Business
Vietnamese billionaire Truong My Lan sentenced to death for $44bn fraud
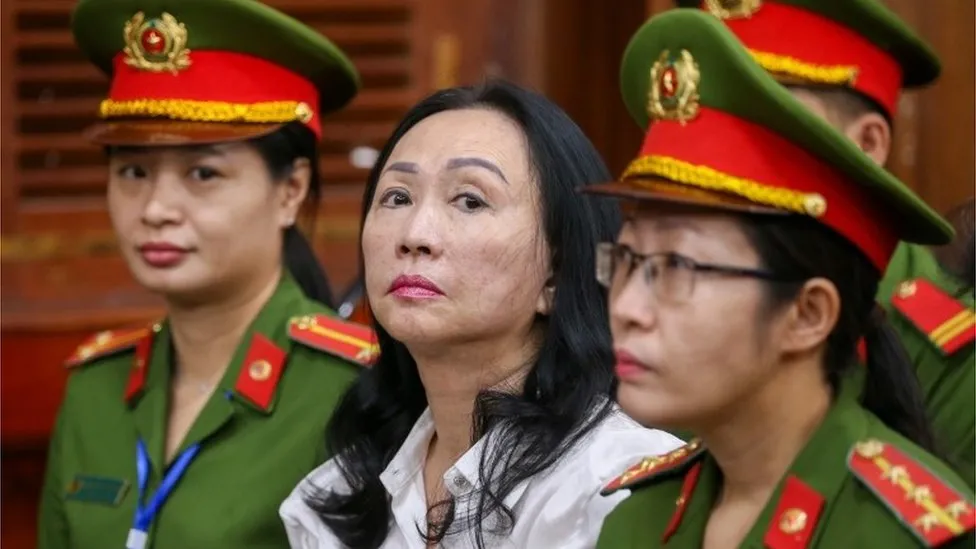

It was the most spectacular trial ever held in Vietnam, befitting one of the greatest bank frauds the world has ever seen.
Behind the stately yellow portico of the colonial-era courthouse in Ho Chi Minh City, a 67-year-old Vietnamese property developer was sentenced to death on Thursday for looting one of the country’s largest banks over a period of 11 years.
It’s a rare verdict – she is one of very few women in Vietnam to be sentenced to death for a white collar crime.
The decision is a reflection of the dizzying scale of the fraud. Truong My Lan was convicted of taking out $44bn (£35bn) in loans from the Saigon Commercial Bank. The verdict requires her to return $27bn, a sum prosecutors said may never be recovered. Some believe the death penalty is the court’s way of putting pressure on her to help locate the missing billions.
The habitually secretive communist authorities were uncharacteristically forthright about this case, going into minute detail for the media. They said 2,700 people were summoned to testify, while 10 state prosecutors and around 200 lawyers were involved.
The evidence was in 104 boxes weighing a total of six tonnes. Eighty-five defendants were tried with Truong My Lan, who denied the charges.
“There has never been a show trial like this, I think, in the communist era,” says David Brown, a retired US state department official with long experience in Vietnam. “There has certainly been nothing on this scale.”
The trial was the most dramatic chapter so far in the “Blazing Furnaces” anti-corruption campaign led by the Communist Party Secretary-General, Nguyen Phu Trong.
A conservative ideologue steeped in Marxist theory, Nguyen Phu Trong believes that popular anger over untamed corruption poses an existential threat to the Communist Party’s monopoly on power. He began the campaign in earnest in 2016 after out-manoeuvring the then pro-business prime minister to retain the top job in the party.
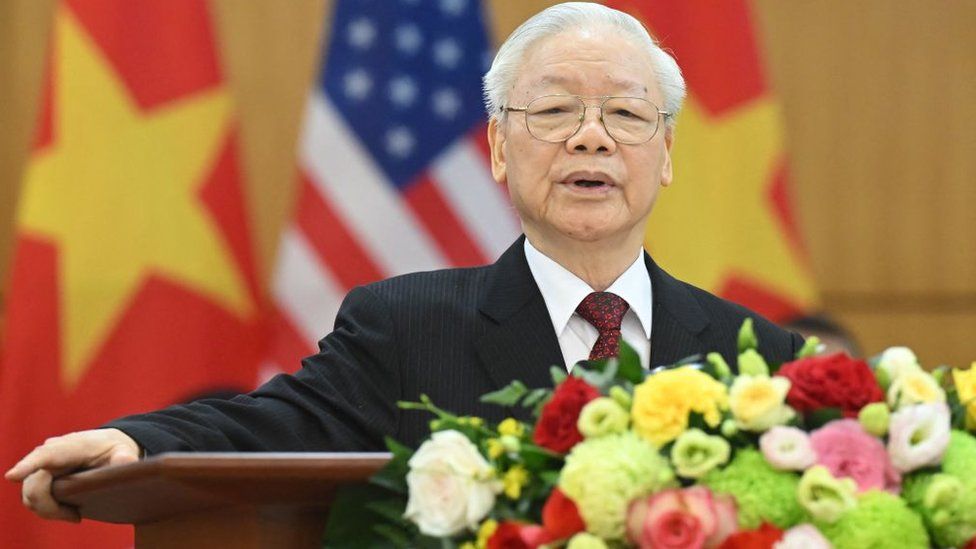

Communist Party General Secretary Nguyen Phu Trong is leading an anti-corruption campaign (BBC)
The campaign has seen two presidents and two deputy prime ministers forced to resign, and hundreds of officials disciplined or jailed. Now one of the country’s richest women has joined their ranks.
Truong My Lan comes from a Sino-Vietnamese family in Ho Chi Minh City, formerly Saigon. It has long been the commercial engine of the Vietnamese economy, dating well back to its days as the anti-communist capital of South Vietnam, with a large, ethnic Chinese community.
She started as a market stall vendor, selling cosmetics with her mother, but began buying land and property after the Communist Party ushered in a period of economic reform, known as Doi Moi, in 1986. By the 1990s, she owned a large portfolio of hotels and restaurants.
Although Vietnam is best known outside the country for its fast-growing manufacturing sector, as an alternative supply chain to China, most wealthy Vietnamese made their money developing and speculating in property.
All land is officially state-owned. Getting access to it often relies on personal relationships with state officials. Corruption escalated as the economy grew, and became endemic.
By 2011, Truong My Lan was a well-known business figure in Ho Chi Minh City, and she was allowed to arrange the merger of three smaller, cash-strapped banks into a larger entity: Saigon Commercial Bank.
Vietnamese law prohibits any individual from holding more than 5% of the shares in any bank. But prosecutors say that through hundreds of shell companies and people acting as her proxies, Truong My Lan actually owned more than 90% of Saigon Commercial.
They accused her of using that power to appoint her own people as managers, and then ordering them to approve hundreds of loans to the network of shell companies she controlled.
The amounts taken out are staggering. Her loans made up 93% of all the bank’s lending.
According to prosecutors, over a period of three years from February 2019, she ordered her driver to withdraw 108 trillion Vietnamese dong, more than $4bn (£2.3bn) in cash from the bank, and store it in her basement.
That much cash, even if all of it was in Vietnam’s largest denomination banknotes, would weigh two tonnes.
She was also accused of bribing generously to ensure her loans were never scrutinised. One of those who was tried used to be a chief inspector at the central bank, who was accused of accepting a $5m bribe.
The mass of officially sanctioned publicity about the case channeled public anger over corruption against Truong My Lan, whose haggard, unmade-up appearance in court was in stark contrast to the glamorous publicity photos people had seen of her in the past.
But questions are also being asked about why she was able to keep on with the alleged fraud for so long.

The trial took place in Ho Chi Minh City, where Saigon Commercial Bank was based (BBC)
“I am puzzled,” says Le Hong Hiep who runs the Vietnam Studies Programme at the ISEAS – Yusof Ishak Institute in Singapore. “Because it wasn’t a secret. It was well known in the market that Truong My Lan and her Van Thinh Phat group were using SCB as their own piggy bank to fund the mass acquisition of real estate in the most prime locations. “It was obvious that she had to get the money from somewhere. But then it is such a common practice. SCB is not the only bank that is used like this. So perhaps the government lost sight because there are so many similar cases in the market.”
David Brown believes she was protected by powerful figures who have dominated business and politics in Ho Chi Minh City for decades. And he sees a bigger factor in play in the way this trial is being run: a bid to reassert the authority of the Communist Party over the free-wheeling business culture of the south. “What Nguyen Phu Trong and his allies in the party are trying to do is to regain control of Saigon, or at least stop it from slipping away.
“Up until 2016 the party in Hanoi pretty much let this Sino-Vietnamese mafia run the place. They would make all the right noises that local communist leaders are supposed to make, but at the same time they were milking the city for a substantial cut of the money that was being made down there.”
At 79 years old, party chief Nguyen Phu Trong is in shaky health, and will almost certainly have to retire at the next Communist Party Congress in 2026, when new leaders will be chosen.
He has been one of the longest-serving and most consequential secretary-generals, restoring the authority of the party’s conservative wing to a level not seen since the reforms of the 1980s. He clearly does not want to risk permitting enough openness to undermine the party’s hold on political power.
But he is trapped in a contradiction. Under his leadership the party has set an ambitious goal of reaching rich country status by 2045, with a technology and knowledge-based economy. This is what is driving the ever-closer partnership with the United States.
Yet faster growth in Vietnam almost inevitably means more corruption. Fight corruption too much, and you risk extinguishing a lot of economic activity. Already there are complaints that bureaucracy has slowed down, as officials shy away from decisions which might implicate them in a corruption case.
“That’s the paradox,” says Le Hong Hiep. “Their growth model has been reliant on corrupt practices for so long. Corruption has been the grease that that kept the machinery working. If they stop the grease, things may not work any more.”
(BBC)
Business
ADB approves support to strengthen power sector reforms in Sri Lanka

The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has approved a $100 million policy-based loan to further support Sri Lanka in strengthening its power sector. This financing builds on earlier initiatives to establish a more stable and financially sustainable power sector.
This second subprogram of ADB’s Power Sector Reforms and Financial Sustainability Program will accelerate the unbundling of the Ceylon Electricity Board (CEB) into independent successor companies for generation, transmission, system operation, and distribution, as mandated by the Electricity Act of 2024 and its 2025 amendment. The phased approach ensures a structured transition, ensuring progress in reform actions and prioritizing financial sustainability.
“Sri Lanka has made important progress in stabilizing its economy and strengthening its fiscal position. A well-functioning power sector is vital for the country’s continued recovery and sustainable growth,” said ADB Country Director for Sri Lanka Takafumi Kadono. “ADB is committed to supporting Sri Lanka’s long-term development and advancing key reforms in the power sector. This initiative will enhance power sector governance, foster private sector participation, and accelerate renewable energy development to drive sustainable recovery, resilience, and inclusive growth.”
To improve financial sustainability, the program will help implement cost-reflective tariffs and a comprehensive debt restructuring plan for the CEB. It will support the new independent successor companies in transparent allocation of existing debts. This will continue to strengthen their financial viability, enhance creditworthiness, and enable these companies to operate on a more sustainable footing.
The program also aims to strengthen renewable energy development and private sector participation by enhancing transparency and supporting power sector entities that are financially sustainable. It will enable competitive procurement for large-scale renewable energy projects and identified priority generation schemes, while upholding strong environmental standards.
Promoting gender equality and social inclusion is integral to the program. Energy sector agencies have implemented annual women’s leadership programs, adopted inclusive policies, and launched feedback mechanisms to ensure equitable participation of female consumers and entrepreneurs. The program includes targeted support for vulnerable groups, such as maintaining lifeline tariffs and implementing measures to soften the impact of tariff adjustments and sector reforms.
ADB will provide an additional $2.5 million technical assistance grant from its Technical Assistance Special Fund to support program implementation, build the capacity of successor companies, and help develop their business plans and power system development plans.
Business
Union Assurance becomes first insurer to earn the YouTube Silver Play Button

Union Assurance, Sri Lanka’s longest-standing private Life Insurer, has achieved a milestone in its digitalisation journey by being awarded the YouTube Silver Play Button, recognising the Company for surpassing 100,000 subscribers on its official channel. This achievement marks a first in Sri Lanka’s Insurance industry, across both Life and General Insurance, and underscores Union Assurance’s pioneering role in digital engagement.
This accomplishment reflects the Company’s unwavering commitment to making Life Insurance accessible, simplified, and engaging for all Sri Lankans. Through innovative content strategies, Union Assurance has successfully transformed complex Insurance concepts into relatable, informative, and inspiring narratives that empower individuals to protect what matters most; health, wealth, family, and future.
Receiving the Silver Play Button is more than a symbolic accolade; it is a testament to the strength and credibility of Union Assurance’s digital presence. In an era where trust and transparency define brand loyalty, this recognition validates the company’s ability to create content that resonates deeply with a growing audience. It enhances the brand’s authority, reinforces its visibility across digital platforms, and further solidifies Union Assurance as a leader in customer engagement.
Celebrating this achievement, Mahen Gunarathna, the Chief Marketing Officer at Union Assurance stated: “This milestone is a testament to the trust and engagement of our audience and reflects our dedication to innovation, transparency, and customer-centric communication.
Business
LOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth

LOLC Finance PLC, the largest non-banking financial institution in Sri Lanka, brings to light the significant role of its Factoring Business Unit in providing indispensable financial solutions to businesses across the country. With a robust network of over 200 branches, LOLC Finance Factoring offers distinctive support to enterprises, ranging from small-scale entrepreneurs to corporate giants.
In light of the recent economic challenges, LOLC Finance Factoring emerged as a lifeline for most businesses, ensuring continuous liquidity to navigate through turbulent times. By facilitating seamless transactions through online platforms and expediting payments, the company played a pivotal role in sustaining essential services, including supermarkets and pharmaceuticals.
Deepamalie Abhaywardane, Head of Factoring at LOLC Finance PLC, emphasized the increasing relevance of factoring in today’s economy. “As economic conditions become more stringent, factoring emerges as the most sought-after financial product for businesses across various sectors. It offers a win-win solution by providing upfront cash up to 85% of the credit sale to suppliers while allowing end-users/buyers better settlement period.”
One of the standout features of LOLC Finance Factoring is its hassle-free application process. Unlike traditional bank loans that require collateral, LOLC Factoring extends credit facilities without such obligations. Furthermore, LOLC Finance Factoring relieves business entities of the burden of receivable management and debt collection. Through nominal service fees, businesses can outsource these tasks, allowing them to focus on core operations while ensuring efficient cash flow management.
For businesses seeking Shariah-compliant factoring solutions, LOLC Al-Falaah’s Wakalah Future-Cash Today offers an efficient and participatory financing model that meets both financial needs and ethical principles. Understanding the diverse challenges faced by businesses, LOLC Finance Factoring deliver tailored solutions that enhance cash flow, reduce credit risk, and support sustainable growth. Working together with LOLC Al-Falaah ensures access to a transparent, well-structured receivable management solution strengthened by the credibility and trust of Sri Lanka’s largest NBFI, LOLC Finance.
The clientele of LOLC Finance Factoring spans into various industries, including manufacturing, trading, transportation, healthcare, textiles, plantations, and other services, all contributing significantly to Sri Lanka’s economic growth. By empowering businesses with accessible and convenient working capital solutions, LOLC Finance’s Factoring arm plays a vital role in fostering economic development and prosperity of the country.
In the upcoming quarter, LOLC Finance Factoring remains committed to delivering innovative financial solutions tailored to meet the evolving needs of businesses. As Sri Lanka’s economic landscape continues to develop, LOLC Finance Factoring stands ready to support enterprises on their journey towards growth and success.
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoWeather disasters: Sri Lanka flooded by policy blunders, weak enforcement and environmental crime – Climate Expert
-
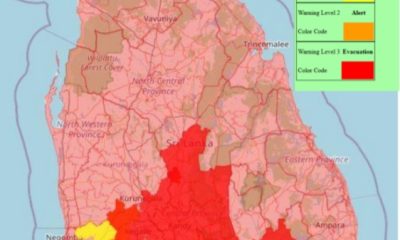
 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoLevel I landslide RED warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Colombo, Gampaha, Kalutara, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurnegala, Natale, Monaragala, Nuwara Eliya and Ratnapura
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoINS VIKRANT deploys helicopters for disaster relief operations
-
News3 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-
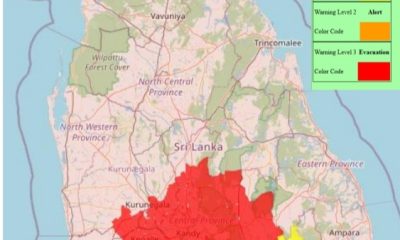
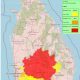 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoLevel III landslide early warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya
-
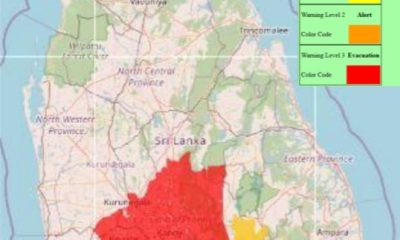
 News2 days ago
News2 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoDitwah: An unusual cyclone
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoUpdated Payment Instructions for Disaster Relief Contributions

























