Features
Unique opportunity for fast-tracked social integration, if only…
by Susantha Hewa
Surely, racism has caused enough damage to us to warrant its erasure from our midst with the condemnation it deserves, without leaving it more room to further flourish in deceptively benign ways. As showcased by the November 14 election results, many Tamils and Muslims, not forgetting Catholics and Hindus, have voted to power the NPP, led by the JVP, which they might have previously labelled, and avoided, as a ‘Sinhalese’ party.
This turning of tables has obviously been triggered by the country’s worsening political and economic conditions, but the story should not end there because people’s unprecedented shift of faith strongly indicates the relaxing of the rigid social and cultural postures which may prove to be more important in a multi-ethnic and multi-religious society. This is because, if used wisely and sensitively, it has the potential to be directed towards the evolution of a society where there wouldn’t be much room for further social fragmentation, hitherto sustained by the biases felt at the deepest levels of our sense of ‘self and other’. Dr. Jehan Perera in his article titled “Reading demands for change” (The Island, November 19, 2024) says, “Unlike in the case of economic recovery for which there are no short-term panaceas, the solution to the ethnic conflict is one that can be resolved soon as it has been discussed, negotiated and publicised on several occasions, but not implemented due to the failure of leadership”. The government may seize the opportunity to “make hay while the sun shines”.
The mercurial nature of ‘identity’ and ‘self’ is well-known. They are a topic of discussion in neuroscience, psychology, humanities, social sciences, religions and, notably, in Buddhism. In humanities and social sciences, ‘identity’ is used to refer to one’s social ‘face’. According to psychology, ‘self’ is a multi-dimensional concept that “includes cognitive and affective judgments about ourselves”. Simply put, it is a social construct and “is shaped by interactions with others, and how a person views themselves in relation to their culture, history, gender, class, and more”. In other words, ‘self’ and ‘identity’ are social constructs; they may not be sufficiently understood as entities independent of the dynamic links between the individual and society.
Given the above insights, it is not hard to understand that our collective gut feeling of ‘identity’ has much room for updating and improvement for us to move ahead as a united nation. It’s not difficult to understand that unity is more conducive to social wellbeing than prudish affirmation of our different identities. In particular, Buddhists shouldn’t find it much difficult to understand ‘identity’ as an illusion, because in Buddhism, “The ‘I’ or sense of self is considered an illusion, and is viewed as fluid and ever-changing”. However, many of us Buddhists don’t seem to have taken this illusory nature of self all that seriously. Of course, one may argue, that it is too deep a concept to be grasped by ‘prthagjana’ (not sufficiently enlightened) people. Perhaps the argument is more expedient than sincere, for it can readily be used to silence those who wantonly accuse us of being wicked. Humour apart, surely, we all have among our acquaintances, those who seem to have understood this concept to the extent that they can view ‘identities’ with more detachment thus contributing to enhance a sense of togetherness, at least in their small circles. And, among them are people of all ethnicities and faiths – Buddhists, Christians, Muslims, Hindus and even those who refuse to follow any established religion; the late Dr. E.W. Adikaram comes to mind easily. Our tendency to cling to the rigid cast of ‘self and other’ comes from the habit of finding security in our accustomed ‘comfort zones’. That is, we thrive in the feeling of togetherness in small communes. In other words, being immersed in the feeling of belonging to this or that ethnicity, religion, caste, gender, etc., is too appealing and reassuring to be got rid of with the weapons of knowledge, judgement and reason you acquire as you grow up.
Such cast-iron ‘identity’ jackets we are proud to wear would do little to help forge a more cohesive society. In all these years, we have had little help from our society, its various institutions, cultures, customs and religions to think in terms of an integrated society, despite all the rhetoric and popularized cosmetic programmes that were made to be soothing to the ear and the eye. The uselessness of all these haphazard and dispersed projects often surfaces when our ‘naturalized’ social instincts begin to assert themselves against wiser counsels. Up to the present, all our political potentates have never lost an opportunity to wax inspirational about ‘unity in diversity’. Their sincerity is in public display today, courtesy their spirited scuffles to enter Parliament through National Lists.
Despite their usual bombast on peace building, our past is scattered with loud assertions of our ‘purity of stock’ where political collusion was too apparent to escape notice. We have not forgotten those horror stories about ‘wanda kottu’, ‘wanda sethkam’, etc. – all supposedly ‘neutering missions’ that stirred communal disharmony. Had the years of political sermonizing, pontification, programmes, launched with much sound and fury to purportedly promote ethnic cohesion, been able to make us any less susceptible to our ancestral instincts?
By the way, how about gender-based discrimination, which most of us are unconcerned about? We have enough academic interest in such fields but not much of it goes to help to subdue the persistent feelings of women who feel being oppressed and discriminated. Of course, it goes without saying that not many religions have addressed the social and cultural oppression of women in a ‘language’ which has made any sufficient dent in our deep-rooted gender biases. As we have seen above, it is the same with other forms of oppression that we have perpetuated and unwittingly fostered at our own peril.
Let’s think for a moment about the rumblings felt in some segments of society about their ‘underrepresentation’ in the new government’s power hierarchy. There is no doubt that these are genuine feelings of disaffection coming from their dormant feelings of being subject to discrimination; for example, with regard to Muslim representation and female representation. There is no doubt that it is better for all of us to assuage these deeply felt hurts as they arise in society to create uproar. However, at what level do we have to address them? Surely, not at the highest levels of their visibility and urgency, which has resulted from prolonged neglect. They should be addressed at their most rudimentary levels for us to get rid of these ‘anomalies’.
Instead of thinking of quick fixes, as has been the practice in the past, it is time we grasped the nettle. The solution to women’s problems is not to find a few more slots for them in Parliament and other powerful positions, although it would instantly satisfy the disgruntled parties. The underrepresentation of women in privileged positions is just a sign of the basic problem of their culturally imposed subservience in the family. It’s not different from the subjugation of social groups on the basis of hoary divisions shielded to perpetuate power structures in different parts of the world. For examples, women’s subservient state in the family is extolled by platitudes about their unrestricted maternal love, sacrifice, self-denial, abstinence, etc., which indirectly help their subjugation effected by overtly discriminatory means. In trying to expose the wrappings of India’s age-old caste system, Arundhati Roy says, “it [casteism] has come to be so fused with … so much that is seen to be kind and good—mysticism, spiritualism, non-violence, tolerance, vegetarianism, Gandhi, yoga, backpackers, the Beatles—that, at least to outsiders, it seems impossible to pry it loose and try to understand it.” As for oppressive systems, casteism is not alone in its capacity for working in complicity with most prevalent forms of human engagement. Can’t we see a similar congruence of seemingly uplifting cultural interventions with regard to deifying ‘motherhood’, which obscures the cultural oppression of women in society.
With regard to the current misgivings about underrepresentation in politics attributed to the lack of concern about ethnicity/religion and gender, perhaps easy solutions will be effective in the short term but they are likely to help perpetuate the basic problems crying for a lasting solution. The unsatisfactory visibility of women in higher ranks, in politics or elsewhere, has to be addressed at the roots by taking awareness to the people of the sociocultural character of the issue. Same applies to any unfairness, whether it is perceived by any community – be it concerning the majority or a minority.
The political and social context we find ourselves in today is a good opportunity which shouldn’t be left unexploited, if we don’t wish to postpone any further the possibility of ushering in a more friendly society with less unwarranted enmities.
Features
The call for review of reforms in education: discussion continues …

 The hype around educational reforms has abated slightly, but the scandal of the reforms persists. And in saying scandal, I don’t mean the error of judgement surrounding a misprinted link of an online dating site in a Grade 6 English language text book. While that fiasco took on a nasty, undeserved attack on the Minister of Education and Prime Minister Harini Amarasuriya, fundamental concerns with the reforms have surfaced since then and need urgent discussion and a mechanism for further analysis and action. Members of Kuppi have been writing on the reforms the past few months, drawing attention to the deeply troubling aspects of the reforms. Just last week, a statement, initiated by Kuppi, and signed by 94 state university teachers, was released to the public, drawing attention to the fundamental problems underlining the reforms https://island.lk/general-educational-reforms-to-what-purpose-a-statement-by-state-university-teachers/. While the furore over the misspelled and misplaced reference and online link raged in the public domain, there were also many who welcomed the reforms, seeing in the package, a way out of the bottle neck that exists today in our educational system, as regards how achievement is measured and the way the highly competitive system has not helped to serve a population divided by social class, gendered functions and diversities in talent and inclinations. However, the reforms need to be scrutinised as to whether they truly address these concerns or move education in a progressive direction aimed at access and equity, as claimed by the state machinery and the Minister… And the answer is a resounding No.
The hype around educational reforms has abated slightly, but the scandal of the reforms persists. And in saying scandal, I don’t mean the error of judgement surrounding a misprinted link of an online dating site in a Grade 6 English language text book. While that fiasco took on a nasty, undeserved attack on the Minister of Education and Prime Minister Harini Amarasuriya, fundamental concerns with the reforms have surfaced since then and need urgent discussion and a mechanism for further analysis and action. Members of Kuppi have been writing on the reforms the past few months, drawing attention to the deeply troubling aspects of the reforms. Just last week, a statement, initiated by Kuppi, and signed by 94 state university teachers, was released to the public, drawing attention to the fundamental problems underlining the reforms https://island.lk/general-educational-reforms-to-what-purpose-a-statement-by-state-university-teachers/. While the furore over the misspelled and misplaced reference and online link raged in the public domain, there were also many who welcomed the reforms, seeing in the package, a way out of the bottle neck that exists today in our educational system, as regards how achievement is measured and the way the highly competitive system has not helped to serve a population divided by social class, gendered functions and diversities in talent and inclinations. However, the reforms need to be scrutinised as to whether they truly address these concerns or move education in a progressive direction aimed at access and equity, as claimed by the state machinery and the Minister… And the answer is a resounding No.
The statement by 94 university teachers deplores the high handed manner in which the reforms were hastily formulated, and without public consultation. It underlines the problems with the substance of the reforms, particularly in the areas of the structure of education, and the content of the text books. The problem lies at the very outset of the reforms, with the conceptual framework. While the stated conceptualisation sounds fancifully democratic, inclusive, grounded and, simultaneously, sensitive, the detail of the reforms-structure itself shows up a scandalous disconnect between the concept and the structural features of the reforms. This disconnect is most glaring in the way the secondary school programme, in the main, the junior and senior secondary school Phase I, is structured; secondly, the disconnect is also apparent in the pedagogic areas, particularly in the content of the text books. The key players of the “Reforms” have weaponised certain seemingly progressive catch phrases like learner- or student-centred education, digital learning systems, and ideas like moving away from exams and text-heavy education, in popularising it in a bid to win the consent of the public. Launching the reforms at a school recently, Dr. Amarasuriya says, and I cite the state-owned broadside Daily News here, “The reforms focus on a student-centered, practical learning approach to replace the current heavily exam-oriented system, beginning with Grade One in 2026 (https://www.facebook.com/reel/1866339250940490). In an address to the public on September 29, 2025, Dr. Amarasuriya sings the praises of digital transformation and the use of AI-platforms in facilitating education (https://www.facebook.com/share/v/14UvTrkbkwW/), and more recently in a slightly modified tone (https://www.dailymirror.lk/breaking-news/PM-pledges-safe-tech-driven-digital-education-for-Sri-Lankan-children/108-331699).
The idea of learner- or student-centric education has been there for long. It comes from the thinking of Paulo Freire, Ivan Illyich and many other educational reformers, globally. Freire, in particular, talks of learner-centred education (he does not use the term), as transformative, transformative of the learner’s and teacher’s thinking: an active and situated learning process that transforms the relations inhering in the situation itself. Lev Vygotsky, the well-known linguist and educator, is a fore runner in promoting collaborative work. But in his thought, collaborative work, which he termed the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) is processual and not goal-oriented, the way teamwork is understood in our pedagogical frameworks; marks, assignments and projects. In his pedagogy, a well-trained teacher, who has substantial knowledge of the subject, is a must. Good text books are important. But I have seen Vygotsky’s idea of ZPD being appropriated to mean teamwork where students sit around and carry out a task already determined for them in quantifying terms. For Vygotsky, the classroom is a transformative, collaborative place.
But in our neo liberal times, learner-centredness has become quick fix to address the ills of a (still existing) hierarchical classroom. What it has actually achieved is reduce teachers to the status of being mere cogs in a machine designed elsewhere: imitative, non-thinking followers of some empty words and guide lines. Over the years, this learner-centred approach has served to destroy teachers’ independence and agency in designing and trying out different pedagogical methods for themselves and their classrooms, make input in the formulation of the curriculum, and create a space for critical thinking in the classroom.
Thus, when Dr. Amarasuriya says that our system should not be over reliant on text books, I have to disagree with her (https://www.newsfirst.lk/2026/01/29/education-reform-to-end-textbook-tyranny ). The issue is not with over reliance, but with the inability to produce well formulated text books. And we are now privy to what this easy dismissal of text books has led us into – the rabbit hole of badly formulated, misinformed content. I quote from the statement of the 94 university teachers to illustrate my point.
“The textbooks for the Grade 6 modules . . . . contain rampant typographical errors and include (some undeclared) AI-generated content, including images that seem distant from the student experience. Some textbooks contain incorrect or misleading information. The Global Studies textbook associates specific facial features, hair colour, and skin colour, with particular countries and regions, and refers to Indigenous peoples in offensive terms long rejected by these communities (e.g. “Pygmies”, “Eskimos”). Nigerians are portrayed as poor/agricultural and with no electricity. The Entrepreneurship and Financial Literacy textbook introduces students to “world famous entrepreneurs”, mostly men, and equates success with business acumen. Such content contradicts the policy’s stated commitment to “values of equity, inclusivity and social justice” (p. 9). Is this the kind of content we want in our textbooks?”
Where structure is concerned, it is astounding to note that the number of subjects has increased from the previous number, while the duration of a single period has considerably reduced. This is markedly noticeable in the fact that only 30 hours are allocated for mathematics and first language at the junior secondary level, per term. The reduced emphasis on social sciences and humanities is another matter of grave concern. We have seen how TV channels and YouTube videos are churning out questionable and unsubstantiated material on the humanities. In my experience, when humanities and social sciences are not properly taught, and not taught by trained teachers, students, who will have no other recourse for related knowledge, will rely on material from controversial and substandard outlets. These will be their only source. So, instruction in history will be increasingly turned over to questionable YouTube channels and other internet sites. Popular media have an enormous influence on the public and shapes thinking, but a well formulated policy in humanities and social science teaching could counter that with researched material and critical thought. Another deplorable feature of the reforms lies in provisions encouraging students to move toward a career path too early in their student life.
The National Institute of Education has received quite a lot of flak in the fall out of the uproar over the controversial Grade 6 module. This is highlighted in a statement, different from the one already mentioned, released by influential members of the academic and activist public, which delivered a sharp critique of the NIE, even while welcoming the reforms (https://ceylontoday.lk/2026/01/16/academics-urge-govt-safeguard-integrity-of-education-reforms). The government itself suspended key players of the NIE in the reform process, following the mishap. The critique of NIE has been more or less uniform in our own discussions with interested members of the university community. It is interesting to note that both statements mentioned here have called for a review of the NIE and the setting up of a mechanism that will guide it in its activities at least in the interim period. The NIE is an educational arm of the state, and it is, ultimately, the responsibility of the government to oversee its function. It has to be equipped with qualified staff, provided with the capacity to initiate consultative mechanisms and involve panels of educators from various different fields and disciplines in policy and curriculum making.
In conclusion, I call upon the government to have courage and patience and to rethink some of the fundamental features of the reform. I reiterate the call for postponing the implementation of the reforms and, in the words of the statement of the 94 university teachers, “holistically review the new curriculum, including at primary level.”
(Sivamohan Sumathy was formerly attached to the University of Peradeniya)
Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.
By Sivamohan Sumathy
Features
Constitutional Council and the President’s Mandate

The Constitutional Council stands out as one of Sri Lanka’s most important governance mechanisms particularly at a time when even long‑established democracies are struggling with the dangers of executive overreach. Sri Lanka’s attempt to balance democratic mandate with independent oversight places it within a small but important group of constitutional arrangements that seek to protect the integrity of key state institutions without paralysing elected governments. Democratic power must be exercised, but it must also be restrained by institutions that command broad confidence. In each case, performance has been uneven, but the underlying principle is shared.
Comparable mechanisms exist in a number of democracies. In the United Kingdom, independent appointments commissions for the judiciary and civil service operate alongside ministerial authority, constraining but not eliminating political discretion. In Canada, parliamentary committees scrutinise appointments to oversight institutions such as the Auditor General, whose independence is regarded as essential to democratic accountability. In India, the collegium system for judicial appointments, in which senior judges of the Supreme Court play the decisive role in recommending appointments, emerged from a similar concern to insulate the judiciary from excessive political influence.
The Constitutional Council in Sri Lanka was developed to ensure that the highest level appointments to the most important institutions of the state would be the best possible under the circumstances. The objective was not to deny the executive its authority, but to ensure that those appointed would be independent, suitably qualified and not politically partisan. The Council is entrusted with oversight of appointments in seven critical areas of governance. These include the judiciary, through appointments to the Supreme Court and Court of Appeal, the independent commissions overseeing elections, public service, police, human rights, bribery and corruption, and the office of the Auditor General.
JVP Advocacy
The most outstanding feature of the Constitutional Council is its composition. Its ten members are drawn from the ranks of the government, the main opposition party, smaller parties and civil society. This plural composition was designed to reflect the diversity of political opinion in Parliament while also bringing in voices that are not directly tied to electoral competition. It reflects a belief that legitimacy in sensitive appointments comes not only from legal authority but also from inclusion and balance.
The idea of the Constitutional Council was strongly promoted around the year 2000, during a period of intense debate about the concentration of power in the executive presidency. Civil society organisations, professional bodies and sections of the legal community championed the position that unchecked executive authority had led to abuse of power and declining public trust. The JVP, which is today the core part of the NPP government, was among the political advocates in making the argument and joined the government of President Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga on this platform.
The first version of the Constitutional Council came into being in 2001 with the 17th Amendment to the Constitution during the presidency of Chandrika Bandaranaike Kumaratunga. The Constitutional Council functioned with varying degrees of effectiveness. There were moments of cooperation and also moments of tension. On several occasions President Kumaratunga disagreed with the views of the Constitutional Council, leading to deadlock and delays in appointments. These experiences revealed both the strengths and weaknesses of the model.
Since its inception in 2001, the Constitutional Council has had its ups and downs. Successive constitutional amendments have alternately weakened and strengthened it. The 18th Amendment significantly reduced its authority, restoring much of the appointment power to the executive. The 19th Amendment reversed this trend and re-established the Council with enhanced powers. The 20th Amendment again curtailed its role, while the 21st Amendment restored a measure of balance. At present, the Constitutional Council operates under the framework of the 21st Amendment, which reflects a renewed commitment to shared decision making in key appointments.
Undermining Confidence
The particular issue that has now come to the fore concerns the appointment of the Auditor General. This is a constitutionally protected position, reflecting the central role played by the Auditor General’s Department in monitoring public spending and safeguarding public resources. Without a credible and fearless audit institution, parliamentary oversight can become superficial and corruption flourishes unchecked. The role of the Auditor General’s Department is especially important in the present circumstances, when rooting out corruption is a stated priority of the government and a central element of the mandate it received from the electorate at the presidential and parliamentary elections held in 2024.
So far, the government has taken hitherto unprecedented actions to investigate past corruption involving former government leaders. These actions have caused considerable discomfort among politicians now in the opposition and out of power. However, a serious lacuna in the government’s anti-corruption arsenal is that the post of Auditor General has been vacant for over six months. No agreement has been reached between the government and the Constitutional Council on the nominations made by the President. On each of the four previous occasions, the nominees of the President have failed to obtain its concurrence.
The President has once again nominated a senior officer of the Auditor General’s Department whose appointment was earlier declined by the Constitutional Council. The key difference on this occasion is that the composition of the Constitutional Council has changed. The three representatives from civil society are new appointees and may take a different view from their predecessors. The person appointed needs to be someone who is not compromised by long years of association with entrenched interests in the public service and politics. The task ahead for the new Auditor General is formidable. What is required is professional competence combined with moral courage and institutional independence.
New Opportunity
By submitting the same nominee to the Constitutional Council, the President is signaling a clear preference and calling it to reconsider its earlier decision in the light of changed circumstances. If the President’s nominee possesses the required professional qualifications, relevant experience, and no substantiated allegations against her, the presumption should lean toward approving the appointment. The Constitutional Council is intended to moderate the President’s authority and not nullify it.
A consensual, collegial decision would be the best outcome. Confrontational postures may yield temporary political advantage, but they harm public institutions and erode trust. The President and the government carry the democratic mandate of the people; this mandate brings both authority and responsibility. The Constitutional Council plays a vital oversight role, but it does not possess an independent democratic mandate of its own and its legitimacy lies in balanced, principled decision making.
Sri Lanka’s experience, like that of many democracies, shows that institutions function best when guided by restraint, mutual respect, and a shared commitment to the public good. The erosion of these values elsewhere in the world demonstrates their importance. At this critical moment, reaching a consensus that respects both the President’s mandate and the Constitutional Council’s oversight role would send a powerful message that constitutional governance in Sri Lanka can work as intended.
by Jehan Perera
Features
Gypsies … flying high
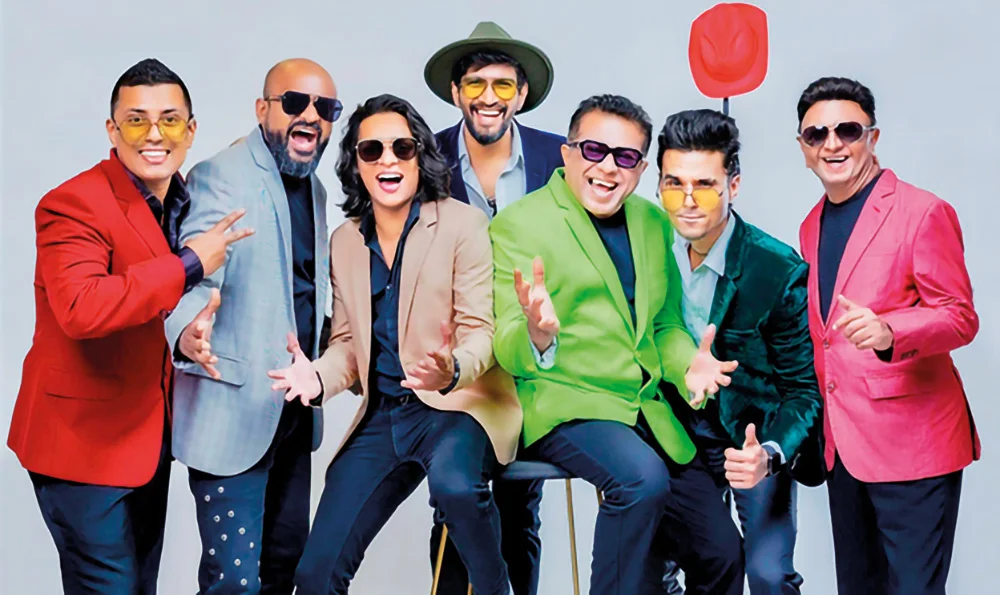

 The scene has certainly changed for the Gypsies and today one could consider them as awesome crowd-pullers, with plenty of foreign tours, making up their itinerary.
The scene has certainly changed for the Gypsies and today one could consider them as awesome crowd-pullers, with plenty of foreign tours, making up their itinerary.
With the demise of Sunil Perera, music lovers believed that the Gypsies would find the going tough in the music scene as he was their star, and, in fact, Sri Lanka’s number one entertainer/singer,
Even his brother Piyal Perera, who is now in charge of the Gypsies, admitted that after Sunil’s death he was in two minds about continuing with the band.
However, the scene started improving for the Gypsies, and then stepped in Shenal Nishshanka, in December 2022, and that was the turning point,
With Shenal in their lineup, Piyal then decided to continue with the Gypsies, but, he added, “I believe I should check out our progress in the scene…one year at a time.”
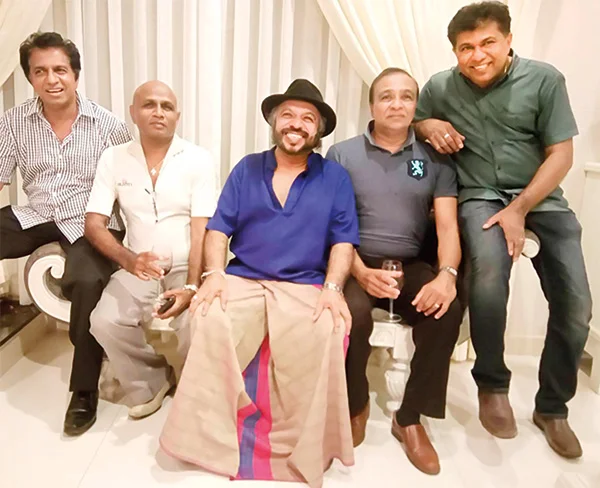

The original Gypsies: The five brothers Lal, Nimal, Sunil, Nihal and Piyal
They had success the following year, 2023, and then decided that they continue in 2024, as well, and more success followed.
The year 2025 opened up with plenty of action for the band, including several foreign assignments, and 2026 has already started on an awesome note, with a tour of Australia and New Zealand, which will keep the Gypsies in that part of the world, from February to March.
Shenal has already turned out to be a great crowd puller, and music lovers in Australia and New Zealand can look forward to some top class entertainment from both Shenal and Piyal.
Piyal, who was not much in the spotlight when Sunil was in the scene, is now very much upfront, supporting Shenal, and they do an awesome job on stage … keeping the audience entertained.
Shenal is, in fact, a rocker, who plays the guitar, and is extremely creative on stage with his baila.
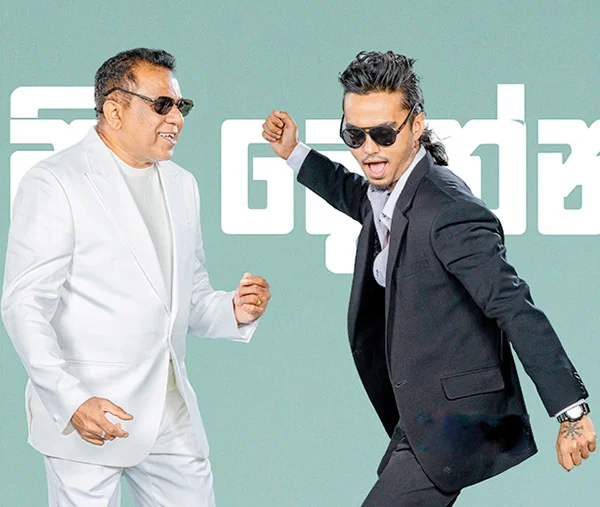

‘Api Denna’ Piyal and Shenal
Piyal and Shenal also move into action as a duo ‘Api Denna’ and have even done their duo scene abroad.
Piyal mentioned that the Gypsies will feature a female vocalist during their tour of New Zealand.
“With Monique Wille’s departure from the band, we now operate without a female vocalist, but if a female vocalist is required for certain events, we get a solo female singer involved, as a guest artiste. She does her own thing and we back her, and New Zealand requested for a female vocalist and Dilmi will be doing the needful for us,” said Piyal.
According to Piyal, he originally had plans to end the Gypsies in the year 2027 but with the demand for the Gypsies at a very high level now those plans may not work out, he says.
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoSri Lanka, the Stars,and statesmen
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoClimate risks, poverty, and recovery financing in focus at CEPA policy panel
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoHayleys Mobility ushering in a new era of premium sustainable mobility
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoAdvice Lab unveils new 13,000+ sqft office, marking major expansion in financial services BPO to Australia
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoArpico NextGen Mattress gains recognition for innovation
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoAltair issues over 100+ title deeds post ownership change
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoSri Lanka opens first country pavilion at London exhibition
-

 Editorial3 days ago
Editorial3 days agoGovt. provoking TUs













