Business
3 reasons why international support for Sri Lanka is forthcoming slowly: policy advisor explains

By Sanath Nanayakkare
Dr. Ganeshan Wignaraja, a non-resident senior fellow at the Institute of South Asia Studies at the National University of Singapore recently gave three reasons why monetary support is not forthcoming from many countries that can extend support to Sri Lanka.
He gave these reasons at a recent webinar titled’ Confronting the Current Foreign Exchange Crisis in Sri Lanka –Lessons from Global Experience’, hosted by the Central Bank of Sri Lanka.
” It could be due to several reasons. First, something like 60% of the poorest countries in the world is under debt distress although they have not quite defaulted.”
“Second, we are at a recession risk globally and the countries we might want support from, are at some sort of risk. So they are naturally concerned about providing assistance to others as they are preoccupied and looking inward. Multilateralism is also under stress in this context.”
“The third reason is; there is an argument made in the eyes of some countries that Sri Lanka’s debt default is seen as a home-grown crisis due to poor macroeconomic management and governance. We hear a lot about why other countries’ taxpayer dollars should be used to support a failed economy like Sri Lanka’s. This is a query thrown at me by people from other countries,” he said.
The following are some select remarks made by him during the webinar.
“Sri Lanka would need US$ 20-25 billion over the next three years from the IMF, multilateral agencies and other friendly countries to put its economy on a decent footing and get growth going, “And remember, that’s about a quarter of Sri Lanka’s GDP. The country needs that kind of money if it really is going to go forward.”
“Along with the assistance from the IMF, bridging finance is also needed urgently from India, China and Western countries not only to provide basic needs for the people such as fuel, food and medicine but also to help stabilise the economy. In this context, Sri Lanka needs to do four things.”
“First, we need to show that we are serious about fixing our economy and convince these countries that we are worthy to gain their confidence. It is important that the IMF programme is implemented in a transparent and credible manner. Sri Lanka has had 16 IMF programmes. I believe that something like half of them was not either properly implemented or perhaps abandoned. I think this time around we will be under the microscope, so we need to implement the programme properly.”
“Second, we need to build a consensus on this IMF programme.There are still people out there that go around saying,” Forget the IMF; we can eat ‘Bathalakola’. That’s something which is not going to cut the mustard for Sri Lanka in the current circumstances. I think that sort of people have to be called out and we have to publicize the implementation of the IMF programme.”
“Third; we have to ensure that any foreign aid we get is fairly distributed to all Sri Lankans in all provinces equitably. It will also have to be ensured that there will be crackdown on any corruption in allocating this aid. We will have to be ‘on the money’; therefore, anti-corruption measures will need to be very strong.”
“Fourth; we need to be serious on our foreign policy without dillydallying. We have to pursue a very strict non-aligned economic and foreign policy. If Sri Lanka does these four, it will have a fair sporting chance to get a decent score on the board and turn Sri Lanka around with trade, investment and foreign assistance,” Dr. Wignaraja said.
Business
A nation reframed through food: Sri Lanka’s historic National Geographic debut

By Ifham Nizam
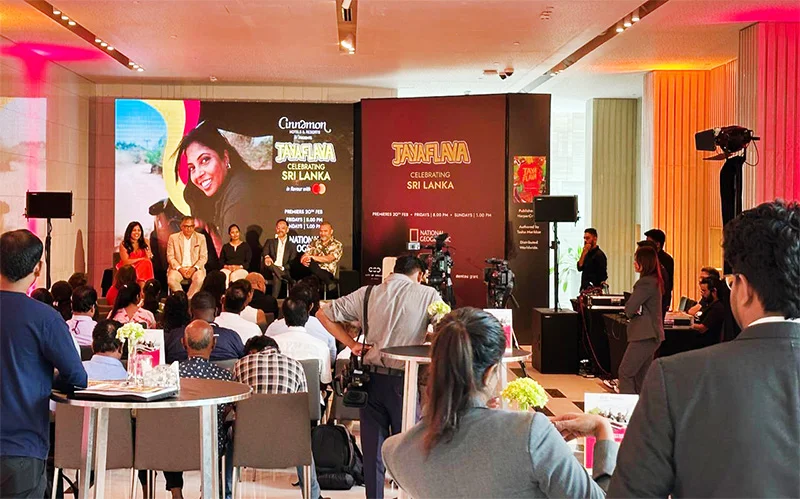
On a bright Colombo morning, beneath the polished lines of Cinnamon Life at City of Dreams Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka quietly redrew the contours of its global image.
This was not merely a programme launch. It was a recalibration.
For the first time, a Sri Lankan-made food and travel series will premiere across South Asia on National Geographic — a platform synonymous with global storytelling. In a region where culinary diplomacy has long been monopolised by larger neighbours, Sri Lanka has chosen its entry point carefully: flavour.
Jayaflava: Celebrating Sri Lanka is a six-part travel and food series hosted by Tasha Marikkar, airing on National Geographic South Asia. It premieres on Friday the 20th at 8.00 p.m., with a repeat on Sunday at 1.00 p.m. The series will broadcast across India, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal and the Maldives — positioning Sri Lanka’s culinary identity before one of the most dynamic regional audiences in the world.
The series is the brainchild of Marikkar — author, food storyteller and an unapologetic champion of Sri Lankan cuisine. What began as a cookbook evolved — through persistence, private backing and creative risk — into a broadcast production that now carries Sri Lanka’s culinary narrative beyond its shores.
“This was never just about recipes,” Marikkar told the audience. “It was about representing Sri Lanka as it truly is — multi-ethnic, modern, chaotic, generous and absolutely obsessed with flavour.”
Her long-time collaborator Afdhel Aziz framed it in strategic terms.
“Sri Lanka has always had depth and brilliance,” Aziz said. “What it hasn’t always had is ownership of its narrative. When you tell your story authentically on a platform like National Geographic, you’re not just entertaining — you’re reframing perception.”
Perception, in tourism economics, is currency.
Bakmee Perera Vice President – Communications Planning and Media Strategy at Dentsu Grant Media, described the partnership with National Geographic India — part of the Jio Star Network and Disney International — as a structural milestone.
“This marks Sri Lanka’s first long-term content partnership agreement with an international network,” she said. “It extends beyond linear television into digital platforms. It is a significant step in global content affiliation.”
For Sri Lanka’s hospitality industry, the timing is strategic. Indian arrivals have rebounded strongly, surpassing pre-2018 levels, and industry leaders see culinary storytelling as a natural extension of destination branding.
Kamal Munasinghe, Senior Vice President – Colombo Hotels at Cinnamon Hotels & Resorts and General Manager of Cinnamon Life, put it plainly.
“We have always spoken about sun, sea and sand,” he said. “But we have not spoken enough about our food. Other destinations have built tourism identities around cuisine. Sri Lanka has not done enough in that space.”
He recalled stopping on the roadside en route to Ella for oil roti served with mushroom curry — a humble meal prepared by a woman supporting her family.
“That is the story we are bringing to the world,” he added. “There is culture, resilience and love in that plate.”
Cinnamon Hotels & Resorts, the title sponsor, features four of its properties in the series, including Cinnamon Grand Colombo, Cinnamon Wild Yala and Cinnamon Bentota Beach — the latter a tropical modernist icon designed by Geoffrey Bawa.
Bawa once reframed Sri Lanka architecturally, merging landscape with structure in ways that drew global admiration. In many respects, Jayaflava attempts a similar reframing — merging food, people and place into a narrative that feels both intimate and expansive.
The series moves through midnight kottu stalls, animated kitchen debates, artists’ studios and coastal bars. It captures contradiction — humour alongside hardship, ambition alongside nostalgia. It is not polished tourism propaganda, but textured storytelling.
Sri Lanka has often been presented to the world as either idyllic escape or troubled headline. Rarely as complex, contemporary and confident. By choosing food — the most universal of connectors — as its narrative vehicle, the country sidesteps cliché and leans into authenticity.
As the morning launch concluded, one message lingered: this is not simply a television debut. It is soft power in motion.
A nation, reframed — one dish at a time.
Business
Bourse buoyed by IMF chief’s positive observations

CSE grading was brisk and investor sentiment rose to a great extent when
the International Monetary Fund’s Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva, who is on a visit to Sri Lanka, made positive remarks on the progress of the local economy.
She made these comments after meeting President Anura Kumara Dissanayake and other relevant officials.
Consequent to these developments both indices moved upwards. The All Share Price Index went up by 37.02 points, while the S and P SL20 rose by 47.12 points.
Turnover stood at Rs 5.66 billion with nine crossings. Those crossings were reported in ACL Cables, where 1.5 million shares crossed to the tune of Rs 154.6 million; its shares traded at Rs 103,CW Macky two million shares crossed for Rs 82 million; its shares sold at Rs 41, Dipped Products 1 million shares crossed for Rs 61 million; its shares traded at Rs 58.
Colombo Dockyard 350,000 shares crossed to the tune of Rs 56.3 million; its shares traded at Rs 151, HNB 100,000 shares crossed for Rs 45.5 million; its shares traded at Rs 455,Royal Ceramics 500,000 crossed for Rs 25.5 million; its shares sold at Rs 51 and JKH one million shares crossed to the tune of Rs 22.4 million; its shares sold at Rs 22.40.
In the retail market top seven companies that mainly contributed to the turnover were; Softlogic Capital Rs 511 million (51.2 million shares traded), ACL Cables Rs 439 million (4.2 million shares traded), Asia Siyaka Rs 307 million (19.5 million shares traded), Sampath Bank Rs 251 million (1.6 million shares traded), HNB Rs 231 million (507,000 shares traded), Softlogic Finance Rs 205 million (31.4 million shares traded) and HNB Finance Rs 171 million (19 million traded). During the day 289.2 million share volumes changed hands in 42524 transactions.
It is said that the banking and manufacturing sectors performed well. Sampath Bank, for instance, was notable. Financial sector too performed well; especially Softlogic Finance.
Yesterday the rupee was quoted at Rs 309.42/44 to the US dollar in the spot market from Rs 309.40/50 the previous day, dealers said, while bond yields were broadly steady.
A bond maturing on 15.10.2029 was quoted at 9.40/45 percent.
A bond maturing on 01.03.2030 was quoted flat at 9.50/53 percent.
A bond maturing on 15.03.2031 was quoted at 9.70/75 percent, from 9.68/72 percent.
A bond maturing on 01.10.2032 was quoted at 10.10/42 percent, up from 10.10/13 percent.
A bond maturing on 01.06.2033 was quoted at 10.38/43 percent, up from 10.35/40 percent.
A bond maturing on 15.06.2036 was quoted at 10.60/65 percent.
An auction of Rs. 60,000 million Treasury bills was going on.
By Hiran H Senewiratne
Business
A photograph of a Jaffna youth becomes a global symbol for Sri Lanka’s stalled reconciliation
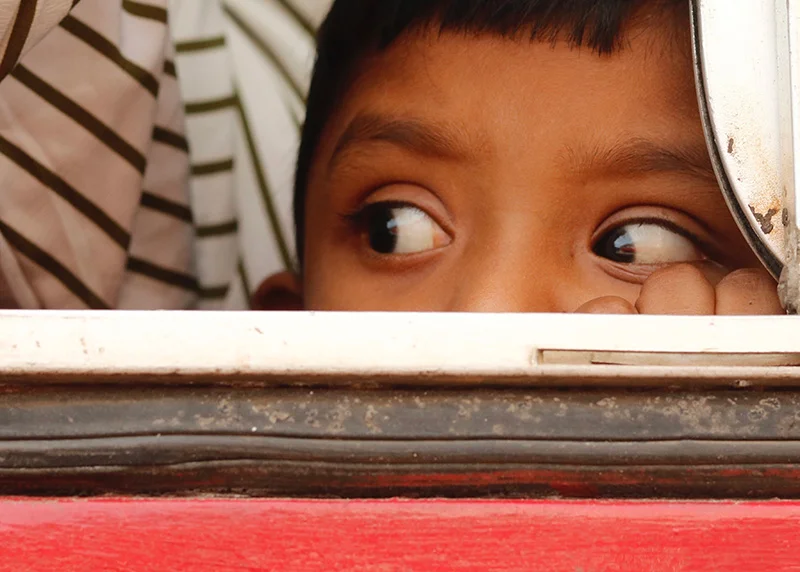

In the world of travel photography, some images do more than showcase a destination; they act as a silent mirror to a nation’s unresolved history. When British photographer Mark Julian Edwards’ portrait, ‘The Boy on the Bus,’ claimed the People’s Choice Award at the 2026 Travel Photographer of the Year (TPOTY) awards, it did more than celebrate technical brilliance. It signaled that the global community is still fixated on the scars of a region where the promise of a post-2009 peace has yet to be fully realised.
While the current NPP government often celebrates a ‘reunited’ Sri Lanka under President Anura Kumara Dissanayake, this award-winning shot turns the gaze toward Jaffna – a city that remains the emotional and political epicenter of the North-South divide. Captured through a rusting bus window, the boy’s expression – described as ‘fragile yet incredibly resilient’ – speaks to the persistent chasm between the North and the South that has remained unbridged nearly two decades after the war’s end.
Whatever the rhetoric from political platforms regarding the end of distrust, the international resonance of this image suggests that the world recognises a different reality. The capture of a northern commute is not merely a travel detail; it is a reminder of a landscape where the path to a predictable future is still viewed through a prism of distrust and uncertainty.
The significance of this win lies in its source: the public vote. Out of 20,000 entries, thousands of people from 160 countries chose this specific face. This global endorsement serves as a poignant reminder that while the local reconciliation process may be stalled in policy and paperwork, the human element of the conflict continues to haunt the international imagination.
The boy represents a generation born after the guns fell silent, yet his quiet, searching eyes reflect the weight of a reconciliation process that many feel has been more about infrastructure than true social healing. In the North, where the dust of history is still settling, such images strip away the veneer of normalcy to reveal the underlying scars that politicians often ignore.
The success of Edwards’ work comes at a time when the Sri Lankan Tourism Bureau and Jetwing Hotels are looking to nurture the next generation of local storytellers. However, the global acclaim for ‘The Boy on the Bus’ suggests that the most vital stories to be told are not the ones that look like postcards, but the ones that acknowledge the sensitivity and professional excellence required to document a people still waiting for a ta truly inclusive future.
As this image makes its way into international galleries and media outlets like the BBC, it stands as a testament to a hard truth: a photograph can win international accolades but the bridging of the political and social chasm remains Sri Lanka’s true, unfinished business.
The 2026 Travel Photographer of the Year winners were showcased and celebrated in Sharjah – UAE, Birmingham – UK and Rome – Italy. This year’s programme includes a special mentorship and winners’ trip to Sri Lanka, hosted by the Sri Lanka Tourist Board and Jetwing Hotels.
By Sanath Nanayakkare
-

 Life style5 days ago
Life style5 days agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoMinistry of Brands to launch Sri Lanka’s first off-price retail destination
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoMonks’ march, in America and Sri Lanka
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoThailand to recruit 10,000 Lankans under new labour pact
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoMassive Sangha confab to address alleged injustices against monks
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoIMF MD here