News
Scientific team completes part of ongoing study on gene pool of 700 Lankan elephants

by Ifham Nizam
An eight-member scientific team has completed a comprehensive part of an ongoing study on the gene pool of 700 Sri Lankan elephants.
Department of Wildlife Conservation (DWC) and Agricultural Biotechnology Centre (AgBC) of the University of Peradeniya, are conducting a research on DNA analysis of wild elephants in Sri Lanka funded by the Ecosystem Conservation and Management Project (ESCAMP).
The scientific team comprises Ranjan Marasinghe, R. M. R. Nilanthi Rajapakse, H.A. Bhagya Hathurusinghe, Chandana Sooriyabandara, Dr. C. H. W. M. R. Bhagya Chandrasekara, Nuwan Jayawardana, M. Madawika Kodagoda, Dr. R. C. Rajapakse and Prof. Pradeepa. C. G. Bandaranayake.
 “The study will clearly indicate the differences of the Sri Lankan elephant as a sub species. Our molecular methodology is based on using elephant dung, and the test is similar to the Covid-19 PCR test”, Researcher R. M. R. Nilanthi Rajapakse told The Sunday Island.
“The study will clearly indicate the differences of the Sri Lankan elephant as a sub species. Our molecular methodology is based on using elephant dung, and the test is similar to the Covid-19 PCR test”, Researcher R. M. R. Nilanthi Rajapakse told The Sunday Island.
“We have already sequenced and assembled the genome of the Sri Lanka Wild Elephant (Elephas maximus maximus), the type subspecies of the Asian elephant. Comparative genomics work continues with available Asian and African elephant genomic data with the objective of identifying specific set of markers for the identification of Sri Lankan elephants”, the team said.
The first part of the research focused on 100 elephants, and it has now increased to 700 with continued focus on elephants in the forest patches etc., they remarked.
The project aims to examine the within-species genetic structure of the wild elephant across its range to better understand how genetically distinctive regional populations are and deviations of Sri Lankan elephants with those of other countries and how that might affect its conservation.
Conservation and management of elephants in Sri Lanka has become an important issue given the escalation of the Human-Elephant Conflict (HEC) and international trade of wild elephants.
The Asian elephant, Elephas maximus, is an umbrella species in tropical forests. Wild elephants play important roles in maintaining forest dynamics such as opening animal trails in the forests, creating open gaps that facilitate seed and acting as a seed disperser for large-seed fruit species. The conservation status of the Asian elephant has been recognized as an endangered species since 1986. Wild Asian elephants are currently distributed mainly in the South and Southeast Asia.
Habitat loss and fragmentation, anthropogenic disturbance, illegal poaching and HEC have been considered as significant threats to the Asian elephants, resulting in population decline and fragmentation. These threats resulted in skewed sex ratio and disruption of social organization.
 Acquiring information of wild populations is important for effective conservation and management of wild elephants.
Acquiring information of wild populations is important for effective conservation and management of wild elephants.
Wild elephants in Sri Lanka is estimated to be between 5,000 and 6,000, according to the last survey conducted by the DWC in 2011. This is a relative high number considering the small size of the country (65,610 sq. km) and the human population of over 21 million.
For management of elephants in the wild, monitoring the changes in the structure and composition of the populations would be far more useful than estimating elephant numbers.
Therefore, genetic methods will be useful for management and conservation plan such as individual and sex identification, population size estimation, population sex ratio, genetic diversity, relatedness among individuals in a population, gene flow among populations, detection of bottleneck event, phylogeography of particular species, detection of hybridization, providing evidence of illegal wildlife poaching, including being a tool for genetic management of a population and long-term monitoring of the managed population.
It provides genetic information of the populations that could not be obtained from field data collection alone. Genetic methods, on the other hand, provide reliable information on population structure and facilitate investigation of genetic effects on small and fragmented populations. Advance genetic methods also provide better estimations on population size with reasonable cost and time.
Further, tracking of ivory poaching would also be possible if a reference genetic database of the natural populations is available.
Molecular genetics studies on elephants’ date back to 1990s. Micro satellite markers have been the preferred choice and have played a major role in ecological, evolutionary and conservation research on elephants over the past 20 years.
However, technical constraints especially related to the specificity of traditionally developed micro satellite markers have brought to question their application, specifically when degraded samples are utilized for analysis. Therefore, the team analyzed the specificity of 24 sets of micro satellite markers frequently used for elephant molecular work.
“First, we optimized the DNA extraction protocol for elephant dung which can even be used for samples reach the lab within a week’s time because all previous studies depended on fresh dung samples collected less than 24 h time”, the team said.
“Comparative wet lab analysis was done with blood and dung DNA in parallel with in silico work. Our data suggest cross-amplification of unspecific products when field-collected dung samples are utilized in assays. The necessity of Asian elephant specific set of micro satellites and or better molecular techniques are highlighted”, the team pointed out.
The necessity of insilico analysis for testing specificity of SSRs is highlighted for other wild animals, for example, leopards. Nevertheless, the current study suggests that the analysis should extend beyond the human genome especially when dung DNA is used as starting materials. Therefore, the specificity of primers is a critical factor deciding the success of traditional SSR based methods adopted for such analysis.
Based on their study, no primer set out of 24 tested SSRs could be recommended for future work when the elephant dung is used as the starting material. If blood samples are drawn carefully with no human or other contamination, those with no multiple hits in the elephant genome, for example, EMU06 and EMU07 could still be used. As such, results of the previous studies done with elephant dung would be questionable with the evidence gathered from current findings.
“Nevertheless, no one could challenge the past since the revolutionary technologies pawed the path for the success of current studies. However, our results suggest the necessity of revisiting available methods. Alternatively, more specific,” the team stressed.
Latest News
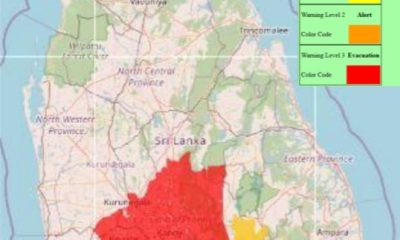
Level III landslide early warnings issued to the Districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale extended

The landslide early warning center of the National Building Research Organisation [NBRO] has extended the Level III RED landslide early warnings issued to the Districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale until 1600hrs on 11th December 2025.
Accordingly,
The LEVEL III RED landslide warnings issued to the the Divisional Secretaries Divisions and surrounding areas of Kundasale, Pasbage Korale, Medadumbara, Ganga Ihala Korale, Hatharaliyadda, Pathadumbara, Doluwa, Panvila, Gangawata Korale, Ududumbara, Akurana, Yatinuwara, Harispattuwa, Deltota, Thumpane, Poojapitiya, Udapalatha, Udunuwara, Minipe and Pathahewaheta in the Kandy district, Aranayaka, Yatiyanthota, Rambukkana, Bulathkohupitiya and Mawanella in the Kegalle district, Mallawapitiya, Mawathagama and Rideegama in the Kurunegala district, and Rattota, Laggala Pallegama, Ukuwela, Matale, Wilgamuwa, Pallepola, Naula, Yatawatta and Ambanganga Korale in the Matale district have been extended.
LEVEL II AMBER landslide early warnings have been issued to the Divisional Secretaries Divisions and surrounding areas of Uva Paranagama, Hali_Ela, Meegahakivula, Badulla, Kandeketiya, Bandarawela, Soranathota, Ella, Haputhale, Lunugala, Welimada, Haldummulla and Passara in the Badulla district, Warakapola, Galigamuwa, Kegalle, Dehiowita, Ruwanwella and Deraniyagala in the Kegalle district, Polgahawela and Alawwa in the Kurunegala district, Kothmale East, Walapane, Thalawakele, Nuwara Eliya, Kothmale West, Nildandahinna, Mathurata, Ambagamuwa Korale, Hanguranketha and Norwood in the Nuwara Eliya district. and Kolonna, Godakawela and Kahawaththa in the Ratnapura district.
LEVEL I YELLOW landslide early warnings have been issued to the Divisional Secretaries Divisions and surrounding areas of Divulapitiya, Attanagalla and Mirigama in the Gampaha district, Narammala in the Kurunegala district, and Kiriella, Eheliyagoda, Balangoda, Kaltota, Openayake, Nivithigala, Imbulpe, Ayagama, Kuruwita, Kalawana, Elapatha, Pelmadulla and Ratnapura in the Ratnapura district.
News
“We cannot allow flooding to become a part of the daily lives of the people in the Colombo District” – PM

Prime Minister Dr. Harini Amarasuriya stated that unauthorized constructions within the Colombo District, nor any form of residential developments that endanger the public carried out under the guise of development agenda will not be allowed.
The Prime Minister made these remarks while addressing the media at the conclusion of the Colombo District Disaster Management Committee meeting held on Tuesday [December 09] at the Colombo District Secretariat.
Addressing further, the Prime Minister stated:
“The Colombo District has become vulnerable to this extent due to the constructions carried out without any proper planning or understanding of regulations, along with personal and politically motivated decisions that have placed both the district and its people at risk.
Compared to the districts that suffered severe loss of life and property due to the recent cyclone, the damage to the Colombo District has been relatively lower. However, special intervention is being carried out together with the relevant institutions to manage the potential future flood risks in the district.
This matter was also given special attention during today’s District Disaster Management Committee meeting. We cannot allow the flooding to become a regular part of the lives of the people in Colombo. All relevant institutions will come together to put forward a common plan for flood control in the district.”
The Prime Minister further stated that discussions are already underway to provide sustainable solutions for the people living in high-risk areas within the Colombo District.
The discussion was attended by the Deputy Minister of Urban Development Eranga Gunasekara, Deputy Minister of Mass Media Kaushalya Ariyaratne, and Colombo District Members of Parliament Aruna Panagoda and Chandana Suriyarachchi.
[Prime Minister’s Media Division]
Latest News
Russia gifts 35 tonnes of Humanitarian Aid to Sri Lanka
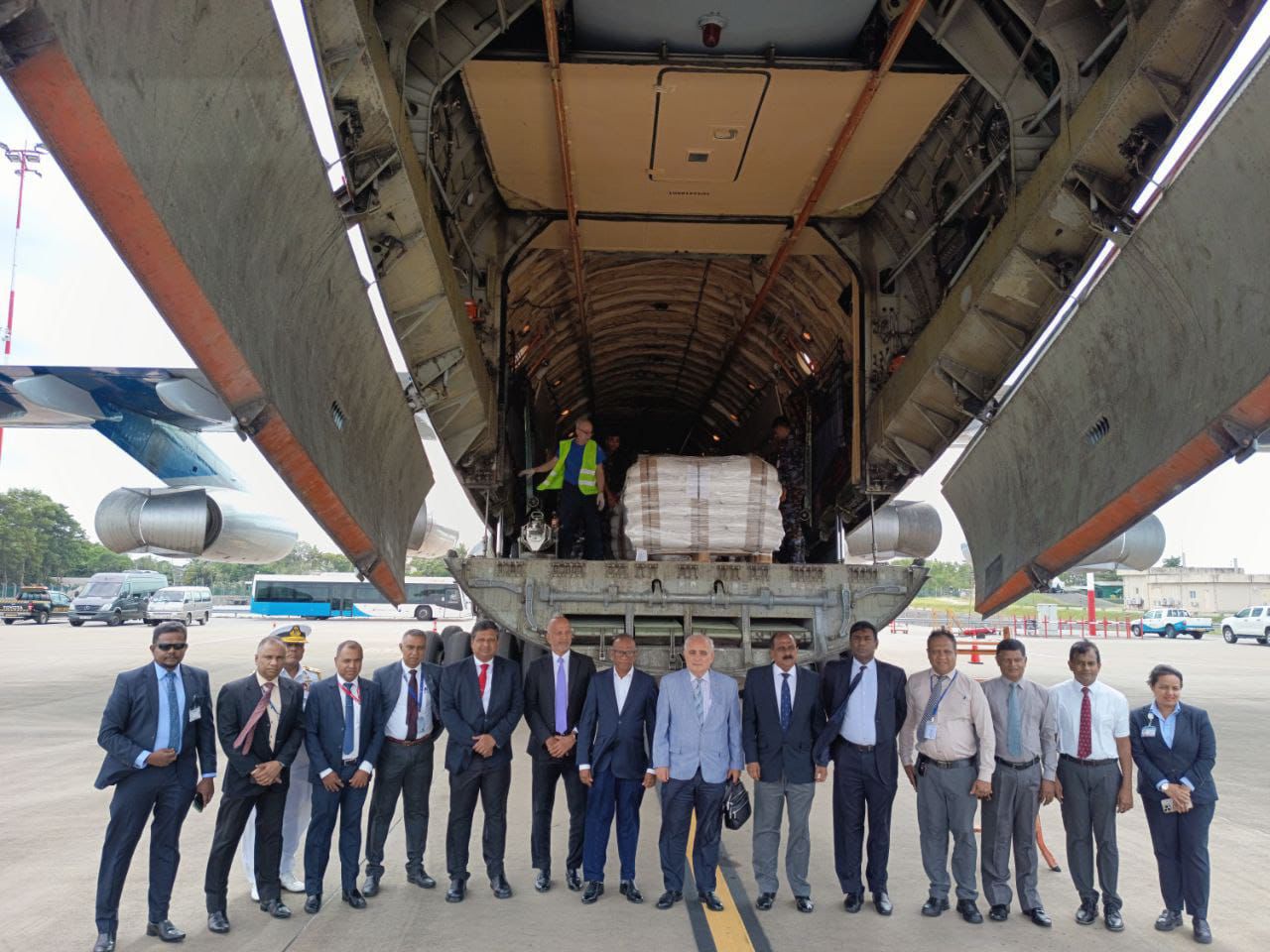

The handover of 35 tonnes of Russian Humanitarian Aid to Sri Lanka, recently affected by the cyclone «Ditwah», took place at Katunayake today (10th December)
The shipment was welcomed at the Katunayake airport by Ambassador of Russia Levan Dzhagaryan, Minister of Ports and Civil Aviation Anura Karunathilaka and Deputy Minister of Defence, Major General Aruna Jayasekara (Retd).
Ambassador Levan Dzhagaryan: said “This delivery is a reflection of long-term friendly relations between Russia and Sri Lanka and reaffirms Moscow’s commitment to support countries in a difficult humanitarian situation.”
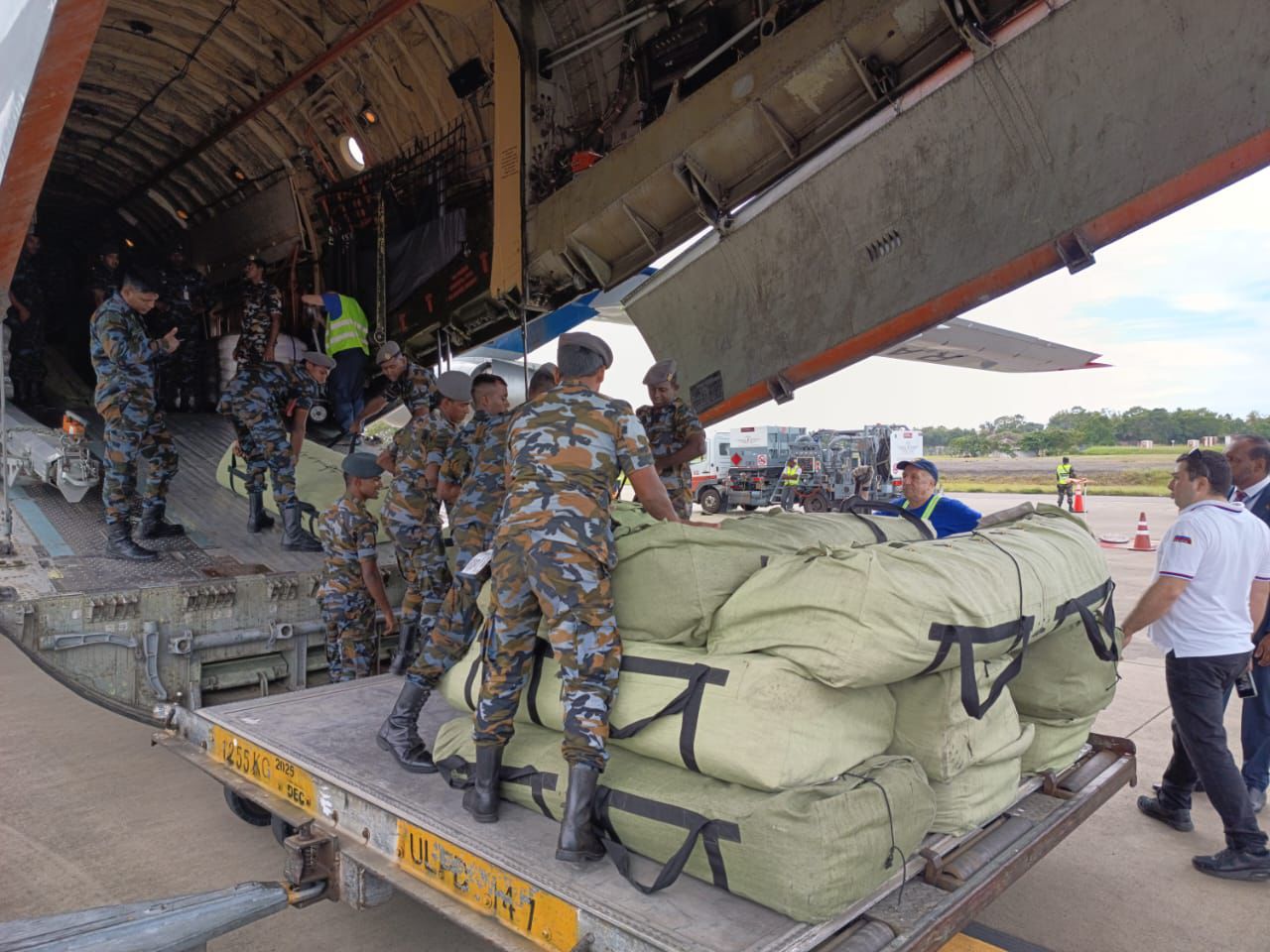
The supplies brought by the EMERCOM (Russian Ministry of Emergency Situations) aircraft comprised a movable 60 kW electric power station, Pumping equipment for water drainage, Summer tents (10-person capacity) and Food supplies (sugar, vegetable oil, rice)
The total cargo weight is 35 metric tonnes. The aid will be distributed among the most affected regions.



-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
 News7 days ago
News7 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoCyclone Ditwah leaves Sri Lanka’s biodiversity in ruins: Top scientist warns of unseen ecological disaster
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoThe Catastrophic Impact of Tropical Cyclone Ditwah on Sri Lanka:













