Features
Ministry of Justice Law Reforms: Clarifying and updating law and finding solutions, or creating more problems and confusion?

By Kalyananda Tiranagama
Executive Director
Lawyers for Human Rights and Development
As reported by the media, over the past one year and more, addressing meetings at various places of lawyers, Judges and public officials and the media, Minister of Justice Ali Sabry, PC has spoken of steps taken by him to modernise the law by reforming and amending outdated laws.
During a visit to the new courts complex building at the Beligaha Junction, Galle on December 23, 2020, and addressing the media the Minister said, ‘To expedite justice process we have made a lot of efforts to enact new laws amending the outdated laws. Within the last three months, we have amended 37 laws and 30 more new laws to be enacted in the coming months.’
Commencing work at the Ministry of Justice for the New Year on 01 January, 2021, the Minister said, ‘After 1947 our legal system has not been updated. Within the last three months we have amended 37 laws. With these amendments unprecedented relief will be granted to the people through courts.
One can get an idea as to how these legal reforms are done from the following passages in a full page advertisement published by the Ministry in all the newspapers in all three languages on January 25, 2021 under the title – Ministry of Justice – Overview of Projected Reforms and Development:
C. i. Increase in Budget allocation
– The Ministry of Justice’s standard Budget allocation over the years has been Rs. 4,500 million
– The government in 2021, allocated an unprecedented sum of Rs. 20,000 million to the justice sector for infrastructure development and digitalisation amongst other key improvements. This reflects the largest ever commitment by a govt in the history of the country towards a complete reform and development of the justice sector.
iii. Special Project Unit of the Ministry of Justice
* The creation of five sub-committees was the brainchild of Mohamed Ali Sabry PC, the Minister of Justice. One of his earliest tasks after taking office was the submission of a comprehensive Cabinet Memorandum setting out the issues clearly and detailing a two year plan to fix laws delays.
* It provides for the creation of five sub-committees headed by dynamic lawyers from the private bar who would work together to come up with a complete solution to the problem. Cabinet Memorandum was approved by the Cabinet, thus giving the Ministry of Justice the green light to go ahead with the plan.
* The Cabinet has allocated an impressive expanse of resources for this project – a full-blown secretariat, staff and all the facilities necessary for the sub-committees to carry out their objective.
* This is the first time that the state has fully backed such a mammoth endeavour to reform the law.
* The terms of reference are precise and reflect a very clear overall plan.
* The five sub-Committees are 1. Infrastructure Development 2. Digitalization and Court Automation 3. Criminal Law Reforms 4. Civil Law Reforms 5. Commercial Law Reforms
As mentioned in this advertisement itself, the Budget allocation of the Ministry has been increased five times from Rs. 4,500 million to Rs. 20,000 million. It is the largest ever commitment by a government in the history of the country for judicial and legal reforms. It is a reflection of the importance the government has attached to legal and judicial reforms expected by the people over decades.
It is a mammoth endeavour to reform the law entrusted to five sub-committees headed by dynamic lawyers from the private bar. The creation of five sub-committees was the brainchild of the Minister. The terms of reference are precise and reflect a very clear overall plan.
As disclosed by the Minister in his public announcements, the number of laws identified for reforms and amendment is going up from month to month. Addressing a meeting at Medawachchiya on 27 October, 2021, the Minister has said that Cabinet had received suggestions for amending 60 laws and a lot of laws would be amended in the next six – 12 months. There are many antiquated laws that were adversely affecting the people. Some of these obstruct development and they needed to be amended.
In an interview with The Sunday Divaina newspaper of 28 November 2021, the Minister stated that since he assumed duties as the Minister of Justice, 14 months ago, steps had been taken to amend 84 laws, already 10 amended, about 20 had been submitted to the Cabinet for approval and about another 30 sent to the Legal Draftsman. Things have never moved so fast.
On the occasion of the opening of the Debt Conciliation Board Office at Gampaha on 29 December 2021, the Minister said that during the last one year 10 new laws enacted reforming outdated laws and steps were being taken to amend 98 laws in the coming days.
In our laws, there are many provisions that are outdated and lack clarity, resulting in injustice or inconsistent with generally accepted norms of human rights, or obstructing the smooth and effective implementation of the law. There are many issues encountered in the administration of criminal justice that need to be addressed, but have remained unaddressed for decades without required legal provisions to address them. There are many areas where the law needs to be further strengthened and improved to address issues encountered in emerging situations.
With these public utterances of the Minister, the legal fraternity and the people of the country undoubtedly expected the Ministry to identify not only a few outdated expressions in the law but also main problem areas and lacunae in the law encountered by the people in their search for justice and by the law enforcement authorities and that need to be urgently addressed with reforms required for smooth and effective implementation. What the country needs is substantial legal reforms aimed at addressing the issues that frequently come up in the administration of justice and enforcement of the law, and not some superficial or ornamental amendments.
The following 30 Acts have been passed by Parliament in 2021. Out of them 23 are Amendments brought to existing Acts and 7 (shown in bold letters) are newly enacted laws. The first 8 Amendment Acts were passed in the first week of January, receiving the endorsement of the Speaker on January 18, 2021.
1.
Shop and Office Employees (Regulation of Employment and Remuneration) (Amendment) Act No. 1 of 2021 – (January 18, 2021)
2.
Employment of Women. Young Persons and Children (Amendment) Act No. 2 of 2021 – (January 18, 2021)
3.
Minimum Wages (Indian Labour) (Amendment) Act No. 3 of 2021 – (January 18, 2021)
4.
Factories (Amendment) Act No. 4 of 2021 – (January 18, 2021)
5.
Penal Code (Amendment) Act No. 5 of 2021 – (January 18, 2021)
6.
Evidence (Amendment) Act No. 6 of 2021 – (January 18, 2021)
7.
Bail (Amendment) Act No. 7 of 2021 – (January 18, 2021)
8.
Intellectual Property (Amendment) Act No. 8 of 2021 – (January 18, 2021)
9.
Value Added Tax (Amendment) Act No. 9 of 2021 – (May 13, 2021)
10.
Inland Revenue (Amendment) Act No. 10 of 2021 – (May 13, 2021)
11.
Colombo Port City Economic Commission Act No. 11 of 2021- ( May 27, 2021)
12.
Fiscal Management (Responsibility) (Amendment) Act No. 12 of 2021 (June 14, 2021)
13.
Sri Lanka Land Development Corporation (Amendment) Act No. 13 of 2021 (June 30, 2021)
14.
Code of Criminal Procedure. (Amendment) Act No. 14 of 2021 (July 15, 2021)
15.
Torture Convention (Amendment) Act No. 15 of 2021 – (July 15, 2021)
16. National Minimum Wage of Workers (Amendment) Act No. 16 of 2021 (August 16, 2021)
17. Coronavirus Disease (Covid-19) (Temporary Provisions) Act No. 17 of 2021 – (August 23, 2021)
18.
Finance Act No 18 of 2021 (September 15, 2021)
19. Securities and Exchange Commission of Sri Lanka Act No. 19 of 2021 – (September 21, 2021)
20. Consumer Affairs Authority (Amendment) Act No. 20 of 2021 – (September 22, 2021)
21.
Petroleum Resources Act No. 21 of 2021
22.
Registration of Electors (Amendment) Act No. 22 of 2021
23.
Employees Provident Fund (Amendment) Act No. 23 of 2021
24.
Youthful Offenders (Training Schools) (Amendment) Act No. 24 of 2021 (2021. 10. 21)
25.
Penal Code (Amendment) Act No. 25 of 2021
26.
Appropriation (Amendment) Act No. 26 of 2021
27.
Immigrants and Emigrants (Amendment) Act No. 27 of 2021 – (12/11/2021)
28
. Minimum Retirement Age of Workers Act No. 28 of 2021
29
. Termination of Employment of Workmen (Special Provisions) (Amendment) Act No. 29 of 2021 – (17/11/2021)
30.
Appropriation Act No. 30 of 2021
However, when one examines the above amendments, it appears that some of them are nominal and superficial, some are meaningless, redundant and ridiculous, and in some others only some marginal issues are touched, ignoring the real ones that need to be urgently addressed, especially in relation to the administration of criminal justice. Some other amendments are totally unnecessary and impracticable and create unnecessary problems.
The first four amendments in the list of Acts amended relate to the increase of the minimum age of employment of children from 14 years to 16 years and the definition of the words, ‘child’ and ‘young person’. The definition of the word ‘child’ has been amended to mean ‘a person under the age of 16 years’ and the definition of the word ‘young person’ has been amended to mean ‘a person who has attained the age of 16 years, but is under the age of 18 years’. All these 4 Acts have been amended by replacing the phrases – ‘a person under the age of 16 years’ with the word ‘child’; ‘a person who has attained the age of 16 years, but is under the age of 18 years’ with the words ‘young person’ and ’14 years’ with ’16 years’ in the relevant sections in the Acts. Though it is a simple, clerical job without requiring much knowledge of law, it is undoubtedly a salutary step taken to protect the interests of children belonging to the age group of 14 – 16 years.
(To be continued)
Features
Ranking public services with AI — A roadmap to reviving institutions like SriLankan Airlines

Efficacy measures an organisation’s capacity to achieve its mission and intended outcomes under planned or optimal conditions. It differs from efficiency, which focuses on achieving objectives with minimal resources, and effectiveness, which evaluates results in real-world conditions. Today, modern AI tools, using publicly available data, enable objective assessment of the efficacy of Sri Lanka’s government institutions.
Among key public bodies, the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka emerges as the most efficacious, outperforming the Department of Inland Revenue, Sri Lanka Customs, the Election Commission, and Parliament. In the financial and regulatory sector, the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) ranks highest, ahead of the Securities and Exchange Commission, the Public Utilities Commission, the Telecommunications Regulatory Commission, the Insurance Regulatory Commission, and the Sri Lanka Standards Institution.
Among state-owned enterprises, the Sri Lanka Ports Authority (SLPA) leads in efficacy, followed by Bank of Ceylon and People’s Bank. Other institutions assessed included the State Pharmaceuticals Corporation, the National Water Supply and Drainage Board, the Ceylon Electricity Board, the Ceylon Petroleum Corporation, and the Sri Lanka Transport Board. At the lower end of the spectrum were Lanka Sathosa and Sri Lankan Airlines, highlighting a critical challenge for the national economy.
Sri Lankan Airlines, consistently ranked at the bottom, has long been a financial drain. Despite successive governments’ reform attempts, sustainable solutions remain elusive.
Globally, the most profitable airlines operate as highly integrated, technology-enabled ecosystems rather than as fragmented departments. Operations, finance, fleet management, route planning, engineering, marketing, and customer service are closely coordinated, sharing real-time data to maximise efficiency, safety, and profitability.
The challenge for Sri Lankan Airlines is structural. Its operations are fragmented, overly hierarchical, and poorly aligned. Simply replacing the CEO or senior leadership will not address these deep-seated weaknesses. What the airline needs is a cohesive, integrated organisational ecosystem that leverages technology for cross-functional planning and real-time decision-making.
The government must urgently consider restructuring Sri Lankan Airlines to encourage:
=Joint planning across operational divisions
=Data-driven, evidence-based decision-making
=Continuous cross-functional consultation
=Collaborative strategic decisions on route rationalisation, fleet renewal, partnerships, and cost management, rather than exclusive top-down mandates
Sustainable reform requires systemic change. Without modernised organisational structures, stronger accountability, and aligned incentives across divisions, financial recovery will remain out of reach. An integrated, performance-oriented model offers the most realistic path to operational efficiency and long-term viability.
Reforming loss-making institutions like Sri Lankan Airlines is not merely a matter of leadership change — it is a structural overhaul essential to ensuring these entities contribute productively to the national economy rather than remain perpetual burdens.
By Chula Goonasekera – Citizen Analyst
Features
Why Pi Day?

International Day of Mathematics falls tomorrow
The approximate value of Pi (π) is 3.14 in mathematics. Therefore, the day 14 March is celebrated as the Pi Day. In 2019, UNESCO proclaimed 14 March as the International Day of Mathematics.
Ancient Babylonians and Egyptians figured out that the circumference of a circle is slightly more than three times its diameter. But they could not come up with an exact value for this ratio although they knew that it is a constant. This constant was later named as π which is a letter in the Greek alphabet.
It was the Greek mathematician Archimedes (250 BC) who was able to find an upper bound and a lower bound for this constant. He drew a circle of diameter one unit and drew hexagons inside and outside the circle such that the sides of each hexagon touch the sides of the circle. In mathematics the circle passing through all vertices of a polygon is called a ‘circumcircle’ and the largest circle that fits inside a polygon tangent to all its sides is called an ‘incircle’. The total length of the smaller hexagon then becomes the lower bound of π and the length of the hexagon outside the circle is the upper bound. He realised that by increasing the number of sides of the polygon can make the bounds get closer to the value of Pi and increased the number of sides to 12,24,48 and 60. He argued that by increasing the number of sides will ultimately result in obtaining the original circle, thereby laying the foundation for the theory of limits. He ended up with the lower bound as 22/7 and the upper bound 223/71. He could not continue his research as his hometown Syracuse was invaded by Romans and was killed by one of the soldiers. His last words were ‘do not disturb my circles’, perhaps a reference to his continuing efforts to find the value of π to a greater accuracy.
Archimedes can be considered as the father of geometry. His contributions revolutionised geometry and his methods anticipated integral calculus. He invented the pulley and the hydraulic screw for drawing water from a well. He also discovered the law of hydrostatics. He formulated the law of levers which states that a smaller weight placed farther from a pivot can balance a much heavier weight closer to it. He famously said “Give me a lever long enough and a place to stand and I will move the earth”.
Mathematicians have found many expressions for π as a sum of infinite series that converge to its value. One such famous series is the Leibniz Series found in 1674 by the German mathematician Gottfried Leibniz, which is given below.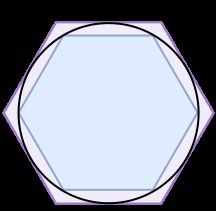
π = 4 ( 1 – 1/3 + 1/5 – 1/7 + 1/9 – ………….)
The Indian mathematical genius Ramanujan came up with a magnificent formula in 1910. The short form of the formula is as follows.
π = 9801/(1103 √8)
For practical applications an approximation is sufficient. Even NASA uses only the approximation 3.141592653589793 for its interplanetary navigation calculations.
It is not just an interesting and curious number. It is used for calculations in navigation, encryption, space exploration, video game development and even in medicine. As π is fundamental to spherical geometry, it is at the heart of positioning systems in GPS navigations. It also contributes significantly to cybersecurity. As it is an irrational number it is an excellent foundation for generating randomness required in encryption and securing communications. In the medical field, it helps to calculate blood flow rates and pressure differentials. In diagnostic tools such as CT scans and MRI, pi is an important component in mathematical algorithms and signal processing techniques.
This elegant, never-ending number demonstrates how mathematics transforms into practical applications that shape our world. The possibilities of what it can do are infinite as the number itself. It has become a symbol of beauty and complexity in mathematics. “It matters little who first arrives at an idea, rather what is significant is how far that idea can go.” said Sophie Germain.
Mathematics fans are intrigued by this irrational number and attempt to calculate it as far as they can. In March 2022, Emma Haruka Iwao of Japan calculated it to 100 trillion decimal places in Google Cloud. It had taken 157 days. The Guinness World Record for reciting the number from memory is held by Rajveer Meena of India for 70000 decimal places over 10 hours.
Happy Pi Day!
The author is a senior examiner of the International Baccalaureate in the UK and an educational consultant at the Overseas School of Colombo.
by R N A de Silva
Features
Sheer rise of Realpolitik making the world see the brink

 The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
As matters stand, there seems to be no credible evidence that the Indian state was aware of the impending torpedoing of the Iranian vessel but these acerbic-tongued politicians of Sri Lanka’s South would have the local public believe that the tragedy was triggered with India’s connivance. Likewise, India is accused of ‘embroiling’ Sri Lanka in the incident on account of seemingly having prior knowledge of it and not warning Sri Lanka about the impending disaster.
It is plain that a process is once again afoot to raise anti-India hysteria in Sri Lanka. An obligation is cast on the Sri Lankan government to ensure that incendiary speculation of the above kind is defeated and India-Sri Lanka relations are prevented from being in any way harmed. Proactive measures are needed by the Sri Lankan government and well meaning quarters to ensure that public discourse in such matters have a factual and rational basis. ‘Knowledge gaps’ could prove hazardous.
Meanwhile, there could be no doubt that Sri Lanka’s sovereignty was violated by the US because the sinking of the Iranian vessel took place in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While there is no international decrying of the incident, and this is to be regretted, Sri Lanka’s helplessness and small player status would enable the US to ‘get away with it’.
Could anything be done by the international community to hold the US to account over the act of lawlessness in question? None is the answer at present. This is because in the current ‘Global Disorder’ major powers could commit the gravest international irregularities with impunity. As the threadbare cliché declares, ‘Might is Right’….. or so it seems.
Unfortunately, the UN could only merely verbally denounce any violations of International Law by the world’s foremost powers. It cannot use countervailing force against violators of the law, for example, on account of the divided nature of the UN Security Council, whose permanent members have shown incapability of seeing eye-to-eye on grave matters relating to International Law and order over the decades.
The foregoing considerations could force the conclusion on uncritical sections that Political Realism or Realpolitik has won out in the end. A basic premise of the school of thought known as Political Realism is that power or force wielded by states and international actors determine the shape, direction and substance of international relations. This school stands in marked contrast to political idealists who essentially proclaim that moral norms and values determine the nature of local and international politics.
While, British political scientist Thomas Hobbes, for instance, was a proponent of Political Realism, political idealism has its roots in the teachings of Socrates, Plato and latterly Friedrich Hegel of Germany, to name just few such notables.
On the face of it, therefore, there is no getting way from the conclusion that coercive force is the deciding factor in international politics. If this were not so, US President Donald Trump in collaboration with Israeli Rightist Premier Benjamin Natanyahu could not have wielded the ‘big stick’, so to speak, on Iran, killed its Supreme Head of State, terrorized the Iranian public and gone ‘scot-free’. That is, currently, the US’ impunity seems to be limitless.
Moreover, the evidence is that the Western bloc is reuniting in the face of Iran’s threats to stymie the flow of oil from West Asia to the rest of the world. The recent G7 summit witnessed a coming together of the foremost powers of the global North to ensure that the West does not suffer grave negative consequences from any future blocking of western oil supplies.
Meanwhile, Israel is having a ‘free run’ of the Middle East, so to speak, picking out perceived adversarial powers, such as Lebanon, and militarily neutralizing them; once again with impunity. On the other hand, Iran has been bringing under assault, with no questions asked, Gulf states that are seen as allying with the US and Israel. West Asia is facing a compounded crisis and International Law seems to be helplessly silent.
Wittingly or unwittingly, matters at the heart of International Law and peace are being obfuscated by some pro-Trump administration commentators meanwhile. For example, retired US Navy Captain Brent Sadler has cited Article 51 of the UN Charter, which provides for the right to self or collective self-defence of UN member states in the face of armed attacks, as justifying the US sinking of the Iranian vessel (See page 2 of The Island of March 10, 2026). But the Article makes it clear that such measures could be resorted to by UN members only ‘ if an armed attack occurs’ against them and under no other circumstances. But no such thing happened in the incident in question and the US acted under a sheer threat perception.
Clearly, the US has violated the Article through its action and has once again demonstrated its tendency to arbitrarily use military might. The general drift of Sadler’s thinking is that in the face of pressing national priorities, obligations of a state under International Law could be side-stepped. This is a sure recipe for international anarchy because in such a policy environment states could pursue their national interests, irrespective of their merits, disregarding in the process their obligations towards the international community.
Moreover, Article 51 repeatedly reiterates the authority of the UN Security Council and the obligation of those states that act in self-defence to report to the Council and be guided by it. Sadler, therefore, could be said to have cited the Article very selectively, whereas, right along member states’ commitments to the UNSC are stressed.
However, it is beyond doubt that international anarchy has strengthened its grip over the world. While the US set destabilizing precedents after the crumbling of the Cold War that paved the way for the current anarchic situation, Russia further aggravated these degenerative trends through its invasion of Ukraine. Stepping back from anarchy has thus emerged as the prime challenge for the world community.
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoWinds of Change:Geopolitics at the crossroads of South and Southeast Asia
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoProf. Dunusinghe warns Lanka at serious risk due to ME war
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoRoyal start favourites in historic Battle of the Blues
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoThe 147th Royal–Thomian and 175 Years of the School by the Sea
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoHistoric address by BASL President at the Supreme Court of India
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoSeven decades of sartorial excellence: The legacy of Linton Master Tailors in Kandy
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoCEBEU warns of operational disruptions amid uncertainty over CEB restructuring




















