Features
Are we slashing the nose to spite the face?

Amending 19th Amendment
By Austin Fernando (Former Secretary to the President)
Recently, the Cabinet of Ministers decided to amend/repeal (?) the 19th Amendment to the Constitution (hereinafter referred to as 19). The media divulged that the government would retain positive features of the 19 and remove the unwanted. Concurrently, to identify and recommend these a Committee of five was appointed
Background of 19
The 19 has a chronological evolution. For conceptual value, let us review one aspect – the public service. The 1947 Constitution enabled an independent Public Service Commission (PSC) for them.
In 1972, the Sirima Bandaranaike government placed the public service under a PSC but brought in the Cabinet control for operationalizing. Through the 1978 Constitution, the JR Jayewardene government also placed public servants under the control of the Cabinet. These were acts of continuous politicization.
The Chandrika Kumaratunga government, by the 17th Amendment (Article 54), depoliticized the public service and other democratic aspects by the appointment of a PSC nominated by a Constitutional Council (CC), consisting of politicians and civilians. Seven similar institutions (e.g., the Election Commission, National Police Commission) also were legislated on-demand.
The Mahinda Rajapaksa government passed the 18th Amendment to establish a government-biased “Parliamentary Council” (PC). The President snatched the depoliticization efforts under the 17th Amendment through Commissions.
By 2014, there were criticisms and deep dissatisfaction with politicization created by the actions of all political parties. This dissatisfaction created revitalized pressure for depoliticization. Ultimately, Mr. Maithripala Sirisena sought a mandate for the presidency on the depoliticization slogan. The 19 was the consequence. It is acknowledged that the passage of 19 would have inevitably failed, sans interventions of President Sirisena.
Are our politicians sticks in the mud?
 The responses of parliamentarians for depoliticization, in general, had been ridiculous. They supported depoliticization by President Kumaratunga (17A); supported politicization (18A) of President Mahinda Rajapaksa. They helped depoliticization (19A) by President Sirisena. Parliamentarians will sponsor the 20th Amendment to empower President Gotabaya Rajapaksa. Strengthening the hands of the already empowered seems a hobby of Parliamentarians!
The responses of parliamentarians for depoliticization, in general, had been ridiculous. They supported depoliticization by President Kumaratunga (17A); supported politicization (18A) of President Mahinda Rajapaksa. They helped depoliticization (19A) by President Sirisena. Parliamentarians will sponsor the 20th Amendment to empower President Gotabaya Rajapaksa. Strengthening the hands of the already empowered seems a hobby of Parliamentarians!
Political reactions created humour when a Minister recently declared that support for 19A was due to a promise made to change the electoral system, which of course, is a sheer necessity. Humorously and unfortunately, politicians who agree to change the Constitution on verbal agreements are elected to Parliament.
The clamor reinstatement of powers removed by 19
There is heavy orchestration that security and development would collapse with 19A. From 1978 to 2009, Sinhala and Tamil youth, especially in the North and East, revolted and thousands of innocents were killed or made to disappear, and suspects were killed in Police cells when Executive powers revoked by the 19A were with incumbent Presidents. The Executive powers were inevitably linked to the onset of conflicts. Therefore, it is a wiser step to find alternative solutions for enhancing human security than to demand the return of powers withdrawn by 19.
The same applies to development. Investment attraction during the tenure of President Jayewardene and infrastructural development during President Mahinda Rajapaksa’s (although both face criticisms) were positive moments before the 19th Amendment removed powers. Despite these powers being intact, some Presidents did not undertake such compelling development. I will not mention names to protect their dignity. Thus, one may argue that development isn’t constitution-centric but leader-centric.
There are shortcomings in the 19A since it is a human product. Before the General Election, President Sirisena said that 19A had good aspects, but its flaws should be rectified. He singled out some drawbacks but did not suggest a Deputy Premier post in the 20th Amendment. But it is rumored so.
Meantime, some like Minister Wimal Weerawansa and parliamentarian Gevindu Kumaratunga, who wished immediate abolishing of 19A during the election campaign, now demand a new Constitution instead of patchworking 19 (e. g., dual citizenship issue). It is unknown why this change of heart. Guess is yours!
The President has made a firm statement on the 20th Amendment in his Throne Speech. Therefore, President Sirisena may have to support the abolishing of 19A. In politics, sacrificing principles for partisanship, hollow promises, and tribal branding are acceptable!
The significant changes in 19A are categorized under, change in the qualifications for presidency and powers of the President, enhancement of the capabilities of the Legislature (= Prime Minister), empowerment of Commissions by the Legislature, and the Right to Information.
Changing powers of the President
It is already stated that Articles 30 (2) and 31 (2) of 19, related to the five-year term of office of the President and the two terms in office and the Right to Information Act, would not be amended.
But the government would need the power to dissolve the Parliament without parliamentary consent or completing the four and half years mentioned in 70(1). While President Jayewadene has taught lessons on using alternative powers (i.e., Referendum) not to dissolve, the present government authorities otherwise learned negative lessons in October 2018.
Also, dual citizens are no longer allowed to be Parliamentarians. [Article 91 (d) (xiii)]. Critics who protest dual citizen Arjuna Mahendran appointed as Governor of the Central Bank do not mind a dual citizen becoming a parliamentarian, Minister, Prime Minister or President. Those who support Minister Namal Rajapaksa’s presidential aspirations (if any) seem not to understand that the change of dual citizenship could jeopardize this aspiration by introducing a competitor. Is the demand by some for a brandnew Constitution instead of amending 19 a response for this potential jeopardy?
When queried on these changes, Ministers GL Peiris and Wimal Weerawansa said that constitutional changes should not be person-centric. Based on Minister Peiris referring to Basil and Namal Rajapaksas by name, if the contention is that 19A was person-centric and has disadvantaged selected persons, then the 20th Amendment raises the question of awarding person-centric advantages to another.
Presidential and National Security
Under Article 43 (2) of 19, the Minister of Defense must be appointed from among the Members of Parliament. It is so in other countries that have more significant defence risks (e.g., India). Now the societal belief is that the President is the Minister of Defence. If true, the President has illegally “snatched” the subject of defence. Nevertheless, I passionately believe that the security function should constitutionally remain with the President.
I take this stance on constitutional grounds, quite impersonally. Article 4 (b) of our Constitution stipulates that the “executive power of the people, including the defence of Sri Lanka,” must be exercised by the President. The term defence’ is a specially chosen here. The President has the power and duty to “declare war and peace” [Article 33 (2) (g)]. The appointment of Military Commanders and the Police Chief is a presidential power (Article 61E), and, under Article 33A, the President is accountable to the Parliament on laws applicable to public security. Accountability to Parliament is about the President’s “own” powers, and not of another Defence Minister. The Ministry of Defence/relevant institutions must be under him to fulfil these functions.
When the President is held accountable for the duties performed by another Defence Minister, he is subjected to moral injustice, and the presidency is demeaned. The security/defence of the country is a constitutional responsibility of the President, and the 19th Amendment should be amended to strengthen his hands on defence and security. Technically “snatching security/defence” as purportedly done now is unacceptable. Also, he should not snatch other ministries on this basis, although he may prefer.
Increasing powers of the Legislature and PM
Sovereignty is “exercised and enjoyed” by the tripod Executive, the Legislature, and the Judiciary under Articles 4 (a), (b), and (c) of our Constitution. But what is heard, seen, and said now insinuates that all three functions should be left to the Executive. It seems to be the government’s political stance. It is not constitutional and decimates democracy.
When the Legislature is considered, the power of the President is weakened in several ways. Examples include the appointment of Ministers [(43(2)], non-Cabinet Ministers [[44(1)] ‘on the advice’ of the Prime Minister [43(2)] and remove any one of them on prime ministerial advice [Article 46 (3)(a)]. The power to remove the Prime Minister or any Minister was with the President [47(a)] in the 1978 Constitution.
The number of Ministers is decided by Article 46(1)(a) and (b). With 145 parliamentarians supporting the government President may opt to reward more portfolios and will require amending it.
Article 44(2) of the 1978 Constitution permits any subject or function unassigned to a Minister to be left with the President. This power was removed by 19, and the 20th Amendment may return this power to the President.
The sudden removal of the Prime Minister (as President Kumaratunga did in 2004 and President Sirisena in October 2018) [70(1)(a) of 1978 Constitutionn] is prohibited now. Such restriction is necessary for the stability of the Legislature and the country. Still, I think the 20th Amendment can be used to prevent the judiciary from rejecting such courses of action.
In this connection, the dissolution of the Cabinet and removal of the Prime Minister were issues. During the October 2018 constitutional crisis, it was argued that the President had this power over Article 48 (1) of the Constitution (Sinhala version), which is not in the English version. The judiciary rejected this. Any President will inevitably rush to regain that decisive power.
However, the extent to which these perfections are democratic is most questionable.
Duties of the CC
The CC plays a leading role in depoliticization in 19A. After abolishing 19A, the alternative to the CC could be the passage of an instrument closest to the 18th Amendment. Further provisions can be added as appropriate to concentrate power in the Executive. The 17th and 19th Amendments proposed a CC (including Members of Parliament and civilians). The 18th Amendment appointed a “Parliamentary Council” (PC) consisting of only Members of Parliament. It was total politicization. Although the PC could make nominations to the Commissions and Scheduled Offices in the 18, the President was allowed constitutionally to overrule them. The 19A allowed these appointments to be made only on recommendations of the CC [Article (41B (1)]. If the President did not appoint them within two weeks, they were considered “as deemed to have been appointed.” [Article [41B (4)] It prevented the President’s ‘monopoly’ of appointing. The President would like to use the 20th Amendment to remove these strictures on him.
Appointments under the 19A were mostly acceptable. The best evidence of the independence of the CC was observed when it (inclusive of Opposition membership) rejected two nominations made by President Sirisena to the Supreme Court and the Court of Appeal. On a handful of occasions when the President did not agree to appoint some of the nominees to Commissions, they were successfully reconciled through dialogue. The CC should not be the cat’s paw of the President; nor should the CC be a dictator. Amendments to 19A for efficient and transparent operationalization of the CC could be undertaken now. But what the government needs is to win, at all costs, because of its two-thirds majority!
Critics of the CC highlight the failure to appoint a Police Chief and the conduct of a Member of the Election Commission. To correct these, they demand abolishing the Commissions! The former, I believe, is a result of public service disciplinary procedures that cannot be ignored by the National Police Commission. Critics could have sought legal redress if Article 41A (8) of the Constitution was insufficient to discipline this Member. Providing in 20th Amendment remedies for such will be more effective than crushing the CC. One should not slash the nose to spite the face!
Another complaint is that even the President cannot appoint a judge. The reason may be the failure of President Sirisena to appoint two persons nominated by him to the judiciary. There were Opposition members in the CC when those decisions were made. Yet, they do not accept these reasonable decisions. These are victories for democracy. Also, they are silent that the CC also considers Chief Justice’s recommendations.
If the monopoly on appointing judges is given to the President, there will be no space for objections in the CC. The President is a ‘political product.’ He is a human being. Therefore, the President can appoint his supporters to higher judicial posts from his professional organizations if he so wishes. The President must respect Lord Chief Justice Hewart’s maxim that justice should not only be done but should be seen to have been done.
Of course, one can criticise the CC for some questionable appointments. Again without slashing the nose to spite the face, the 20th Amendment could propose cleaner operational guidelines. In a country where judicial appointments were made (though rarely) based on personal consideration before the 19A, these critics should value the CC machinery as superior to pure presidential whim and fancy.
Information law and action
Some question whether the Right to Information Act is adequately implemented due to deliberated delays by the authorities. Although this is not changed, it is appropriate to strengthen operations through the 20th Amendment. I note that not only the RTI Act but also other Commissions may require similar legal changes.
The value of caution
It is not surprising that a two-thirds majority or a government capable of manipulating that superpower would somehow pursue achieving its goals. Everyone who came to power thought that power was eternal, though it is impermanent. It is also not surprising seeing leadership that utilized the 18th Amendment attempting to regain lost powers. Even the present Opposition may pray for rejuvenation of powers of the 1978 Constitution; because politicians are greedy for power. Therefore, it is not surprising that they are also fluid about 20A.
But it should be kept in mind that if a constitution that cannot be amended again without a 2/3 majority is promulgated today, it could endanger the constitutional complexity another day. The vision and aspirations of the incumbent President may be pure. He may not be entertaining dictatorial goals, as alleged. But we must not be blind, that one day someone like Robert Mugabe or Idi Amin will not emerge. Therefore, it would be better to fertilize democracy without cutting the nose to spite the face when dealing with 19A.
Features
A life in colour and song: Rajika Gamage’s new bird guide captures Sri Lanka’s avian soul

Sri Lanka wakes each morning to wings.
From the liquid whistle of a magpie robin in a garden hedge to the distant circling silhouette of an eagle above a forest canopy, birds define the rhythm of the island’s days.
Their colours ignite the imagination; their calls stir memory; their presence offers reassurance that nature still breathes alongside humanity. For conservation biologist Rajika Gamage, these winged lives are more than fleeting beauty—they are a lifelong calling.
Now, after years of patient observation, artistic collaboration, and scientific dedication, Gamage’s latest book, An Illustrated Field Guide to the Fauna of Sri Lanka – Birds, is set to reach readers when it hits the market on March 6.
The new edition promises to become one of the most comprehensive and visually rich bird guides ever produced for Sri Lanka.
Speaking to The Island, Gamage reflected on the inspiration behind his work and the enduring fascination birds hold for people across the country.
“Birds are an incredibly diverse group,” he said. “Their bright colours, distinct songs and calls, and showy displays contribute to their uniqueness, which is appreciated by all bird-loving individuals.”
Birds, he explained, occupy a special place in the natural world because they are among the most visible forms of wildlife. Unlike elusive mammals or secretive reptiles, birds share human spaces openly.
“Birds are widely distributed in all parts of the globe in large enough populations, making them the most common wildlife around human habitations,” Gamage said. “This offers a unique opportunity for observing and monitoring their diverse plumage and behaviours for conservation and recreational purposes.”
This accessibility has made birdwatching one of the most popular forms of wildlife observation in Sri Lanka, attracting everyone from seasoned scientists to curious schoolchildren.
A remarkable island of avian diversity
Despite its small size, Sri Lanka possesses extraordinary bird diversity.
According to Gamage, the country’s geographic position, varied climate, and diverse habitats—from coastal wetlands and rainforests to montane cloud forests and dry-zone scrublands—have created ideal conditions for birdlife.
“Sri Lanka is home to a rich diversity of birdlife, with a total of 522 bird species recorded in the country,” he said. “These species are spread across 23 orders, 89 families, and 267 genera.”
Of these, 478 species have been fully confirmed. Among them, 209 are breeding residents, meaning they live and reproduce on the island throughout the year.
Even more remarkable is Sri Lanka’s high level of endemism.
“Thirty-five of these breeding resident species are endemic to Sri Lanka,” Gamage noted. “They are confined entirely to the island, making them globally significant.”
These endemic species—from forest-dwelling flycatchers to vividly coloured barbets—represent evolutionary lineages shaped by Sri Lanka’s long geological isolation and ecological uniqueness.
In addition to resident birds, Sri Lanka also serves as a seasonal refuge for migratory species traveling thousands of kilometres.
“There are regular migrants that arrive annually, as well as irregular migrants that visit less predictably,” Gamage explained. “Vagrants, birds that appear outside their typical migratory routes, have also been spotted occasionally.”
Such unexpected visitors often generate excitement among birdwatchers and scientists alike, providing valuable insights into migration patterns and environmental change.
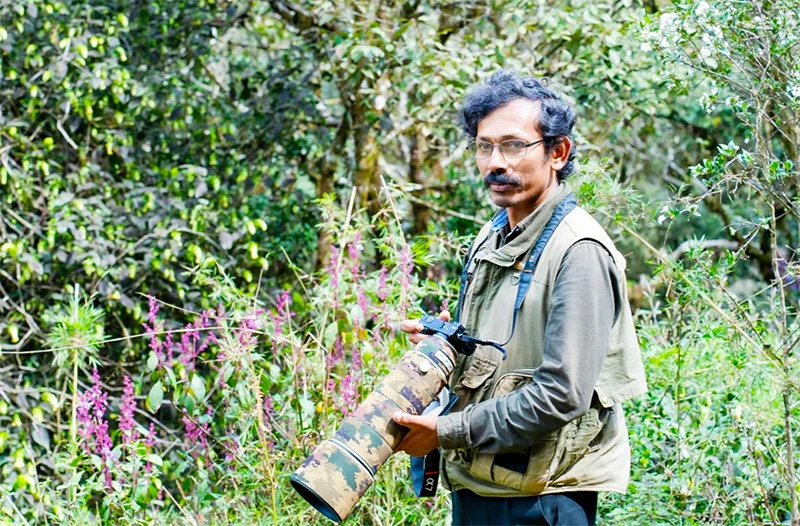

Rajika Gamage
A guide born from passion and necessity
The new field guide represents the culmination of years of research and builds upon Gamage’s earlier publication, which was released in 2017.
“The stimulus for this bird guide was due to the success of my first book,” he said. “This new edition aims to facilitate identification and provide an idea of what to look for in observed habitats or regions.”
The book is designed not merely as a scientific reference but as an accessible companion for anyone interested in birds. Its structure reflects this dual purpose.
“The first section is dedicated to the introduction, geography, and life history of Sri Lankan birds,” Gamage explained. “The second section is the main body of the guide, which illustrates 532 species of birds.”
Each illustration has been carefully crafted in colour to capture the distinctive plumage of each species.
“All illustrations are designed to show each bird’s significant and distinct plumage,” he said. “Where possible, the breeding, non-breeding, and juvenile plumages are provided.”
This attention to detail is especially important because many birds change appearance as they mature.
“Some groups, especially gulls, display many plumages between juveniles and adults,” Gamage noted. “Many take several years to develop full adult plumage and pass through semi-adult stages.”
By illustrating these stages, the guide helps birdwatchers avoid misidentification and deepen their understanding of avian development.
New discoveries and evolving science
One of the most exciting aspects of the new edition is its inclusion of newly recorded species and updated scientific classifications.
“Changes in the bird list of Sri Lanka, especially newly added endemic birds such as the Sri Lankan Shama, Sri Lanka Lesser Flameback, and Greater Flameback, are now included,” Gamage said.
Scientific names and classifications are not static; they evolve as researchers learn more about genetic relationships and species boundaries. The guide reflects these changes, ensuring it remains scientifically current.
The book also incorporates conservation status information based on the latest National Red Data Report and global assessments.
“The conservation status of Sri Lankan birds, as listed in the 2022 National Red Data Report and the global Red Data Report, are included,” Gamage said.
This information is vital for conservation planning and public awareness, highlighting which species face the greatest risk of extinction.
The guide also documents rare and accidental visitors, including species such as the Blue-and-white Flycatcher, Rufous-tailed Rock-thrush, and European Honey-buzzard.
“These represent accidental visitors and newly recorded vagrants,” Gamage said. “Altogether, the first edition offers some 25 additional species, all illustrated.”
Art and science in harmony
Unlike many field guides that rely heavily on photographs, Gamage’s book emphasises detailed illustrations. This choice reflects the unique advantages of scientific art.
Illustrations can emphasise diagnostic features, eliminate distracting backgrounds, and present birds in standardised poses, making identification easier.
“The principal birds on each page are painted to a standard scale,” Gamage explained. “Flight and behavioural sketches are shown at smaller scales.”
The guide also includes descriptions of habitats, distribution, nesting behaviour, and alternative names in English, Sinhala, and Tamil.
“The majority of birds have more than one English, Sinhala, and Tamil name,” he said. “All of these are included.”
This multilingual approach reflects Sri Lanka’s cultural diversity and ensures the guide is accessible to a wider audience.
A tool for conservation and connection

Beyond its scientific value, Gamage believes the book serves a deeper purpose: strengthening the bond between people and nature.
By helping readers identify birds and understand their lives, the guide fosters appreciation and responsibility.
“This field guide aims to facilitate identification and provide a general introduction to birds,” he said.
In an era of rapid environmental change, such knowledge is essential. Habitat loss, climate change, and human activity continue to threaten bird populations worldwide, including in Sri Lanka.
Yet birds also offer hope.
Their presence in gardens, wetlands, and forests reminds people of nature’s resilience—and their own role in protecting it.
Gamage hopes the guide will inspire both seasoned ornithologists and beginners alike.
“All these changes will make An Illustrated Field Guide to the Fauna of Sri Lanka – Birds one of the most comprehensive and accurate guides available within Sri Lanka,” he said.
A lifelong devotion takes flight
For Rajika Gamage, birds are not merely subjects of study—they are companions in a lifelong journey of discovery.
Each call heard at dawn, each silhouette glimpsed against the sky, each feathered visitor from distant lands reinforces the wonder that first drew him to ornithology.
With the release of his new book on March 6, that wonder will now be shared more widely than ever before.
In its pages, readers will find not only identification keys and scientific facts, but also something more enduring—the story of an island, told through wings, colour, and song.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
Letting go: A Buddhist perspective

Buddhism, one of the world’s oldest religions, offers profound insights into the nature of existence and the ways we can alleviate our suffering. As one of the world’s most profound spiritual traditions, it offers a transformative solution: the art of letting go. Unlike simply losing interest in things or giving up, letting go in Buddhism is about liberation, releasing ourselves from the chain of attachment that prevents us from experiencing true peace and happiness. Letting go is a profound philosophical concept in Buddhism, deeply intertwined with an understanding of suffering, attachment, and the nature of reality. This philosophy encourages us to release our grip on desires, attachments, and on what we hold dear- whether relationships, material goods, or even their identities, ultimately leading to greater peace and enlightenment. Our tendency to cling tightly to the various aspects of life leads to a significant source of stress. We tend to grasp at things, perceiving them as solid and permanent, yet much of what we hold onto is transient and subject to change. This mistaken belief in permanence can trap us in cycles of worry, fear, and anxiety.
The challenge of letting go is especially evident during difficult periods in life. We may find ourselves ruminating over lost opportunities, failed relationships, and unmet expectations. Such thoughts can keep us ensnared in emotions like hurt, guilt, and shame, hindering our ability to move forward. By holding onto the past, we often prevent ourselves from embracing the present and future.
At the heart of Buddhist practice lies the concept of letting go, often encapsulated in the term “non-attachment.” Letting go is a crucial concept in both Buddhism and Christianity, emphasising the release of attachments that bind us and contribute to our suffering. At its core, letting go is about finding freedom from desires and acknowledging that both relationships and material possessions are fleeting and transient.
In Buddhism, letting go, or non-attachment, is fundamental for achieving inner peace. The First Noble Truth acknowledges that life is filled with suffering, often rooted in our cravings and attachment to things. The Second Noble Truth teaches that by letting go of this craving, we can transcend the cycles of life and attain enlightenment.
Spiritually, Buddhism emphasises the impermanence of all things (annica). We tend to cling to people, experiences, and even our identities, but everything is fleeting. Recogniing this helps us appreciate the present moment and fosters compassion. Instead of allowing attachments to cloud our relationships, letting go encourages us to engage with others without judgment or expectation, fostering deeper connections.
Philosophically, Buddhism challenges the notion of a permanent self (anatta) that is often the focus of human attachment. It teaches that our identity is not a fixed entity but a collection of experiences and perceptions in constant flux. Understanding this can help us see the futility of clinging to desires and identities, paving the way for a liberated state of being built on wisdom cultivated through meditation and mindfulness.
From a psychological standpoint, letting go can significantly improve our emotional health and well-being. Attachment often breeds fear, anxiety, and stress, while non-attachment promotes resilience and adaptability. When we embrace the idea of impermanence, we become more capable of handling life’s challenges without being overwhelmed. Mindfulness—being present and accepting our emotions without judgment—allows us to process difficult feelings constructively, making it easier to let go of what we cannot control.
Letting go is also an essential concept in Christianity, which emphasises surrender and trust in God. Biblical teachings encourage believers to let go of worries and anxieties, placing their faith in divine providence. For instance, verses like Matthew 6:34 remind individuals not to be anxious about tomorrow, but to focus on the present. By surrendering our burdens to God, we find peace and freedom from the weight of excessive attachment.
Moreover, both traditions highlight the importance of community. In Buddhism, the sangha, or community of practitioners, supports individuals on their journeys toward non-attachment. Similarly, the Christian community encourages believers to lean on one another for support, fostering a sense of belonging and shared faith that helps mitigate the loneliness that comes with attachment.
Ultimately, the concept of letting go serves as a powerful antidote to suffering in both Buddhism and Christianity. By embracing impermanence, cultivating wisdom, and practising mindfulness or faith, individuals can experience profound liberation. In our chaotic world, the principles of letting go offer a clear path toward inner peace, fulfilment, and deeper connections with ourselves, others, and the divine.
Buddhism explores the profound concept of letting go, providing valuable insights into the human experience and pathways to alleviating suffering. Rooted in one of the world’s oldest spiritual traditions, Buddhism presents letting go as a transformative practice, distinct from mere disengagement or giving up. Instead, it encompasses liberation from the chains of attachment that hinder us from experiencing genuine peace and happiness. Christianity too explore this profound concept in its teachings
At the core of Buddhist philosophy lies the idea of non-attachment, which encourages individuals to free themselves from desires and possessions, ultimately leading to tranquility and enlightenment. Letting go is intertwined with an understanding of suffering, attachment, and the transient nature of existence. This philosophy instructs us to relinquish our grip on what we hold dear—whether relationships, material goods, or even our identities—recognising that these are impermanent.
Buddhism’s First Noble Truth acknowledges that life inherently involves suffering, often stemming from our cravings and attachments. The Second Noble Truth reveals that overcoming this craving is key to transcending the cycles of life and achieving enlightenment. Emphasising the impermanence of all things, Buddhism invites us to appreciate the present moment and fosters compassion by helping us detach from fixed identities and experiences. This awareness enriches our relationships, allowing us to connect with others free from judgment or expectation.
Philosophically, Buddhism challenges the notion of a static self (anatta), asserting that our identity is not a fixed concept but rather a fluid collection of experiences. Recognising this notion helps highlight the futility of clinging to desires and identities, opening the door to a liberated existence founded on wisdom cultivated through meditation and mindfulness practices.
From a psychological perspective, the act of letting go can significantly enhance emotional health and well-being. Attachment often fuels fear, anxiety, and stress, while embracing non-attachment cultivates resilience and adaptability. By accepting impermanence, we equip ourselves to face life’s challenges with greater ease. Practicing mindfulness—being present and accepting emotions without judgment—further facilitates the process of releasing what is beyond our control.
In Christianity, the theme of letting go is also prominent, emphasizing surrender and trust in God. Scripture encourages believers to release their worries and anxieties by placing their faith in divine providence. For example, Matthew 6:34 advises individuals to focus on the present rather than fret over the future. By surrendering our burdens to God, we can experience relief from the weight of excessive attachment.
Both traditions underscore the significance of community in supporting the journey of letting go. In Buddhism, the sangha, or community of practitioners, encourages the pursuit of non-attachment. Likewise, Christian fellowship fosters belonging and shared faith, helping believers lean on one another for strength and mitigating the loneliness that can arise from attachment.
Ultimately, the concept of letting go serves as a powerful antidote to suffering in both Buddhism and Christianity. Embracing impermanence, nurturing wisdom, and practising mindfulness or trust can lead individuals toward profound liberation. In an increasingly chaotic world, the principles of letting go illuminate a pathway to inner peace, fulfilment, and deeper connections with ourselves, others, and the divine. By understanding and embodying this philosophy, we can navigate life’s complexities with grace and openness.////Buddhism delves into the profound concept of letting go, offering valuable insights into the human experience and pathways to alleviating suffering. As one of the world’s oldest spiritual traditions, Buddhism presents letting go as a transformative practice that goes beyond mere disengagement or resignation. It represents liberation from the chains of attachment that prevent us from experiencing true peace and happiness. Similarly, Christianity explores this profound concept in its teachings.
At the heart of Buddhist philosophy is the idea of non-attachment, which encourages individuals to free themselves from desires and possessions, ultimately leading to tranquility and enlightenment. Letting go is closely related to an understanding of suffering, attachment, and the impermanent nature of existence. This philosophy guides us to loosen our hold on what we cherish—be it relationships, material possessions, or even our own identities—recognizing that everything is transient. Through this understanding, we can cultivate a deeper sense of peace and fulfillment in our lives.
 BY Dr. Justice Chandradasa Nanayakkara
BY Dr. Justice Chandradasa Nanayakkara
Features
Brilliant Navy officer no more
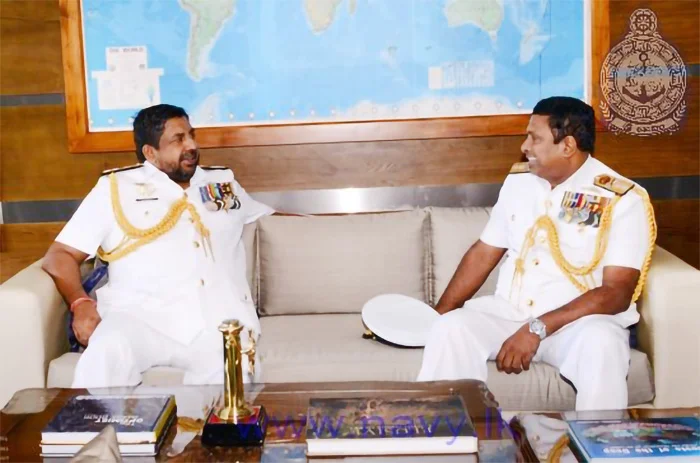

Rear Admiral Udaya Bandara, VSV, USP (retired)
This incident happened in 2006 when I was the Director Naval Operations, Special Forces and Maritime Surveillance under then Commander of the Navy Vice Admiral Wasantha Karannagoda. Udaya (fondly known as Bandi) was a trusted Naval Assistant (NA) to the Commander.
We were going through a very hard time fighting the LTTE Sea Tigers’ explosive-laden suicide boats that our Fast Attack Craft (s) and elite SBS’ Arrow Boats encountered in our littoral sea battles.
Brilliant Marine Engineer Commander (then) Chaminda Dissanayake, who was known for his “out of the box” thinking and superior technical skills on research and development, met me at my office at Naval Headquarters and showed me a blueprint of an explosive- laden remotely controlled small boat.
Udaya’s Naval Assistant’s office was next to mine, the Director Naval Operations office. Both places are very close to the Navy Commander’s office. I walked into Bandi’s office with Commander Dissa and showed this blueprint a brilliant idea. Being a Marine Engineer “par excellence”, Bandi immediately understood the great design. I urged him to brief the Commander of the Navy with Commander Dissa.
My burden was over! Bandi took over the project and within a few weeks we tested our first prototype “Explosive-laden Remotely Controlled arrow boat “at sea off Coral Cove in the Naval Base Trincomalee. It was a complete success.
This remotely controlled boats went out to sea with our SBS arrow boats fleet and had devastating effects against LTTE suicide boats and their small boats fleet. Thanks, Bandi, for your contribution. The present-day Admiral of the Fleet used to tell us during those days “you cannot buy a Navy – you have to build one”!
We built our own small boats squadrons at our boat yards in Welisara and Trincomalee to bring LTTE Sea Tigers. The Special Boats Squadron (SBS) and rapid action boats squadron (RABS) being so useful with remotely controlled explosive-laden arrow boats to win sea battles convincingly.
Bandi used to say, “Navy is a technical service and we should give ALL SRI LANKA NAVY OFFICERS FIRST A TECHNICAL DEGREE AT OUR ACADEMY (BTec degree).” That idea did not receive much attention here, but the Indian Navy—Bandi graduated as a Marine Engineer- at Indian Navy Engineering College SLNS Shivaji in Lonavala, Pune, India— understood this idea well over two decades ago. Indian Navy Commissioned their new Naval Academy at Ezhimala (in Kerala State) which is the largest Naval Academy in Asia (Campus covers area of 2,452 acres) starts its Naval officers training with a BTech degree, regardless of what branch of the navy one joined.
Bandi’s technical expertise was not limited to SLN. He was the pioneer of “Mini – Hydro Power projects” in Sri Lanka. When I was a young officer, he urged me to invest some money in one of these projects and advised me “Sir! as long as water flows through turbines, you will get money from the CEB, which is always short of electricity”. I regret that I did not heed Bandi’s advice.
When he worked under me when I was Commander Southern Naval Area, as my senior Technical Officer, I observed pencil marks on walls of his chalet and I inquired from him what they were. He said it was the result of his “pencil shooting training”, a drill Practical Pistol Firers do to improve their skills. He used to practice “draw and fire” drills and pencil shooting drills late into nights to be a good Practical Pistol firer in Sri Lanka Navy team. He didn’t stop at that. He represented Sri Lanka National Practical Pistol Firing team and won International Championships.
As the Officer in charge of Technical Training in the Navy, he worked as Training Commander to train Royal Oman Navy Engineering Artificers in Sri Lanka, especially on Fast Attack Craft Main Engine Overhauls. The Royal Oman Navy Commander was so impressed with the knowledge acquired by Artificers that he donated money for the construction of a four-storey accommodation building for Sri Lanka Navy Naval and Maritime Academy, Trincomalee now known as “Oman Building”. The credit for this project should go to Bandi.
Bandi’s wife was a senior Judge of Kegalle High Court, and she retired a few years ago. Their only child, a son studied at the British School, Colombo and followed in his mother’s footsteps became a lawyer. Bandi was so much attached to his family and very proud of his son’s accomplishments.
When Bandi was due to retire in 2016 as a Rear Admiral and Director General Training, after distinguished service of 34 years, and reaching retirement age of 55 years, I requested him to serve for some more years after mobilising him into our Naval Reserve Force. He had other plans. He wanted to take his mini-Hydro Power projects to East African countries.
His demise after a very brief illness at age of 64 years was a shock to his family and friends. His funeral was held on Feb. 27 with Full Military Honors befitting a Rear Admiral at his home town Aranayake.
Dear Bandi, the beautiful Sri Lanka Navy, Naval and Maritime Academy in Trincomalee, which was built with your efforts will serve for Sri Lanka Navy Officer Trainees and sailors for a very long time and remember you forever.
May dear Bandi attain the supreme bliss of Nirvana!

Naval and Maritime Academy, Trincomalee
By Admiral Ravindra C Wijegunaratne
WV, RWP and Bar, RSP, VSV, USP, NI (M) (Pakistan), ndc, psn, Bsc
(Hons) (War Studies) (Karachi) MPhil (Madras)
Former Navy Commander and Former Chief of Defence Staff
Former Chairman, Trincomalee Petroleum Terminals Ltd,
Former Managing Director Ceylon Petroleum Corporation,
Former High Commissioner to Pakistan
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-
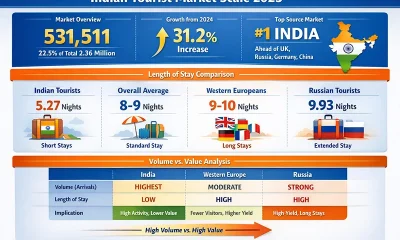
 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBuilding on Sand: The Indian market trap
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoFuture must be won
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog partners with Xiaomi to introduce Redmi Note 15 5G Series in Sri Lanka
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository
-

 Sports7 days ago
Sports7 days agoCEA halts development at Mandativu grounds until EIA completion













