Opinion
Addressing loss and damage finance: It’s more than money
BY Ashish Barua
The main objective of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is to stabilise greenhouse gas (GHG) concentration in Earth’s atmosphere. Over the last three decades, it has achieved the opposite because of our indifference and disregard for the millions of climate-vulnerable people in Global South, now extended to the North as well, who are suffering the adverse impacts of climate change. The UNFCCC started with a focus on mitigation and gradually moved on to adaptation. It is evident that those are not enough, and tackling “loss and damage” is a must-do now.
The 19th climate conference, held in Warsaw, Poland in 2013, established the Warsaw International Mechanism (WIM), which works as a policy framework on the issue of loss and damage. Then the Santiago Network on Loss and Damage (SNLD) at COP25 started as a technical assistance provider in addition to knowledge and resources. However, the financial mechanism has remained a big question for a long time.
The good news came ahead of COP27 when issues related to funding arrangements to respond to loss and damage caused by human-induced climate change were incorporated as a sub-agenda under finance-related matters. After having different opinions, debates, and negotiations throughout the two-week-long climate conference in Egypt this year, the parties found a common ground and agreed on the finance mechanism for loss and damage during the extended period.
So COP27 decided to establish a new funding arrangement to assist developing countries regarding loss and damage, which is “new and additional.” It also decided to establish a fund and a Transitional Committee to operationalise the new funding arrangement. The committee has been suggested to make recommendations to operationalise the funding arrangement at COP28 due to be held in Dubai next year, which will be a critical outline for how the funds are mobilised and utilised.
To make the fund operational, the parties also agreed to establish institutional arrangements, modalities, structure, governance, and terms of reference; define the elements of the new funding arrangements; identify and expand funding sources; and ensure coordination and complementarity with the existing arrangements.
There will be critical challenges for the Transitional Committee, such as who will provide the fund or how the new fund will be generated, and how it will be utilised. etc.
Beyond the UNFCCC process, there has been good news. The Scottish government, the pioneer in loss and damage funding, has come forward with its enhanced pledges. The Wallonia province of Belgium and Denmark were also there with their commitment; Austria and New Zealand also came forward, creating peer pressure on Global North to come out of their backsliding mindset.
They came forward with their actions on two fundamental principles. The first one is climate justice, challenging the unjust impact on climate-vulnerable nations who are not responsible for the crisis. The second one is moral obligations, and the responsibility of the developed countries.
The solidarity of the global community must be at the centre of the loss and damage finance facility. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has presented enormous scientific evidence, enough data and information on the table. The gravity, scope, and frequency of loss and damage are growing all over the world. Hence, the parties to the climate change convention must take an informed political position and enhanced pledges. The developed and developing countries’ accountability now is to keep the positive spirit up so that the empty promise of USD 100 billion every year for adaptation is not repeated.
Most importantly, climate-vulnerable nations and communities live amid the effects of climate change; they act, respond, and know how to address loss and damage on the ground. They do it with their best efforts and the least resources – they need support to do it right. And here comes the question of solidarity and empathy, which is more valuable than money.
As the loss and damage funding arrangement is already agreed upon, the fund mechanisms are critical as community needs are urgent and need to be grounded. For developing countries, this will work only if the fund is accessible, flexible, and fast to deliver to the affected communities, unlike other funding facilities such as the Green Climate Fund and Global Environment Facility. It is essential to determine how much funding is reaching the affected communities and, with this, how fast they can address the loss and damage issues in their lives and livelihoods.
Climate-vulnerable countries can take a proactive role in feeding the Transitional Committee with their actions on the ground so that the committee can go ahead with the right information and inputs. For example, Bangladesh has earmarked its fund from the Climate Change Trust Fund, which can put real-life learning to use. Helvetas Bangladesh, Young Power in Social Action, and the International Centre for Climate Change and Development (ICCCAD) are partnering with the Scottish government and Climate Justice Resilience Fund, which can help put actions forward in both economic and non-economic sectors of loss and damage.
(The Daily Star/ANN)
Ashish Barua is programme manager for the Climate Change and Sustainable Development programme of Helvetas Swiss Intercooperation in Bangladesh.
Opinion
Disasters do not destroy nations; the refusal to change does

Sri Lanka has endured both kinds of catastrophe that a nation can face, those caused by nature and those created by human hands. A thirty-year civil war tore apart the social fabric, deepening mistrust between communities and leaving lasting psychological wounds, particularly among those who lived through displacement, loss, and fear. The 2004 tsunami, by contrast, arrived without warning, erasing entire coastal communities within minutes and reminding us of our vulnerability to forces beyond human control.
These two disasters posed the same question in different forms: did we learn, and did we change? After the war ended, did we invest seriously in repairing relationships between Sinhalese and Tamil communities, or did we equate peace with silence and infrastructure alone? Were collective efforts made to heal trauma and restore dignity, or were psychological wounds left to be carried privately, generation after generation? After the tsunami, did we fundamentally rethink how and where we build, how we plan settlements, and how we prepare for future risks, or did we rebuild quickly, gratefully, and then forget?
Years later, as Sri Lanka confronts economic collapse and climate-driven disasters, the uncomfortable truth emerges. we survived these catastrophes, but we did not allow them to transform us. Survival became the goal; change was postponed.
History offers rare moments when societies stand at a crossroads, able either to restore what was lost or to reimagine what could be built on stronger foundations. One such moment occurred in Lisbon in 1755. On 1 November 1755, Lisbon-one of the most prosperous cities in the world, was almost completely erased. A massive earthquake, estimated between magnitude 8.5 and 9.0, was followed by a tsunami and raging fires. Churches collapsed during Mass, tens of thousands died, and the royal court was left stunned. Clergy quickly declared the catastrophe a punishment from God, urging repentance rather than reconstruction.
One man refused to accept paralysis as destiny. Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, later known as the Marquês de Pombal, responded with cold clarity. His famous instruction, “Bury the dead and feed the living,” was not heartless; it was revolutionary. While others searched for divine meaning, Pombal focused on human responsibility. Relief efforts were organised immediately, disease was prevented, and plans for rebuilding began almost at once.
Pombal did not seek to restore medieval Lisbon. He saw its narrow streets and crumbling buildings as symbols of an outdated order. Under his leadership, Lisbon was rebuilt with wide avenues, rational urban planning, and some of the world’s earliest earthquake-resistant architecture. Moreover, his vision extended far beyond stone and mortar. He reformed trade, reduced dependence on colonial wealth, encouraged local industries, modernised education, and challenged the long-standing dominance of aristocracy and the Church. Lisbon became a living expression of Enlightenment values, reason, science, and progress.
Back in Sri Lanka, this failure is no longer a matter of opinion. it is documented evidence. An initial assessment by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) following Cyclone Ditwah revealed that more than half of those affected by flooding were already living in households facing multiple vulnerabilities before the cyclone struck, including unstable incomes, high debt, and limited capacity to cope with disasters (UNDP, 2025). The disaster did not create poverty; it magnified it. Physical damage was only the visible layer. Beneath it lay deep social and economic fragility, ensuring that for many communities, recovery would be slow, uneven, and uncertain.
The world today offers Sri Lanka another lesson Lisbon understood centuries ago: risk is systemic, and resilience cannot be improvised, it must be planned. Modern climate science shows that weather systems are deeply interconnected; rising ocean temperatures, changing wind patterns, and global emissions influence extreme weather far beyond their points of origin. Floods, landslides, and cyclones affecting Sri Lanka are no longer isolated events, but part of a broader climatic shift. Rebuilding without adapting construction methods, land-use planning, and infrastructure to these realities is not resilience, it is denial. In this context, resilience also depends on Sri Lanka’s willingness to learn from other countries, adopt proven technologies, and collaborate across borders, recognising that effective solutions to global risks cannot be developed in isolation.
A deeper problem is how we respond to disasters: we often explain destruction without seriously asking why it happened or how it could have been prevented. Time and again, devastation is framed through religion, fate, karma, or divine will. While faith can bring comfort in moments of loss, it cannot replace responsibility, foresight, or reform. After major disasters, public attention often focuses on stories of isolated religious statues or buildings that remain undamaged, interpreted as signs of protection or blessing, while far less attention is paid to understanding environmental exposure, construction quality, and settlement planning, the factors that determine survival. Similarly, when a single house survives a landslide, it is often described as a miracle rather than an opportunity to study soil conditions, building practices, and land-use decisions. While such interpretations may provide emotional reassurance, they risk obscuring the scientific understanding needed to reduce future loss.
The lesson from Lisbon is clear: rebuilding a nation requires the courage to question tradition, the discipline to act rationally, and leadership willing to choose long-term progress over short-term comfort. Until Sri Lanka learns to rebuild not only roads and buildings, but relationships, institutions, and ways of thinking, we will remain a country trapped in recovery, never truly reborn.
by Darshika Thejani Bulathwatta
Psychologist and Researcher
Opinion
A wise Christmas

Important events in the Christian calendar are to be regurlarly reviewed if they are to impact on the lives of people and communities. This is certainly true of Christmas.
Community integrity
Years ago a modest rural community did exactly this, urging a pre-Christmas probe of the events around Jesus’ birth. From the outset, the wisemen aroused curiosity. Who were these visitors? Were they Jews? No. were they Christians? Of course not. As they probed the text, the representative character of those around the baby, became starkly clear. Apart from family, the local shepherds and the stabled animals, the only others present that first Christmas, were sages from distant religious cultures.
With time, the celebration of Christmas saw a sharp reversal. The church claimed exclusive ownership of an inclusive gift and deftly excluded ‘outsiders’ from full participation.
But the Biblical version of the ‘wise outsiders’ remained. It affirmed that the birth of Jesus inspired the wise to initiate a meeting space for diverse religious cultures, notwithstanding the long and ardous journey such initiatives entail. Far from exclusion, Jesus’ birth narratives, announced the real presence of the ‘outsider’ when the ‘Word became Flesh’.
The wise recognise the gift of life as an invitation to integrate sincere explanations of life; true religion. Religion gone bad, stalls these values and distorts history.
There is more to the visit of these sages.
Empire- When Jesus was born, Palestine was forcefully occcupied by the Roman empire. Then as now, empire did not take kindly to other persons or forces that promised dignity and well being. So, when rumours of a coming Kingdom of truth, justice and peace, associated with the new born baby reached the local empire agent, a self appointed king; he had to deliver. Information on the wherabouts of the baby would be diplomatically gleaned from the visiting sages.
But the sages did not only read the stars. They also read the signs of the times. Unlike the local religious authorities who cultivated dubious relations with a brutal regime hated by the people, the wise outsiders by-pass the waiting king.
The boycott of empire; refusal to co-operate with those who take what it wills, eliminate those it dislikes and dare those bullied to retaliate, is characteristic of the wise.
Gifts of the earth
A largely unanswered question has to do with the gifts offered by the wise. What happened to these gifts of the earth? Silent records allow context and reason to speak.
News of impending threats to the most vulnerable in the family received the urgent attention of his anxious parent-carers. Then as it is now, chances of survival under oppressive regimes, lay beyond borders. As if by anticipation, resources for the journey for asylum in neighbouring Egypt, had been provided by the wise. The parent-carers quietly out smart empire and save the saviour to be.
Wise carers consider the gifts of the earth as resources for life; its protection and nourishment. But, when plundered and hoarded, resources for all, become ‘wealth’ for a few; a condition that attempts to own the seas and the stars.
Wise choices
A wise christmas requires that the sages be brought into the centre of the discourse. This is how it was meant to be. These visitors did not turn up by chance. They were sent by the wisdom of the ages to highlight wise choices.
At the centre, the sages facilitate a preview of the prophetic wisdom of the man the baby becomes.The choice to appropriate this prophetic wisdom has ever since summed up Christmas for those unable to remain neutral when neighbour and nature are violated.
Wise carers
The wisdom of the sages also throws light on the life of our nation, hard pressed by the dual crises of debt repayment and post cyclonic reconstruction. In such unrelenting circumstances, those in civil governance take on an additional role as national carers.
The most humane priority of the national carer is to ensure the protection and dignity of the most vulnerable among us, immersed in crisis before the crises. Better opportunities, monitored and sustained through conversations are to gradually enhance the humanity of these equal citizens.
Nations in economic crises are nevertheless compelled to turn to global organisations like the IMF for direction and reconstruction. Since most who have been there, seldom stand on their own feet, wise national carers may not approach the negotiating table, uncritically. The suspicion, that such organisations eventually ‘grow’ ailing nations into feeder forces for empire economics, is not unfounded.
The recent cyclone gave us a nasty taste of these realities. Repeatedly declared a natural disaster, this is not the whole truth. Empire economics which indiscriminately vandalise our earth, had already set the stage for the ravage of our land and the loss of loved ones and possessions. As always, those affected first and most, were the least among us.
Unless we learn to manouvre our dealings for recovery wisely; mindful of our responsibilities by those relegated to the margins as well as the relentles violence and greed of empire, we are likely to end up drafted collaborators of the relentless havoc against neighbour and nature.
If on the other hand the recent and previous disasters are properly assessed by competent persons, reconstruction will be seen as yet another opportunity for stabilising content and integrated life styles for all Lankans, in some harmony with what is left of our dangerously threatened eco-system. We might then even stand up to empire and its wily agents, present everywhere. Who knows?
With peace and blessings to all!
Bishop Duleep de Chickera
Opinion
Ranwala crash: Govt. lays bare its true face
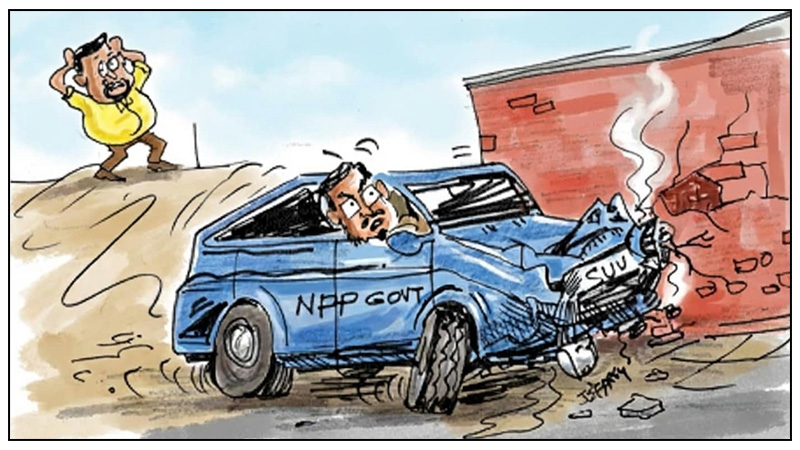

The NPP government is apparently sinking into a pit dug by the one of its members, ‘Dr’ Asoka Ranwala; perhaps a golden pit (Ran Wala) staying true to his name! Some may accuse me of being unpatriotic by criticising a government facing the uphill task of rebuilding the country after an unprecedented catastrophe. Whilst respecting their sentiment, I cannot help but point out that it is the totally unwarranted actions of the government that is earning much warranted criticism, as well stated in the editorial “Smell of Power” (The Island, 15 December). Cartoonist Jeffrey, in his brilliance, has gone a step further by depicting Asoka Ranwala as a giant tsunami wave rushing to engulf the tiny NPP house in the shore, AKD is trying to protect. (The Island, 18 December).
The fact that Asoka Ranwala is very important to the JVP, for whatever reason, became evident when he was elected the Speaker of Parliament despite his lack of any parliamentary experience. When questions were raised about his doctorate in Parliament, Ranwala fiercely defended his position, ably supported by fellow MPs. When the Opposition kept on piling pressure, producing evidence to the contrary, Ranwala stepped aside, claiming that he had misplaced the certificate but would stage a comeback, once found. A year has passed and he is yet to procure a copy of the certificate, or even a confirmatory letter from the Japanese university!
The fact that AKD did not ask Ranwala to give up his parliamentary seat, a decision he may well be regretting now following recent events, shows that either AKD is not a strong leader who can be trusted to translate his words to action or that Ranwala is too important to be got rid of. In fact, AKD should have put his foot down, as it was revealed that Ranwala was a hypocrite, even if not a liar. Ranwala led the campaign to dismantle the private medical school set up by Dr Neville Fernando, which was earning foreign exchange for the country by recruiting foreign students, in addition to saving the outflow of funds for educating Sri Lankan medical graduates abroad. He headed the organisation of parents of state medical students, claiming that they would be adversely affected, and some of the photographs of the protests he led refer to him as Professor Ranwala! Whilst leading the battle against private medical education, Ranwala claims to have obtained his PhD from a private university in Japan. Is this not the height of hypocrisy?
The recent road traffic accident he was involved in would have been inconsequential had Ranwala been decent enough to leave his parliamentary seat or, at least, being humble enough to offer an apology for his exaggerated academic qualifications. After all, he is not the only person to have been caught in the act of embellishing a CV. As far as the road traffic accident is concerned, too, it may not be his entire responsibility. Considering the chaotic traffic, in and around Colombo, coupled with awful driving standards dictated by lack of patience and consideration, it is a surprise that more accidents do not happen in Sri Lanka. Following the accident, may be to exonerate from the first count, a campaign was launched by NPP supporters stating that a man should be judged on his achievements, not qualifications, further implying that he does not have the certificate because he got it in a different name!
What went wrong was not the accident, but the way it was handled. Onlookers claim that Ranwala was smelling of alcohol but there is no proof yet. He could have admitted it even if he had taken any alcohol, which many do and continue to drive in Sri Lanka. After all, the Secretary to the Ministry overseeing the Police was able to get the charge dropped after causing multiple accidents while driving under the influence of liquor! He, with another former police officer, sensing the way the wind was blowing formed a retired police collective to support the NPP and were adequately rewarded by being given top jobs, despite a cloud hanging over them of neglect of duty during the Easter Sunday attacks. This naïve political act brought the integrity of the police into question. The way the police behaved after Ranwala’s accident confirmed the fears in the minds of right-thinking Sri Lankans.
In the euphoria of the success of a party promising a new dawn, unfortunately, many political commentators kept silent but it is becoming pretty obvious that most are awaking to the reality of a false dawn. It could not have come at a worse time for the NPP: in spite of the initial failures to act on the warnings regarding the devastating effects of Ditwah, the government was making good progress in sorting problems out, when Ranwala met with an accident.
The excuses given by the police for not doing a breathalyser test, or blood alcohol levels, promptly, are simply pathetic. Half-life of alcohol is around 4-5 hours and unless Ranwala was dead drunk, it is extremely unlikely any significant amounts of alcohol would be detected in a blood sample taken after 24 hours. Maybe the knowledge of this that made government Spokesmen to claim boldly that proper action would be taken irrespective of the position held. Now that the Government Analyst has not found any alcohol in the blood, no action is needed! Instead, the government seems to have got the IGP to investigate the police. Would any police officers suffer for doing a favour to the government? That is the million-dollar question!
Unfortunately, all this woke up a sleeping giant; a problem that the government hoped would be solved by the passage of time. If the government is hoping that the dishonesty of one of its prominent members would be forgotten with the passage of time, it will be in for a rude shock. When questioned by journalists repeated, the Cabinet spokesman had to say action would be taken if the claim of the doctorate was false. However, he added that the party has not decided what that action would be! What about the promise to rid Parliament of crooks?
It is now clear that the NPP government is not any different from the predecessors and that Sri Lankan voters are forced to contend with yet another false dawn!
by Dr Upul Wijayawardhana ✍️
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoMembers of Lankan Community in Washington D.C. donates to ‘Rebuilding Sri Lanka’ Flood Relief Fund
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoUnlocking Sri Lanka’s hidden wealth: A $2 billion mineral opportunity awaits
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoArmy engineers set up new Nayaru emergency bridge
-

 Latest News6 days ago
Latest News6 days agoLandslide early warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Kandy, Kurunegala, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya extended till 8AM on Sunday (21)
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoTISL, civil society flay NPP govt. for holding up Auditor General’s appointment
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoThe Maha Jana Handa at Nugegoda, cyclone destruction, and contenders positioning for power in post-NPP Sri Lanka – II
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoTannane goal from own half sets Morocco on way to FIFA Arab Cup 2025 title
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoSri Lankans rescued from cybercrime centers in Myanmar repatriated













