Features
75 Years – What have they done?

It is a paradise misplaced
by Capt. Elmos Jayawardena
elmojay@gmail.com
Our island was called Lanka in pre-King Vijaya times. Valmiki’s immortal Ramayanaya had King Ravana ruling the land from the city of Lankapura. That was almost 4,000 years ago. The Arab traders termed it Jaziratul-Yaqut, island of rubies. Some called it Serendib, some Ceilan, from which the Portuguese picked Ceilao and the European mapmakers coined Ceylon. Many were the names from the many that came. Bar none, everyone agreed and noted in their chronicles that this
Island was indeed the complete Paradise.
We never created it. Let’s be honest about that part. We simply inherited. The gods from their celestial dome, in their infinite kindness, gifted this Paradise to us, the beautiful island of Lanka, to the people of Sri Lanka.
The privilege of being born to such a serendipitous place can only be expressed if one could take away the corruption that has besieged us all since independence. We need to look through the veils of racial and religious disharmony that obscure the overwhelming beauty that lies beyond. The purity of the land still remains, vastly unspoiled. The occupants of Paradise, still smile, despite the battering they had received from the time they were reborn after the colonials left. Mother Lanka dawdles, whilst her sons and daughters drowse in ignorance, an ominous prelude to the torrential disasters that loom in the near horizon.
Times are sad and the question is paramount in any mind that carries an iota of sanity. “75 years, WHAT HAVE THEY DONE?” The sum total of the misfortunes that the majority of the proletariat suffer is directly related to the bad governance of the country. It is not the vegetable seller that is responsible nor the fisherman or the cobbler. It is neither the schoolteacher nor the clerical battalion. None of these Lilliputian shareholders of Paradise are responsible for the doom that is staring at us in gloom. Who is directly responsible for this catastrophe? It must be the gods, not those on Mount Olympus but the ones from Diyawanna Oya. Everyone who sits in those 225 thrones, whether they were proposers or opposers or the ones who raised their hands in agreement or those who sinned in silence abstaining from their sworn duty. They are all responsible for raping this land.
The ‘Misplacing of Paradise’ is directly related to Diyawanna Oya. It is from there the fountains of corruption gush out from every orifice to drown the trampled denizens of Paradise.
And now they want to celebrate 75 years of independent ruination?
Galle Face gave birth to the Aragalaya. It was not born to racial or religious parents, not to political surrogate fathers or international stepmothers. Hired ‘andabera karayo’ (tom tom beaters) and unethical scribes may attempt to blacken the purity of the protest that raised its head when living in Paradise became unbearable. But such camouflage will not eradicate the deep-felt anger that has soaked the ordinary man, woman and child who walked to Galle Face to give life to the Aragalaya.
Their participation in the protest had nothing to do with politics. There may have been a thief or two in the jury, but the majority came because they could not breathe any more. The suffocation of the common man and woman who were down to their knees is what made them gather at the Galle Face Green.
The mighty may assume the Aragalaya has fizzled out. Many were arrested and some were jailed. The political pack was re-shuffled and puppeteers looking for those willing to dance gifted high pedestals. Nothing changed at Diyawanna Oya. It is still the same stage, only some actors are different. Mother Lanka weeps at the perpetual tragedy. The once bubbling Aragalaya breathes softly like a slow-burning fuse. It is the idea that remains, and ideas do not die, nor can they be eradicated.
When the sun goes down and the pavements become bedchambers for the super poor who pray for the rains to hold till morning.
Little children hear the music of the ‘Choon Paan’ tuk tuk and wonder when they can afford a ‘kimbula bunis’ again.
Schools re-open, book lists are out but where is the money to buy?
Hospitals have no drugs; power cuts are a daily torment, and they talk about extending the dark hours.
Tourists trickle in while Sri Lankans of all races and religions are queuing in hoards to jump ship and vanish to wherever they can.
These are no fairy tales of my redundant imagination. They are the stories of Paradise. The day-to-day events play sad and silent along with the cacophony of achievements and flash-pan plans to celebrate 75 years of independence. Don’t tell me the suffering is isolated; oh no, not by a long shot.
They are the unheard and the ignored of the displaced congregation of Paradise. The ‘boast of heraldry’ is loud and clear, so is the ‘pomp of power’ announcing to the world and beyond the inflated paths of progress. The air is filled with milk and honey stories and rainbow visions for the morrow. But isn’t there a big question mark? Isn’t there some serious filtering needed to seek and give room to the truth?
I am not talking of March local elections or who is joining hands with whom to ruin the country more. Politics do not interest me. I’m like the kids that run after the ‘Choon Paan’ tuk tuk with empty pockets.
Hope is there but with hardly any reality. Just totally confused between right and wrong and where lies the light or is it only a long dark tunnel? I’m writing of the core expectation, the very basics that humans search for. We need peace and honest governance, the pursuit of happiness to which we are all entitled, like the simple ‘Kimbula Bunis’ the kids crave for. This is what Paradise should be made of, which unfortunately is missing. Yes, our Paradise is mired in a total political mess at present devoid of any reasonable and practical answers.
Everyone is trying to go abroad. Why do all these people leave Mother Lanka? Something must have gone wrong in the system. The exodus only began after we were reborn as an independent nation. Ludowyke and Van Sanden left in the sixties, Somasundaram and Gunesekara in the eighties the entire ‘jimband’ started migrating at the turn of the century. Hence, the blame is not with the colonials and their international shackles. It is ours and ours alone, lying firmly in the Pontius hands of the custodians who were chosen to charter our future. Isn’t it crystal clear today that the political leadership we voted for and sent to Diyawanna Oya has failed miserably in their delivery?
Let’s get back to the theme of the hour, the forthcoming independence celebration. I wonder what we are celebrating after 75 years of ruling by the sons and daughters of mother paradise. Is it the egg that is 75 rupees or the half kilo of dhal selling at 300 or the loaf of bread at 180? Maybe the 170 for the Sunlight soap has to be celebrated and the red onions at 720 a kilo. The coconut is over 100 rupees and a mere 400 gram packet of Rathi milk powder is 1,200 rupees.
No wonder the children are almost starving, and the parents roll onto a reed-mat after a hard day’s work on empty stomachs.
Yet we are celebrating independence to tell the world how great our Paradise is. Never mind the begging bowl we carry internationally; on Feb. 4 morning the marching multitudes and the rolling armour must be on display. The cost of the aerial circus will be astounding. There will be at least four sets of different aeroplanes flying in formation over the heads of gods and demigods sitting under VVIP shade at the Galle Face green which is the scene of celebration.
You have to practice flying these air-displays. From a week before Feb. 4 you will hear their engines roar from Kalutara to Katunayake. The jets shrieking, training for the fly-pass, will shatter the clear blue skies and disturb every student writing the ‘A’ level exams in that area. The F-7 fighter-jets in this aero-ballet burn 40 liters of fuel a minute at low levels. And we the minions of Paradise loiter in snaking queues down below with our QR codes to get 20 liters of fuel for one week. If I call it a mockery, that will be gross flattery. Need to mint a new word to describe this folly.
Do I have to say any more? We the majority may be struggling for the crumbs that fall off the table, but the show must go on. After all it is independence, and it must be celebrated.
There are some solid silver lines too in our 75-year-old dark cloud. The free education is a wonderful achievement and so is the free health care scheme. Yes, at present the hospitals may struggle with the lack of drugs, but the system is there to help and heal any patient. The credit goes to the powers that were in a bygone era. There are other consolations too, one cannot be totally paranoid. Factory jobs are there for those without a trade. Stitching for Marks and Spencer and their likes help thousands to keep their home fires burning.
Some no-skills Paradisians pawn their souls to go abroad as domestics and for minor employment. They are the local Dick Whittingtons charging into the unknown, exploited at every toll gate. They slave in alien third-class status to send pitifully earned dollars to their loved ones to survive in Paradise. Wasn’t it their brothers and fathers who fought and died in the 30-year war to save their motherland?
Seventy-five years have gone by from the day of independence. The blameless blame, the nameless suffer and the shameless go on, rough-shodding their way to erode and annihilate Paradise. No need to further elaborate, the reasons are obvious. Some things are best left unsaid. Let me be the coward and let discretion become the better part of my limited attempts at journalism.
Call me a fool if it pleases you and I will accept it. But let me trickle some sanity to your thoughts. Just to kindle an interest. Totally non-political. I cannot and do not separate the villain from the venerated. The line is too thin, and the facts are wildly scattered. The truth certainly is in masquerade.
The Lankan Paradise is not lost, at least, not yet. It is certainly misplaced. That much can be clearly seen, lest one be blind. What happens in the end to things that are misplaced? They never get found and as time goes by, they will go permanently missing.
Ours is a Paradise misplaced. Let us all valiantly search for answers, it is not too late. Let us collectively find ourselves and our land, before it vanishes beyond the limits and becomes a Paradise Lost.
Features
Ramadan 2026: Fasting hours around the world
The Muslim holy month of Ramadan is set to begin on February 18 or 19, depending on the sighting of the crescent moon.
During the month, which lasts 29 or 30 days, Muslims observing the fast will refrain from eating and drinking from dawn to dusk, typically for a period of 12 to 15 hours, depending on their location.
Muslims believe Ramadan is the month when the first verses of the Quran were revealed to the Prophet Muhammad more than 1,400 years ago.
The fast entails abstinence from eating, drinking, smoking and sexual relations during daylight hours to achieve greater “taqwa”, or consciousness of God.
Why does Ramadan start on different dates every year?
Ramadan begins 10 to 12 days earlier each year. This is because the Islamic calendar is based on the lunar Hijri calendar, with months that are 29 or 30 days long.
For nearly 90 percent of the world’s population living in the Northern Hemisphere, the number of fasting hours will be a bit shorter this year and will continue to decrease until 2031, when Ramadan will encompass the winter solstice, the shortest day of the year.
For fasting Muslims living south of the equator, the number of fasting hours will be longer than last year.
Because the lunar year is shorter than the solar year by 11 days, Ramadan will be observed twice in the year 2030 – first beginning on January 5 and then starting on December 26.

Fasting hours around the world
The number of daylight hours varies across the world.
Since it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, this Ramadan, people living there will have the shortest fasts, lasting about 12 to 13 hours on the first day, with the duration increasing throughout the month.
People in southern countries like Chile, New Zealand, and South Africa will have the longest fasts, lasting about 14 to 15 hours on the first day. However, the number of fasting hours will decrease throughout the month.

[Aljazeera]
Features
The education crossroads:Liberating Sri Lankan classroom and moving ahead

Education reforms have triggered a national debate, and it is time to shift our focus from the mantra of memorising facts to mastering the art of thinking as an educational tool for the children of our land: the glorious future of Sri Lanka.
The 2026 National Education Reform Agenda is an ambitious attempt to transform a century-old colonial relic of rote-learning into a modern, competency-based system. Yet for all that, as the headlines oscillate between the “smooth rollout” of Grade 01 reforms and the “suspension of Grade 06 modules,” due to various mishaps, a deeper question remains: Do we truly and clearly understand how a human being learns?
Education is ever so often mistaken for the volume of facts a student can carry in his or her head until the day of an examination. In Sri Lanka the “Scholarship Exam” (Grade 05) and the O-Level/A-Level hurdles have created a culture where the brain is treated as a computer hard drive that stores data, rather than a superbly competent processor of information.
However, neuroscience and global success stories clearly project a different perspective. To reform our schools, we must first understand the journey of the human mind, from the first breath of infancy to the complex thresholds of adulthood.
The Architecture of the Early Mind: Infancy to Age 05
The journey begins not with a textbook, but with, in tennis jargon, a “serve and return” interaction. When a little infant babbles, and a parent responds with a smile or a word or a sentence, neural connections are forged at a rate of over one million per second. This is the foundation of cognitive architecture, the basis of learning. The baby learns that the parent is responsive to his or her antics and it is stored in his or her brain.
In Scandinavian countries like Finland and Norway, globally recognised and appreciated for their fantastic educational facilities, formal schooling does not even begin until age seven. Instead, the early years are dedicated to play-based learning. One might ask why? It is because neuroscience has clearly shown that play is the “work” of the child. Through play, children develop executive functions, responsiveness, impulse control, working memory, and mental flexibility.
In Sri Lanka, we often rush like the blazes on earth to put a pencil in the hand of a three-year-old, and then firmly demanding the child writes the alphabet. Contrast this with the United Kingdom’s “Birth to 5 Matters” framework. That initiative prioritises “self-regulation”, the ability to manage emotions and focus. A child who can regulate their emotions is a child who can eventually solve a quadratic equation. However, a child who is forced to memorise before they can play, often develops “school burnout” even before they hit puberty.
The Primary Years: Discovery vs. Dictation
As children move into the primary years (ages 06 to 12), the brain’s “neuroplasticity” is at its peak. Neuroplasticity refers to the malleability of the human brain. It is the brain’s ability to physically rewire its neural pathways in response to new information or the environment. This is the window where the “how” of learning becomes a lot more important than the “what” that the child should learn.
Singapore is often ranked number one in the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) scores. It is a worldwide study conducted by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) that measures the scholastic performance of 15-year-old students in mathematics, science, and reading. It is considered to be the gold standard for measuring “education” because it does not test whether students can remember facts. Instead, it tests whether they can apply what they have learned to solve real-world problems; a truism that perfectly aligns with the argument that memorisation is not true or even valuable education. Singapore has moved away from its old reputation for “pressure-cooker” education. Their current mantra is “Teach Less, Learn More.” They have reduced the syllabus to give teachers room to facilitate inquiry. They use the “Concrete-Pictorial-Abstract” approach to mathematics, ensuring children understand the logic of numbers before they are asked to memorise formulae.
In Japan, the primary curriculum emphasises Moral Education (dotoku) and Special Activities (tokkatsu). Children learn to clean their own classrooms and serve lunch. This is not just about performing routine chores; it really is as far as you can get away from it. It is about learning collaboration and social responsibility. The Japanese are wise enough to understand that even an absolutely brilliant scientist who cannot work in a team is a liability to society.
In Sri Lanka, the current debate over the 2026 reforms centres on the “ABCDE” framework: Attendance, Belongingness, Cleanliness, Discipline, and English. While these are noble goals, we must be careful not to turn “Belongingness” into just another checkbox. True learning in the primary years happens when a child feels safe enough to ask “Why?” without the fear of being told “Because it is in the syllabus” or, in extreme cases, “It is not your job to question it.” Those who perpetrate such remarks need to have their heads examined, because in the developed world, the word “Why” is considered to be a very powerful expression, as it demands answers that involve human reasoning.
The Adolescent Brain: The Search for Meaning
Between ages 12 and 18, the brain undergoes a massive refashioning or “pruning” process. The prefrontal cortex of the human brain, the seat of reasoning, is still under construction. This is why teenagers are often impulsive but also capable of profound idealism. However, with prudent and gentle guiding, the very same prefrontal cortex can be stimulated to reach much higher levels of reasoning.
The USA and UK models, despite their flaws, have pioneered “Project-Based Learning” (PBL). Instead of sitting for a history lecture, students might be tasked with creating a documentary or debating a mock trial. This forces them to use 21st-century skills, like critical thinking, communication, and digital literacy. For example, memorising the date of the Battle of Danture is a low-level cognitive task. Google can do it in 0.02 seconds or less. However, analysing why the battle was fought, and its impact on modern Sri Lankan identity, is a high-level cognitive task. The Battle of Danture in 1594 is one of the most significant military victories in Sri Lankan history. It was a decisive clash between the forces of the Kingdom of Kandy, led by King Vimaladharmasuriya 1, and the Portuguese Empire, led by Captain-General Pedro Lopes de Sousa. It proved that a smaller but highly motivated force with a deep understanding of its environment could defeat a globally dominant superpower. It ensured that the Kingdom of Kandy remained independent for another 221 years, until 1815. Without this victory, Sri Lanka might have become a full Portuguese colony much earlier. Children who are guided to appreciate the underlying reasons for the victory will remember it and appreciate it forever. Education must move from the “What” to the “So What about it?“
The Great Fallacy: Why Memorisation is Not Education
The most dangerous myth in Sri Lankan education is that a “good memory” equals a “good education.” A good memory that remembers information is a good thing. However, it is vital to come to terms with the concept that understanding allows children to link concepts, reason, and solve problems. Memorisation alone just results in superficial learning that does not last.
Neuroscience shows that when we learn through rote recall, the information is stored in “silos.” It stays put in a store but cannot be applied to new contexts. However, when we learn through understanding, we build a web of associations, an omnipotent ability to apply it to many a variegated circumstance.
Interestingly, a hybrid approach exists in some countries. In East Asian systems, as found in South Korea and China, “repetitive practice” is often used, not for mindless rote, but to achieve “fluency.” Just as a pianist practices scales to eventually play a concerto with soul sounds incorporated into it, a student might practice basic arithmetic to free up “working memory” for complex physics. The key is that the repetition must lead to a “deep” approach, not a superficial or “surface” one.
Some Suggestions for Sri Lanka’s Reform Initiatives
The “hullabaloo” in Sri Lanka regarding the 2026 reforms is, in many ways, a healthy sign. It shows that the country cares. That is a very good thing. However, the critics have valid points.
* The Digital Divide: Moving towards “digital integration” is progressive, but if the burden of buying digital tablets and computers falls on parents in rural villages, we are only deepening the inequality and iniquity gap. It is our responsibility to ensure that no child is left behind, especially because of poverty. Who knows? That child might turn out to be the greatest scientist of all time.
* Teacher Empowerment: You cannot have “learner-centred education” without “independent-thinking teachers.” If our teachers are treated as “cogs in a machine” following rigid manuals from the National Institute of Education (NIE), the students will never learn to think for themselves. We need to train teachers to be the stars of guidance. Mistakes do not require punishments; they simply require gentle corrections.
* Breadth vs. Depth: The current reform’s tendency to increase the number of “essential subjects”, even up to 15 in some modules, ever so clearly risks overwhelming the cognitive and neural capacities of students. The result would be an “academic burnout.” We should follow the Scandinavian model of depth over breadth: mastering a few things deeply is much better than skimming the surface of many.
The Road to Adulthood
By the time a young adult reaches 21, his or her brain is almost fully formed. The goal of the previous 20 years should not have been to fill a “vessel” with facts, but to “kindle a fire” of curiosity.
The most successful adults in the 2026 global economy or science are not those who can recite the periodic table from memory. They are those who possess grit, persistence, adaptability, reasoning, and empathy. These are “soft skills” that are actually the hardest to teach. More importantly, they are the ones that cannot be tested in a three-hour hall examination with a pen and paper.
A personal addendum
As a Consultant Paediatrician with over half a century of experience treating children, including kids struggling with physical ailments as well as those enduring mental health crises in many areas of our Motherland, I have seen the invisible scars of our education system. My work has often been the unintended ‘landing pad’ for students broken by the relentless stresses of rote-heavy curricula and the rigid, unforgiving and even violently exhibited expectations of teachers. We are currently operating a system that prioritises the ‘average’ while failing the individual. This is a catastrophe that needs to be addressed.
In addition, and most critically, we lack a formal mechanism to identify and nurture our “intellectually gifted” children. Unlike Singapore’s dedicated Gifted Education Programme (GEP), which identifies and provides specialised care for high-potential learners from a very young age, our system leaves these bright minds to wither in the boredom of standard classrooms or, worse, treats their brilliance as a behavioural problem to be suppressed. Please believe me, we do have equivalent numbers of gifted child intellectuals as any other nation on Mother Earth. They need to be found and carefully nurtured, even with kid gloves at times.
All these concerns really break my heart as I am a humble product of a fantastic free education system that nurtured me all those years ago. This Motherland of mine gave me everything that I have today, and I have never forgotten that. It is the main reason why I have elected to remain and work in this country, despite many opportunities offered to me from many other realms. I decided to write this piece in a supposedly valiant effort to anticipate that saner counsel would prevail finally, and all the children of tomorrow will be provided with the very same facilities that were afforded to me, right throughout my career. Ever so sadly, the current system falls ever so far from it.
Conclusion: A Fervent Call to Action
If we want Sri Lanka to thrive, we must stop asking our children, “What did you learn today?” and start asking, “What did you learn to question today?“
Education reform is not just about changing textbooks or introducing modules. It is, very definitely, about changing our national mindset. We must learn to equally value the artist as much as the doctor, and the critical thinker as much as the top scorer in exams. Let us look to the world, to the play of the Finns, the discipline of the Japanese, and the inquiry of the British, and learn from them. But, and this is a BIG BUT…, let us build a system that is uniquely Sri Lankan. We need a system that makes absolutely sure that our children enjoy learning. We must ensure that it is one where every child, without leaving even one of them behind, from the cradle to the graduation cap, is seen not as a memory bank, but as a mind waiting to be set free.
by Dr B. J. C. Perera
MBBS(Cey), DCH(Cey), DCH(Eng), MD(Paed), MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin), FRCP(Lond), FRCPCH(UK), FSLCPaed, FCCP, Hony. FRCPCH(UK), Hony. FCGP(SL)
Specialist Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Fellow, Postgraduate Institute of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka.
Joint Editor, Sri Lanka
Journal of Child Health]
Section Editor, Ceylon Medical Journal
Features
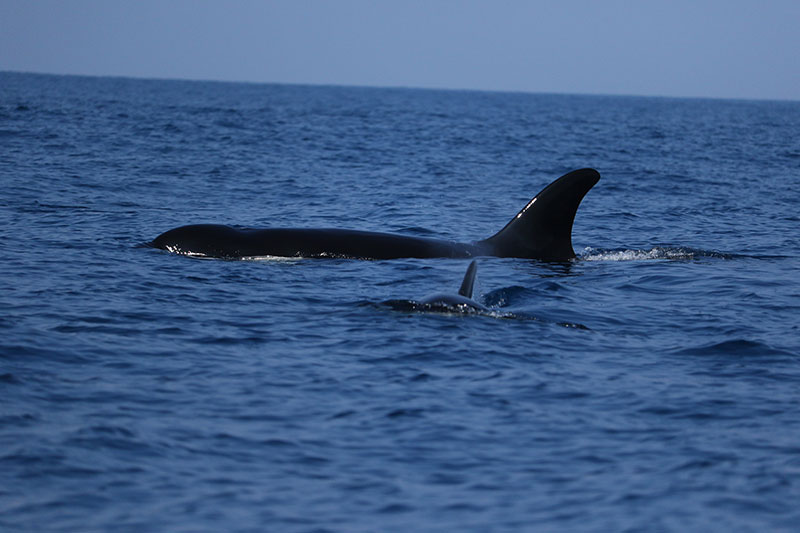
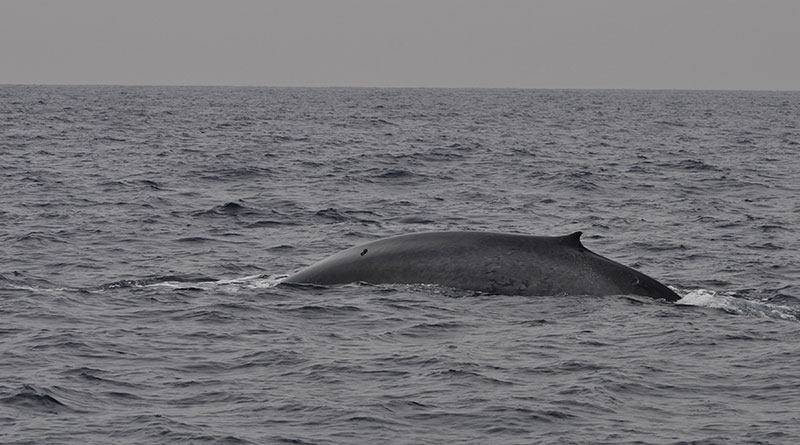
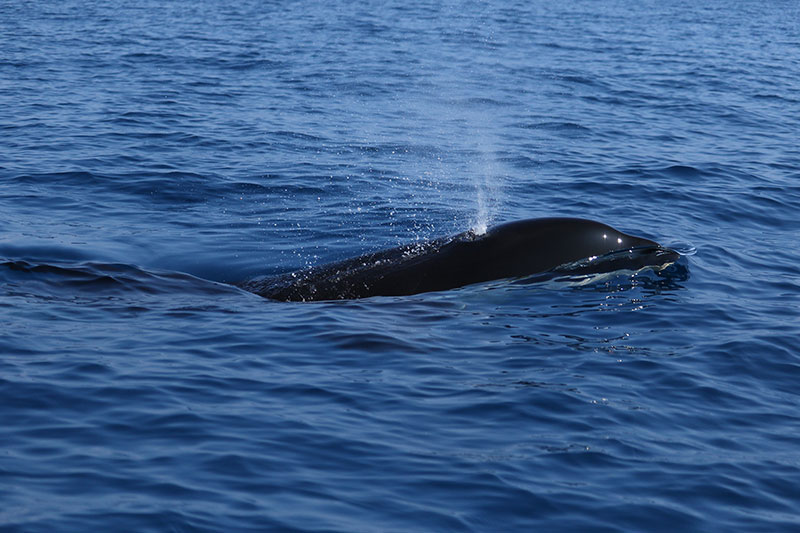
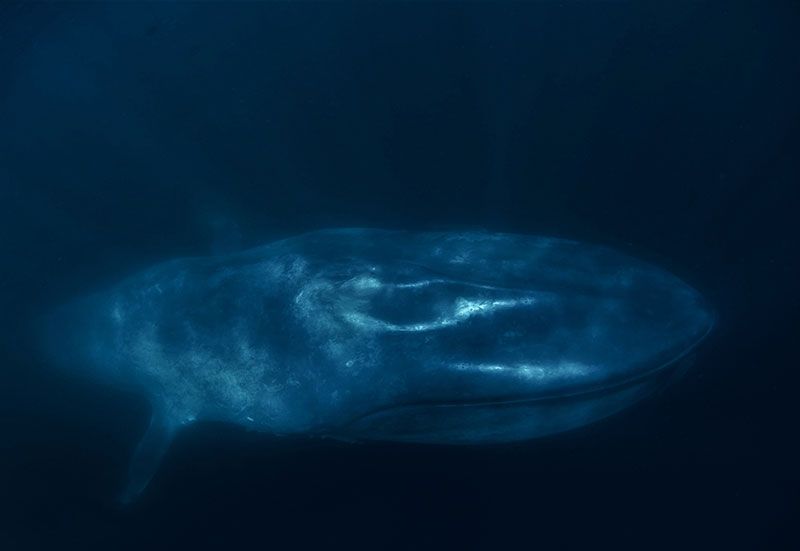
Giants in our backyard: Why Sri Lanka’s Blue Whales matter to the world

Standing on the southern tip of the island at Dondra Head, where the Indian Ocean stretches endlessly in every direction, it is difficult to imagine that beneath those restless blue waves lies one of the greatest wildlife spectacles on Earth.
Yet, according to Dr. Ranil Nanayakkara, Sri Lanka today is not just another tropical island with pretty beaches – it is one of the best places in the world to see blue whales, the largest animals ever to have lived on this planet.
“The waters around Sri Lanka are particularly good for blue whales due to a unique combination of geography and oceanographic conditions,” Dr. Nanayakkara told The Island. “We have a reliable and rich food source, and most importantly, a unique, year-round resident population.”
In a world where blue whales usually migrate thousands of kilometres between polar feeding grounds and tropical breeding areas, Sri Lanka offers something extraordinary – a non-migratory population of pygmy blue whales (Balaenoptera musculus indica) that stay around the island throughout the year. Instead of travelling to Antarctica, these giants simply shift their feeding grounds around the island, moving between the south and east coasts with the monsoons.
The secret lies beneath the surface. Seasonal monsoonal currents trigger upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich water, which fuels massive blooms of phytoplankton. This, in turn, supports dense swarms of Sergestidae shrimps – tiny creatures that form the primary diet of Sri Lanka’s blue whales.
- “Engineers of the ocean system”
“Blue whales require dense aggregations of these shrimps to meet their massive energy needs,” Dr. Nanayakkara explained. “And the waters around Dondra Head and Trincomalee provide exactly that.”
Adding to this natural advantage is Sri Lanka’s narrow continental shelf. The seabed drops sharply into deep oceanic canyons just a few kilometres from the shore. This allows whales to feed in deep waters while remaining close enough to land to be observed from places like Mirissa and Trincomalee – a rare phenomenon anywhere in the world.
Dr. Nanayakkara’s journey into marine research began not in a laboratory, but in front of a television screen. As a child, he was captivated by the documentary Whales Weep Not by James R. Donaldson III – the first visual documentation of sperm and blue whales in Sri Lankan waters.
“That documentary planted the seed,” he recalled. “But what truly set my path was my first encounter with a sperm whale off Trincomalee. Seeing that animal surface just metres away was humbling. It made me realise that despite decades of conflict on land, Sri Lanka harbours globally significant marine treasures.”
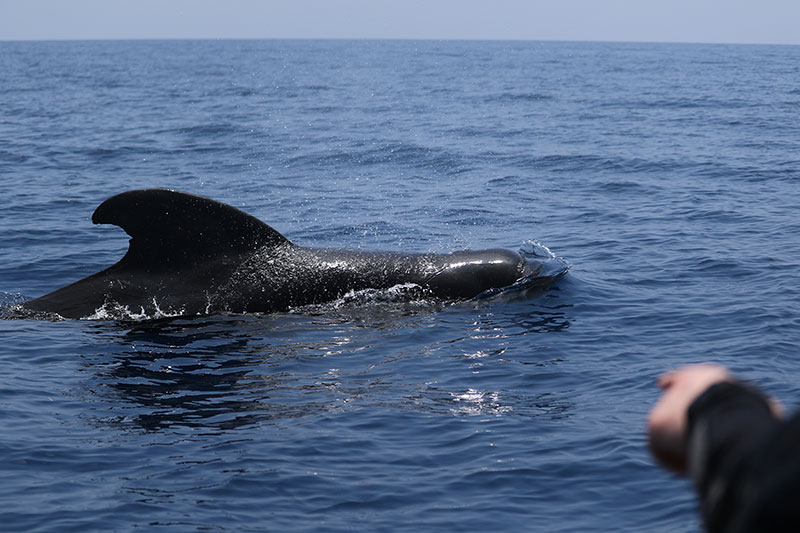
Since then, his work has focused on cetaceans – from blue whales and sperm whales to tropical killer whales and elusive beaked whales. What continues to inspire him is both the scientific mystery and the human connection.
“These blue whales do not follow typical migration patterns. Their life cycles, communication and adaptability are still not fully understood,” he said. “And at the same time, seeing the awe in people’s eyes during whale watching trips reminds me why this work matters.”
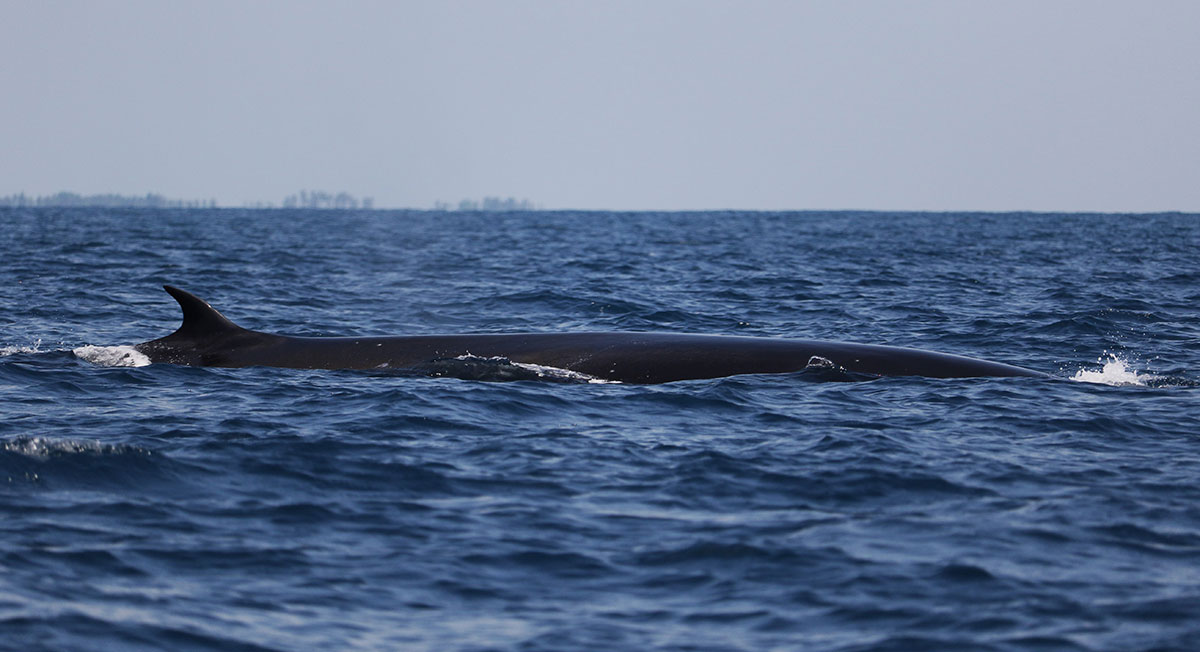
Whale watching has become one of Sri Lanka’s fastest-growing tourism industries. On the south coast alone, thousands of tourists head out to sea every year in search of a glimpse of the giants. But Dr. Nanayakkara warned that without strict regulation, this boom could become a curse.
“We already have good guidelines – vessels must stay at least 100 metres away and maintain slow speeds,” he noted. “The problem is enforcement.”
Speaking to The Island, he stressed that Sri Lanka stands at a critical crossroads. “We can either become a global model for responsible ocean stewardship, or we can allow short-term economic interests to erode one of the most extraordinary marine ecosystems on the planet. The choice we make today will determine whether these giants continue to swim in our waters tomorrow.”
Beyond tourism, a far more dangerous threat looms over Sri Lanka’s whales – commercial shipping traffic. The main east-west shipping lanes pass directly through key blue whale habitats off the southern coast.
“The science is very clear,” Dr. Nanayakkara told The Island. “If we move the shipping lanes just 15 nautical miles south, we can reduce the risk of collisions by up to 95 percent.”
Such a move, however, requires political will and international cooperation through bodies like the International Maritime Organization and the International Whaling Commission.
“Ships travelling faster than 14 knots are far more likely to cause fatal injuries,” he added. “Reducing speeds to 10 knots in high-risk areas can cut fatal strikes by up to 90 percent. This is not guesswork – it is solid science.”
To most people, whales are simply majestic animals. But in ecological terms, they are far more than that – they are engineers of the ocean system itself.
Through a process known as the “whale pump”, whales bring nutrients from deep waters to the surface through their faeces, fertilising phytoplankton. These microscopic plants absorb vast amounts of carbon dioxide, making whales indirect allies in the fight against climate change.
“When whales die and sink, they take all that carbon with them to the deep sea,” Dr. Nanayakkara said. “They literally lock carbon away for centuries.”
Even in death, whales create life. “Whale falls” – carcasses on the ocean floor – support unique deep-sea communities for decades.
“Protecting whales is not just about saving a species,” he said. “It is about protecting the ocean’s ability to function as a life-support system for the planet.”
For Dr. Nanayakkara, whales are not abstract data points – they are individuals with personalities and histories.
One of his most memorable encounters was with a female sperm whale nicknamed “Jaw”, missing part of her lower jaw.
“She surfaced right beside our boat, her massive eye level with mine,” he recalled. “In that moment, the line between observer and observed blurred. It was a reminder that these are sentient beings, not just research subjects.”
Another was with a tropical killer whale matriarch called “Notch”, who surfaced with her calf after a hunt.
“It felt like she was showing her offspring to us,” he said softly. “There was pride in her movement. It was extraordinary.”
Looking ahead, Dr. Nanayakkara envisions Sri Lanka as a global leader in a sustainable blue economy – where conservation and development go hand in hand.
“The ultimate goal is shared stewardship,” he told The Island. “When fishermen see healthy reefs as future income, and tour operators see protected whales as their greatest asset, conservation becomes everyone’s business.”
In the end, Sri Lanka’s greatest natural inheritance may not be its forests or mountains, but the silent giants gliding through its surrounding seas.
“Our ocean health is our greatest asset,” Dr. Nanayakkara said in conclusion. “If we protect it wisely, these whales will not just survive – they will define Sri Lanka’s place in the world.”
By Ifham Nizam
-

 Life style2 days ago
Life style2 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Midweek Review6 days ago
Midweek Review6 days agoA question of national pride
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoWill computers ever be intelligent?
-

 Business17 hours ago
Business17 hours agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:



















