Features
Paris and some of its habitues and JRJ, Cyril Mathew and their storm troops
Excerpted from volume ii of the Sarath Amunugama autobiography

(Continued from last week)
As a member of the Sri Lankan delegation I began to attend the meetings of the Communications sector of UNESCO. International meetings of this group were held in Paris while regional meetings were held in Bangkok and New Delhi. As mentioned earlier the Paris meetings were the main driver of the global debate. Special attention was focused on the African countries which were lacking in both manpower and technical resources.
Increasingly what was highlighted was the imbalance in news flows between the developed and developing countries. The answer was to transfer technology and training opportunities to the developing countries through funding from multilateral and bilateral sources, basically coming from the industrialized countries. From this stance came the call for setting up a new institution in UNESCO for the promotion of Communication Development. It was to be called the International Programme for the Development of Communication [IPDC] with its own Governing Council, Director and Secretariat.
Our annual visits to Paris for UNESCO meetings which usually lasted about a week with a weekend in between was a good opportunity to savour the life of that beautiful city which has been called the ‘City of Light’. We were lodged in a hotel close to UNESCO in Place de Fontenot’ in Paris 16, which was the elite district or arondissement. It was close to the Eiffel Tower and Ecole Militaire which is the major military school for the elite officers of the French Army.
A stroll after meetings took us to the most ‘posh’ areas of the city including the Invalides – the Military Museum -mostly devoted to Napoleon. We could also walk in the numerous immaculately maintained parks close to the tower and the Invalides. A longer walk would take us to the famous `Pont de Paris’ or Paris bridges which spanned the river Seine and linked the right Bank with Left Bank [Rive Gauche].
One day while the meeting was going on we received news of the death of Jean Paul Satre and his funeral the following day at the cemetery at Montparnasse which was not too far from Place de Fontenot’. That afternoon I excused myself and with Navaz of our tourist office in Paris joined the thousands of mourners who assembled near the entrance to the cemetery to bid farewell to France’s best known intellectual.
Many who flocked to the cemetery were the young people of the sixties, now close to middle age, who had been inurrectionists against the De Gaulle regime. They came to pay homage to an older man who had taken their side and marched with them in the Quartier Latin. Though Satre was a thorn in his flesh, De Gaulle, in a typical Gallic gesture, had ordered the police not to touch the philosopher-hero. He remembered that Satre had encouraged ‘the resistance’ when France was under Hitler’s jackboot and Frenchmen looked to De Gaulle as their savior.
We had to push through the teeming crowds to follow the black hearse carrying Satre’s remains to his final resting place. At the last minute there was a hush and a famous film star Simone Signoret, came to place a bowl of roses on the coffin which was then slowly lowered into the open grave. Whenever I visit Paris I go to the Montparnasse cemetery to pay my respects and also rekindle my memories of a city I knew so well a long time ago.
At that time the Sri Lanka Embassy in Rue D’Astorg was our home away from home. The Ambassador was Vernon Mendis who was a very senior Foreign Service officer who had managed the administrative side of the Non-Aligned meeting in Colombo. But as soon as he reached retirement age he was hired by UNESCO to be their representative in Cairo. The Director-General of UNESCO M’Bow was well known for his patronage of Ambassadors who were loyal to him.
Mendis was succeeded by Balasubramanium who too was a senior in the service. But Bala too was at the end of his career and was ill with a terminal disease. Most of the relations with the French public was handled by Manu Ginige who was a fluent French speaker and a Francophile. Manu who became my very close friend was a legendary character among the Sri Lankans abroad. A graduate of Peradeniya he followed up on his fascination with international politics by joining Air Ceylon as their representative in Paris.
An ardent Trotskyite in Peradeniya he had a wide circle of leftist friends. Among them was Ratnasiri Wickremanayake who was a law student in London at that time. Ratnasiri had cut short his stay in the UK because he was summoned to contest the Horana seat in the 1960 General Election. His elder brother Munidasa, who had been Philip Gunawardene’s MEP candidate, had been killed a few months before the election. Ratnasiri won the seat, crossed over to the SLFP and later became the Prime Minister.
He never went back to his studies and Europe but maintained his links with his London comrades. These friends formed a trio – Ratnasiri, Willa Wickremasinghe and Manu Ginige. After leaving Air Ceylon Manu joined UTA, the French airline that flew to Colombo, on the invitation of Minister Leslie Goonewardene of the LSSP who was the Cabinet Minister of Transport and Aviation.
Through Air Ceylon and UTA Manu became indispensable to any one with connections to Colombo and Paris because air travel was their lifeline. After the fall of the Bandaranaike regime in 1977 he left UTA and freelanced for a while and even spent some time in Cologne with his German wife and daughter. He came back to Paris as Hameed’s interpreter and confidante.
When our delegation comprising Esmond, Arthur Clarke and myself went to Paris for UNESCO meetings he was our liaison with the secretariat as he was fluent in French. He became indispensable to Esmond and with Hameed’s backing became a crucial member of our Embassy having lived in Paris for over 20 years. Chandrika Bandaranaike and her friends who had moved with him closely in Paris were angry with him for serving the UNP regime but Manu was a professional officer who gave his services to the country by working in the Embassy.
He maintained the friendships of his younger days and remained a close friend of Ratnasiri. Only a few close friends of Ratnasiri hailed him by his pet name ‘Danu’ and Manu was one of them. Very few know that when Dr. N.M. Perera visited Europe for the last time, after he was diagnosed with a cancer, he wished to make a sentimental visit to Paris with Dr. Dora Fonseka who was known to be his girlfriend.
It was Manu who arranged this visit and made his apartment available to them. To the last he retained his radical views. When I stayed in his apartment in Paris I requested him to arrange meetings with the Trotskyite leaders who were our icons in our University days. We met Michel Pablo. It was a secretive meeting which I will describe in the next volume of my autobiography.
Manu and I followed the cortege of Trotskyite ideologue Ernst Mandel in the Pere Lachaise cemetery in North Paris together with a dwindling gathering of old men of the Fourth International who soldiered on. Distancing themselves from these superannuated ideologues a new group of young Trotskyites emerged in the Universities and workplaces and one charismatic young leader even contested the Presidential election though he was only an ‘also ran’.
Violence
JRJ claimed to be a Gandhian who believed in ‘Non-Violence’. But as Clifford Geertz has written in his essay on Gandhi, ‘non-violence’ can only succeed if the Satyagrahi has the potential of unleashing violence as an alternative. Without that fear the opponent does not take the challenger seriously. Thus nonviolence becomes a part of the power game. As Geertz writes, “The argument that a sacred pledge to abstain from the use of force can have moral reality only with respect to people who have a genuine possibility of effectively using force is surely correct”.
JRJ was a Gandhian who always kept his ‘Powder dry’. Once in power he ceased to be a Satyagrahi. One highly disconcerting fact about the JRJ administration was its condoning of violence. When his plans met with organized resistance JRJ had no hesitation in bringing in his thuggish Trade Unionists under Mathew to attack his opponents. Though during the times of previous regimes there were incidents of violence directed at ethnic groups such as the 1958 riots, well described by Tarzie Vittachi, the state did not encourage it.
For instance the Government Agent of Polnnaruwa, Derrick Aluvihare, confronted the rioters, blocked their path with police and Army assistance and prevented a bloodbath. Lakshmi Naganathan, daughter of Federal Party leader E.M.V. Naganathan, told me that when her father and his comrades were bundled up from Galle Face green and incarcerated in Galle Face Hotel, Mrs. Bandaranaike on the PM’s instructions, had sent him food cooked in the Bandaranaike kitchen.
When Mrs. Bandaranaike lost the election only Lakshmi of all the Foreign Service officials went to her home to bid their former Minister and PM goodbye. I had personally seen Left firebrands like Philip and Colvin restraining their supporters from getting into fights. In fact it was the left that was set on by Goonesinha and Kotelawela’s goons. In fairness to the so-called LSSP and CP revolutionaries, not one of them encouraged workers to attack others in the workplace or outside.
NM was the quintessential patient and analytical trade union negotiator. Every year NM would spend a few months in the UK in the company of Dora Fonseka. Even Capitalist negotiators knew that he would skillfully wind up his bargaining just in time to catch his flight to London. Bandaranaike loved to give tongue lashings but except when he praised the ‘Imbulgoda Veeraya’ for obstructing JRJs march, was a peace-loving leader who tolerated the taunt of `Sevala Banda’ which was later adopted even by his murderers. In all his speeches he never accused the Tamil leaders of provoking the Sinhalese.
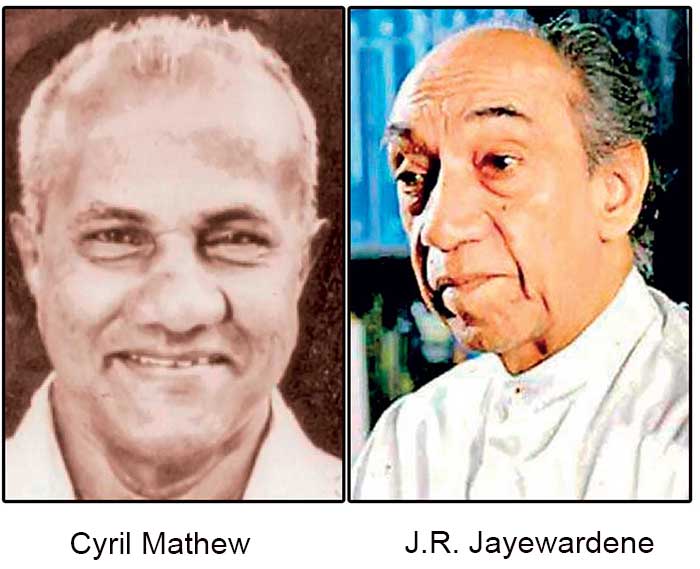
JRJ on the other hand, for all his lip service to non-violence used violence as a political weapon. As an admirer of Napoleon’s tactics he must have thought that controlled violence was a useful tool for governance. Having I 1977 won a five sixths majority fair and square, be sought to preserve it with unacceptable means. His ‘Major Domo’ was Cyril Mathew who was also the boss of the UNP trade unions.
Mathew proceeded to staff his numerous Boards with his violence prone unionists who in turn packed them with party working class stalwarts. The big state Corporations were seething with tension because of the opposition of leftist workers who had earlier ruled the roost. The Left also made a mistake which they later acknowledged, of forcing a showdown with JRJ early by calling a general strike, with a demand for all-round higher wages. With Thondaman on his side JRJ was spoiling for a fight. He wanted to teach the leftist workers a lesson they will not forget.
JRJ was supported to the hilt by Premadasa who wanted to stuff the Government offices with his own fanatical supporters from Colombo Central. The Marxist theory and practice of the general strike is clear. It should only be a struggle of the last resort because there is no possibility of further escalation. It is a question of win or die for a workers’ party. Indeed the call for a strike by the Left leaders was designed to play themselves back into the game after the disastrous results of the 1977 election where they could not win a single seat.
I was in my office on the day of the general strike. Mathew’s goons led by the UNPs trade Union the JSS launched a murderous attack on the strikers near the Lake House roundabout. They had come armed with clubs, knives and knuckle dusters. One worker was killed and the others ran helter skelter to escape the killers. Alavi Moulana and Sarath Muttetuwegama ran into my room in the ministry on Sir Baron Jayatilaka mawatha as they were being pursued by murderous thugs. I immediately shut the door and got my two friends to sit down and drink a cup of tea while their tormentors on the street rushed past us.
Alavi’s shirt was drenched in blood, and I got my driver Fonseka to bring him a new shirt. Then I smuggled Alavi and Sarath into my official car and had them driven safely home. The Lake House roundabout was like a war zone with placards, shoes, slippers and files strewn all over. I must say that both Alavi and Sarath did not forget this adventure and when much later in the Mahinda Cabinet there were disagreements with Mahinda, Alavi and Dinesh took my side and resolved controversial issues.
Cyril Mathew’s goons did not stop there. They launched an unprovoked attack on distinguished cultural personalities who were critical of the open economy. Popular culture, especially with the coming of TV, that was growing after 1977 was a threat to their sensibility as well as social position. They launched a well-supported opposition to the open economy and its cultural effects. Even their moderate and sensible arguments irritated JRJ and Mathew who knew only too well that the debacle of 1956 started similarly with cultural and religious opposition to the UNP.
There is no doubt that JRJ was behind these attacks. The meeting held at the Buddhist Congress Hall under the leadership of Maduluwawe Sobhita and Sarachchandra was attacked and the two leaders were hospitalized. What was more disconcerting was that ministers, save my minister Anandatissa, were gloating about the discomfiture of the cultural icons. Ananda and I went to see Sarcthchandra who was not seriously hurt. But this jubilation about use of violence which seemed a way of currying favour with JRJ had grave consequences, particularly on the ethnic issue.
There is no doubt that JRJ was behind these attacks. The meeting held at the Buddhist Congress Hall under the leadership of Maduluwawe Sobhita and Sarathchandra was attacked and the two leaders were hospitalized. What was more disconcerting was that ministers, save my minister Anandatissa, were gloating about the discomfiture of the cultural icons. Ananda and I went to see Sarathchandra who was not seriously hurt. But this jubilation about use of violence which seemed a way of currying favour with JRJ had grave consequences, particularly on the ethnic issue.
(To be continued)
Features
Rebuilding Sri Lanka Through Inclusive Governance

In the immediate aftermath of Cyclone Ditwah, the government has moved swiftly to establish a Presidential Task Force for Rebuilding Sri Lanka with a core committee to assess requirements, set priorities, allocate resources and raise and disburse funds. Public reaction, however, has focused on the committee’s problematic composition. All eleven committee members are men, and all non-government seats are held by business personalities with no known expertise in complex national development projects, disaster management and addressing the needs of vulnerable populations. They belong to the top echelon of Sri Lanka’s private sector which has been making extraordinary profits. The government has been urged by civil society groups to reconsider the role and purpose of this task force and reconstitute it to be more representative of the country and its multiple needs.
The group of high-powered businessmen initially appointed might greatly help mobilise funds from corporates and international donors, but this group may be ill equipped to determine priorities and oversee disbursement and spending. It would be necessary to separate fundraising, fund oversight and spending prioritisation, given the different capabilities and considerations required for each. International experience in post disaster recovery shows that inclusive and representative structures are more likely to produce outcomes that are equitable, efficient and publicly accepted. Civil society, for instance, brings knowledge rooted in communities, experience in working with vulnerable groups and a capacity to question assumptions that may otherwise go unchallenged.
A positive and important development is that the government has been responsive to these criticisms and has invited at least one civil society representative to join the Rebuilding Sri Lanka committee. This decision deserves to be taken seriously and responded to positively by civil society which needs to call for more representation rather than a single representative. Such a demand would reflect an understanding that rebuilding after a national disaster cannot be undertaken by the state and the business community alone. The inclusion of civil society will strengthen transparency and public confidence, particularly at a moment when trust in institutions remains fragile. While one appointment does not in itself ensure inclusive governance, it opens the door to a more participatory approach that needs to be expanded and institutionalised.
Costly Exclusions
Going down the road of history, the absence of inclusion in government policymaking has cost the country dearly. The exclusion of others, not of one’s own community or political party, started at the very dawn of Independence in 1948. The Father of the Nation, D S Senanayake, led his government to exclude the Malaiyaha Tamil community by depriving them of their citizenship rights. Eight years later, in 1956, the Oxford educated S W R D Bandaranaike effectively excluded the Tamil speaking people from the government by making Sinhala the sole official language. These early decisions normalised exclusion as a tool of governance rather than accommodation and paved the way for seven decades of political conflict and three decades of internal war.
Exclusion has also taken place virulently on a political party basis. Both of Sri Lanka’s post Independence constitutions were decided on by the government alone. The opposition political parties voted against the new constitutions of 1972 and 1977 because they had been excluded from participating in their design. The proposals they had made were not accepted. The basic law of the country was never forged by consensus. This legacy continues to shape adversarial politics and institutional fragility. The exclusion of other communities and political parties from decision making has led to frequent reversals of government policy. Whether in education or economic regulation or foreign policy, what one government has done the successor government has undone.
Sri Lanka’s poor performance in securing the foreign investment necessary for rapid economic growth can be attributed to this factor in the main. Policy instability is not simply an economic problem but a political one rooted in narrow ownership of power. In 2022, when the people went on to the streets to protest against the government and caused it to fall, they demanded system change in which their primary focus was corruption, which had reached very high levels both literally and figuratively. The focus on corruption, as being done by the government at present, has two beneficial impacts for the government. The first is that it ensures that a minimum of resources will be wasted so that the maximum may be used for the people’s welfare.
Second Benefit
The second benefit is that by focusing on the crime of corruption, the government can disable many leaders in the opposition. The more opposition leaders who are behind bars on charges of corruption, the less competition the government faces. Yet these gains do not substitute for the deeper requirement of inclusive governance. The present government seems to have identified corruption as the problem it will emphasise. However, reducing or eliminating corruption by itself is not going to lead to rapid economic development. Corruption is not the sole reason for the absence of economic growth. The most important factor in rapid economic growth is to have government policies that are not reversed every time a new government comes to power.
For Sri Lanka to make the transition to self-sustaining and rapid economic development, it is necessary that the economic policies followed today are not reversed tomorrow. The best way to ensure continuity of policy is to be inclusive in governance. Instead of excluding those in the opposition, the mainstream opposition in particular needs to be included. In terms of system change, the government has scored high with regard to corruption. There is a general feeling that corruption in the country is much reduced compared to the past. However, with regard to inclusion the government needs to demonstrate more commitment. This was evident in the initial choice of cabinet ministers, who were nearly all men from the majority ethnic community. Important committees it formed, including the Presidential Task Force for a Clean Sri Lanka and the Rebuilding Sri Lanka Task Force, also failed at first to reflect the diversity of the country.
In a multi ethnic and multi religious society like Sri Lanka, inclusivity is not merely symbolic. It is essential for addressing diverse perspectives and fostering mutual understanding. It is important to have members of the Tamil, Muslim and other minority communities, and women who are 52 percent of the population, appointed to important decision making bodies, especially those tasked with national recovery. Without such representation, the risk is that the very communities most affected by the crisis will remain unheard, and old grievances will be reproduced in new forms. The invitation extended to civil society to participate in the Rebuilding Sri Lanka Task Force is an important beginning. Whether it becomes a turning point will depend on whether the government chooses to make inclusion a principle of governance rather than treat it as a show of concession made under pressure.
by Jehan Perera
Features
Reservoir operation and flooding

Former Director General of Irrigation, G.T. Dharmasena, in an article, titled “Revival of Innovative systems for reservoir operation and flood forecasting” in The Island of 17 December, 2025, starts out by stating:
“Most reservoirs in Sri Lanka are agriculture and hydropower dominated. Reservoir operators are often unwilling to acknowledge the flood detention capability of major reservoirs during the onset of monsoons. Deviating from the traditional priority for food production and hydropower development, it is time to reorient the operational approach of major reservoirs operators under extreme events, where flood control becomes a vital function. While admitting that total elimination of flood impacts is not technically feasible, the impacts can be reduced by efficient operation of reservoirs and effective early warning systems”.
Addressing the question often raised by the public as to “Why is flooding more prominent downstream of reservoirs compared to the period before they were built,” Mr. Dharmasena cites the following instances: “For instance, why do (sic) Magama in Tissamaharama face floods threats after the construction of the massive Kirindi Oya reservoir? Similarly, why does Ambalantota flood after the construction of Udawalawe Reservoir? Furthermore, why is Molkawa, in the Kalutara District area, getting flooded so often after the construction of Kukule reservoir”?
“These situations exist in several other river basins, too. Engineers must, therefore, be mindful of the need to strictly control the operation of the reservoir gates by their field staff. (Since) “The actual field situation can sometimes deviate significantly from the theoretical technology… it is necessary to examine whether gate operators are strictly adhering to the operational guidelines, as gate operation currently relies too much on the discretion of the operator at the site”.
COMMENT
For Mr. Dharmasena to bring to the attention of the public that “gate operation currently relies too much on the discretion of the operator at the site”, is being disingenuous, after accepting flooding as a way of life for ALL major reservoirs for decades and not doing much about it. As far as the public is concerned, their expectation is that the Institution responsible for Reservoir Management should, not only develop the necessary guidelines to address flooding but also ensure that they are strictly administered by those responsible, without leaving it to the arbitrary discretion of field staff. This exercise should be reviewed annually after each monsoon, if lives are to be saved and livelihoods are to be sustained.
IMPACT of GATE OPERATION on FLOODING
According to Mr. Dhamasena, “Major reservoir spillways are designed for very high return periods… If the spillway gates are opened fully when reservoir is at full capacity, this can produce an artificial flood of a very large magnitude… Therefore, reservoir operators must be mindful in this regard to avoid any artificial flood creation” (Ibid). Continuing, he states: “In reality reservoir spillways are often designed for the sole safety of the reservoir structure, often compromising the safety of the downstream population. This design concept was promoted by foreign agencies in recent times to safeguard their investment for dams. Consequently, the discharge capacities of these spill gates significantly exceed the natural carrying capacity of river(s) downstream” (Ibid).
COMMENT
The design concept where priority is given to the “sole safety of the structure” that causes the discharge capacity of spill gates to “significantly exceed” the carrying capacity of the river is not limited to foreign agencies. Such concepts are also adopted by local designers as well, judging from the fact that flooding is accepted as an inevitable feature of reservoirs. Since design concepts in their current form lack concern for serious destructive consequences downstream and, therefore, unacceptable, it is imperative that the Government mandates that current design criteria are revisited as a critical part of the restoration programme.
CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN GATE OPENINGS and SAFETY MEASURES
It is only after the devastation of historic proportions left behind by Cyclone Ditwah that the Public is aware that major reservoirs are designed with spill gate openings to protect the safety of the structure without factoring in the consequences downstream, such as the safety of the population is an unacceptable proposition. The Institution or Institutions associated with the design have a responsibility not only to inform but also work together with Institutions such as Disaster Management and any others responsible for the consequences downstream, so that they could prepare for what is to follow.
Without working in isolation and without limiting it only to, informing related Institutions, the need is for Institutions that design reservoirs to work as a team with Forecasting and Disaster Management and develop operational frameworks that should be institutionalised and approved by the Cabinet of Ministers. The need is to recognize that without connectivity between spill gate openings and safety measures downstream, catastrophes downstream are bound to recur.
Therefore, the mandate for dam designers and those responsible for disaster management and forecasting should be for them to jointly establish guidelines relating to what safety measures are to be adopted for varying degrees of spill gate openings. For instance, the carrying capacity of the river should relate with a specific openinig of the spill gate. Another specific opening is required when the population should be compelled to move to high ground. The process should continue until the spill gate opening is such that it warrants the population to be evacuated. This relationship could also be established by relating the spill gate openings to the width of the river downstream.
The measures recommended above should be backed up by the judicious use of the land within the flood plain of reservoirs for “DRY DAMS” with sufficient capacity to intercept part of the spill gate discharge from which excess water could be released within the carrying capacity of the river. By relating the capacity of the DRY DAM to the spill gate opening, a degree of safety could be established. However, since the practice of demarcating flood plains is not taken seriously by the Institution concerned, the Government should introduce a Bill that such demarcations are made mandatory as part of State Land in the design and operation of reservoirs. Adopting such a practice would not only contribute significantly to control flooding, but also save lives by not permitting settlement but permitting agricultural activities only within these zones. Furthermore, the creation of an intermediate zone to contain excess flood waters would not tax the safety measures to the extent it would in the absence of such a safety net.
CONCLUSION
Perhaps, the towns of Kotmale and Gampola suffered severe flooding and loss of life because the opening of spill gates to release the unprecedented volumes of water from Cyclone Ditwah, was warranted by the need to ensure the safety of Kotmale and Upper Kotmale Dams.
This and other similar disasters bring into focus the connectivity that exists between forecasting, operation of spill gates, flooding and disaster management. Therefore, it is imperative that the government introduce the much-needed legislative and executive measures to ensure that the agencies associated with these disciplines develop a common operational framework to mitigate flooding and its destructive consequences. A critical feature of such a framework should be the demarcation of the flood plain, and decree that land within the flood plain is a zone set aside for DRY DAMS, planted with trees and free of human settlements, other than for agricultural purposes. In addition, the mandate of such a framework should establish for each river basin the relationship between the degree to which spill gates are opened with levels of flooding and appropriate safety measures.
The government should insist that associated Agencies identify and conduct a pilot project to ascertain the efficacy of the recommendations cited above and if need be, modify it accordingly, so that downstream physical features that are unique to each river basin are taken into account and made an integral feature of reservoir design. Even if such restrictions downstream limit the capacities to store spill gate discharges, it has to be appreciated that providing such facilities within the flood plain to any degree would mitigate the destructive consequences of the flooding.
By Neville Ladduwahetty
Features
Listening to the Language of Shells

The ocean rarely raises its voice. Instead, it leaves behind signs — subtle, intricate and enduring — for those willing to observe closely. Along Sri Lanka’s shores, these signs often appear in the form of seashells: spiralled, ridged, polished by waves, carrying within them the quiet history of marine life. For Marine Naturalist Dr. Malik Fernando, these shells are not souvenirs of the sea but storytellers, bearing witness to ecological change, resilience and loss.
“Seashells are among the most eloquent narrators of the ocean’s condition,” Dr. Fernando told The Island. “They are biological archives. If you know how to read them, they reveal the story of our seas, past and present.”
A long-standing marine conservationist and a member of the Marine Subcommittee of the Wildlife & Nature Protection Society (WNPS), Dr. Fernando has dedicated much of his life to understanding and protecting Sri Lanka’s marine ecosystems. While charismatic megafauna often dominate conservation discourse, he has consistently drawn attention to less celebrated but equally vital marine organisms — particularly molluscs, whose shells are integral to coastal and reef ecosystems.
“Shells are often admired for their beauty, but rarely for their function,” he said. “They are homes, shields and structural components of marine habitats. When shell-bearing organisms decline, it destabilises entire food webs.”
Sri Lanka’s geographical identity as an island nation, Dr. Fernando says, is paradoxically underrepresented in national conservation priorities. “We speak passionately about forests and wildlife on land, but our relationship with the ocean remains largely extractive,” he noted. “We fish, mine sand, build along the coast and pollute, yet fail to pause and ask how much the sea can endure.”
Through his work with the WNPS Marine Subcommittee, Dr. Fernando has been at the forefront of advocating for science-led marine policy and integrated coastal management. He stressed that fragmented governance and weak enforcement continue to undermine marine protection efforts. “The ocean does not recognise administrative boundaries,” he said. “But unfortunately, our policies often do.”
He believes that one of the greatest challenges facing marine conservation in Sri Lanka is invisibility. “What happens underwater is out of sight, and therefore out of mind,” he said. “Coral bleaching, mollusc depletion, habitat destruction — these crises unfold silently. By the time the impacts reach the shore, it is often too late.”
 Seashells, in this context, become messengers. Changes in shell thickness, size and abundance, Dr. Fernando explained, can signal shifts in ocean chemistry, rising temperatures and increasing acidity — all linked to climate change. “Ocean acidification weakens shells,” he said. “It is a chemical reality with biological consequences. When shells grow thinner, organisms become more vulnerable, and ecosystems less stable.”
Seashells, in this context, become messengers. Changes in shell thickness, size and abundance, Dr. Fernando explained, can signal shifts in ocean chemistry, rising temperatures and increasing acidity — all linked to climate change. “Ocean acidification weakens shells,” he said. “It is a chemical reality with biological consequences. When shells grow thinner, organisms become more vulnerable, and ecosystems less stable.”
Climate change, he warned, is no longer a distant threat but an active force reshaping Sri Lanka’s marine environment. “We are already witnessing altered breeding cycles, migration patterns and species distribution,” he said. “Marine life is responding rapidly. The question is whether humans will respond wisely.”
Despite the gravity of these challenges, Dr. Fernando remains an advocate of hope rooted in knowledge. He believes public awareness and education are essential to reversing marine degradation. “You cannot expect people to protect what they do not understand,” he said. “Marine literacy must begin early — in schools, communities and through public storytelling.”
It is this belief that has driven his involvement in initiatives that use visual narratives to communicate marine science to broader audiences. According to Dr. Fernando, imagery, art and heritage-based storytelling can evoke emotional connections that data alone cannot. “A well-composed image of a shell can inspire curiosity,” he said. “Curiosity leads to respect, and respect to protection.”
Shells, he added, also hold cultural and historical significance in Sri Lanka, having been used for ornamentation, ritual objects and trade for centuries. “They connect nature and culture,” he said. “By celebrating shells, we are also honouring coastal communities whose lives have long been intertwined with the sea.”
However, Dr. Fernando cautioned against romanticising the ocean without acknowledging responsibility. “Celebration must go hand in hand with conservation,” he said. “Otherwise, we risk turning heritage into exploitation.”
He was particularly critical of unregulated shell collection and commercialisation. “What seems harmless — picking up shells — can have cumulative impacts,” he said. “When multiplied across thousands of visitors, it becomes extraction.”
As Sri Lanka continues to promote coastal tourism, Dr. Fernando emphasised the need for sustainability frameworks that prioritise ecosystem health. “Tourism must not come at the cost of the very environments it depends on,” he said. “Marine conservation is not anti-development; it is pro-future.”

Dr. Malik Fernando
Reflecting on his decades-long engagement with the sea, Dr. Fernando described marine conservation as both a scientific pursuit and a moral obligation. “The ocean has given us food, livelihoods, climate regulation and beauty,” he said. “Protecting it is not an act of charity; it is an act of responsibility.”
He called for stronger collaboration between scientists, policymakers, civil society and the private sector. “No single entity can safeguard the ocean alone,” he said. “Conservation requires collective stewardship.”
Yet, amid concern, Dr. Fernando expressed cautious optimism. “Sri Lanka still has immense marine wealth,” he said. “Our reefs, seagrass beds and coastal waters are resilient, if given a chance.”
Standing at the edge of the sea, shells scattered along the sand, one is reminded that the ocean does not shout its warnings. It leaves behind clues — delicate, enduring, easily overlooked. For Dr. Malik Fernando, those clues demand attention.
“The sea is constantly communicating,” he said. “In shells, in currents, in changing patterns of life. The real question is whether we, as a society, are finally prepared to listen — and to act before silence replaces the story.”
By Ifham Nizam
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoBritish MP calls on Foreign Secretary to expand sanction package against ‘Sri Lankan war criminals’
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoStreet vendors banned from Kandy City
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoChief selector’s remarks disappointing says Mickey Arthur
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoDisasters do not destroy nations; the refusal to change does
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoSri Lanka’s coastline faces unfolding catastrophe: Expert
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoLankan aircrew fly daring UN Medevac in hostile conditions in Africa
-

 Midweek Review7 days ago
Midweek Review7 days agoYear ends with the NPP govt. on the back foot
-

 Sports2 days ago
Sports2 days agoGurusinha’s Boxing Day hundred celebrated in Melbourne










