Features
Ekagei kaema (polyandry) – a way of life in the Kandyan highlands

by Jayantha Perera
Hingula is a small bazaar 60 miles from Colombo on the Colombo-Kandy Road. A narrow, tarred road starts from there, and a signboard says, ‘To Aluth Nuwara Devalayala.’ The logo of the Archaeological Department on the signboard indicates the devalaya (temple) is a state-protected archaeological site.
The temple is about two miles from the bazaar. The road winds through a breathtaking vista of green rice terraces cascading from low hills to narrow lowlands. The rice terraces, like thin carpets with precise lengths and widths, create a mesmerising sight. Large Mara (Samanea saman) trees and patches of tall teak trees provide shade to pedestrians. A rubber plantation and tiny homesteads with arecanut palms interspersed with clove gardens, fruit trees, and pepper vines displaying vibrant colours in sunlight. The winding road takes a right turn by a large open hut. It goes over the shoe bridge that spans a dry stream bed before arriving at the Devalgama Junction. There are several kiosks, and one of them is a tea boutique where old men read newspapers and chit-chat without any hurry to leave. My research assistant, the jeep driver, and I entered the kiosk and ordered tea with seen banis (a small round bun with melted sugar).
Our arrival at the village was met with a palpable sense of caution. This initial reaction is significant, reflecting the villagers’ wariness towards outsiders. Those at the kiosk, though initially reluctant to engage in conversation, studied our Mitsubishi Jeep with a mix of suspicion and curiosity. A man, perhaps the boldest among them, asked, “Policye mahathwaruda?” (Are you Police officers?) I reassured them that we were not and explained our plan to study the cooperative aspects of farming, particularly in rice farming and irrigation water management. However, they quickly dispersed, leaving the tea kiosk empty.
We visited the temple and worshipped the Dadimunda Deiyo (God). When we came out of the temple, Kapu Mahaththaya (the lay official of the temple) was waiting for us. He was a charming middle-aged man with a friendly smile. He had received a message from the Government Agent of Kegalle District that a team of researchers from Colombo was coming to Devalgama. He invited us for lunch at his aunt’s house. The house was an old waluwwa (mansion). Old paintings and photographs covered the walls of the large dining room. Two giant elephant tusks mounted on two mahogany blocks stood at the entrance.
I told Kapu Mahattaya we were looking for a hamlet to research the cooperative aspects of farming. He recommended Devith hamlet. I asked him to help us find a place to stay for a few months. He said residents might refuse to keep three young men in their homes. He advised us to remain where caste does not hamper our work.
Kapu Mahattaya informed us he owns a hut in a rice field. His wage workers seasonally stay there. The hut has a cement floor and a thatched roof. Two large windows open to the rice fields, bringing in sunlight and a cooling breeze. The two windows and the only door can be locked from inside. He showed us a shallow well just by the rice fields. There is a small toilet behind the house. He promised to find a woman to cook our meals.
We walked to the rice fields behind the house. The closest mountain formed a horseshoe with a small flat area in the middle for a pathaha (pond). A natural spring from a mountain watered it. Local legends say Dadimunda Deiyo caused a water spring to send water to the pond by striking the ground with his staff. We could see the mist gradually covering the hilltops and felt cold.
Kapu Mahattaya walked with us to meet an old woman. She agreed to cook our meals and told us to come to her hut for lunch and dinner. She wanted us to buy rice, vegetables, curry and chilli powder, salt, cooking oil, and coconuts from a nearby boutique. She told us we should have lunch before noon and dinner by 5.30 pm. We gave her Rs. 100 as an advance, which she happily accepted.
We unloaded our bags and sent the ARTI jeep back to Colombo. Kapu Mahattaya visited us in the evening. I told him we were happy to stay in the hut and thanked him for his generosity. When I asked him how to lock the hut from the outside, he promised to buy a padlock and a hasp from Hingula. He took us to the boutique behind the hut and introduced us to its owner and his wife. They offered us tea and hulang viscothu (air biscuits). We bought five pounds of rice, eggs, a packet of curry powder, salt, coconuts, vegetables, and a bottle of cooking oil from the boutique and delivered them to our cook. She cooked rice and a brinjal curry and prepared pol sambal for dinner.
We had kimbula banis (flat, hard buns) and sweetened plain tea for breakfast at the kadey. We then visited a randomly selected few houses, introduced ourselves, and explained why we stayed in the village. The villagers were cordial and particularly interested in our caste, marital status, and employment. This interest in our personal information is significant as it underscores the importance of social status and personal history in the community. An old man told us that there were two unresolved murder cases in the village. He wondered whether we were CID (police intelligence) officers who wanted to reopen the murder investigations.
Our interaction with villagers improved when Kanthi joined us as a field assistant. She was a Kapu Mahattaya’s relative. She was in her late thirties, divorced, and came from a pelanthiya (high social status group) in a nearby hamlet. She graduated from Peradeniya University with a degree in economics and worked as a research assistant in a development project. While in Kandy, she married a colleague against her parents’ advice. They ostracised her from the family for marrying an outsider. The marriage failed in two years, and she returned to her parents.
Kanthi introduced villagers to us, paying attention to their caste, class, and employment status. First, she introduced us to three feudal pelanthiya families who owned most of the village land. Kapu Mahattaya’s family was one of them. Then she introduced us to several goigama (cultivator caste) middle-class families. Some owned small pieces of land, and others were tenants. Kanthi took us to high-caste and goigama families before visiting achari (blacksmith) and vahumpura (potter) families. They were service castes who played an essential role in the temple’s festivals. Some of them cultivated temple land on lease and performed temple duties.
The villagers considered Kanthi to be a reliable person. They were happy to talk to us when she was with us. At our initial interviews, Kanthi answered the questions before the villagers answered them! She was a walking databank. Villagers checked their facts and numbers with her before answering our questions. They respected her because of her work to educate poor children and her readiness to help them regardless of their caste or class. After her father’s death, she became the de facto chief of her family. She managed rice and other crop cultivation on her ancestral lands.
Kanthi stayed with us for fieldwork from 9 am to 5.30 pm. She never visited us at our hut or invited us home. She preferred to discuss fieldwork arrangements at the tea boutique before the villagers. However, after two weeks, the villagers lost interest in our work and did not linger to listen to our discussions.
Kanthi taught us the structure of the village community and how economic, social, and political alliances overlap. She explained how pelantiyas go up and down in the social status ladder mainly because of debt, litigation, and gambling. I was interested in studying Kandyan marriage alliances such as diga (virilocal) and binna (matrilocal) and inheritance customs. However, she was reluctant to discuss issues with me because she did not want to reveal family tensions over inheritance in the context of her divorce.
One day, Kanthi brought a large cane basket of food. Her family had returned from a wedding and brought lots of food; she got a portion for us. While enjoying the food at the tea kiosk, she introduced us to a young man named Vijay. Vijay lived in Colombo, where he had a motorcycle business. Later, I asked Kanthi about him. She smiled and told me he visited his home only once a month. He was a married man, and his wife lived in the hamlet. Then she said Vijay and his brother, Ratne, shared one wife. It was a polyandrous marital arrangement known as ‘ekgei kanawa’ (eat and live together as one household). The three – Vijay, Ratne, and their wife, Kumari – maintained one household.
Kanthi was an excellent storyteller. One day she delved into the ekgei kaema institution in detail. Kumari was her friend and shared her secrets with her. As I was not a member of the village community, Kanthi did not mind telling me what she knew. Although Kumari was married to the two brothers, her favourite was Ratne, a farmer who lived in the village. Vijay wanted to keep Kumari from his elder brother, Ratne. He yielded to his parents’ pressure and agreed to share Kumari with Ratne in one household. The parents of Vijay and Ratne owned a large tract of ancestral land. They wanted to keep it from fragmenting through inheritance and succession. Their strategy was to get a ‘common’ wife for the two brothers and accept their ‘common’ children as heirs to the ancestral estate.
Vijay wanted to sell his property share to raise money and start a business in Kegalle. But his father opposed the proposal and told him to live with his brother and Kumari or leave the family. Vijay hesitated and then agreed to keep a joint household with his brother and Kumari. Kumari’s parents told her to marry Ratne and later insisted that she accept Vijay as her co-husband. She did not refuse because she knew her parents were keen to improve their social and economic status by having access to the large rice field jointly owned by Vijay and Ratne.
The two brothers informed Kumari in advance of their sleeping plans with her. Vijay and Ratne had no problem in this regard, as Vijay lived outside the village. Ratne and Kumari had lived a happy family life. Vijay’s monthly conjugal access to Kumari for a day or two did not disturb their peace at home. Soon, Vijay became a drunkard. When he returned home for a few days, he went out with his friends to Hingula and returned home after midnight. Ratne respected the ekgei kaema arrangement and always found an excuse to leave home when Vijay came home. Ratne was worried about Kumari, as, on several occasions, Vijay had assaulted her.
Kanthi explained the root cause of the new tension at Kumari’s house. Ratne wanted a child, but Vijay did not. Vijay feared that Ratne might impregnate Kumari as they were usually together. Ratne was willing to suspend his access to his wife for a month or more so that Vijay could impregnate Kumari, but on one condition—the next child had to be his. Kanthi said the proposal was risky and was against tradition. The children of a household that followed ekgei kaema rules were considered ‘common’ children of co-husbands, making them co-heirs to their parent’s property.
Knowing a child’s biological father might encourage the co-father to ill-treat the child. Also, if Vijay or Ratne were infertile, the proposed arrangement would not work. Such tensions would destroy the ekgei kana marriage, affecting the undivided property. Ratne was willing to treat Vijay’s child as his own if Ratne failed to beget an heir. Vijay was resentful of such arrangements and thought Kumari was behind such proposals. Kanthi worried that one day, the two brothers would resort to violence to resolve their relationship with Kumari, who had no voice in the proposals and negotiations.
Kanthi knew several other families that followed the ekgei kana arrangement. Tensions it could generate over children, spouses, and undivided property were usually kept as family secrets and never revealed to outsiders.
Devith hamlet is not an idyllic village community. It always has social tensions arising from caste, class, social status, and social arrangements such as ekgei kaema. People have developed tension management schemes as part of the village social organisation. The critical tension management lever is the rigid caste hierarchy and associated purity or impurity. Another is the belief that the mighty God, Dadimunda, controls the area and keeps an eye on the moral character of the local population. The temple murals depict the God as an elite Kandyan aristocrat. He punishes those who violate norms, customs, and rituals. The belief in fate also plays a crucial role in legitimising the caste hierarchy and managing tensions.
One is born into a low-caste family or lives a comfortable life as a feudal landlord because of past bad or good karma (action). The power of gossip and rumour is more potent than any of the above levers. Kanthi always cautioned me about gossip and rumours. She told me if I had visited her at her home, her neighbours and relatives would have suspected that she had found a lover or a man to marry her. They would have built a ‘reality’ on that assumption as part of the village narrative.
Features
Ranking public services with AI — A roadmap to reviving institutions like SriLankan Airlines

Efficacy measures an organisation’s capacity to achieve its mission and intended outcomes under planned or optimal conditions. It differs from efficiency, which focuses on achieving objectives with minimal resources, and effectiveness, which evaluates results in real-world conditions. Today, modern AI tools, using publicly available data, enable objective assessment of the efficacy of Sri Lanka’s government institutions.
Among key public bodies, the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka emerges as the most efficacious, outperforming the Department of Inland Revenue, Sri Lanka Customs, the Election Commission, and Parliament. In the financial and regulatory sector, the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) ranks highest, ahead of the Securities and Exchange Commission, the Public Utilities Commission, the Telecommunications Regulatory Commission, the Insurance Regulatory Commission, and the Sri Lanka Standards Institution.
Among state-owned enterprises, the Sri Lanka Ports Authority (SLPA) leads in efficacy, followed by Bank of Ceylon and People’s Bank. Other institutions assessed included the State Pharmaceuticals Corporation, the National Water Supply and Drainage Board, the Ceylon Electricity Board, the Ceylon Petroleum Corporation, and the Sri Lanka Transport Board. At the lower end of the spectrum were Lanka Sathosa and Sri Lankan Airlines, highlighting a critical challenge for the national economy.
Sri Lankan Airlines, consistently ranked at the bottom, has long been a financial drain. Despite successive governments’ reform attempts, sustainable solutions remain elusive.
Globally, the most profitable airlines operate as highly integrated, technology-enabled ecosystems rather than as fragmented departments. Operations, finance, fleet management, route planning, engineering, marketing, and customer service are closely coordinated, sharing real-time data to maximise efficiency, safety, and profitability.
The challenge for Sri Lankan Airlines is structural. Its operations are fragmented, overly hierarchical, and poorly aligned. Simply replacing the CEO or senior leadership will not address these deep-seated weaknesses. What the airline needs is a cohesive, integrated organisational ecosystem that leverages technology for cross-functional planning and real-time decision-making.
The government must urgently consider restructuring Sri Lankan Airlines to encourage:
=Joint planning across operational divisions
=Data-driven, evidence-based decision-making
=Continuous cross-functional consultation
=Collaborative strategic decisions on route rationalisation, fleet renewal, partnerships, and cost management, rather than exclusive top-down mandates
Sustainable reform requires systemic change. Without modernised organisational structures, stronger accountability, and aligned incentives across divisions, financial recovery will remain out of reach. An integrated, performance-oriented model offers the most realistic path to operational efficiency and long-term viability.
Reforming loss-making institutions like Sri Lankan Airlines is not merely a matter of leadership change — it is a structural overhaul essential to ensuring these entities contribute productively to the national economy rather than remain perpetual burdens.
By Chula Goonasekera – Citizen Analyst
Features
Why Pi Day?

International Day of Mathematics falls tomorrow
The approximate value of Pi (π) is 3.14 in mathematics. Therefore, the day 14 March is celebrated as the Pi Day. In 2019, UNESCO proclaimed 14 March as the International Day of Mathematics.
Ancient Babylonians and Egyptians figured out that the circumference of a circle is slightly more than three times its diameter. But they could not come up with an exact value for this ratio although they knew that it is a constant. This constant was later named as π which is a letter in the Greek alphabet.
It was the Greek mathematician Archimedes (250 BC) who was able to find an upper bound and a lower bound for this constant. He drew a circle of diameter one unit and drew hexagons inside and outside the circle such that the sides of each hexagon touch the sides of the circle. In mathematics the circle passing through all vertices of a polygon is called a ‘circumcircle’ and the largest circle that fits inside a polygon tangent to all its sides is called an ‘incircle’. The total length of the smaller hexagon then becomes the lower bound of π and the length of the hexagon outside the circle is the upper bound. He realised that by increasing the number of sides of the polygon can make the bounds get closer to the value of Pi and increased the number of sides to 12,24,48 and 60. He argued that by increasing the number of sides will ultimately result in obtaining the original circle, thereby laying the foundation for the theory of limits. He ended up with the lower bound as 22/7 and the upper bound 223/71. He could not continue his research as his hometown Syracuse was invaded by Romans and was killed by one of the soldiers. His last words were ‘do not disturb my circles’, perhaps a reference to his continuing efforts to find the value of π to a greater accuracy.
Archimedes can be considered as the father of geometry. His contributions revolutionised geometry and his methods anticipated integral calculus. He invented the pulley and the hydraulic screw for drawing water from a well. He also discovered the law of hydrostatics. He formulated the law of levers which states that a smaller weight placed farther from a pivot can balance a much heavier weight closer to it. He famously said “Give me a lever long enough and a place to stand and I will move the earth”.
Mathematicians have found many expressions for π as a sum of infinite series that converge to its value. One such famous series is the Leibniz Series found in 1674 by the German mathematician Gottfried Leibniz, which is given below.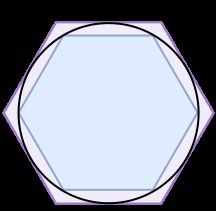
π = 4 ( 1 – 1/3 + 1/5 – 1/7 + 1/9 – ………….)
The Indian mathematical genius Ramanujan came up with a magnificent formula in 1910. The short form of the formula is as follows.
π = 9801/(1103 √8)
For practical applications an approximation is sufficient. Even NASA uses only the approximation 3.141592653589793 for its interplanetary navigation calculations.
It is not just an interesting and curious number. It is used for calculations in navigation, encryption, space exploration, video game development and even in medicine. As π is fundamental to spherical geometry, it is at the heart of positioning systems in GPS navigations. It also contributes significantly to cybersecurity. As it is an irrational number it is an excellent foundation for generating randomness required in encryption and securing communications. In the medical field, it helps to calculate blood flow rates and pressure differentials. In diagnostic tools such as CT scans and MRI, pi is an important component in mathematical algorithms and signal processing techniques.
This elegant, never-ending number demonstrates how mathematics transforms into practical applications that shape our world. The possibilities of what it can do are infinite as the number itself. It has become a symbol of beauty and complexity in mathematics. “It matters little who first arrives at an idea, rather what is significant is how far that idea can go.” said Sophie Germain.
Mathematics fans are intrigued by this irrational number and attempt to calculate it as far as they can. In March 2022, Emma Haruka Iwao of Japan calculated it to 100 trillion decimal places in Google Cloud. It had taken 157 days. The Guinness World Record for reciting the number from memory is held by Rajveer Meena of India for 70000 decimal places over 10 hours.
Happy Pi Day!
The author is a senior examiner of the International Baccalaureate in the UK and an educational consultant at the Overseas School of Colombo.
by R N A de Silva
Features
Sheer rise of Realpolitik making the world see the brink

 The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
As matters stand, there seems to be no credible evidence that the Indian state was aware of the impending torpedoing of the Iranian vessel but these acerbic-tongued politicians of Sri Lanka’s South would have the local public believe that the tragedy was triggered with India’s connivance. Likewise, India is accused of ‘embroiling’ Sri Lanka in the incident on account of seemingly having prior knowledge of it and not warning Sri Lanka about the impending disaster.
It is plain that a process is once again afoot to raise anti-India hysteria in Sri Lanka. An obligation is cast on the Sri Lankan government to ensure that incendiary speculation of the above kind is defeated and India-Sri Lanka relations are prevented from being in any way harmed. Proactive measures are needed by the Sri Lankan government and well meaning quarters to ensure that public discourse in such matters have a factual and rational basis. ‘Knowledge gaps’ could prove hazardous.
Meanwhile, there could be no doubt that Sri Lanka’s sovereignty was violated by the US because the sinking of the Iranian vessel took place in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While there is no international decrying of the incident, and this is to be regretted, Sri Lanka’s helplessness and small player status would enable the US to ‘get away with it’.
Could anything be done by the international community to hold the US to account over the act of lawlessness in question? None is the answer at present. This is because in the current ‘Global Disorder’ major powers could commit the gravest international irregularities with impunity. As the threadbare cliché declares, ‘Might is Right’….. or so it seems.
Unfortunately, the UN could only merely verbally denounce any violations of International Law by the world’s foremost powers. It cannot use countervailing force against violators of the law, for example, on account of the divided nature of the UN Security Council, whose permanent members have shown incapability of seeing eye-to-eye on grave matters relating to International Law and order over the decades.
The foregoing considerations could force the conclusion on uncritical sections that Political Realism or Realpolitik has won out in the end. A basic premise of the school of thought known as Political Realism is that power or force wielded by states and international actors determine the shape, direction and substance of international relations. This school stands in marked contrast to political idealists who essentially proclaim that moral norms and values determine the nature of local and international politics.
While, British political scientist Thomas Hobbes, for instance, was a proponent of Political Realism, political idealism has its roots in the teachings of Socrates, Plato and latterly Friedrich Hegel of Germany, to name just few such notables.
On the face of it, therefore, there is no getting way from the conclusion that coercive force is the deciding factor in international politics. If this were not so, US President Donald Trump in collaboration with Israeli Rightist Premier Benjamin Natanyahu could not have wielded the ‘big stick’, so to speak, on Iran, killed its Supreme Head of State, terrorized the Iranian public and gone ‘scot-free’. That is, currently, the US’ impunity seems to be limitless.
Moreover, the evidence is that the Western bloc is reuniting in the face of Iran’s threats to stymie the flow of oil from West Asia to the rest of the world. The recent G7 summit witnessed a coming together of the foremost powers of the global North to ensure that the West does not suffer grave negative consequences from any future blocking of western oil supplies.
Meanwhile, Israel is having a ‘free run’ of the Middle East, so to speak, picking out perceived adversarial powers, such as Lebanon, and militarily neutralizing them; once again with impunity. On the other hand, Iran has been bringing under assault, with no questions asked, Gulf states that are seen as allying with the US and Israel. West Asia is facing a compounded crisis and International Law seems to be helplessly silent.
Wittingly or unwittingly, matters at the heart of International Law and peace are being obfuscated by some pro-Trump administration commentators meanwhile. For example, retired US Navy Captain Brent Sadler has cited Article 51 of the UN Charter, which provides for the right to self or collective self-defence of UN member states in the face of armed attacks, as justifying the US sinking of the Iranian vessel (See page 2 of The Island of March 10, 2026). But the Article makes it clear that such measures could be resorted to by UN members only ‘ if an armed attack occurs’ against them and under no other circumstances. But no such thing happened in the incident in question and the US acted under a sheer threat perception.
Clearly, the US has violated the Article through its action and has once again demonstrated its tendency to arbitrarily use military might. The general drift of Sadler’s thinking is that in the face of pressing national priorities, obligations of a state under International Law could be side-stepped. This is a sure recipe for international anarchy because in such a policy environment states could pursue their national interests, irrespective of their merits, disregarding in the process their obligations towards the international community.
Moreover, Article 51 repeatedly reiterates the authority of the UN Security Council and the obligation of those states that act in self-defence to report to the Council and be guided by it. Sadler, therefore, could be said to have cited the Article very selectively, whereas, right along member states’ commitments to the UNSC are stressed.
However, it is beyond doubt that international anarchy has strengthened its grip over the world. While the US set destabilizing precedents after the crumbling of the Cold War that paved the way for the current anarchic situation, Russia further aggravated these degenerative trends through its invasion of Ukraine. Stepping back from anarchy has thus emerged as the prime challenge for the world community.
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoPeradeniya Uni issues alert over leopards in its premises
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoWinds of Change:Geopolitics at the crossroads of South and Southeast Asia
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoProf. Dunusinghe warns Lanka at serious risk due to ME war
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoRoyal start favourites in historic Battle of the Blues
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoHeat Index at ‘Caution Level’ in the Sabaragamuwa province and, Colombo, Gampaha, Kurunegala, Anuradhapura, Vavuniya, Hambanthota and Monaragala districts
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoThe final voyage of the Iranian warship sunk by the US














