Lanka as a leader in insurance discussions, fostering regional collaboration and innovation.
by Claude Gunasekera
Business
Sri Lanka’s first public allergy awareness wristbands

LAUGFS Life Sciences, in collaboration with the Medical Research Institute (MRI), Colombo, has launched Sri Lanka’s first-ever publicly driven allergy awareness wristbands, a groundbreaking initiative aimed at improving patient safety and preparedness in medical emergencies. The wristbands provide essential information about drug sensitivities, allowing healthcare professionals to respond quickly and effectively when time is critical.
The official handover ceremony featured distinguished medical experts, including Dr. Dhanushka Dassanayake, Consultant Immunologist and Head of the Department of Immunology – MRI, Dr. Rajiva De Silva, Senior Consultant Immunologist – MRI and Dr. Prabath Amerasinghe, Deputy Director – MRI, marking a historic milestone in patient care in the country.
Commenting on the initiative, Dr. Rajiv Perera, CEO of LAUGFS Life Sciences, said, we are proud to partner with the Medical Research Institute to launch Sri Lanka’s first-ever publicly driven allergy awareness wristbands. This initiative underscores our commitment to patient-centric healthcare by providing critical information that can save lives during emergencies. We believe that thoughtful collaborations like this can have a meaningful impact on patient safety, and we look forward to expanding the program to cover additional drugs and allergens, further advancing healthcare standards across the country.
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoSajith: Ashoka Chakra replaces Dharmachakra in Buddhism textbook
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoDialog and UnionPay International Join Forces to Elevate Sri Lanka’s Digital Payment Landscape
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoThe Paradox of Trump Power: Contested Authoritarian at Home, Uncontested Bully Abroad
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoSubject:Whatever happened to (my) three million dollars?
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoLevel I landslide early warnings issued to the Districts of Badulla, Kandy, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya extended
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoNational Communication Programme for Child Health Promotion (SBCC) has been launched. – PM
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days ago65 withdrawn cases re-filed by Govt, PM tells Parliament
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoThe minstrel monk and Rafiki, the old mandrill in The Lion King – II











